线程池介绍
那究竟什么是线程池呢?
线程池是一种线程使用模式.
线程过多会带来调度开销,进而影响缓存局部性和整体性能.
而线程池维护着多个线程,等待着监督管理者分配可并发执行的任务.
这避免了在处理短时间任务时创建与销毁线程的代价.
线程池不仅能够保证内核的充分利用,还能防止过分调度.
前面我们介绍过生产者消费者模型,线程池其实看作是它的一个变型
它把任务队列和消费者(线程)进行了封装,统称为server
用户不需要再关心线程创建的问题,只需要构建好任务,把它直接送往server里面即可,server会帮我们解决对应的任务

具体的应用场景有哪些呢?
-
- 需要大量的线程来完成任务,且完成任务的时间比较短.
WEB服务器完成网页请求这样的任务,使用线程池技术是非常合适的.因为单个任务小,而任务数量巨大,你可以想象一个热门网站的点击次数.
- 需要大量的线程来完成任务,且完成任务的时间比较短.
-
- 对性能要求苛刻的应用,比如要求服务器迅速响应客户请求。
-
- 接受突发性的大量请求,但不至于使服务器因此产生大量线程的应用。突发性大量客户请求,在没有线程池情况下,将产生大量线程,虽然理论上大部分操作系统线程数目最大值不是问题,短时间内产生大量线程可能使内存到达极限,从而出现错误
第一个版本(基本框架搭建)
了解基本概念后,我们就可以具体实现相应的代码
本质上就是创建一个类
不过该类里面会自动封装相应的锁,条件变量,以及对应创建销毁线程的方法
一旦实例化,就有相应的线程为我们服务,用户不需要再考虑线程创建的问题,而只需要传任务即可
具体代码如下:
-
- 任务队列我们依旧用queue进行实现,并且不对任务的上限做约束
-
- 线程数目我们先设定为5个,如果有需求,再进行对应的调整即可
1 #pragma once2 #include <iostream>3 #include <vector>4 #include <queue>5 #include "Task.hpp"6 #include <pthread.h>7 8 const static int N = 5; //默认线程数量9 template <class T>10 class ThreadPool11 {12 public:13 ThreadPool(int num = N):_num(num),_threads(num)14 {15 pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex,nullptr);16 pthread_cond_init(&_cond,nullptr);17 }18 ~ThreadPool()19 {20 pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);21 pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond);22 }23 void LockQueue()24 {25 pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex); //给任务队列上锁26 }27 void UnlockQueue()28 {29 pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex); //给任务队列解锁30 } 31 void ThreadWait()32 {33 pthread_cond_wait(&_cond,&_mutex); //没有任务,线程自动进入等待34 }35 void ThreadWakeUp()36 {37 pthread_cond_signal(&_cond); //唤醒任务队列里面的线程38 }39 //判断任务队列是否为空 40 bool Isempty()41 {42 return _tasks.empty();43 }44 T popTask()45 {46 T t = _tasks.front();47 _tasks.pop();48 return t;49 }50 void PushTask(const T&t)51 {52 LockQueue(); //给任务队列加锁53 _tasks.push(t); //任务入列54 ThreadWakeUp(); //唤醒线程进行工作55 UnlockQueue(); //任务队列解锁56 }57 static void* ThreadRoutine(void* args)58 {59 //每个线程自己挂接,这样自动销毁60 pthread_detach(pthread_self());61 //将传进啦的this指针,转成我们的对象,这样即可访问里面的方法和成员变量62 ThreadPool<Task>* tp = static_cast<ThreadPool<Task> *>(args);63 while (true)64 {65 tp->LockQueue(); //每个线程访问任务队列时,都必须先加锁66 //任务队列不为空67 while(tp->Isempty())68 {69 tp->ThreadWait(); //假如没有任务,则等待 70 }71 //有任务,取出对应的任务72 T t = tp->popTask();73 //归还锁,让其它线程也能够拿到74 tp->UnlockQueue();75 t(); //执行任务76 std::cout << "ThreadRoutine done:" << t.formatRes() << std::endl;77 }78 }79 //创建对应的线程80 void start()81 { 82 //创建对应的线程83 for(int i = 0;i < _num;i++)84 {85 pthread_create(&_threads[i],nullptr,ThreadRoutine,(void*)this);86 }87 }88 private:89 std::vector<pthread_t> _threads; //线程编号向量90 int _num; //线程数量91 92 std::queue<T> _tasks; //任务数量93 pthread_mutex_t _mutex; //锁94 pthread_cond_t _cond; //条件变量95 };第二个版本(封装自己的线程)
在第一个版本中,我们采用的是原生线程库里面的线程进行的封装
但我们还可以进一步进行改造,用我们之前自己封装的线程,来实现线程池.
//自己封装的线程
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
class Thread{
public:typedef enum{NEW = 0,RUNNING,EXITED}ThreadStatus;typedef void* (*func_t)(void*);
public:Thread(int num,func_t func,void* args):_tid(0),_status(NEW),_func(func),_args(args){//名字由于还要接收用户给的编号,因此在构造函数内进行初始化char buffer[128];snprintf(buffer,sizeof(buffer),"thread-%d",num);_name = buffer;}~Thread(){}//返回线程的状态int status() {return _status;}//返回线程的名字std::string name() {return _name;}//返回线程的id//只有线程在运行的时候,才会有对应的线程idpthread_t GetTid(){if (_status == RUNNING){return _tid;}else{return 0;}}//pthread_create函数默认第三个参数是void *(*start_routine) (void *)//而类成员函数具有默认参数this指针,直接传并不匹配,所以我们用static修饰,使其变成类成员函数//但是会有新的问题——无法访问类内成员,也就无法调用_funcstatic void * ThreadRun(void* args){Thread* ts = (Thread*)args; //此时就获取到我们对象的指针// _func(args); //无法回调相应的方法(成员变量无法直接被访问)(*ts)(); //传this指针进来,用仿函数回调_funcreturn nullptr;}void operator()() //仿函数{//假如传进来的线程函数不为空,则调用相应的函数if(_func != nullptr) _func(_args);}//线程运行void Run(){//线程创建的参数有四个int n = pthread_create(&_tid,nullptr,ThreadRun,this);if(n != 0) exit(0);_status = RUNNING;}//线程等待void Join(){int n = pthread_join(_tid,nullptr);if (n != 0){std::cerr << "main thread join error :" << _name << std::endl;return;}_status = EXITED;}
private:pthread_t _tid; //线程idstd::string _name; //线程的名字func_t _func; //未来要回调的函数void*_args;ThreadStatus _status; //目前该线程的状态
};
//V2版本
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include "Task.hpp"
#include <pthread.h>const static int N = 5; //默认线程数量
template <class T>
class ThreadPool
{
public:ThreadPool(int num = N):_num(num),_threads(num){pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex,nullptr);pthread_cond_init(&_cond,nullptr);}~ThreadPool(){pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond);}void LockQueue(){pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex); //给任务队列上锁}void UnlockQueue(){pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex); //给任务队列解锁}void ThreadWait(){pthread_cond_wait(&_cond,&_mutex); //没有任务,线程自动进入等待}void ThreadWakeUp(){pthread_cond_signal(&_cond); //唤醒任务队列里面的线程}//判断任务队列是否为空bool Isempty(){return _tasks.empty();}T popTask(){T t = _tasks.front();_tasks.pop();return t;}void PushTask(const T&t){LockQueue(); //给任务队列加锁_tasks.push(t); //任务入列ThreadWakeUp(); //唤醒线程进行工作UnlockQueue(); //任务队列解锁}static void* ThreadRoutine(void* args){//每个线程自己挂接,这样自动销毁pthread_detach(pthread_self());//将传进啦的this指针,转成我们的对象,这样即可访问里面的方法和成员变量ThreadPool<Task>* tp = static_cast<ThreadPool<Task> *>(args);while (true){tp->LockQueue(); //每个线程访问任务队列时,都必须先加锁//任务队列不为空while(tp->Isempty()){tp->ThreadWait(); //假如没有任务,则等待}//有任务,取出对应的任务T t = tp->popTask();//归还锁,让其它线程也能够拿到tp->UnlockQueue();t(); //执行任务std::cout << "ThreadRoutine done:" << t.formatRes() << std::endl;}}//创建对应的线程void start(){ //创建对应的线程for(int i = 0;i < _num;i++){pthread_create(&_threads[i],nullptr,ThreadRoutine,(void*)this);}}
private:std::vector<pthread_t> _threads; //线程编号向量int _num; //线程数量std::queue<T> _tasks; //任务数量pthread_mutex_t _mutex; //锁pthread_cond_t _cond; //条件变量
};
第三个版本(封装自己的锁)
在第二个版本中,我们用自己封装的线程,来实现线程池.
再进一步改造,我们还可以用我们自己封装的锁,来进一步进行封装.
//自己封装的锁
#pragma once#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>class Mutex
{
public:Mutex(pthread_mutex_t* mutex):pmutex(mutex){}~Mutex(){}void Lock(){pthread_mutex_lock(pmutex);}void Unlock(){pthread_mutex_unlock(pmutex);}
private:pthread_mutex_t* pmutex;
};class LockGuard
{
public:LockGuard(pthread_mutex_t* mutex):_mutex(mutex){//在创建的时候,就自动上锁_mutex.Lock();}~LockGuard(){//销毁的时候,自动解锁_mutex.Unlock();}private:Mutex _mutex;
};
我们自己实现的锁,会在创建时,自动上锁;出了作用域后,自动进行解锁
因此我们原来线程池代码可以进一步进行优化
给任务队列进行上锁,解锁的成员函数,都可以直接删除
假如要上锁,只需要创建对应LockGuard对象即可,然后把临界区的代码用中括号全部括起来
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include "Task.hpp"
#include <pthread.h>
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include "mymutex.hpp"const static int N = 5; //默认线程数量
template <class T>
class ThreadPool
{
public:ThreadPool(int num = N):_num(num){pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex,nullptr);pthread_cond_init(&_cond,nullptr);}~ThreadPool(){for(auto &t:_threads){t.Join();}pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond);}pthread_mutex_t* Getlock(){return &_mutex;}void ThreadWait(){pthread_cond_wait(&_cond,&_mutex); //没有任务,线程自动进入等待}void ThreadWakeUp(){pthread_cond_signal(&_cond); //唤醒任务队列里面的线程}//判断任务队列是否为空bool Isempty(){return _tasks.empty();}T popTask(){T t = _tasks.front();_tasks.pop();return t;}void PushTask(const T&t){LockGuard lockguard(&_mutex);_tasks.push(t); //任务入列ThreadWakeUp(); //唤醒线程进行工作}static void* ThreadRoutine(void* args){//将传进啦的this指针,转成我们的对象,这样即可访问里面的方法和成员变量ThreadPool<Task>* tp = static_cast<ThreadPool<Task> *>(args);while (true){T t;//任务队列不为空{LockGuard lockguard(tp->Getlock());while(tp->Isempty()){tp->ThreadWait(); //假如没有任务,则等待}//有任务,取出对应的任务t = tp->popTask();}t(); //执行任务std::cout << " Routine done:" << t.formatRes() << std::endl;}}//创建对应的线程void Init(){for(int i = 0;i < _num;i++){_threads.push_back(Thread(i,ThreadRoutine,(void*)this));} }void start(){for (auto &t:_threads){ t.Run(); //调用自定义线程里面的Run函数,创建相应的线程}}void Check(){for(auto &t:_threads){std::cout << t.name()<< " is Running..." <<std::endl;}}
private:std::vector<Thread> _threads; //线程编号向量int _num; //线程数量std::queue<T> _tasks; //任务数量pthread_mutex_t _mutex; //锁pthread_cond_t _cond; //条件变量
};我们可以用我们实现的线程池,完成加减乘除的任务
首先实现一个Task类,该类会用传入其中的x,y,运算符创建对象
调用对应的仿函数,即可完成对应的四则运算任务
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>class Task
{
public://无参构造Task(){}Task(int x,int y,char op):_x(x),_y(y),_op(op),_result(0),_exitflag(0){}~Task(){}void operator()(){switch(_op){case '+':{_result = _x + _y;break;}case '-':{_result = _x - _y;break;}case '*':{_result = _x * _y;break;}case '/':{if(_y == 0)_exitflag = -1;else_result = _x / _y;break;}case '%':{ if (_y == 0)_exitflag = -2;else_result = _x % _y;break;}default:break;}}std::string formatArgs(){return std::to_string(_x) + _op + std::to_string(_y) + "="; }std::string formatRes(){return std::to_string(_result) + "(" + std::to_string(_exitflag) + ")";}
private:int _x;int _y;char _op; //运算符int _result; //运算的结果int _exitflag; //退出成功与否
};
主函数传参时,把对应构建好的Task类对象传入即可,剩下的工作,线程池会自动帮我们创建好对应的线程,执行并显示我们的任务
#include <iostream>
#include "Task.hpp"
#include <unistd.h>
#include <memory>
//#include "ThreadPool_V1.hpp"
//#include "ThreadPool_V2.hpp"
#include "ThreadPool_V3.hpp"
int main()
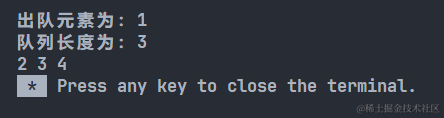
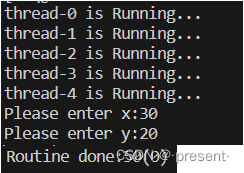
{ThreadPool<Task>* tp = new ThreadPool<Task>();tp->Init();tp->start(); //线程池启动tp->Check(); //看线程是否启动成功while(true){int x,y;char op;std::cout << "Please enter x:";std::cin >> x;std::cout << "Please enter y:";std::cin >> y;std::cout << "Please enter op(+-*/%):";std::cin >> op;Task t(x,y,op);tp->PushTask(t); //将任务传入线程池中即可}return 0;
}
结果显示:
第四个版本(线程安全版本)
IT行业这么火, 涌入的人很多. 俗话说林子大了啥鸟都有. 大佬和菜鸡们两极分化的越来越严重. 为了让菜鸡们不太拖大佬的后腿,
于是大佬们针对一些经典的常见的场景, 给定了一些对应的解决方案, 这个就是 设计模式
其中单例模式就是设计模式中的一种
所谓的单例模式就是指,有一个特殊类,有且只有用它来创建一个对象
为什么要设计这种模式呢?
拿我们线程池来举例,线程池这个对象,大多数时候,我们并不需要创建多个,假如任务很多,我们只要相应调节线程池里面的线程数目即可,假如创建多个线程池对象,这样其实效率并不高.
单例对象的最终目的就是为了提高效率
那具体如何设计这个特殊类呢?(懒汉模式)
1.构造函数私有化,拷贝,赋值函数删除(这样外面的用户也就不能再创建对象了)
2.类成员变量中加入类指针,并用static进行修饰
3.在类内提供相应接口函数,每次用户调用该接口时,用类指针创建对象,但是假如类指针不为空,也就是已经创建了一个对象,则直接返回该对象的指针,不会再创建新的对象
具体改造后的代码如下:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include "Task.hpp"
#include <pthread.h>
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include "mymutex.hpp"const static int N = 5; //默认线程数量
template <class T>
class ThreadPool
{
private:ThreadPool(int num = N):_num(num){pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex,nullptr);pthread_cond_init(&_cond,nullptr);}ThreadPool(const ThreadPool<T>& tp) = delete; //删除构造函数void operator=(const ThreadPool<T>& tp) = delete; //删除赋值函数public:static ThreadPool<T>* GetInstance(){if(nullptr == instance)//提高效率 {LockGuard lockguard(&instance_lock); if(nullptr == instance) //保证有且只有一个线程可以创建对象{instance = new ThreadPool<T>();instance->Init();instance->start();}}return instance;}~ThreadPool(){for(auto &t:_threads){t.Join();}pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond);}pthread_mutex_t* Getlock(){return &_mutex;}void ThreadWait(){pthread_cond_wait(&_cond,&_mutex); //没有任务,线程自动进入等待}void ThreadWakeUp(){pthread_cond_signal(&_cond); //唤醒任务队列里面的线程}//判断任务队列是否为空bool Isempty(){return _tasks.empty();}T popTask(){T t = _tasks.front();_tasks.pop();return t;}void PushTask(const T&t){LockGuard lockguard(&_mutex);_tasks.push(t); //任务入列ThreadWakeUp(); //唤醒线程进行工作}static void* ThreadRoutine(void* args){//将传进啦的this指针,转成我们的对象,这样即可访问里面的方法和成员变量ThreadPool<Task>* tp = static_cast<ThreadPool<Task> *>(args);while (true){T t;//任务队列不为空{LockGuard lockguard(tp->Getlock());while(tp->Isempty()){tp->ThreadWait(); //假如没有任务,则等待}//有任务,取出对应的任务t = tp->popTask();}t(); //执行任务std::cout << " Routine done:" << t.formatRes() << std::endl;}}//创建对应的线程void Init(){for(int i = 0;i < _num;i++){_threads.push_back(Thread(i,ThreadRoutine,(void*)this));} }void start(){for (auto &t:_threads){ t.Run(); //调用自定义线程里面的Run函数,创建相应的线程}}void Check(){for(auto &t:_threads){std::cout << t.name()<< " is Running..." <<std::endl;}}
private:std::vector<Thread> _threads; //线程编号向量int _num; //线程数量std::queue<T> _tasks; //任务数量pthread_mutex_t _mutex; //锁pthread_cond_t _cond; //条件变量static ThreadPool<T>* instance; //类对象指针static pthread_mutex_t instance_lock; //类对象锁
};//对对象指针进行初始化
template <class T>
ThreadPool<T>* ThreadPool<T>::instance = nullptr;//对类对象锁进行初始化
template <class T>
pthread_mutex_t ThreadPool<T>::instance_lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
这里有个细节需要注意
在实现GetInstance函数时,我们采取双检查加锁的方式
原因在于,加锁解锁必定要在临界区之前,否则将毫无意义,依旧会出现多个线程创建多个对象,出现并发问题
但是单例只会被创建一次,申请锁这个操作本身是一种消耗
因此我们在外层再套一层判断,假如不为空,则不会进去,也就不会再因为申请锁这个操作而白白消耗
提高效率的同时,还保证了线程安全