198. House Robber
题意:你是一个强盗,你要去抢劫,每个房子都有特定金额的钱,但是不能拿相邻的房子的钱
我的思路
有点像动态规划,但是首先把每个结点空一格的后缀和得到,2n
之后从(i=n-1;i>=0;i--)dp[i]=(nums[i]-nums[i+2])+max(dp[i+2],dp[i+3]);
代码 Runtime0 ms Beats 100% Memory7.9 MB Beats 19.97%
哈哈哈这都给我做出来了.jpg
class Solution {
public:int rob(vector<int>& nums) {int n=nums.size();if(n==1)return nums[n-1];else if(n==2)return max(nums[0],nums[1]);vector<int>dp(n,0);for(int i=n-3;i>=0;i=i-2) nums[i]=nums[i]+nums[i+2];for(int i=n-4;i>=0;i=i-2) nums[i]=nums[i]+nums[i+2];dp[n-1]=nums[n-1]; dp[n-2]=nums[n-2]; dp[n-3]=nums[n-3];if(n==3)return max(nums[0],nums[1]);for(int i=n-4;i>=0;i--)dp[i]=(nums[i]-nums[i+2])+max(dp[i+2],dp[i+3]);return max(dp[0],dp[1]);}
};标答 更简洁的动态规划
注意dp是从1开始的,因为这样,dp[i-2]就不用特判了;dp[i]表示的是在i结点之前拿到的最大的钱
状态转移方程为dp[i]=max(dp[i-1],dp[i-2]+nums[i-1]);因为当前的结点要么拿要么不拿
如果拿了,dp[i]=dp[i-2]+num[i-1];如果没拿,dp[i]=dp[i-1]
代码 Runtime 0 ms Beats 100% Memory7.9 MB Beats 6.50%
class Solution {
public:int rob(vector<int>& nums) {if(nums.size()==0)return 0;int n=nums.size(); vector<int> dp(n+1,0);dp[1]=nums[0];for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)dp[i]=max(dp[i-1],dp[i-2]+nums[i-1]);return dp[n];}
};标答 空间更少的动态规划
不创建dp了,用prev和curr
代码 Runtime0 ms Beats 100% Memory7.7 MB Beats 76.93%
class Solution {
public:int rob(vector<int>& nums) {if(nums.size()==0)return 0;int n=nums.size(); int prev=0,curr=nums[0],tmp;for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){tmp=max(curr,prev+nums[i-1]);prev=curr; curr=tmp;}return curr;}
};199. Binary Tree Right Side View
题意: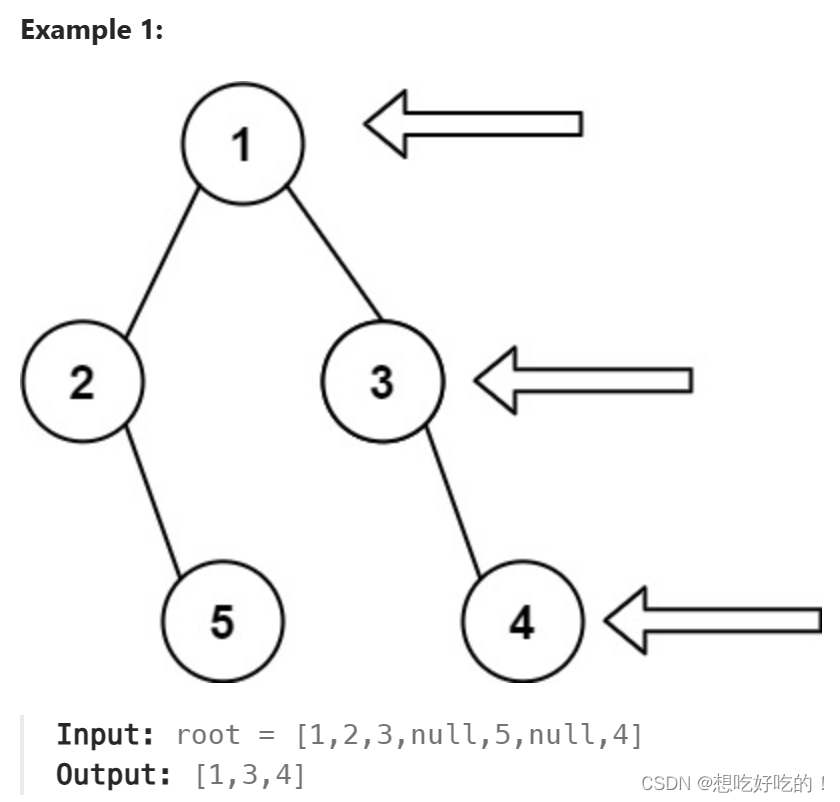
我的思路
先层序遍历,之后把每一层的最右边加入
看了标答 dfs也可以
代码 Runtime 0 ms Beats 100% Memory 12 MB Beats 61.69%
class Solution {
public:vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {if(root==NULL)return {};queue<TreeNode* >q;vector<int> ans;ans.push_back(root->val);if(root->left!=NULL)q.push(root->left);if(root->right!=NULL)q.push(root->right);while(!q.empty()){int n=q.size();for(int i=0;i<n;i++){TreeNode* tmp=q.front();if(i==n-1)ans.push_back(tmp->val);if(tmp->left!=NULL)q.push(tmp->left);if(tmp->right!=NULL)q.push(tmp->right);q.pop();}}return ans;}
};标答 DFS
ans是答案,如果root为空,return;因为一层一个答案,所以当ans需要第一个答案,id=0的时候,就把当前根的值放入;注意之后先递归right的结点,这样之后到当前层的时候可以先把这个节点的val放入ans中
代码 Runtime3 ms Beats 65.44% Memory11.9 MB Beats 81.60%
class Solution {
public:void sol(TreeNode* root,vector<int> &ans,int id){if(!root)return ;if(ans.size()==id)ans.push_back(root->val);sol(root->right,ans,id+1);//注意先递归右边sol(root->left,ans,id+1);}vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> ans;sol(root,ans,0);return ans;}
};200. Number of Islands
题意:有多少片陆地,1是陆地,0是水

我的思路
BFS,看看有几次
代码 Runtime29 ms Beats 76.28% Memory18.2 MB Beats 30.61%
class Solution {
public:bool vis[302][302];void BFS(int x,int y,vector<vector<char>>& grid,int n,int m){queue <pair<int,int>>q;int dx[]={0,0,1,-1};int dy[]={1,-1,0,0};vis[x][y]=1;q.push({x,y});while(!q.empty()){int mx=q.front().first;int my=q.front().second;q.pop();for(int i=0;i<4;i++){int nx=dx[i]+mx;int ny=dy[i]+my;if(0>nx||n<=nx||0>ny||m<=ny||grid[nx][ny]=='0'||vis[nx][ny])continue;vis[nx][ny]=1;q.push({nx,ny});}}return;}int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {int n=grid.size();int m=grid[0].size();int cnt=0;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){for(int j=0;j<m;j++){if(!vis[i][j]&&grid[i][j]!='0'){cnt++; BFS(i,j,grid,n,m);}}}return cnt;}
};标答 DFS
标答的空间复杂度小了,其实上面的代码也可以不要vis的,grid改成2说不定也可以起到vis的效果
代码 Runtime21 ms Beats 98.21% Memory12.3 MB Beats 66.71%
class Solution {
public:void DFS(int i,int j,vector<vector<char>>& grid,int n,int m){if(0>i||n<=i||0>j||m<=j||grid[i][j]!='1')return;grid[i][j]='2'; //省去了visDFS(i+1,j,grid,n,m);DFS(i-1,j,grid,n,m);DFS(i,j+1,grid,n,m);DFS(i,j-1,grid,n,m);}int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {int n=grid.size();int m=grid[0].size();int cnt=0;for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++)if(grid[i][j]=='1'){cnt++;DFS(i,j,grid,n,m);}return cnt;}
};206. Reverse Linked List
题意:把链表倒过来
我的思路
递归,DFS返回的是从右到左的倒过来的指针,尾指针是返回的头部
哈哈这都被我做出来了.jpg
class Solution {
public:ListNode* DFS(ListNode* head){if(!(head->next))return head;ListNode* q=DFS(head->next);q->next=head;return head;}ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(!head)return NULL;ListNode* tail=head;while(tail->next!=NULL)tail=tail->next;DFS(head)->next=NULL;return tail;}
};标答 更简洁的递归
递归如图所示,主要就是head->next->next=head;head->next=NULL比较关键
h2指针从最深的递归返回后就一直没变过,所以h2就是最后的尾指针

代码 Runtime4 ms Beats 74.12% Memory8.6 MB Beats 6.1%
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;ListNode* prev = NULL;ListNode* h2 = reverseList(head->next);head->next->next = head;head->next=prev;return h2;}
};标答 不用递归
初始化一个past指针和curr指针,之后一个个向后处理;我用了三个指针让它看起来更易于理解
代码 Runtime4 ms Beats 74.12% Memory8.3 MB Beats 66.48%
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head){if(!head) return NULL;ListNode* past = head;ListNode* current = head -> next;past -> next = NULL;while(current){ListNode* next = current -> next;current -> next = past;past = current;current = next;}return past;}
};class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head==NULL)return head;ListNode* past=NULL;ListNode* curr=head;ListNode* prev=head->next;//初始化三个指针while(curr!=NULL){curr->next=past;past=curr;curr=prev;if(curr)prev=curr->next;}return past;}
};
207. Course Schedule
题意:判断环路,用拓扑排序
我的思路
不记得拓扑排序了,首先用vector建个图,2000个结点,5000条边
prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that you must take course bi first if you want to take course ai
有一个vector pair<int,int> 进入的次数,点的序号;【遍历一次】进入的次数为0的时候,次数记为-1,vector[点的序号]中的所有点在vector的次数-1
代码 Runtime23 ms Beats 58.79% Memory13.3 MB Beats 84.44%
一开始以为要先ai才能bi,搞反了,但ac了,想了想反正只是判断有无环
class Solution {
public:bool canFinish(int n, vector<vector<int>>& pre) {int mp[20004]={0}; vector<int>vec[20004];for(int i=0;i<pre.size();i++){vec[pre[i][1]].push_back(pre[i][0]);mp[pre[i][0]]++;//入度++}//建完了bool flag=1;int cnt=0;//flag判断是否还有为0的,cnt是消掉的点while(flag){flag=0;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if(mp[i])continue;for(int j=0;j<vec[i].size();j++){mp[vec[i][j]]--;if(mp[vec[i][j]]==0)flag=1;}mp[i]=-1;cnt++;}}if(cnt!=n)return 0;return 1;}
};标答 拓扑排序
首先建立邻接表,degree计算每个点的入度;之后用队列判断,先扫一遍入度表,如果为0就放到队列中;当队列不为0时,把队列中的节点一个个拿出来,之后把这个点pop掉,并且把它前往的点的入度--;如果前往的节点的入度为0,把它放到队列中;
队列为空的时候看看是否pop掉所有节点
代码 Runtime16 ms Beats 90.55% Memory13.2 MB Beats 84.44%
class Solution {
public:bool canFinish(int n, vector<vector<int>>& pre) {vector<vector<int>> vec(n, vector<int>());vector<int> mp(n, 0);for(int i=0;i<pre.size();i++){vec[pre[i][1]].push_back(pre[i][0]);mp[pre[i][0]]++;//入度++}//建完了queue<int>q;for(int i=0;i<n;i++)if(!mp[i])q.push(i);while(!q.empty()){int tmp=q.front();q.pop();n--;for(auto& p:vec[tmp]){mp[p]--;if(!mp[p])q.push(p);}}return n==0;}
};标答 DFS 没看
DFS看上去好难,算了
代码 Runtime15 ms Beats 94.18% Memory14.7 MB Beats 17.31%
class Solution {
public:bool detectcycle(vector<vector<int>>&v,int src,vector<int>&rst,vector<int>&vis){vis[src]=1;rst[src]=1;for(auto x:v[src]){if(!vis[x]&&detectcycle(v,x,rst,vis)) return true;else if(rst[x]==1) return true;}rst[src]=0;return false;}bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {vector<vector<int>>v(numCourses); stack<int>s;vector<int>vis(numCourses),rst(numCourses);for(auto x: prerequisites) v[x[1]].push_back(x[0]);for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++){if(!vis[i])if(detectcycle(v,i,rst,vis)) return false;}return true;}
};208. Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
题意:建一个前缀树,实现insert,search,startwith功能
我的思路
模板题
代码 Runtime 31 ms Beats 99.69% Memory 78.8 MB Beats 11.17%
class Trie {
public:int nxt[30904][26]={0};int cnt=0;bool ex[30904]={0};Trie() {}void insert(string word) {int p=0;for(int i=0;word[i];i++){if(!nxt[p][word[i]-'a'])nxt[p][word[i]-'a']=++cnt;p=nxt[p][word[i]-'a'];}ex[p]=1;}bool search(string word) {int p=0;for(int i=0;word[i];i++){if(!nxt[p][word[i]-'a'])return 0;p=nxt[p][word[i]-'a'];}if(ex[p])return 1;return 0;}bool startsWith(string prefix) {int p=0;for(int i=0;prefix[i];i++){if(!nxt[p][prefix[i]-'a'])return 0;p=nxt[p][prefix[i]-'a'];}return 1;}
};标答 链表 没细看
思路差不多,主要是要建立TrieNode这个节点,要注意指针初始化为NULL
代码 Runtime 30 ms Beats 99.81% Memory 43.4 MB Beats 76.60%
class TrieNode{
public:TrieNode *child[26];bool isword;TrieNode(): isword(false){for(auto &a:child) a=nullptr;}
};
class Trie {
public:Trie() {root = new TrieNode();}void insert(string word) {TrieNode *p = root;for(auto c:word){if(p->child[c-'a'] == nullptr)p->child[c-'a'] = new TrieNode();p = p->child[c-'a'];}p->isword = true;}bool search(string word) {TrieNode *p = root;for(auto c:word){if(p->child[c-'a'] == nullptr) return false;p = p->child[c-'a'];}return p->isword;}bool startsWith(string prefix) {TrieNode *p = root;for(auto c:prefix){if(p->child[c-'a'] == nullptr) return false;p = p->child[c-'a'];}return true;}
private:TrieNode* root;
};215. Kth Largest Element in an Array
题意:返回数组中第K大的元素,数组中有重复元素,数组未排序,要求不排序
我的思路
直接哈希做,一共就2e4个数字
代码 Runtime61 ms Beats 96.2% Memory55.4 MB Beats 12.47%
class Solution {
public:int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {int vis[20001]={0};for(int q:nums) vis[q+10000]++;for(int i=20000;i>=0;i--){k=k-vis[i];if(k<=0)return i-10000;}return -1;}
};标答 优先队列
stl的优先队列最小堆greater,先给前k个建堆;之后遍历剩下的数组,如果数组v[i]比q.top()小,就把q.top()弹出,v[i]加入,最后返回堆顶就可以了
代码 Runtime 88 ms Beats 59.41% Memory 56.4 MB Beats 11.13%
class Solution {
public:int findKthLargest(vector<int>& v, int k) {priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q(v.begin(),v.begin()+k);for(int i=k;i<v.size();i++){//是从k开始if(q.top()<v[i]){q.pop();q.push(v[i]);}}return q.top();}
};标答 Quicksort TLE
虽然不知道为什么TLE了,但是理论上这个是O(n);注意find的输出是第k小,k从0开始
原理:因为快排一次(假设排序是从小到大的)可以确定一个位置,这个位置tmp的左边都是比它小的,右边都是大于等于它的;
如果tmp==k,返回a[tmp];如果tmp+1>k,find(left, tmp-1);如果tmp+1<k,find(tmp+1, right)
代码 TLE 不过听说随机化快排能过,之后研究一下
class Solution {
public:int quicksort(vector<int>& a,int left,int right){int mid=a[left];while (left<right){while (left<right&&mid<=a[right]) right--;a[left] = a[right];while (left<right&&a[left]<=mid)left++;a[right] = a[left];}a[left]=mid;return left;}int find(vector<int>& a,int left, int right, int k){ int tem=quicksort(a,left,right);if(k==tem) return a[k];else if(k-1<tem) return find(a,left,tem-1,k);return find(a,tem+1,right,k);}int findKthLargest(vector<int>& v, int k) {ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);int n=v.size();return find(v,0,n-1,n-k);}
};226. Invert Binary Tree
题意: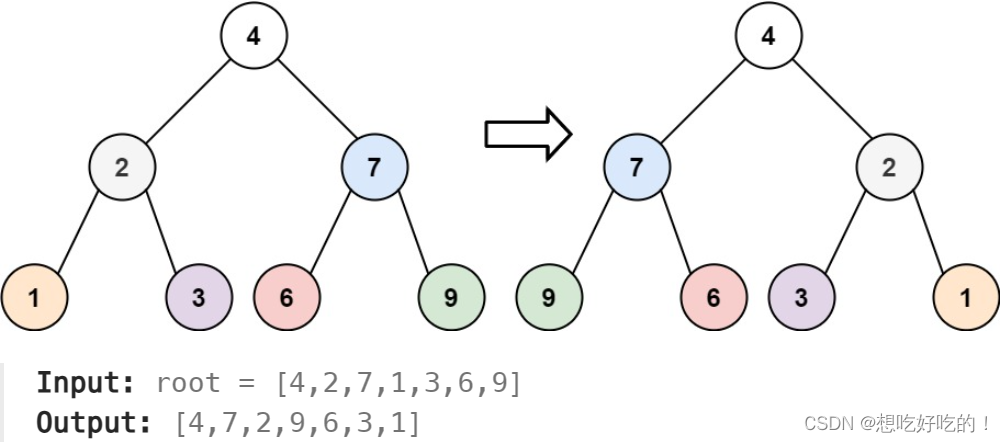
我的思路
递归,类似于第101题 Leetcode Top 100 Liked Questions(序号75~104)
但是对于这个例子不知道怎么做,我只知道swap值
root=[1, 2],Expected=[1,null,2]
看了标答后:swap时,应该是swap(root->left, root->right),而不是swap(l, r)
标答 DFS
不得不说,它确实和101题不太一样
代码 Runtime0 ms Beats 100% Memory 9.7 MB Beats 65.11%
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if (root) {invertTree(root->left);invertTree(root->right);swap(root->left, root->right);}return root;}
};看了标答后,我修改了我蹩脚的代码
class Solution {
public:void sol(TreeNode* r){if(r->left==NULL&&r->right==NULL)return;swap(r->left,r->right); if(r->left==NULL) sol(r->right);else if(r->right==NULL) sol(r->left);else{sol(r->right);sol(r->left);}}TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if(!root)return root;sol(root); return root;}
};标答 不递归 用栈(队列也可以)
类似于层序遍历
代码 Runtime0 ms Beats 100% Memory9.9 MB Beats 5.3%
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> stk;stk.push(root); while (!stk.empty()) {TreeNode* p = stk.top();stk.pop();if (p) {stk.push(p->left);stk.push(p->right);swap(p->left, p->right);}}return root;}
};230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST
题意:给一个二叉排序树,给出第K小的元素
我的思路
根据第215题,做法有哈希,优先队列
因为是排序树,所以中序序列就是顺序
所以中序遍历一遍就可以了
代码 Runtime7 ms Beats 98.62% Memory24.1 MB Beats 71.82%
用来两个引用
class Solution {
public:void dfs(TreeNode* root,int &k,int& ans){if(root==NULL||ans!=-1)return ;dfs(root->left,k,ans);k--;if(k==0)ans=root->val;dfs(root->right,k,ans);}int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {int ans=-1;dfs(root,k,ans);return ans;}
};234. Palindrome Linked List
题意:看看链表是不是回文的
我的思路
可以用vector.map 也许递归也可以,结点个数1e5
不会dfs,用vector吧
代码 Runtime 187 ms Beats 66.11% Memory 128.3 MB Beats 20.36%
class Solution {
public:vector<int>ans;bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {ListNode* p=head;while(p!=NULL){ans.push_back(p->val);p=p->next;}int n=ans.size();for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if(ans[i]!=ans[n-i-1]) return 0;}return 1;}
};标答 Reverse
标答说可以用Reverse,那么就可以206的方法做这题,不过这样破坏了原来的链表,写到一半不想写了,Reverse的思路是用快慢指针找到中点,之后两端都指向中点,最后slow到尾,fast=head,两遍同时向中间遍历判断
直接贴上来,不自己写了
代码 Runtime 117 ms Beats 99.85% Memory 110.4 MB Beats 98.10%
class Solution {
public:bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head;ListNode* prev, * next = new ListNode();while(fast && fast -> next){slow = slow -> next;fast = fast -> next -> next;next = head -> next;head -> next = prev;prev = head;head = next;}if(fast) slow = slow -> next;head = prev;while(slow){if(slow->val!=head->val) return false;slow = slow -> next; head = head -> next;}return true;}
};