今日内容
零、 复习昨日
一、循环
二、流程控制关键词
零、 复习昨日
8个基本数据类型
变量的使用步骤
1)声明2)赋值3)使用
- 声明,数据类型 变量名
不一定非得是基本类型 int a;
String s; Scanner scanner;- 赋值,只要符合类型(能默认转换)就能赋值
int a = 1;
double d = 1;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner();- 使用,可以是输出,运算,判断,方法传参等等
&和&&的区别
区别: &,前一个表达式如果错了,后面那个还就会执行
&&,前一个表达式如果错了,后面那个不执行简述if-else的执行流程
break什么作用
位置: 用在switch,loop中的
作用: 结束/中断/破坏当前结构,让当前结构不执行
作业
package com.qf.homework;import java.util.Scanner;/**** @desc 作业* ------------------* 技巧:* 1) 以结果倒推(以最终效果为导向)* 2) 把自己带人场景(你写功能,你自己当做客户去用)* 3) 尽量减少重复,有重复抽取出来,复用*/
public class Homework {/*** 选做题:* 模拟超市付款: 商品单价 商品数量* 键盘上输入商品单价,以及商品数量,* 然后计算应付总额* 提示用户可以有4种付款方式* 不同的付款方式有不同的折扣: 先展示四种付款方式* 现金没有折扣* 微信 0.95折* 支付宝 鼓励金付款金额的10% 鼓励金可以直接折算到付款金额中* 刷卡 满100-20* @param args*/public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(" ----------- java2313超市结账系统 ----------- " );Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入商品单价:" );double price = scanner.nextDouble( );System.out.println("请输入商品数量:" );int total = scanner.nextInt( );System.out.println("请选择付款方式: ");System.out.println("1. 现金,没有折扣");System.out.println("2. 微信,0.95折");System.out.println("3. 支付宝,9折");System.out.println("4. 刷卡 满100-20");System.out.print("您的付款方式是:" );double money = 0.0;int num = scanner.nextInt();if (num == 1) {System.out.println("您选择的现金支付,没有折扣哦~" );money = price * total ;} else if (num == 2) {System.out.println("您选择的微信支付,95折哦~" );money = price * total * 0.95;} else if (num == 3) {System.out.println("您选择的支付宝支付,9折哦~" );money = price * total * 0.9 ;} else if (num == 4) {System.out.println("您选择刷卡支付满100减20哦~" );if ((price * total) >= 100) {money = price * total - 20;} else {money = price * total;}} else {System.out.println("没有该付款方式!" );}System.out.println("应付金额:" + money + "元");}
}
变量作用域
关于变量,已知
- 变量要先声明后赋值再使用
- 变量名可以随便定义,见名知意即可
- 使用就是拿着变量做输出,运算,判断等等
还有一个注意事项
- 变量有作用域,即使用范围,就是离它最近的一对儿{} 内,超出范围变量不可用
- 在范围内可以随便使用,
- 在范围内不能重复声明,
- 互不影响的范围有重复声明的变量,没关系
一、循环
还是属于流程控制语句,可以控制代码走向
循环可以做到让某段代码重复执行的功能
实现循环的语句有三种方案:
- while [重要 ]
- dowhile [ 了解 ]
- for[ 最重要]
1.1 while
while , 当型循环,当条件为对,就执行循环
package com.qf.loop;/*** |-----------------------------------------------* | ____ _ _____ _ _ _ |* | / __ \ (_) / ____|| | (_)(_) |* || | | | _ _ _ | (___ | |__ _ _ _ _ |* || | | || || | | | \___ \ | '_ \ | || || | | ||* || |__| || || |_| | ____) || | | || || || |_| ||* | \___\_\|_| \__,_||_____/ |_| |_||_|| | \__,_||* | _/ | |* | |__/ |* |-----------------------------------------------* | 天道酬勤 |* | 代码敲烂 月薪过万 |* L----------------------------------------------* <p>* 什么时候需要使用循环语句? 代码重复量超过2次,就考虑使用循环语句** @desc while循环*/
public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 语法:* while (布尔表达式) {* 循环内容;* }* 执行流程:* 1) 执行到while开始判断* 2) 判断为true,执行{}内,继续回头再判断while后表达式* 3) 重复执行第2步,当有一次判断为false,那就结束循环,* 执行后续代码* 技巧:(循环有四要素)* 1) 循环初始值* 2) 循环控制条件* 3) 循环体* 4) 循环迭代(初始值在变化)*/// 打印5遍int a = 1; // 循环初始值while (a < 6) {// 循环控制条件System.out.println("好好学习 day day up");// 循环体a++;// 循环迭代}System.out.println("后续....");System.out.println("-----------------");// 打印1-10int b = 1;while (b < 11) {System.out.println(b);b++;}System.out.println("-----------------");// 输出10-1int c = 10;while (c > 0) {System.out.println(c);c--;}System.out.println("-----------------");// 输出1-100中的偶数int d = 1;while (d < 101) {if (d % 2 == 0) {System.out.println(d);}d++;}System.out.println("-----------------");// 输出1-100,每10个数,换一行输出// 当输出有好多行,可以使用\t进行制表// \t 是转义字符int e = 1;while (e < 101) {System.out.print(e+"\t");if (e % 10 == 0) {System.out.println( );// 换行}e++;}System.out.println("-----------------");// 输出1-100的和// 1+2+3+4+...+100int f = 1;int sum = 0;while (f < 101) {sum = f + sum;f++;}System.out.println("1-100的和:" + sum );}
}
1.2 do-while
do-while,直到型循环,直到条件为false就结束循环
语法:
do {// 循环体 } while(布尔表达式);执行:
- 先执行do内代码
- 后再判断布尔表达式,结果为true,就回头do内代码
- 直到判断结果为false,就跳过循环
package com.qf.loop;/**** @desc*/
public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 输出1-10int a = 1;do {System.out.println(a );a++;}while(a < 11);System.out.println("--------------" );// 10-1int b = 10;do {System.out.println(b );b--;}while (b > 0);System.out.println("--------------" );// 1-100偶数和int c= 1;int sum = 0;do {if (c % 2 == 0) {sum += c;}c++;} while (c < 101);System.out.println("1-100的偶数和:" + sum );}}
do-while和while的区别
- dowhile先执行一次后判断,while先判断如果对后执行
- 无论如何dowhile至少执行一次
// 区别int d = 1;// do {// System.out.println(d );// d++;// }while (d < 0);// 以上代码会执行一次while (d < 0) {System.out.println(d );d++;}// 以上代码不会执行
ps: dowhile不重要,了解即可
1.3 for [重点]
语法:
for(初始值;控制条件;迭代){循环体; }执行流程:
- 先执行初始化(只执行一次)
- 接着判断,判断为ture,会向下执行循环体
- 执行完后,再向上执行迭代
- 迭代完再执行判断,如果为true,继续向下执行(2,3,4步骤重复)
- 直到判断为false跳出循环,循环结束
package com.qf.loop;/*** @desc*/
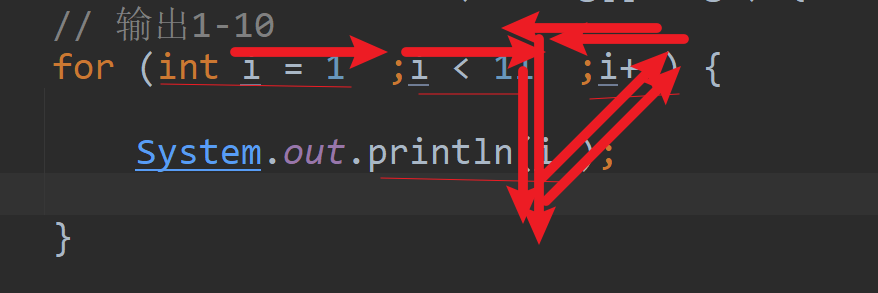
public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 输出1-10for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {System.out.println(i);}// 输出10-1for (int i = 10;i > 0;i--) {System.out.println(i );}// 输出1-100的奇数,并每5个奇数换行for (int i = 1;i < 101;i++) {if (i % 2 == 1) {System.out.print(i +"\t");}if (i % 10 == 0) {System.out.println( );}}System.out.println("-----------------" );int count = 0;// 计数器for (int i = 1;i < 101;i++) {if (i % 2 == 1) {count++;System.out.print(i +"\t");}if (count == 5) {System.out.println( );count = 0;}}// 计算1-100的和int sum = 0;for (int i = 1; i < 101; i++) {sum += i;}System.out.println("sum = " + sum );}
}
1.4 双层for循环
package com.qf.loop;/*** @desc*/
public class Demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 4行10列* *********** *********** *********** *********** 输出语句,只能输出一个**/// 外层循环控制行数for (int i = 1;i < 5;i++) {// 内层循环控制列数for (int j = 1;j < 11;j++) {System.out.print("*" );}System.out.println( );// 换行}// 场景: 每层楼,每个宿舍发传单/*** ** *** **** ***** ****** *******/for (int i = 1;i < 7;i++) {for (int j = 1;j <= i;j++) {System.out.print("*" );}System.out.println( );// 换行}/*** ******* ****** ***** **** *** **/for(int i = 1;i < 7;i++){for (int j = 6;j >= i; j--) {System.out.print("*" );}System.out.println( );}/*** ** **** ****** ******** **********/for (int i = 1;i < 6;i++) {for (int k = 4;k >= i;k--){System.out.print(" " );}for (int j = 1;j <= 2*i-1;j++) {System.out.print("*" );}System.out.println( );}// 打印9*9口诀表}
}
1.5 死循环
死循环, 是循环一致执行不再结束
while(true) {}// 死循环// int i = 1;// for (;;){// System.out.println(i );// i++;// }for (int i = 1;;i++){System.out.println(i );}
1.6 技巧
代码重复要使用循环,那么使用哪一个?
- 循环次数未知,建议用while
- 循环次数已知,建议用for
二、流程控制关键词
是指在if,switch,while,for这些流程控制语句中使用的关键词
- break
- continue
用来改变语句执行
2.1 break
位置: break只能在switch或者循环中使用
作用: 打断破坏当前结构,使其不执行
- 中断switch
- 中断所在这一层循环
package com.qf.loop;import java.util.Scanner;/*** |-----------------------------------------------* | ____ _ _____ _ _ _ |* | / __ \ (_) / ____|| | (_)(_) |* || | | | _ _ _ | (___ | |__ _ _ _ _ |* || | | || || | | | \___ \ | '_ \ | || || | | ||* || |__| || || |_| | ____) || | | || || || |_| ||* | \___\_\|_| \__,_||_____/ |_| |_||_|| | \__,_||* | _/ | |* | |__/ |* |-----------------------------------------------* | 天道酬勤 |* | 代码敲烂 月薪过万 |* L----------------------------------------------** @desc*/
public class Demo6 {public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {System.out.println(i);if (i == 5) {break;}}System.out.println("-----------");for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {for (int j = 1; j < 11; j++) {System.out.println("j=" + j);if (j == 5) {break;}}System.out.println("i=" + i);}System.out.println("后续");/*** 一直录入两个数字,判断大小* 直到录入 886 时,结束程序*/Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);while (true) {System.out.print("请输入数字a:");int a = scanner.nextInt( );if (a == 886) {System.out.println("程序结束,再见");break;}System.out.print("请输入数字b:");int b = scanner.nextInt( );if (a > b) {System.out.println("a大,a=" + a);} else if (a < b) {System.out.println("b大,b=" + b);} else {System.out.println("a == b = " + a);}}}
}
2.2 continue
continue 继续
位置: 只能在循环中使用
作用: 中断这一次循环,继续下次循环
练习题
* ATM机账户,登录* ps: 假设666666* 1) 最多允许输错5次* 2) 在5次内有一次正确,就可以登录成功,程序结束* 3) 如果输错,要给出提示语** ----------------------------------* ps: 可以带入产品经理角色,设计更人性的提示
总结
附录
loop 循环
num 数字
count 计数
total 总共
table 表格
sum 和