1. 前言
这段时间,在使用 natario1/CameraView 来实现带滤镜的预览、拍照、录像功能。
由于CameraView封装的比较到位,在项目前期,的确为我们节省了不少时间。
但随着项目持续深入,对于CameraView的使用进入深水区,逐渐出现满足不了我们需求的情况。
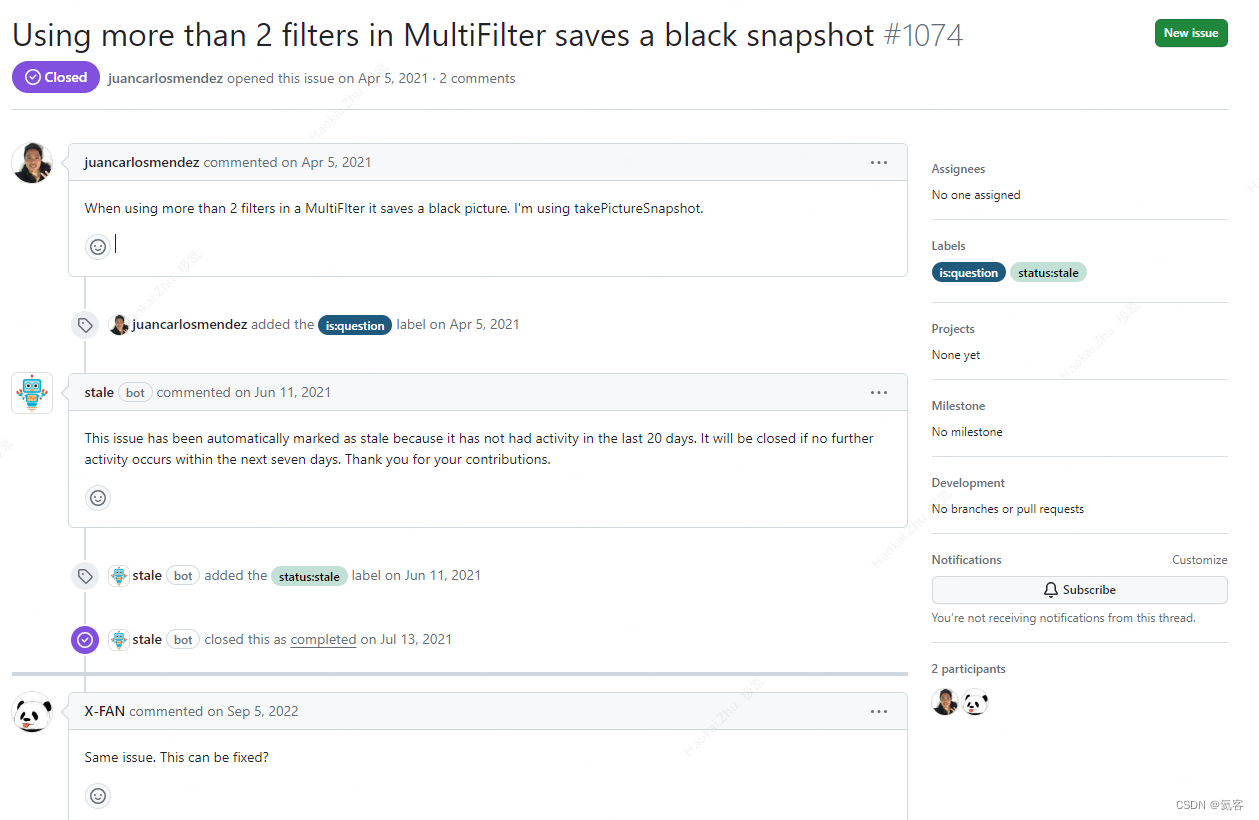
特别是对于使用MultiFilter,叠加2个滤镜拍照是正常的,叠加2个以上滤镜拍照,预览时正常,拍出的照片就会全黑。
Github中的issues中,也有不少提这个BUG的,但是作者一直没有修复该问题。
上篇文章,我们已经对带滤镜拍照的整个流程有了大概的了解,这篇文章,我们重点来看takeFrame方法,这是带滤镜拍照的核心代码。
接下来我们就来解析takeFrame的源码
2. 创建EGL窗口
首先,会创建EGL窗口,这里创建了一个假的,前台不可见的一个EGL窗口,专门用来保存图片
// 0. EGL window will need an output.
// We create a fake one as explained in javadocs.
final int fakeOutputTextureId = 9999;
SurfaceTexture fakeOutputSurface = new SurfaceTexture(fakeOutputTextureId);
fakeOutputSurface.setDefaultBufferSize(mResult.size.getWidth(), mResult.size.getHeight());
3. 创建EGL Surface
接着,来创建EglSurface
// 1. Create an EGL surface
final EglCore core = new EglCore(eglContext, EglCore.FLAG_RECORDABLE);
final EglSurface eglSurface = new EglWindowSurface(core, fakeOutputSurface);
eglSurface.makeCurrent();
3.1 EglSurface
其中,这个com.otaliastudios.opengl.EglSurface是作者自己创建的,继承自EglNativeSurface
public open class EglNativeSurface internal constructor(internal var eglCore: EglCore,internal var eglSurface: EglSurface) {private var width = -1private var height = -1/*** Can be called by subclasses whose width is guaranteed to never change,* so we can cache this value. For window surfaces, this should not be called.*/@Suppress("unused")protected fun setWidth(width: Int) {this.width = width}/*** Can be called by subclasses whose height is guaranteed to never change,* so we can cache this value. For window surfaces, this should not be called.*/@Suppress("unused")protected fun setHeight(height: Int) {this.height = height}/*** Returns the surface's width, in pixels.** If this is called on a window surface, and the underlying surface is in the process* of changing size, we may not see the new size right away (e.g. in the "surfaceChanged"* callback). The size should match after the next buffer swap.*/@Suppress("MemberVisibilityCanBePrivate")public fun getWidth(): Int {return if (width < 0) {eglCore.querySurface(eglSurface, EGL_WIDTH)} else {width}}/*** Returns the surface's height, in pixels.*/@Suppress("MemberVisibilityCanBePrivate")public fun getHeight(): Int {return if (height < 0) {eglCore.querySurface(eglSurface, EGL_HEIGHT)} else {height}}/*** Release the EGL surface.*/public open fun release() {eglCore.releaseSurface(eglSurface)eglSurface = EGL_NO_SURFACEheight = -1width = -1}/*** Whether this surface is current on the* attached [EglCore].*/@Suppress("MemberVisibilityCanBePrivate")public fun isCurrent(): Boolean {return eglCore.isSurfaceCurrent(eglSurface)}/*** Makes our EGL context and surface current.*/@Suppress("unused")public fun makeCurrent() {eglCore.makeSurfaceCurrent(eglSurface)}/*** Makes no surface current for the attached [eglCore].*/@Suppress("unused")public fun makeNothingCurrent() {eglCore.makeCurrent()}/*** Sends the presentation time stamp to EGL.* [nsecs] is the timestamp in nanoseconds.*/@Suppress("unused")public fun setPresentationTime(nsecs: Long) {eglCore.setSurfacePresentationTime(eglSurface, nsecs)}
}
3.2 EglCore
可以看到EglNativeSurface内部其实基本上就是调用的EglCore,EglCore内部封装了EGL相关的方法。
这里的具体实现我们不需要细看,只需要知道EglSurface是作者自己实现的一个Surface就可以了,内部封装了EGL,可以实现和GlSurfaceView类似的一些功能,在这里使用的EglSurface是专门给拍照准备的。
这样做的好处在于拍照的时候,预览界面(GLSurfaceView)不会出现卡顿的现象,但是坏处也显而易见,就是可能会出现预览效果和拍照的实际效果不一致的情况。(也就是本文所遇到的BUG的情况)
OpenGL是一个跨平台的操作GPU的API,OpenGL需要本地视窗系统进行交互,就需要一个中间控制层。
EGL就是连接OpenGL ES和本地窗口系统的接口,引入EGL就是为了屏蔽不同平台上的区别。
public expect class EglCore : EglNativeCorepublic open class EglNativeCore internal constructor(sharedContext: EglContext = EGL_NO_CONTEXT, flags: Int = 0) {private var eglDisplay: EglDisplay = EGL_NO_DISPLAYprivate var eglContext: EglContext = EGL_NO_CONTEXTprivate var eglConfig: EglConfig? = nullprivate var glVersion = -1 // 2 or 3init {eglDisplay = eglGetDefaultDisplay()if (eglDisplay === EGL_NO_DISPLAY) {throw RuntimeException("unable to get EGL14 display")}if (!eglInitialize(eglDisplay, IntArray(1), IntArray(1))) {throw RuntimeException("unable to initialize EGL14")}// Try to get a GLES3 context, if requested.val chooser = EglNativeConfigChooser()val recordable = flags and FLAG_RECORDABLE != 0val tryGles3 = flags and FLAG_TRY_GLES3 != 0if (tryGles3) {val config = chooser.getConfig(eglDisplay, 3, recordable)if (config != null) {val attributes = intArrayOf(EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION, 3, EGL_NONE)val context = eglCreateContext(eglDisplay, config, sharedContext, attributes)try {Egloo.checkEglError("eglCreateContext (3)")eglConfig = configeglContext = contextglVersion = 3} catch (e: Exception) {// Swallow, will try GLES2}}}// If GLES3 failed, go with GLES2.val tryGles2 = eglContext === EGL_NO_CONTEXTif (tryGles2) {val config = chooser.getConfig(eglDisplay, 2, recordable)if (config != null) {val attributes = intArrayOf(EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION, 2, EGL_NONE)val context = eglCreateContext(eglDisplay, config, sharedContext, attributes)Egloo.checkEglError("eglCreateContext (2)")eglConfig = configeglContext = contextglVersion = 2} else {throw RuntimeException("Unable to find a suitable EGLConfig")}}}/*** Discards all resources held by this class, notably the EGL context. This must be* called from the thread where the context was created.* On completion, no context will be current.*/internal open fun release() {if (eglDisplay !== EGL_NO_DISPLAY) {// Android is unusual in that it uses a reference-counted EGLDisplay. So for// every eglInitialize() we need an eglTerminate().eglMakeCurrent(eglDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT)eglDestroyContext(eglDisplay, eglContext)eglReleaseThread()eglTerminate(eglDisplay)}eglDisplay = EGL_NO_DISPLAYeglContext = EGL_NO_CONTEXTeglConfig = null}/*** Makes this context current, with no read / write surfaces.*/internal open fun makeCurrent() {if (!eglMakeCurrent(eglDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, eglContext)) {throw RuntimeException("eglMakeCurrent failed")}}/*** Destroys the specified surface. Note the EGLSurface won't actually be destroyed if it's* still current in a context.*/internal fun releaseSurface(eglSurface: EglSurface) {eglDestroySurface(eglDisplay, eglSurface)}/*** Creates an EGL surface associated with a Surface.* If this is destined for MediaCodec, the EGLConfig should have the "recordable" attribute.*/internal fun createWindowSurface(surface: Any): EglSurface {// Create a window surface, and attach it to the Surface we received.val surfaceAttribs = intArrayOf(EGL_NONE)val eglSurface = eglCreateWindowSurface(eglDisplay, eglConfig!!, surface, surfaceAttribs)Egloo.checkEglError("eglCreateWindowSurface")if (eglSurface === EGL_NO_SURFACE) throw RuntimeException("surface was null")return eglSurface}/*** Creates an EGL surface associated with an offscreen buffer.*/internal fun createOffscreenSurface(width: Int, height: Int): EglSurface {val surfaceAttribs = intArrayOf(EGL_WIDTH, width, EGL_HEIGHT, height, EGL_NONE)val eglSurface = eglCreatePbufferSurface(eglDisplay, eglConfig!!, surfaceAttribs)Egloo.checkEglError("eglCreatePbufferSurface")if (eglSurface === EGL_NO_SURFACE) throw RuntimeException("surface was null")return eglSurface}/*** Makes our EGL context current, using the supplied surface for both "draw" and "read".*/internal fun makeSurfaceCurrent(eglSurface: EglSurface) {if (eglDisplay === EGL_NO_DISPLAY) logv("EglCore", "NOTE: makeSurfaceCurrent w/o display")if (!eglMakeCurrent(eglDisplay, eglSurface, eglSurface, eglContext)) {throw RuntimeException("eglMakeCurrent failed")}}/*** Makes our EGL context current, using the supplied "draw" and "read" surfaces.*/internal fun makeSurfaceCurrent(drawSurface: EglSurface, readSurface: EglSurface) {if (eglDisplay === EGL_NO_DISPLAY) logv("EglCore", "NOTE: makeSurfaceCurrent w/o display")if (!eglMakeCurrent(eglDisplay, drawSurface, readSurface, eglContext)) {throw RuntimeException("eglMakeCurrent(draw,read) failed")}}/*** Calls eglSwapBuffers. Use this to "publish" the current frame.* @return false on failure*/internal fun swapSurfaceBuffers(eglSurface: EglSurface): Boolean {return eglSwapBuffers(eglDisplay, eglSurface)}/*** Sends the presentation time stamp to EGL. Time is expressed in nanoseconds.*/internal fun setSurfacePresentationTime(eglSurface: EglSurface, nsecs: Long) {eglPresentationTime(eglDisplay, eglSurface, nsecs)}/*** Returns true if our context and the specified surface are current.*/internal fun isSurfaceCurrent(eglSurface: EglSurface): Boolean {return eglContext == eglGetCurrentContext()&& eglSurface == eglGetCurrentSurface(EGL_DRAW)}/*** Performs a simple surface query.*/internal fun querySurface(eglSurface: EglSurface, what: Int): Int {val value = IntArray(1)eglQuerySurface(eglDisplay, eglSurface, what, value)return value[0]}public companion object {/*** Constructor flag: surface must be recordable. This discourages EGL from using a* pixel format that cannot be converted efficiently to something usable by the video* encoder.*/internal const val FLAG_RECORDABLE = 0x01/*** Constructor flag: ask for GLES3, fall back to GLES2 if not available. Without this* flag, GLES2 is used.*/internal const val FLAG_TRY_GLES3 = 0x02}
}
4. 修改transform
这里的mTextureDrawer是GlTextureDrawer,GlTextureDrawer是一个绘制的管理类,无论是GlCameraPreview(预览)还是SnapshotGlPictureRecorder(带滤镜拍照),都是调用GlTextureDrawer.draw()来渲染openGL的。
public class GlTextureDrawer {//...省略了不重要的代码...private final GlTexture mTexture;private float[] mTextureTransform = Egloo.IDENTITY_MATRIX.clone();public void draw(final long timestampUs) {//...省略了不重要的代码...if (mProgramHandle == -1) {mProgramHandle = GlProgram.create(mFilter.getVertexShader(),mFilter.getFragmentShader());mFilter.onCreate(mProgramHandle);}GLES20.glUseProgram(mProgramHandle);mTexture.bind();mFilter.draw(timestampUs, mTextureTransform);mTexture.unbind();GLES20.glUseProgram(0);}public void release() {if (mProgramHandle == -1) return;mFilter.onDestroy();GLES20.glDeleteProgram(mProgramHandle);mProgramHandle = -1;}
}
而transform ,也就是mTextureTransform,会传到Filter.draw()中,最终会改变OpenGL绘制的坐标矩阵,也就是GLSL中的uMVPMatrix变量。
而这边就是修改transform 的值,从而对图像进行镜像、旋转等操作。
final float[] transform = mTextureDrawer.getTextureTransform();// 2. Apply preview transformations
surfaceTexture.getTransformMatrix(transform);
float scaleTranslX = (1F - scaleX) / 2F;
float scaleTranslY = (1F - scaleY) / 2F;
Matrix.translateM(transform, 0, scaleTranslX, scaleTranslY, 0);
Matrix.scaleM(transform, 0, scaleX, scaleY, 1);// 3. Apply rotation and flip// If this doesn't work, rotate "rotation" before scaling, like GlCameraPreview does.Matrix.translateM(transform, 0, 0.5F, 0.5F, 0); // Go back to 0,0Matrix.rotateM(transform, 0, rotation + mResult.rotation, 0, 0, 1); // Rotate to OUTPUTMatrix.scaleM(transform, 0, 1, -1, 1); // Vertical flip because we'll use glReadPixelsMatrix.translateM(transform, 0, -0.5F, -0.5F, 0); // Go back to old position
5. 绘制Overlay
这个没有研究过,似乎是用来绘制覆盖层。这不重要,这里跳过,一般也不会进入这个逻辑。
// 4. Do pretty much the same for overlays
if (mHasOverlay) {// 1. First we must draw on the texture and get latest imagemOverlayDrawer.draw(Overlay.Target.PICTURE_SNAPSHOT);// 2. Then we can apply the transformationsMatrix.translateM(mOverlayDrawer.getTransform(), 0, 0.5F, 0.5F, 0);Matrix.rotateM(mOverlayDrawer.getTransform(), 0, mResult.rotation, 0, 0, 1);Matrix.scaleM(mOverlayDrawer.getTransform(), 0, 1, -1, 1); // Vertical flip because we'll use glReadPixelsMatrix.translateM(mOverlayDrawer.getTransform(), 0, -0.5F, -0.5F, 0);
}
mResult.rotation = 0;
6. 绘制并保存
这里就是带滤镜拍照部分,核心中的核心代码了。
这里主要分为两步
mTextureDrawer.draw: 绘制滤镜eglSurface.toByteArray: 将画面保存为JPEG格式的Byte数组
// 5. Draw and save
long timestampUs = surfaceTexture.getTimestamp() / 1000L;
LOG.i("takeFrame:", "timestampUs:", timestampUs);
mTextureDrawer.draw(timestampUs);
if (mHasOverlay) mOverlayDrawer.render(timestampUs);
mResult.data = eglSurface.toByteArray(Bitmap.CompressFormat.JPEG);
这部分具体的代码具体详见下篇文章
7. 释放资源
// 6. Cleanup
eglSurface.release();
mTextureDrawer.release();
fakeOutputSurface.release();
if (mHasOverlay) mOverlayDrawer.release();
core.release();
dispatchResult();
8. 其他
8.1 解决CameraView滤镜黑屏系列
Android 解决CameraView叠加2个以上滤镜拍照黑屏的BUG (一)_氦客的博客-CSDN博客
Android 解决CameraView叠加2个以上滤镜拍照黑屏的BUG (二)_氦客的博客-CSDN博客
Android 解决CameraView叠加2个以上滤镜拍照黑屏的BUG (三)_氦客的博客-CSDN博客
8.2 Android Camera2 系列
更多Camera2相关文章,请看
十分钟实现 Android Camera2 相机预览_氦客的博客-CSDN博客
十分钟实现 Android Camera2 相机拍照_氦客的博客-CSDN博客
十分钟实现 Android Camera2 视频录制_氦客的博客-CSDN博客
8.3 Android 相机相关文章
Android 使用CameraX实现预览/拍照/录制视频/图片分析/对焦/缩放/切换摄像头等操作_氦客的博客-CSDN博客
Android 从零开发一个简易的相机App_android开发简易app_氦客的博客-CSDN博客
Android 使用Camera1实现相机预览、拍照、录像_android 相机预览_氦客的博客-CSDN博客