依赖
建一个工程,两个Module:
1. springboot模块,表示springboot框架的源码实现
2. user包,表示用户业务系统,用来写业务代码来测试我们所模拟出来的SpringBoot
首先,SpringBoot是基于的Spring,所以我们要依赖Spring,然后我希望我们模拟出来的
SpringBoot也支持Spring MVC的那一套功能,所以也要依赖Spring MVC,包括Tomcat等,所以在
SpringBoot模块中要添加以下依赖
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>5.3.18</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-web</artifactId><version>5.3.18</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId><version>5.3.18</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>javax.servlet</groupId><artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId><version>4.0.1</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId><artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId><version>9.0.60</version></dependency></dependencies> 在User模块下我们进行正常的开发就行了,比如先添加SpringBoot依赖:
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.example</groupId><artifactId>springboot</artifactId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId><artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId><artifactId>jetty-server</artifactId><version>9.4.43.v20210629</version></dependency></dependencies> 然后定义相关的Controller和Service:

@RestControllerpublic class UserController {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@GetMapping("test")public String test(){return userService.test();}} 因为我们模拟实现的是SpringBoot,而不是SpringMVC,所以我直接在user包下定义了
UserController和UserService,最终我希望能运行MyApplication中的main方法,就直接启动了项
目,并能在浏览器中正常的访问到UserController中的某个方法。
核心注解和核心类
我们在真正使用SpringBoot时,核心会用到SpringBoot一个类和注解:
1. @SpringBootApplication,这个注解是加在应用启动类上的,也就是main方法所在的类
2. SpringApplication,这个类中有个run()方法,用来启动SpringBoot应用的
所以我们也来模拟实现他们
一个@ZhouyuSpringBootApplication注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Configuration@ComponentScanpublic @interface ZhouyuSpringBootApplication {} 一个用来实现启动逻辑的ZhouyuSpringApplication类。
public class ZhouyuSpringApplication {public static void run(Class clazz){}} 注意run方法需要接收一个Class类型的参数,这个class是用来干嘛的,等会就知道了。
有了以上两者,我们就可以在MyApplication中来使用了,比如:
@ZhouyuSpringBootApplicationpublic class MyApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {ZhouyuSpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class);}} 现在用来是有模有样了,但中看不中用,所以我们要来好好实现以下run方法中的逻辑了。
run方法
run方法中需要实现什么具体的逻辑呢?
首先,我们希望run方法一旦执行完,我们就能在浏览器中访问到UserController,那势必在run方法 中要启动Tomcat,通过Tomcat就能接收到请求了。
大家如果学过Spring MVC的底层原理就会知道,在SpringMVC中有一个Servlet非常核心,那就是 DispatcherServlet,这个DispatcherServlet需要绑定一个Spring容器,因为DispatcherServlet接收 到请求后,就会从所绑定的Spring容器中找到所匹配的Controller,并执行所匹配的方法。
所以,在run方法中,我们要实现的逻辑如下:
1. 创建一个Spring容器
2. 创建Tomcat对象
3. 生成DispatcherServlet对象,并且和前面创建出来的Spring容器进行绑定
4. 将DispatcherServlet添加到Tomcat中
5. 启动Tomcat
创建Spring容器
这个步骤比较简单,代码如下
public class ZhouyuSpringApplication {public static void run(Class clazz){AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext applicationContext = new
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();applicationContext.register(clazz);applicationContext.refresh();}} 我们创建的是一个AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext容器,并且把run方法传入进来的class 作为容器的配置类,比如在MyApplication的run方法中,我们就是把MyApplication.class 传入到了 run方法中,最终MyApplication就是所创建出来的Spring容器的配置类,并且由于MyApplication类 上有@ZhouyuSpringBootApplication注解,而@ZhouyuSpringBootApplication注解的定义上又 存在@ComponentScan注解,所以AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext容器在执行refresh时,就会解析MyApplication这个配置类,从而发现定义了@ComponentScan注解,也就知道了要 进行扫描 ,只不过扫描路径为空,而AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext容器会处理这种情 况,如果扫描路径会空,则会将MyApplication所在的包路径做为扫描路径 ,从而就会扫描到UserService和UserController。
所以Spring容器创建完之后,容器内部就拥有了UserService和UserController这两个Bean。
启动Tomcat
我们用的是Embed-Tomcat,也就是内嵌的Tomcat,真正的SpringBoot中也用的是内嵌的Tomcat,
而对于启动内嵌的Tomcat,也并不麻烦,代码如下:
public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer{@Overridepublic void start() {System.out.println("启动Tomcat");}public static void startTomcat(WebApplicationContext applicationContext){Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();Server server = tomcat.getServer();Service service = server.findService("Tomcat");Connector connector = new Connector();connector.setPort(8081);Engine engine = new StandardEngine();engine.setDefaultHost("localhost");Host host = new StandardHost();host.setName("localhost");String contextPath = "";Context context = new StandardContext();context.setPath(contextPath);context.addLifecycleListener(new Tomcat.FixContextListener());host.addChild(context);engine.addChild(host);service.setContainer(engine);service.addConnector(connector);tomcat.addServlet(contextPath, "dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(applicationContext));context.addServletMappingDecoded("/*", "dispatcher");try {tomcat.start();} catch (LifecycleException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
代码虽然看上去比较多,但是逻辑并不复杂,比如配置了Tomcat绑定的端口为8081,后面向当前 Tomcat中添加了DispatcherServlet,并设置了一个Mapping关系,最后启动,其他代码则不用太过
关心。
而且在构造DispatcherServlet对象时,传入了一个ApplicationContext对象,也就是一个Spring容 器,就是我们前文说的,DispatcherServlet对象和一个Spring容器进行绑定。
接下来,我们只需要在run方法中,调用startTomcat即可:
接下来,我们只需要在run方法中,调用startTomcat即可:
public static void run(Class clazz){
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext applicationContext = new
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();applicationContext.register(clazz);
applicationContext.refresh(); startTomcat(applicationContext);} 实际上代码写到这,一个极度精简版的SpringBoot就写出来了,比如现在运行MyApplication,就能正常的启动项目,并能接收请求。
启动能看到Tomcat的启动日志:
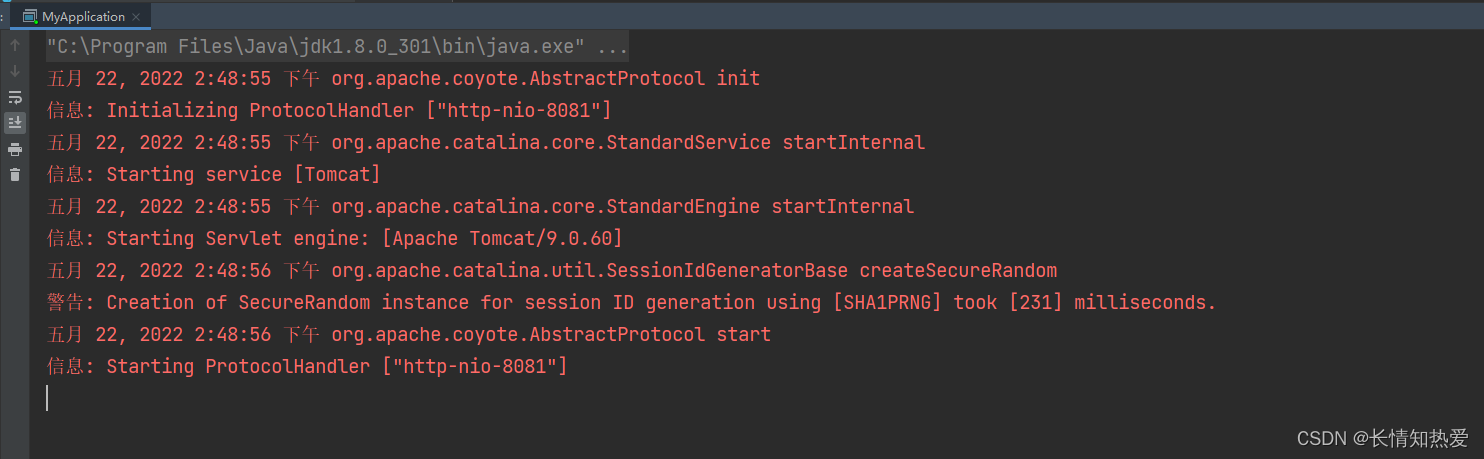
然后在浏览器上访问: http://localhost:8081/test
也能正常的看到结果:

此时,你可以继续去写其他的Controller和Service了,照样能正常访问到,而我们的业务代码中仍然 只用到了ZhouyuSpringApplication类和@ZhouyuSpringBootApplication注解。
实现Tomcat和Jetty的切换
虽然我们前面已经实现了一个比较简单的SpringBoot,不过我们可以继续来扩充它的功能,比如现在 我有这么一个需求,这个需求就是我现在不想使用Tomcat了,而是想要用Jetty,那该怎么办?
我们前面代码中默认启动的是Tomcat,那我现在想改成这样子:
1. 如果项目中有Tomcat的依赖,那就启动Tomcat
2. 如果项目中有Jetty的依赖就启动Jetty
3. 如果两者都没有则报错
4. 如果两者都有也报错
这个逻辑希望SpringBoot自动帮我实现,对于程序员用户而言,只要在Pom文件中添加相关依赖就可以了,想用Tomcat就加Tomcat依赖,想用Jetty就加Jetty依赖。
那SpringBoot该如何实现呢?
我们知道,不管是Tomcat还是Jetty,它们都是应用服务器,或者是Servlet容器,所以我们可以定义 接口来表示它们,这个接口叫做WebServer(别问我为什么叫这个,因为真正的SpringBoot源码中也 叫这个)。
并且在这个接口中定义一个start方法:
public interface WebServer {public void start();} 有了WebServer接口之后,就针对Tomcat和Jetty提供两个实现类:
public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer{@Overridepublic void start() {System.out.println("启动Jetty");}}public class JettyWebServer implements WebServer{@Overridepublic void start() {System.out.println("启动Tomcat");}}而在ZhouyuSpringApplication中的run方法中,我们就要去获取对应的WebServer,然后启动对应的webServer,代码为:
public static void run(Class clazz){
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext applicationContext = new
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();applicationContext.register(clazz);
applicationContext.refresh(); WebServer webServer = getWebServer(applicationContext);
webServer.start(); }public static WebServer getWebServer(ApplicationContext applicationContext){return null;} 这样,我们就只需要在getWebServer方法中去判断到底该返回TomcatWebServer还是
JettyWebServer。
前面提到过,我们希望根据项目中的依赖情况,来决定到底用哪个WebServer,我就直接用
SpringBoot中的源码实现方式来模拟了。
模拟实现条件注解
首先我们得实现一个条件注解@ZhouyuConditionalOnClass,对应代码如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Conditional(ZhouyuOnClassCondition.class)public @interface ZhouyuConditionalOnClass {String value() default "";}注意核心为@Conditional(ZhouyuOnClassCondition.class)中的ZhouyuOnClassCondition,因为
它才是真正得条件逻辑:
public class ZhouyuOnClassCondition implements Condition {@Overridepublic boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {Map<String, Object> annotationAttributes =
metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ZhouyuConditionalOnClass.class.getName());String className = (String) annotationAttributes.get("value");try {context.getClassLoader().loadClass(className);return true;} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {return false;}}}具体逻辑为,拿到@ZhouyuConditionalOnClass中的value属性,然后用类加载器进行加载,如果加载到了所指定的这个类,那就表示符合条件,如果加载不到,则表示不符合条件。
模拟实现自动配置类
有了条件注解,我们就可以来使用它了,那如何实现呢?
这里就要用到自动配置类的概念,我们先看代码:
@Configuration
public class WebServiceAutoConfiguration {@Bean@ZhouyuConditionalOnClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat")public TomcatWebServer tomcatWebServer(){return new TomcatWebServer();}@Bean@ZhouyuConditionalOnClass("org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server")public JettyWebServer jettyWebServer(){return new JettyWebServer();}
} 这个代码还是比较简单的,通过一个WebServiceAutoConfiguration的Spring配置类,在里面定义了 两个Bean,一个TomcatWebServer,一个JettyWebServer,不过这两个要生效的前提是符合当前所指定的条件,比如:
只有存在"org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat"类,那么才有TomcatWebServer这个Bean
只有存在"org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server"类,那么才有TomcatWebServer这个Bean 并且我们只需要在ZhouyuSpringApplication中getWebServer方法,如此实现:
public static WebServer getWebServer(ApplicationContext applicationContext){// key为beanName, value为Bean对象
Map<String, WebServer> webServers =
applicationContext.getBeansOfType(WebServer.class);if (webServers.isEmpty()) {
throw new NullPointerException(); }if (webServers.size() > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException(); }// 返回唯一的一个return webServers.values().stream().findFirst().get();} 这样整体SpringBoot启动逻辑就是这样的:
1. 创建一个AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext容器
2. 解析MyApplication类,然后进行扫描
3. 通过getWebServer方法从Spring容器中获取WebServer类型的Bean
4. 调用WebServer对象的start方法
有了以上步骤,我们还差了一个关键步骤,就是Spring要能解析到WebServiceAutoConfiguration这 个自动配置类,因为不管这个类里写了什么代码,Spring不去解析它,那都是没用的,此时我们需要 SpringBoot在run方法中,能找到WebServiceAutoConfiguration这个配置类并添加到Spring容器 中。
MyApplication是Spring的一个配置类,但是MyApplication是我们传递给SpringBoot,从而添加到 Spring容器中去的,而WebServiceAutoConfiguration就需要SpringBoot去自动发现,而不需要程 序员做任何配置才能把它添加到Spring容器中去,而且要注意的是,Spring容器扫描也是扫描不到 WebServiceAutoConfiguration这个类的,因为我们的扫描路径是"com.zhouyu.user",而
WebServiceAutoConfiguration所在的包路径为"com.zhouyu.springboot"。
那SpringBoot中是如何实现的呢?通过SPI,当然SpringBoot中自己实现了一套SPI机制,也就是我们 熟知的spring.factories文件,那么我们模拟就不搞复杂了,就直接用JDK自带的SPI机制。
发现自动配置类
为了实现这个功能,以及为了最后的效果演示,我们需要把springboot源码和业务代码源码拆分两个 maven模块,也就相当于两个项目,最后的源码结构为

现在我们只需要在springboot项目中的resources目录下添加如下目录(META-INF/services)和文
件:
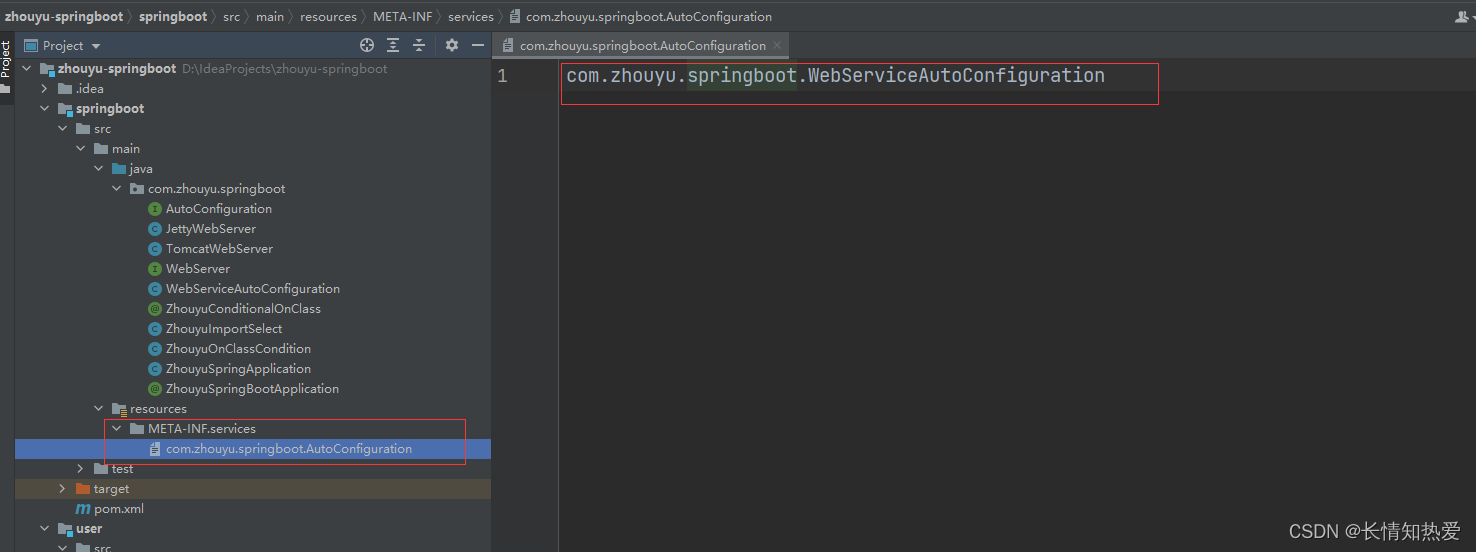
SPI的配置就完成了,相当于通过com.zhouyu.springboot.AutoConfiguration文件配置了
springboot中所提供的配置类。
并且提供一个接口:
public interface AutoConfiguration {} 并且WebServiceAutoConfiguration实现该接口:
@Configuration
public class WebServerAutoConfiguration implements AutoConfiguration {@Bean@ConditionalOnClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat")public TomcatWebServer tomcatWebServer(){return new TomcatWebServer();}@Bean@ConditionalOnClass("org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server")public JettyWebServer jettyWebServer(){return new JettyWebServer();}
} 然后我们再利用spring中的@Import技术来导入这些配置类,我们在
@ZhouyuSpringBootApplication的定义上增加如下代码:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
@Import(ZhouyuImportSeclet.class)
public @interface ZhouyuSpringBootApplication {
} ZhouyuImportSelect类为:
public class ZhouyuImportSeclet implements DeferredImportSelector {@Overridepublic String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {// 自动配置ServiceLoader<AutoConfiguration> loader = ServiceLoader.load(AutoConfiguration.class);List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();for (AutoConfiguration configuration : loader) {list.add(configuration.getClass().getName());}return list.toArray(new String[0]);}
}
这就完成了从com.zhouyu.springboot.AutoConfiguration文件中获取自动配置类的名字,并导入到
Spring容器中,从而Spring容器就知道了这些配置类的存在,而对于user项目而言,是不需要修改代 码的。
此时运行MyApplication,就能看到启动了Tomcat:
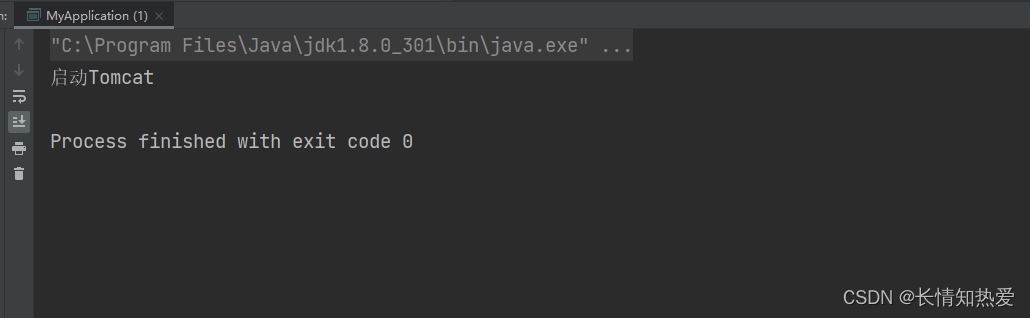
因为SpringBoot默认在依赖中添加了Tomcat依赖,而如果在User模块中再添加jetty的依赖:
<dependencies><dependency>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency><dependency>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-server</artifactId>
<version>9.4.43.v20210629</version> 1</dependency></dependencies> 那么启动MyApplication就会报错:
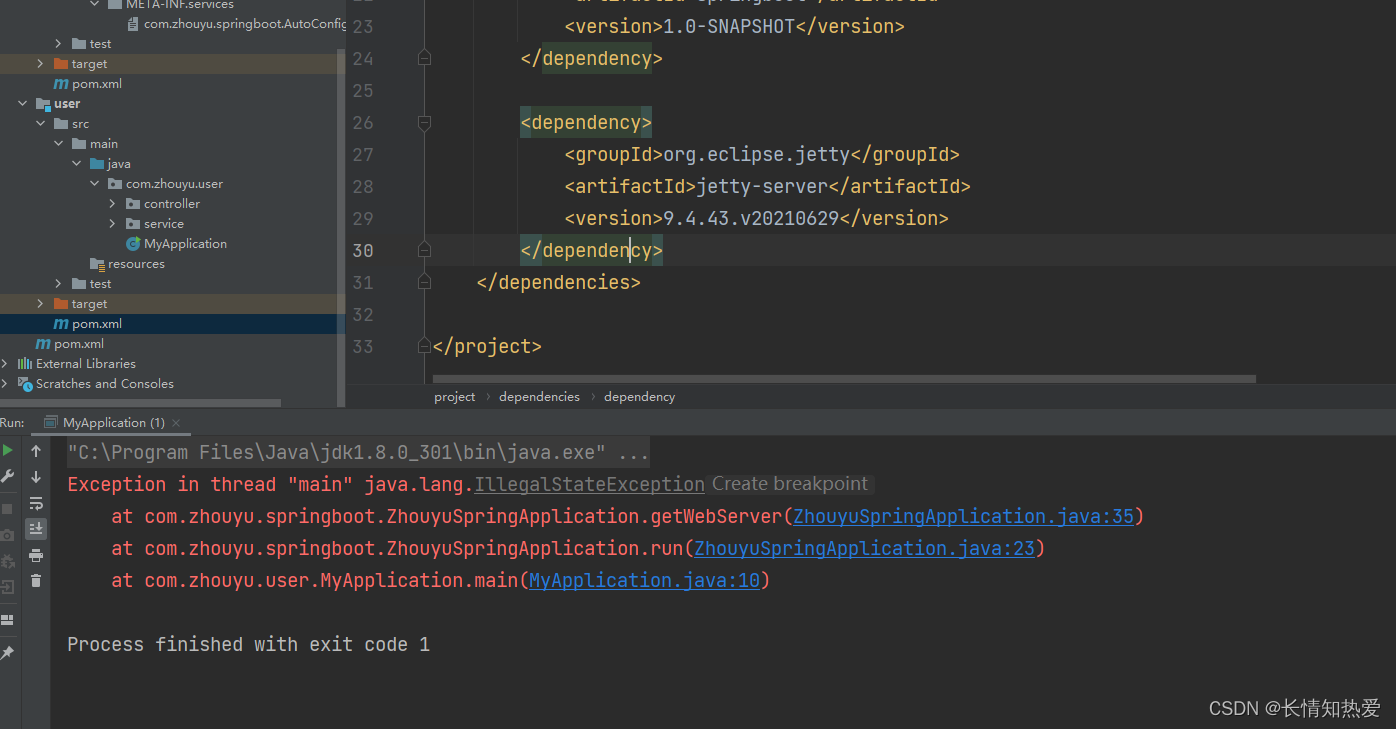
只有先排除到Tomcat的依赖,再添加Jetty的依赖才能启动Jetty: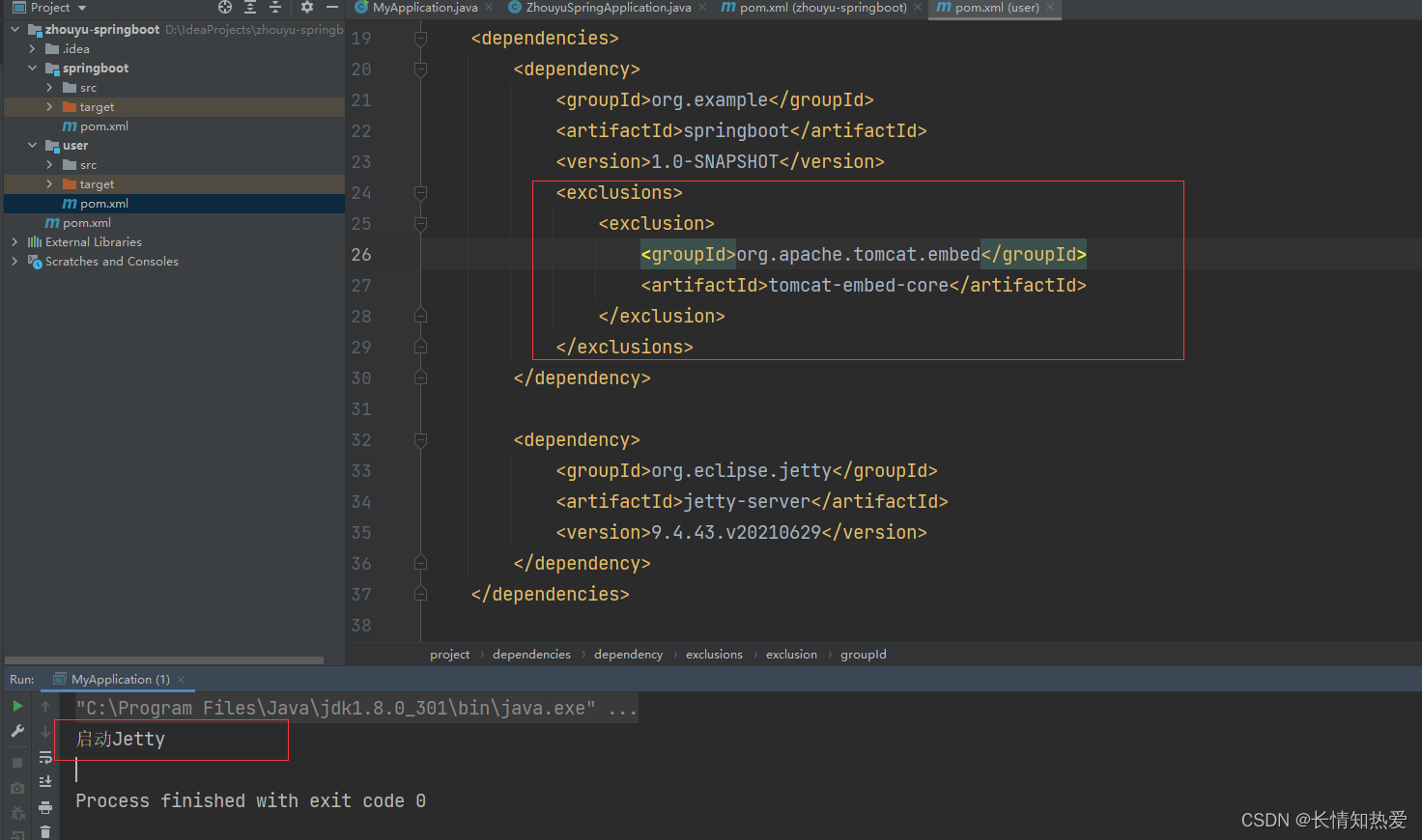
注意:由于没有了Tomcat的依赖,记得把最开始写的startTomcat方法给注释掉,并删除掉相关依
赖
![[陇剑杯 2021]日志分析](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d6ff11ae73244e82b58624a6c1a9e324.png)