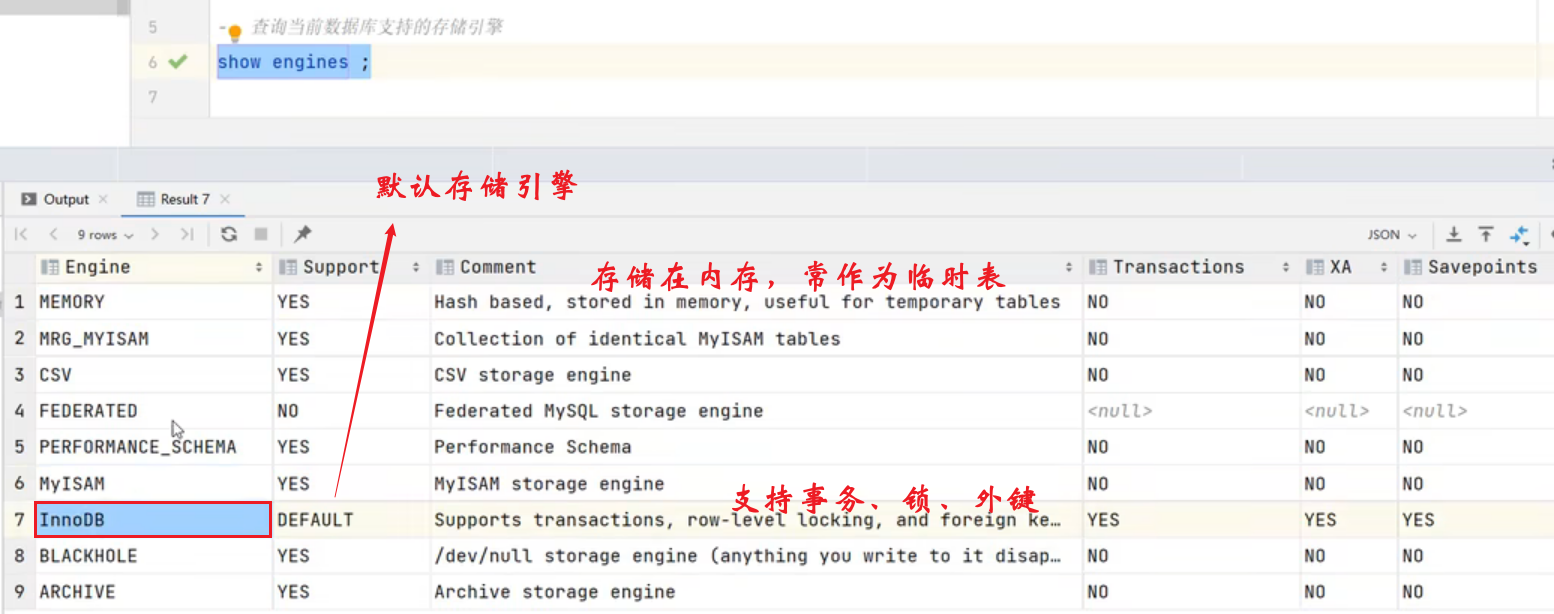
链式二叉树的建立
- 前言
- 一、层序遍历的概念和实现
- 二、判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
- 总结
前言
来喽来喽~ 二叉树的层序遍历来喽~
层序遍历那是相当有趣滴!
我的朋友,请不要迷惘,你要记住,你终有鲲鹏一日!
加油吧!从现在开始~
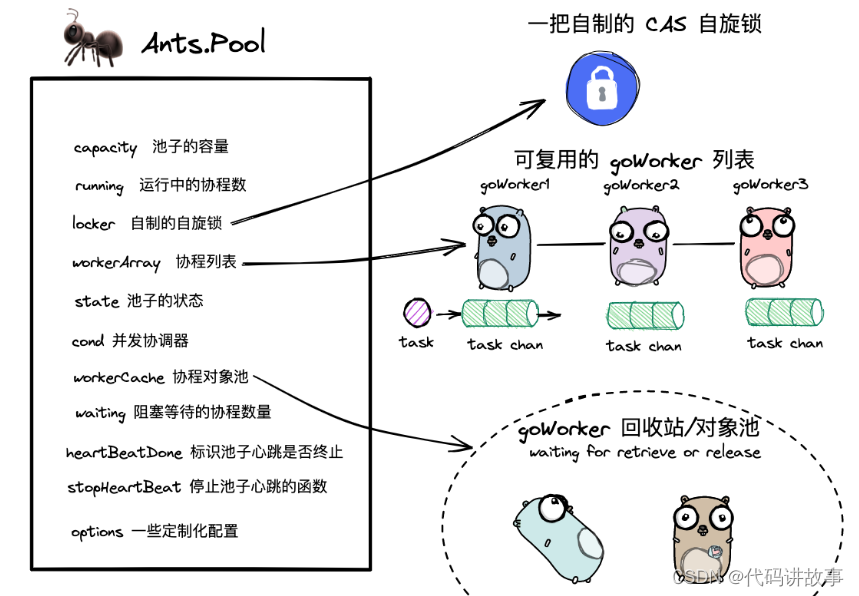
一、层序遍历的概念和实现
层序遍历:除了先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历外,还可以对二叉树进行层序遍历。设二叉树的根节点所在层数为1,层序遍历就是从所在二叉树的根节点出发,首先访问第一层的树根节点,然后从左到右访问第2层上的节点,接着是第三层的节点,以此类推,自上而下,自左至右逐层访问树的结点的过程就是层序遍历。
既然了解了层序遍的概念,那么要层序遍历二叉树那么首先就应该想到利用队列来进行!

大家对于层序遍历已经有了一些基础的认知了吧,那么现在开始代码实现吧!
1.头文件的声明
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
2.二叉树接口的定义
typedef char BTDataType;//类型重命名typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{BTDataType data;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;//左子树struct BinaryTreeNode* right;//右子树
}BTNode;
3.队列接口的定义
这里有涉及到之前队列的知识,如果对于队列不是太了解的话可以看看之前的文章!
栈和队列
//链表接口定义
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType data;
}QNode;//队列接口定义
typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Que;void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}//否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL;
}void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}//查找队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->tail == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);//判断队列指针指向是否为空assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//判断队列里面的数据是否为空if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}pq->size--;
}
4.前序遍历构建二叉树
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int* pi) {if (a[*pi] == '#') {//如果字符为#,则说明此处为空(*pi)++;//读取字符串中的下一个字符return NULL;}BTNode* root = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));root->data = a[*pi];(*pi)++;root->left = BinaryTreeCreate(a, pi);//构建左子树root->right = BinaryTreeCreate(a, pi);//构建右子树return root;
}

此处#转化为NULL
5.层序遍历代码实现
// 层序遍历
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root) {Que q;//定义一个队列QueueInit(&q);//初始化队列if (root)QueuePush(&q, root);//如果根节点不为空则入队列while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) {BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);//指针指向队头printf("%c ", front->data);//输出队头字符if(front->left!=NULL)//如果左子树存在则将其入队列QueuePush(&q, front->left);if(front->right!=NULL)//如果右子树存在则将其入队列QueuePush(&q, front->right);QueuePop(&q);//将头结点删除,并将下一个结点变为队头}printf("\n");QueueDestroy(&q);//销毁队列
}

6.二叉树的销毁
利用后序遍历思想,从左子树,右子树,根依次销毁结点
// 二叉树销毁
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root) {if (root == NULL) {return;}BinaryTreePrevOrder((*root)->left);BinaryTreePrevOrder((*root)->right);free(*root);
}
7.主函数的定义
int main() {char arr[] = "ABD##E#H##CF##G##";BinaryTreeLevelOrder(arr);return 0;
}
8.运行结果
二、判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
例子:数组"ABD##E#H##CF##G##"
思路解析:
这道题理所当担要用到层序遍历思想!

代码实现:
int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root) {Que q;QueueInit(&q);if (root)QueuePush(&q, root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) {BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);//front指向队头if (front == NULL)//当队头为NULL时退出入队break;QueuePush(&q, front->left);//左子树入队QueuePush(&q, front->right);//右子树入队QueuePop(&q);//删除队头}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) {BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);//front指向队头,即NULL结点QueuePop(&q);//if (front != NULL) {//当队头不为BULL,则说明这不是完全二叉树QueueDestroy(&q);//销毁队列return false;}}QueueDestroy(&q);return true;//如果从队列中的第一个NULL开始后面也全为NULL,则说明是完全二叉树
}
总结
不知道有没有难住你呢!
相信你不会被这些小困难绊倒!
说给你,更说给我,现在的努力至少不会辜负这一点青春时光!