栈和队列的建立
- 前言
- 一、栈
- 1.栈的概念
- 2.栈的实现
- 3.代码示例
- (1)Stack.h
- (2)Stack.c
- (3)Test.c
- (4)运行结果
- (5)完整代码演示
- 二、队列
- 1.队列的概念
- 2.队列的实现
- 3.代码示例
- (1)Queue.h
- (2)Queue.c
- (3)Test.c
- (4)运行结果
- (5)完整代码演示
- 三、栈的应用例题
- 方法一
- 方法二
- 总结
前言
今天我们来学习栈和队列的简易建立!
在后面还会有一道栈的应用题,检测大家的用功程度!
加油吧!
一、栈
1.栈的概念
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。 进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。 压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
模型图示例:


2.栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
图片示例:


3.代码示例
(1)Stack.h
1.头文件的声明
//头文件的声明
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
2.栈的接口定义
//栈的接口定义
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;
3.初始化和销毁函数的声明
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
4.入栈和出栈函数的声明
//插入
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//删除
void STPop(ST* ps);
5.查找栈顶元素和长度计算函数以及判空函数的声明
//插入
//查找栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
//长度计算
int STSize(ST* ps);
//判断是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
(2)Stack.c
1.头文件的声明
#include "Stack.h"
2.初始化和销毁函数的定义
/初始化
void STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = 0;ps->top = 0;
}//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
3.入栈和出栈函数的定义
//插入
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}//删除栈顶元素
void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);--ps->top;
}
4.查找栈顶元素和长度计算函数以及判空函数的定义
//查找栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}//长度计算
int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}//判断是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}
(3)Test.c
1.头文件的声明
#include "Stack.h"
2.测试函数的定义
void TestStack()
{ST st;STInit(&st);STPush(&st, 1);STPush(&st, 2);STPush(&st, 3);STPush(&st, 4);STPush(&st, 5);while (!STEmpty(&st)){printf("%d ", STTop(&st));STPop(&st);}printf("\n");STPush(&st, 6);STPush(&st, 7);STPush(&st, 8);STPush(&st, 9);STPush(&st, 10);while (!STEmpty(&st)){printf("%d ", STTop(&st));STPop(&st);}printf("\n");STDestroy(&st);
}
3.主函数的定义
int main()
{TestStack();return 0;
}
(4)运行结果

(5)完整代码演示
1.Stack.h
#pragma once
//头文件的声明
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>//栈的接口定义
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
//插入
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//删除
void STPop(ST* ps);
//查找栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
//长度计算
int STSize(ST* ps);
//判断是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
2.Stack.c
#include "Stack.h"//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = 0;ps->top = 0;
}//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}//插入
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}//删除栈顶元素
void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);--ps->top;
}//查找栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}//长度计算
int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}//判断是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}
3.Test.c
#include "Stack.h"void TestStack1()
{ST st;STInit(&st);STPush(&st, 1);STPush(&st, 2);STPush(&st, 3);STPush(&st, 4);STPush(&st, 5);while (!STEmpty(&st)){printf("%d ", STTop(&st));STPop(&st);}printf("\n");STPush(&st, 6);STPush(&st, 7);STPush(&st, 8);STPush(&st, 9);STPush(&st, 10);while (!STEmpty(&st)){printf("%d ", STTop(&st));STPop(&st);}printf("\n");STDestroy(&st);
}int main()
{TestStack1();return 0;
}
二、队列
1.队列的概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
模型图示例:

2.队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
图片示例:

3.代码示例
(1)Queue.h
1.头文件的声明
#pragma once
//头文件的声明
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
2.队列接口的定义
//链表接口定义
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType data;
}QNode;//队列接口定义
typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Que;3.初始化和销毁函数的声明
//队列初始化
void QueueInit(Que* pq);
//队列销毁
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq);
4.入队列和出队列函数的声明
//插入
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x);
//删除
void QueuePop(Que* pq);
5.查找队头、查找队尾函数的声明
//查找队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq);
//查找队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq);
6.判空以及长度计算函数的声明
//判断是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq);
//计算长度
int QueueSize(Que* pq);
(2)Queue.c
1.头文件的声明
#include "Queue.h"
2.初始化和销毁函数的定义
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
3.入队列和出队列函数的定义
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->tail == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//判断队列指针指向是否为空assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//判断队列里面的数据是否为空if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}pq->size--;
}
4.查找队头、查找队尾函数的定义
//查找队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}//查找队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}
5.判空以及长度计算函数的定义
//判断是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL;
}//长度计算
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}
(3)Test.c
1.头文件的声明
#include "Queue.h"
2.测试函数的定义
void QueueTest() {Que pq;QueueInit(&pq);QueuePush(&pq, 1);QueuePush(&pq, 2);QueuePush(&pq, 3);QueuePush(&pq, 4);QueuePush(&pq, 5);while (!QueueEmpty(&pq)) {printf("%d ", QueueFront(&pq));QueuePop(&pq);}QueueDestroy(&pq);
}
3.主函数的定义
int main() {QueueTest();return 0;
}
(4)运行结果

(5)完整代码演示
1.Queue.h
#pragma once
//头文件的声明
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>//链表接口定义
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType data;
}QNode;//队列接口定义
typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Que;//队列初始化
void QueueInit(Que* pq);
//队列销毁
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq);
//插入
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x);
//删除
void QueuePop(Que* pq);
//查找队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq);
//查找队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq);
//判断是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq);
//计算长度
int QueueSize(Que* pq);2.Queue.c
#include "Queue.h"void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->tail == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//判断队列指针指向是否为空assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//判断队列里面的数据是否为空if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}pq->size--;
}//查找队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}//查找队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}//判断是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL;
}//长度计算
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}
3.Test.c
#include "Queue.h"void QueueTest() {Que pq;QueueInit(&pq);QueuePush(&pq, 1);QueuePush(&pq, 2);QueuePush(&pq, 3);QueuePush(&pq, 4);QueuePush(&pq, 5);while (!QueueEmpty(&pq)) {printf("%d ", QueueFront(&pq));QueuePop(&pq);}QueueDestroy(&pq);
}int main() {QueueTest();return 0;
}
三、栈的应用例题
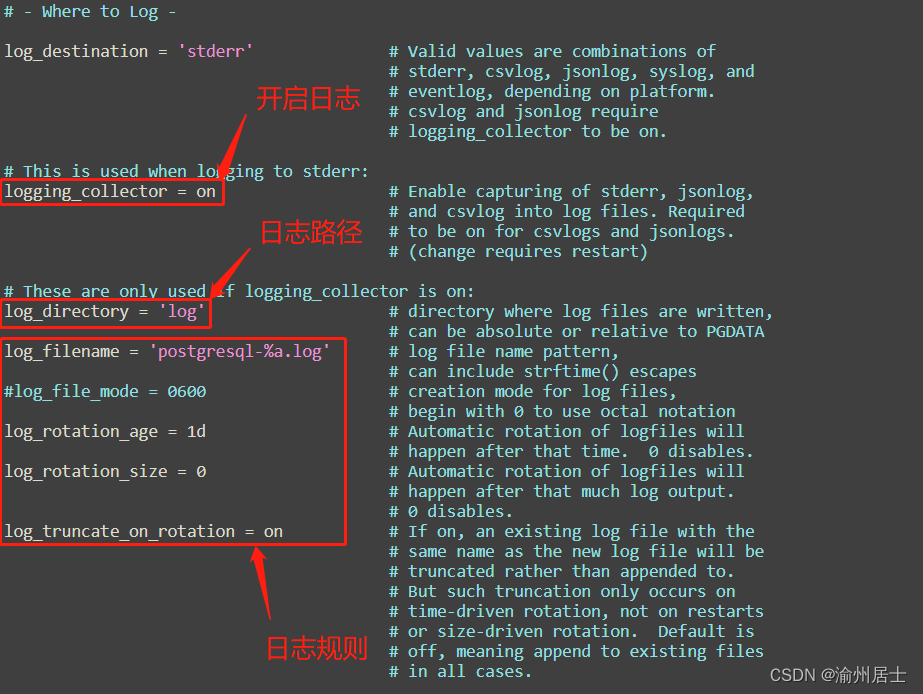
题目:括号匹配问题
题目链接
提示:
. 1 <= s.length <= 104
. s 仅由括号 ‘()[]{}’ 组成
解题思路:
这道题我有两种解法!
建栈法和暴力破解法!
方法一
首先第一种就是利用栈来解决:
1.左括号,入栈;
2.右括号与栈中的栈顶括号进行匹配;
图例:

代码示例:
引用之前栈的建立函数:
//栈的接口定义
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
//插入
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//删除
void STPop(ST* ps);
//查找栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
//长度计算
int STSize(ST* ps);
//判断是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = 0;ps->top = 0;
}//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}//插入
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}//删除栈顶元素
void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);--ps->top;
}//查找栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}//长度计算
int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}//判断是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}
功能函数的定义
bool isValid(char* s) {ST st;STInit(&st);char topVal;while (*s ) {if (*s == '(' || *s == '[' || *s == '{') {STPush(&st, *s);}else {//数量不匹配if (STEmpty(&st)){STDestroy(&st);return false;}topVal = STTop(&st);STPop(&st);if ((*s == ']' && topVal != '[')|| (*s == ']' && topVal != '[')|| (*s == ']' && topVal != '[')) {STDestroy(&st);return false;}}++s;}bool ret = STEmpty(&st);STDestroy(&st);return ret;
}
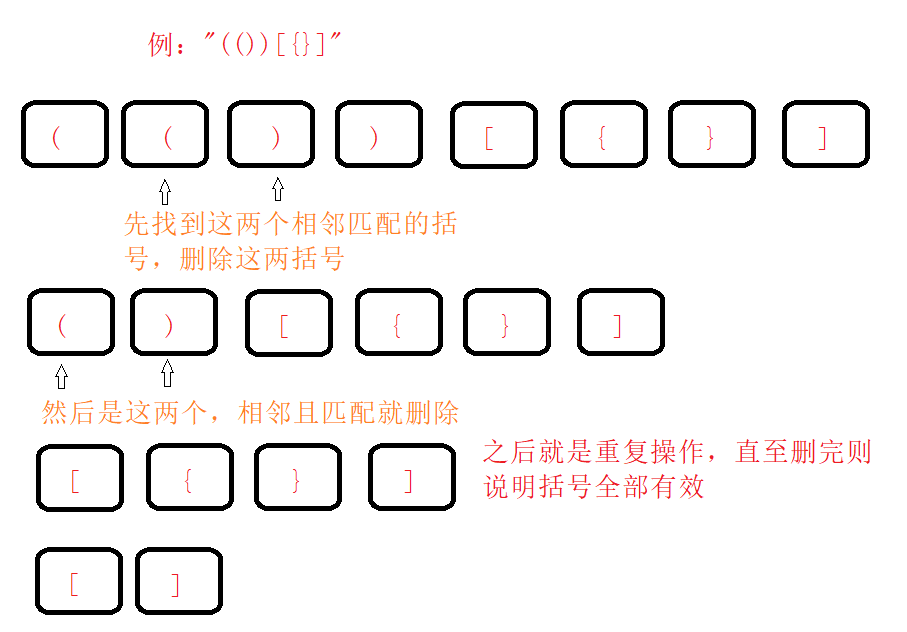
方法二
第二种方法就是例子中如果不存在无效括号的话,那么至少有一个是左右括号相邻的;
所以先找到相邻且匹配的括号将其移除,然后慢慢一点一点全部都移除的话则说明全部括号有效!
图例
代码演示:
bool isValid(char* s) {char* p = s;while (*p) {p = s;while (*p) {if (*p + 1 == *(p + 1) || *p + 2 == *(p + 1)) {//查看assii码表了解符号的大小char* move = p;while (true) {*move = *(move + 2);if(*move=='\0')break;move++;}break;}else {p++;}}if (*p == '\0' && *s != '\0')return false;}return true;
}
总结
今天的内容有点多,希望大家仔细观看,细细揣摩!
好好学习,天天向上!
不变的真理!






![[C语言]分支与循环](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c95192dbb42d41d482d54c719008166f.png)