一、核函数
kernel_func.py
import numpy as npdef linear():"""线性核函数:return:"""def _linear(x_i, x_j):return np.dot(x_i, x_j)return _lineardef poly(degree=3, coef0=1.0):"""多项式核函数:param degree: 阶次:param coef: 常数项:return:"""def _poly(x_i, x_j):return np.power(np.dot(x_i, x_j) + coef0, degree)return _polydef rbf(gamma=1.0):"""高斯核函数:param gamma: 超参数:return:"""def _rbf(x_i, x_j):x_i, x_j = np.asarray(x_i), np.asarray(x_j)if x_i.ndim <= 1:return np.exp(-np.dot(x_i - x_j, x_i - x_j) / (2 * gamma ** 2))else:return np.exp(-np.multiply(x_i - x_j, x_i - x_j).sum(axis=1) / (2 * gamma ** 2))return _rbf
二、SVM算法的实现
svm_smo_classifier.py
import copy
import randomimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport kernel_func
import numpy as npclass SVMClassifier:"""支持向量机二分类算法:硬间隔、软间隔、核函数,可做线性可分、非线性可分。SMO算法1. 训练样本的目标值限定编码为{0, 1}. SVM在fit时把0类别重编码为-1"""def __init__(self, C=1.0, gamma=1.0, degree=3, coef0=1.0, kernel=None, kkt_tol=1e-3, alpha_tol=1e-3,max_epochs=100):self.C = C # 软间隔硬间隔的参数,硬间隔:适当增大C的值,软间隔:减少C值,允许部分样本不满足约束条件# self.gamma = gamma # 径向基函数/高斯核函数超参数# self.degree = degree # 多项式核函数的阶次# self.coef0 = coef0 # 多项式核函数的常数项self.kernel = kernel # 选择的核函数if self.kernel is None or self.kernel.lower() == "linear":self.kernel_func = kernel_func.linear() # self.kernel_func(x_i, x_j)elif self.kernel.lower() == "poly":self.kernel_func = kernel_func.poly(degree, coef0) # self.kernel_func(x_i, x_j)elif self.kernel.lower() == "rbf":self.kernel_func = kernel_func.rbf(gamma)else:print("仅限linear、poly或rbf,值为None则默认为Linear线性核函数...")self.kernel_func = kernel_func.linear()self.alpha_tol = alpha_tol # 支持向量容忍度self.kkt_tol = kkt_tol # 在精度内检查self.max_epochs = max_epochsself.alpha = None # 松弛变量self.E = None # 误差self.w, self.b = None, None # SVM的模型系数self.support_vectors = [] # 记录支持向量的索引self.support_vectors_alpha = [] # 支持向量所对应的松弛变量self.support_vectors_x, self.support_vectors_y = [], [] # 支持向量所对应的样本和目标self.cross_entropy_loss = [] # 优化过程中的交叉熵损失def init_params(self, x_train, y_train):"""初始化必要参数:param x_train: 训练集:param y_train: 编码后的目标集:return:"""n_samples, n_features = x_train.shapeself.w, self.b = np.zeros(n_features), 0.0 # 模型系数初始化为0值self.alpha = np.zeros(n_samples) # 松弛变量self.E = self.decision_func(x_train) - y_train # 初始化误差,所有样本类别取反def decision_func(self, x):"""SVM模型的预测计算,:param x: 可以是样本集,也可以是单个样本:return:"""if len(self.support_vectors) == 0: # 当前没有支持向量if x.ndim <= 1: # 标量或单个样本return 0else:return np.zeros(x.shape[0]) # np.zeros(x.shape[:-1])else:if x.ndim <= 1:wt_x = 0.0 # 模型w^T * x + b的第一项求和else:wt_x = np.zeros(x.shape[0])for i in range(len(self.support_vectors)):# 公式:w^T * x = sum(alpha_i * y_i * k(xi, x))wt_x += self.support_vectors_alpha[i] * self.support_vectors_y[i] * \self.kernel_func(x, self.support_vectors_x[i])return wt_x + self.bdef _meet_kkt(self, x_i, y_i, alpha_i, sample_weight_i):"""判断当前需要优化的alpha是否满足KKT条件:param x_i: 已选择的样本:param y_i: 已选择的目标:param alpha_i: 需要优化的alpha:return: bool:满足True,不满足False"""if alpha_i < self.C * sample_weight_i:return y_i * self.decision_func(x_i) >= 1 - self.kkt_tolelse:return y_i * self.decision_func(x_i) <= 1 + self.kkt_toldef _select_best_j(self, best_i):"""基于已经选择的第一个alpha_i,寻找使得|E_i - E_j|最大的best_j:param best_i: 已选择的第一个alpha_i索引:return:"""valid_j_list = [j for j in range(len(self.alpha)) if self.alpha[j] > 0 and best_i != j]if len(valid_j_list) > 0:idx = np.argmax(np.abs(self.E[best_i] - self.E[valid_j_list])) # 在可选的j列表中查找绝对误差最大的索引best_j = valid_j_list[int(idx)] # 最佳的jelse:idx = list(range(len(self.alpha))) # 所有样本索引seq = idx[:best_i] + idx[best_i + 1:] # 排除best_ibest_j = random.choice(seq) # 随机选择return best_jdef _clip_alpha_j(self, y_i, y_j, alpha_j_unc, alpha_i_old, alpha_j_old, sample_weight_j):"""修剪第2个更新的alpha值:param y_i: 当前选择的第1个y目标值:param y_j: 当前选择的第2个y目标值:param alpha_j_unc: 当前未修剪的第2个alpha值:param alpha_i_old: 当前选择的第1个未更新前的alpha值:param alpha_j_old: 当前选择的第2个未更新前的alpha值:return:"""C = self.C * sample_weight_jif y_i == y_j:inf = max(0, alpha_i_old + alpha_j_old - C) # Lsup = min(self.C, alpha_i_old + alpha_j_old) # Helse:inf = max(0, alpha_j_old - alpha_i_old) # Lsup = min(C, C + alpha_j_old - alpha_i_old) # H# if alpha_j_unc < inf:# alpha_j_new = inf# elif alpha_j_unc > sup:# alpha_j_new = sup# else:# alpha_j_new = alpha_j_uncalpha_j_new = [inf if alpha_j_unc < inf else sup if alpha_j_unc > sup else alpha_j_unc]return alpha_j_new[0]def _update_error(self, x_train, y_train, y):"""更新误差,计算交叉熵损失:param x_train: 训练样本集:param y_train: 目标集:param y: 编码后的目标集:return:"""y_predict = self.decision_func(x_train) # 当前优化过程中的模型预测值self.E = y_predict - y # 误差loss = -(y_train.T.dot(np.log(self.sigmoid(y_predict))) +(1 - y_train).T.dot(np.log(1 - self.sigmoid(y_predict))))self.cross_entropy_loss.append(loss / len(y)) # 平均交叉熵损失def fit(self, x_train, y_train, samples_weight=None):"""SVM的训练:SMO算法实现1. 按照启发式方法选择一对需要优化的alpha2. 对参数alpha、b、w、E等进行更新、修剪:param x_train: 训练集:param y_train: 目标集:return:"""x_train, y_train = np.asarray(x_train), np.asarray(y_train)if samples_weight is None:samples_weight = np.array([1.0] * x_train.shape[0])class_values = np.sort(np.unique(y_train)) # 类别的不同取值if class_values[0] != 0 or class_values[1] != 1:raise ValueError("仅限二分类,类别编码为{0、1}...")y = copy.deepcopy(y_train)y[y == 0] = -1 # SVM类别限定为{-1, 1}self.init_params(x_train, y) # 参数的初始化n_samples = x_train.shape[0] # 样本量for epoch in range(self.max_epochs):if_all_match_kkt_condition = True # 表示所有样本都满足KKT条件# 1. 选择一对需要优化的alpha_i和alpha_jfor i in range(n_samples): # 外层循环x_i, y_i = x_train[i, :], y[i] # 当前选择的第1个需要优化的样本所对应的索引alpha_i_old, err_i_old = self.alpha[i], self.E[i] # 取当前未更新的alpha和误差if not self._meet_kkt(x_i, y_i,alpha_i_old, samples_weight[i]): # 不满足KKT条件if_all_match_kkt_condition = False # 表示存在需要优化的变量j = self._select_best_j(i) # 基于alpha_i选择alpha_jalpha_j_old, err_j_old = self.alpha[j], self.E[j] # 当前第2个需要优化的alpha和误差x_j, y_j = x_train[j, :], y[j] # 第2个需要优化的样本所对应的索引# 2. 基于已经选择的alpha_i和alpha_j,对alpha、b、E和w进行更新# 首先获取未修建的第2个需要更新的alpha值,并对其进行修建k_ii = self.kernel_func(x_i, x_i)k_jj = self.kernel_func(x_j, x_j)k_ij = self.kernel_func(x_i, x_j)eta = k_ii + k_jj - 2 * k_ijif np.abs(eta) < 1e-3: # 避免分母过小,表示选择更新的两个样本比较接近continuealpha_j_unc = alpha_j_old - y_j * (err_j_old - err_i_old) / eta # 未修剪的alpha_j# 修剪alpha_j使得0< alpha_j < Calpha_j_new = self._clip_alpha_j(y_i, y_j, alpha_j_unc, alpha_i_old,alpha_j_old, samples_weight[j])# 3. 通过修剪后的alpha_j_new更新alpha_ialpha_j_delta = alpha_j_new - alpha_j_oldalpha_i_new = alpha_i_old - y_i * y_j * alpha_j_deltaself.alpha[i], self.alpha[j] = alpha_i_new, alpha_j_new # 更新回存# 4. 更新模型系数w和balpha_i_delta = alpha_i_new - alpha_i_old# w的更新仅与已更新的一对alpha有关self.w = self.w + alpha_i_delta * y_i * x_i + alpha_j_delta * y_j * x_jb_i_delta = -self.E[i] - y_i * k_ii * alpha_i_delta - y_i * k_ij * alpha_j_deltab_j_delta = -self.E[j] - y_i * k_ij * alpha_i_delta - y_i * k_jj * alpha_j_deltaif 0 < alpha_i_new < self.C * samples_weight[i]:self.b += b_i_deltaelif 0 < alpha_j_new < self.C * samples_weight[j]:self.b += b_j_deltaelse:self.b += (b_i_delta + b_j_delta) / 2# 5. 更新误差E,计算损失self._update_error(x_train, y_train, y)# 6. 更新支持向量相关信息,即重新选取self.support_vectors = np.where(self.alpha > self.alpha_tol)[0]self.support_vectors_x = x_train[self.support_vectors, :]self.support_vectors_y = y[self.support_vectors]self.support_vectors_alpha = self.alpha[self.support_vectors]if if_all_match_kkt_condition: # 没有需要优化的alpha,则提前停机breakdef get_params(self):"""获取SVM的模型系数:return:"""return self.w, self.bdef predict_proba(self, x_test):"""预测测试样本所属类别的概率:param x_test: 测试样本集:return:"""x_test = np.asarray(x_test)y_test_hat = np.zeros((x_test.shape[0], 2)) # 存储每个样本的预测概率y_test_hat[:, 1] = self.sigmoid(self.decision_func(x_test))y_test_hat[:, 0] = 1.0 - y_test_hat[:, 1]return y_test_hatdef predict(self, x_test):"""预测测试样本的所属类别:param x_test: 测试样本集:return:"""return np.argmax(self.predict_proba(x_test), axis=1)@staticmethoddef sigmoid(x):"""sigmodi函数,为避免上溢或下溢,对参数x做限制:param x: 可能是标量数据,也可能是数组:return:"""x = np.asarray(x) # 为避免标量值的布尔索引出错,转换为数组x[x > 30.0] = 30.0 # 避免下溢x[x < -50.0] = -50.0 # 避免上溢return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))def plt_loss_curve(self, is_show=True):"""可视化交叉熵损失函数:param is_show::return:"""if is_show:plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))plt.plot(self.cross_entropy_loss, "k-", lw=1)plt.xlabel("Training Epochs", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})plt.ylabel("The Mean of Cross Entropy Loss", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})plt.title("The SVM Loss Curve of Cross Entropy")plt.grid(ls=":")if is_show:plt.show()def plt_svm(self, X, y, is_show=True, is_margin=False):"""可视化支持向量机模型:分类边界、样本、间隔、支持向量:param X::param y::param is_show::return:"""X, y = np.asarray(X), np.asarray(y)if is_show:plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))if X.shape[1] != 2:print("Warning: 仅限于两个特征的可视化...")return# 可视化分类填充区域x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1xi, yi = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, 100), np.linspace(y_min, y_max, 100))zi = self.predict(np.c_[xi.ravel(), yi.ravel()])zi = zi.reshape(xi.shape) # 等值线的x、y和z的维度必须一致plt.contourf(xi, yi, zi, cmap="winter", alpha=0.3)# 可视化正例、负例样本positive, negative = X[y == 1.0], X[y == 0.0]plt.plot(positive[:, 0], positive[:, 1], "*", label="Positive Samples")plt.plot(negative[:, 0], negative[:, 1], "x", label="Negative Samples")# 可视化支持向量if len(self.support_vectors) != 0:plt.scatter(self.support_vectors_x[:, 0], self.support_vectors_x[:, 1], s=80,c="none", edgecolors="k", label="Support Vectors")if is_margin and (self.kernel is None or self.kernel.lower() == "linear"):w, b = self.get_params()xi_ = np.linspace(x_min, x_max, 100)yi_ = -(w[0] * xi_ + b) / w[1]margin = 1 / w[1]plt.plot(xi_, yi_, "r-", lw=1.5, label="Decision Boundary")plt.plot(xi_, yi_ + margin, "k:", label="Maximum Margin")plt.plot(xi_, yi_ - margin, "k:")plt.title("Support Vector Machine Decision Boundary", fontdict={"fontsize": 14})plt.xlabel("X1", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})plt.xlabel("X2", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})plt.legend(frameon=False)plt.axis([x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max])if is_show:plt.show()三、SVM算法的测试
test_svm_classifier.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification, load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from svm_smo_classifier import SVMClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_reportX, y = make_classification(n_samples=200, n_features=2, n_classes=2, n_informative=1,n_redundant=0, n_repeated=0, n_clusters_per_class=1,class_sep=1.5, random_state=42)# iris = load_iris()
# X, y = iris.data[:100, :2], iris.target[:100]X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, shuffle=True)# C = 1000,倾向于硬间隔
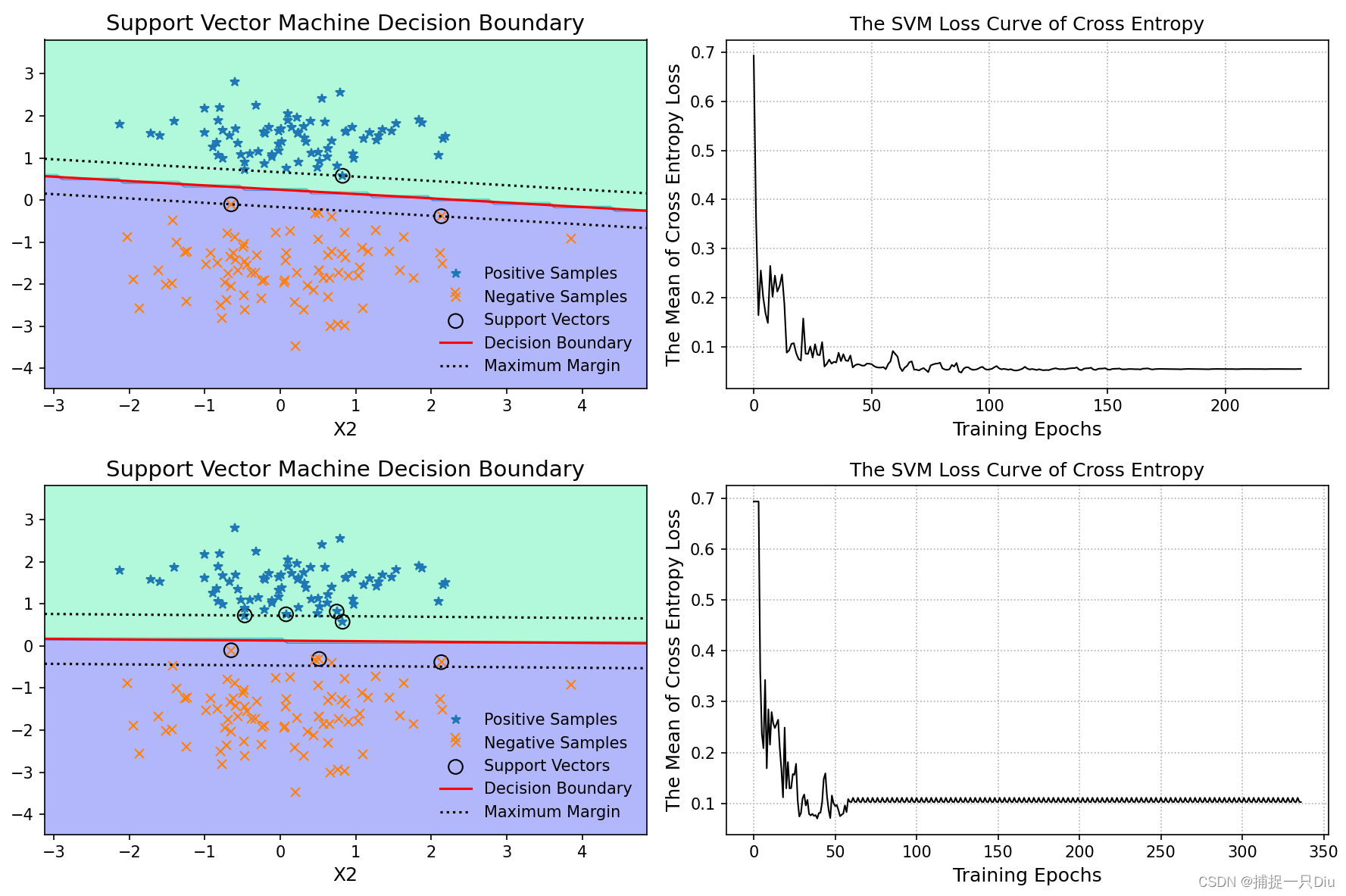
svm = SVMClassifier(C=1000)
svm.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = svm.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
plt.subplot(221)
svm.plt_svm(X_train, y_train, is_show=False, is_margin=True)
plt.subplot(222)
svm.plt_loss_curve(is_show=False)# C = 1,倾向于软间隔
svm = SVMClassifier(C=1)
svm.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = svm.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))plt.subplot(223)
svm.plt_svm(X_train, y_train, is_show=False, is_margin=True)
plt.subplot(224)
svm.plt_loss_curve(is_show=False)plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
test_svm_kernel_classifier.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification, make_moons
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from svm_smo_classifier import SVMClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_reportX, y = make_moons(n_samples=200, noise=0.1)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, shuffle=True)svm_rbf = SVMClassifier(C=10.0, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.5)
svm_rbf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = svm_rbf.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))
print("=" * 60)
svm_poly = SVMClassifier(C=10.0, kernel="poly", degree=3)
svm_poly.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = svm_poly.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
plt.subplot(221)
svm_rbf.plt_svm(X_train, y_train, is_show=False)
plt.subplot(222)
svm_rbf.plt_loss_curve(is_show=False)plt.subplot(223)
svm_poly.plt_svm(X_train, y_train, is_show=False)
plt.subplot(224)
svm_poly.plt_loss_curve(is_show=False)plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

test_svm_kernel_classifier2.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification, make_moons
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from svm_smo_classifier import SVMClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_reportX, y = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_classes=2, n_informative=1,n_redundant=0, n_repeated=0, n_clusters_per_class=1,class_sep=0.8, random_state=21)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, shuffle=True)svm_rbf1 = SVMClassifier(C=10.0, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.1)
svm_rbf1.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = svm_rbf1.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))
print("=" * 60)
svm_rbf2 = SVMClassifier(C=1.0, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.5)
svm_rbf2.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = svm_rbf2.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))
print("=" * 60)svm_poly1 = SVMClassifier(C=10.0, kernel="poly", degree=3)
svm_poly1.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = svm_poly1.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))
svm_poly2 = SVMClassifier(C=10.0, kernel="poly", degree=6)
svm_poly2.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = svm_poly2.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred))X, y = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_classes=2, n_informative=1,n_redundant=0, n_repeated=0, n_clusters_per_class=1,class_sep=0.8, random_state=21)
X_train1, X_test1, y_train1, y_test1 = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, shuffle=True)svm_linear1 = SVMClassifier(C=10.0, kernel="linear")
svm_linear1.fit(X_train1, y_train1)
y_test_pred1 = svm_linear1.predict(X_test1)
print(classification_report(y_test1, y_test_pred1))
svm_linear2 = SVMClassifier(C=10.0, kernel="linear")
svm_linear2.fit(X_train1, y_train1)
y_test_pred = svm_linear2.predict(X_test1)
print(classification_report(y_test1, y_test_pred1))plt.figure(figsize=(21, 10))
plt.subplot(231)
svm_rbf1.plt_svm(X_train, y_train, is_show=False)
plt.subplot(232)
svm_rbf2.plt_svm(X_train, y_train, is_show=False)
plt.subplot(233)
svm_poly1.plt_svm(X_train, y_train, is_show=False)
plt.subplot(234)
svm_poly2.plt_svm(X_train, y_train, is_show=False)
plt.subplot(235)
svm_linear1.plt_svm(X_train1, y_train1, is_show=False, is_margin=True)
plt.subplot(236)
svm_linear2.plt_svm(X_train1, y_train1, is_show=False, is_margin=True)plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()