http://cplusoj.com/d/senior/p/SS231114D
重新梳理一下题目
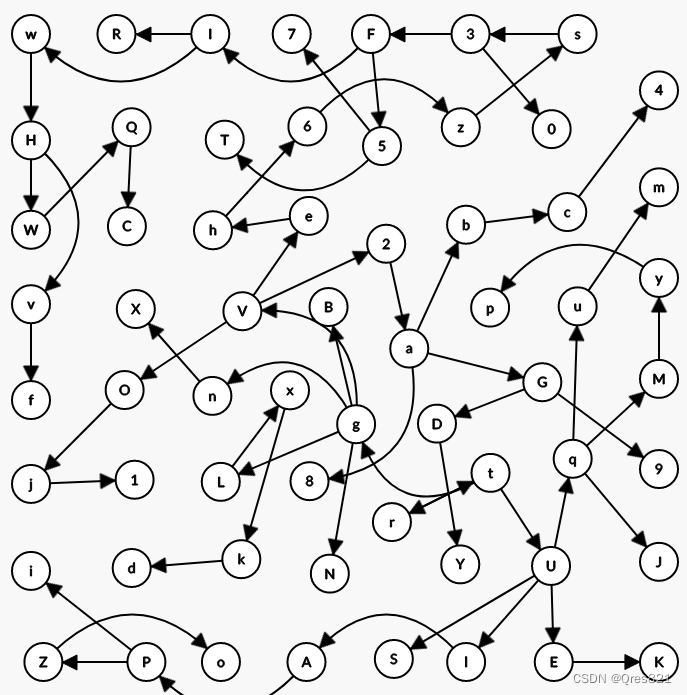
我们先建图 x → y x\to y x→y,然后对点分类:原串出现点,原串未出现点。
假如我们对一个原串出现点进行了操作,那么它剩余所有出边我们立刻去操作必然没有影响。所以我们只要所有原串出现点都操作一遍即可(如果有出边),那么我们就把边问题变成了点问题。
考虑一次置换过程抽象为原串上的一条链,那必然会造成一个损失。而要消除这个损失,一个方法是使链的尾端为原串未出现点。
对于图上路径问题,我们可以直接缩点,因为一个强连通里,我们必然可以从一个进一个出。最后变成了一个DAG。
这就变成了一个二分图问题。每个点可以向其连通的点连边,只要满足这个点还有出度,或者这个点为原串未出现点。
而左边为匹配的点就是代价了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#ifdef LOCAL#define debug(...) fprintf(stdout, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#else#define debug(...) void(0)
#endif
//#define int long long
inline int read(){int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||
ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48);ch=getchar();}return x*f;}
#define Z(x) (x)*(x)
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
//srand(time(0));
#define N 150
//#define M
//#define mo
namespace Flow {#define int long longstruct mf_graph {struct node {int x, y, z, n; }; vector<node>d; vector<int>h, H, dep; queue<int>q; int k; int u, v, w, S, T, ans=0; void reset(int n) {h.resize(n+5); k=1; d.resize(2); H.resize(n+5); dep.resize(n+5); }void cun(int x, int y, int z) {++k; d.pb({x, y, z, h[x]}); d[k].n=h[x]; h[x]=k;}void add_edge(int x, int y, int z) {
// swap(x, y);
// debug("%lld -> %lld %lld\n", x, y, z); cun(x, y, z); cun(y, x, 0); }int bfs() {while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); fill(dep.begin(), dep.end(), -1); h=H; dep[S]=1; q.push(S); while(!q.empty()) {u=q.front(); q.pop(); for(int g=h[u]; g; g=d[g].n) {v=d[g].y; w=d[g].z; if(w<=0 || dep[v]!=-1) continue; dep[v]=dep[u]+1; q.push(v); }}return dep[T]!=-1; }int dfs(int x, int w) {if(x==T) return w;if(!w) return 0; int ans=0, s; for(int &i=h[x]; i; i=d[i].n) {int y=d[i].y, z=d[i].z; if(dep[y]!=dep[x]+1) continue; if(z<=0) continue; s=dfs(y, min(w, z)); ans+=s; w-=s; d[i].z-=s; d[i^1].z+=s; if(!w) break; }return ans; }int flow(int SS, int TT) {S=SS; T=TT; H=h; while(bfs()) ans+=dfs(S, 1e18); return ans; }}; #undef int
}
using namespace Flow;
int n, m, i, j, k, S, T, TT;
vector<int>G[N], Ge[N];
int c[N], p[N], dfn[N], low[N], col[N], pan[N];
int vis[N][N], tot, tott, x, y, ans, cnt, shu[N], pp[N];
char str[N];
stack<int>z; void init() {for(i=0; i<=150; ++i) G[i].clear(), Ge[i].clear(); memset(c, 0, sizeof(c)); memset(p, 0, sizeof(p)); memset(dfn, 0, sizeof(dfn)); memset(low, 0, sizeof(low)); memset(col, 0, sizeof(col)); memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); memset(shu, 0, sizeof(shu)); memset(pp, 0, sizeof(pp)); tott=0;
}void dfs(int x) {
// debug("> %d %c\n", x, x); dfn[x]=low[x]=++tott; z.push(x); for(int y : G[x]) {if(dfn[y]==-1) continue; if(!dfn[y]) dfs(y), low[x]=min(low[x], low[y]); else low[x]=min(low[x], dfn[y]); }if(dfn[x]==low[x]) {
// debug("tot : %d\n", tot); ++tot; while(z.top()!=x) col[z.top()]=tot, dfn[z.top()]=-1, z.pop(); col[z.top()]=tot, z.pop(); dfn[x]=-1; }
// dfn[x]=-1;
}void dfs2(int x, int st) {vis[st][x]=1; pan[x]=1;
// debug("%d <=> %d\n", x, st); for(int y : Ge[x]) {if(pan[y]) continue; dfs2(y, st); }
}signed main()
{
// freopen("machine.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("machine.out", "w", stdout);#ifdef LOCALfreopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);#endifTT=read();while(TT--) {init(); scanf("%s", str+1); m=read(); for(i=1; str[i]; ++i) c[str[i]]++; for(i=k=0; i<=128; ++i) if(c[i]) ++k; //k为种类 n=k; debug("n : %lld\n", n); for(i=1; i<=m; ++i) {scanf("%s", str+1); x=str[1]; y=str[2];
// swap(x, y);
// printf("%c %c\n", x, y);
// if(!c[x]) continue; G[x].pb(y); p[x]=p[y]=1; if(c[x]) pp[x]=1; }mf_graph Gow; Gow.reset(600); tott=tot=0; S=599; T=S-1; for(i=0; i<=128; ++i) if(p[i] && !dfn[i]) {dfs(i); //debug(">> %lld\n", i); }for(i=0; i<=128; ++i) if(p[i] || c[i]) debug("%c %d %d %d | %d\n", i, c[i], p[i], pp[i], col[i]);
// for(i=0; i<=128; ++i) if(p[i] && c[i] && !pp[i]) --n; // printf("tot : %d | %d\n", tot, n); for(x=0; x<=128; ++x) if(p[x]) {for(int y : G[x]) if(col[x]!=col[y]) {
// printf("# (%d %d) %d -> %d\n", x, y, col[x], col[y]); Ge[col[x]].pb(col[y]); }}
// continue; for(i=1; i<=128; ++i) {if(pp[i]) shu[col[i]]|=1; if(c[i]) shu[col[i]]|=2; }for(i=1, cnt=0; i<=tot; ++i) {
// debug("shu[%d] = %d\n", i, shu[i]); if((shu[i]&1)==0) continue; memset(pan, 0, sizeof(pan)); dfs2(i, i); ++cnt; debug("Kuai : %d\n", i); for(j=1; j<=tot; ++j) if(vis[i][j]) {if(i==j) continue; if((shu[j]&1)==1 && (shu[j]&2)==0) continue; if((shu[j]&1)==0) continue;
// printf("%d %d\n", i, j); Gow.add_edge(i, j+150, 1);
// Gow.add_edge(j, i+150, 1); }for(j=0; j<=128; ++j) if(p[j] && !c[j] && vis[i][col[j]]) {debug("Col %d -> %d\n", i, j); Gow.add_edge(i, j+300, 1); }}debug("cnt : %d\n", cnt); for(i=0; i<150; ++i) Gow.add_edge(S, i, 1); for(i=151; i<=500; ++i) Gow.add_edge(i, T, 1); ans=Gow.flow(S, T); debug("ans1 : %d\n", ans); ans=cnt-ans; debug("ans2 : %d\n", ans); ans=n-ans; printf("%d\n", ans); }return 0;
}

![23111701[含文档+PPT+源码等]计算机毕业设计javaweb点餐系统全套餐饮就餐订餐餐厅](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/5ba3b2e41f5bf233bf4cddda4a3181af.png)