个人主页 : zxctscl
如有转载请先通知
文章目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. list源码
- 3. 初始化
- 3.1 构造
- 3.2 拷贝构造
- 3.3 赋值
- 3.4 析构
- 4. 迭代器
- 4.1 后置加加和前置加加
- 4.2 后置减减和前置减减
- 4.3 解引用
- 4.4 `!=`和`==`
- 4.5 begin 和 end
- 4.6 const迭代器
- 4.7 迭代器优化
- 5. Modifiers
- 5.1 insert
- 5.2 push_back
- 5.3 push_front
- 5.4 erase
- 5.5 pop_back
- 5.6 pop_front
- 5.7 重载operator->
- 5.8 swap
- 5.9 clear
- 6. 附代码
1. 前言
在前面一篇博客中分享了list的相关介绍 【C++】list介绍,这次来模拟实现一下list。
2. list源码
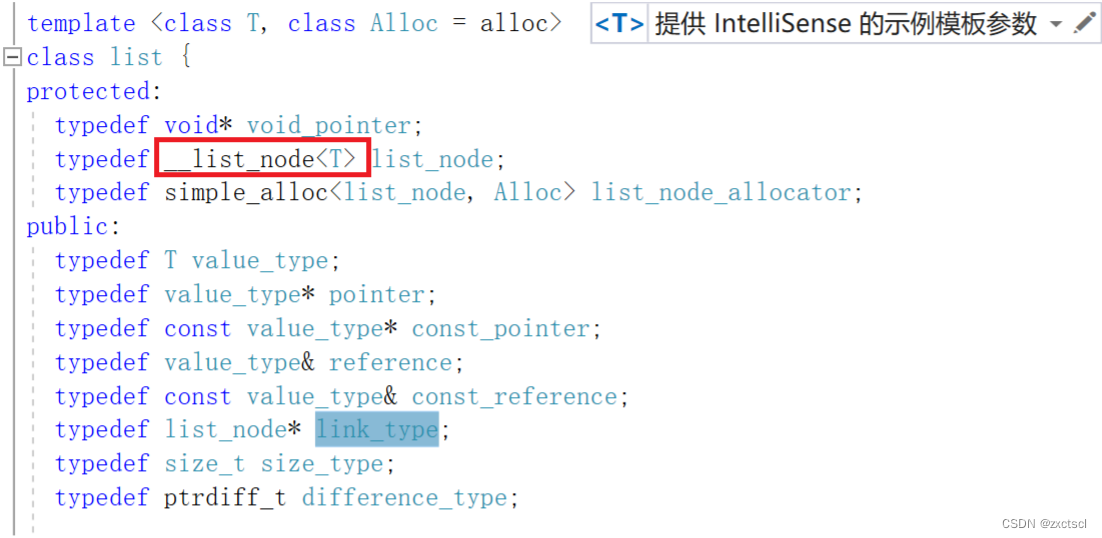
成员变量:

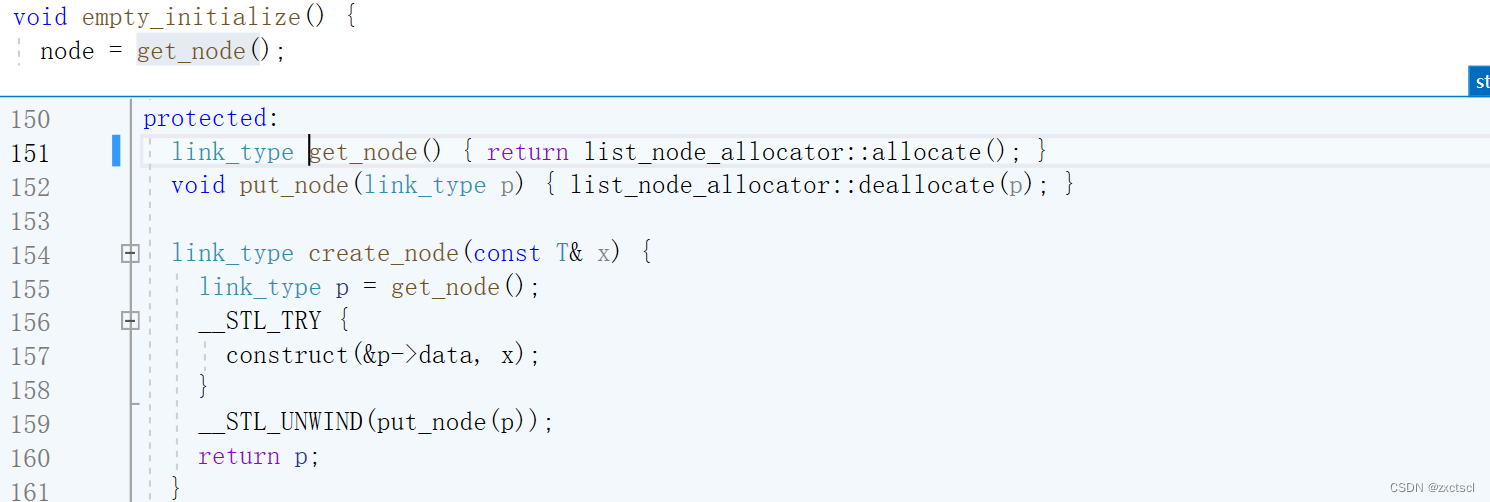
无参构造:


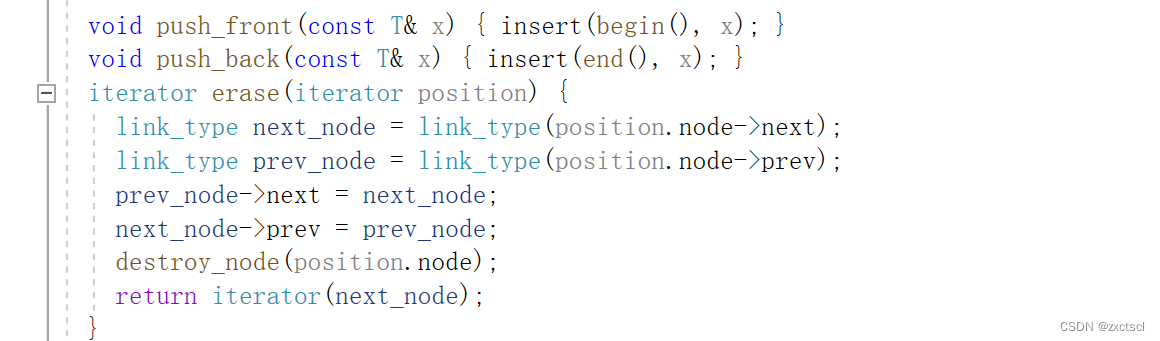
插入:
3. 初始化
在库里面定义节点需要全部公有时用到的就是struct:

这里我们也用相同方法自己定义出一个节点:
template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _data;ListNode(const T& x = T()):_next(nullptr),_prev(nullptr),_data(x){}};
然后在写list类时候就要用到上面结构体。
list类里面成员变量就有:
private:Node* _head;3.1 构造
先来一个无参构造,实现的双向带头循环链表,先定义哨兵位节点,让它的next和prev都指向自己:
list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}
3.2 拷贝构造
链表的拷贝构造,先写一个初始化链表的函数:
void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}
就直接在初始化的基础上,遍历拷贝的数据,再把数据全部插入到新链表就可以了:
list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}
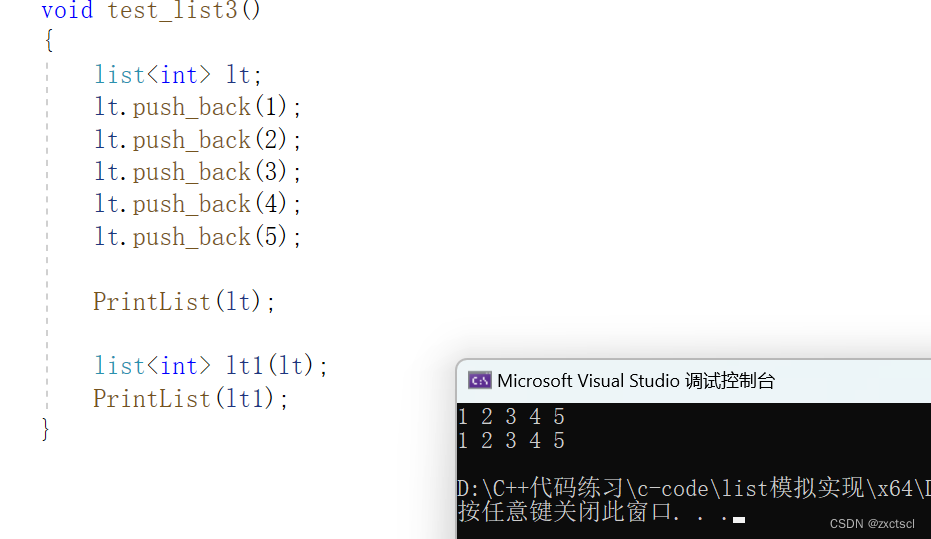
测试一下:
void test_list3(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);PrintList(lt);list<int> lt1(lt);PrintList(lt1);}
3.3 赋值
直接复用swap,出了作用域lt之前的数据会销毁,再返回*this就可以了。
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}
3.4 析构
析构在clear的基础上,要把哨兵位也删除
~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}
怎么判断要不要析构?
如果需要析构,一般就需要自己写深拷贝
如果不需要析构,一般就不需要自己写深拷贝,默认浅拷贝就可以
4. 迭代器
这里原生指针不能充当迭代器,list物理空间不连续,这里Node*加加不能到下一个节点,而且解引用Node*是Node也不能找到数据。这时Node*已经不能满足需求了,这里就得封装一个类。内置类型不能满足需求,就自定义类型。
来看看库里面是怎么实现的:

来实现一下:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T> Self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}4.1 后置加加和前置加加
实现加加,加加就到下一个位置,需要迭代器去访问
代码实现:
Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}
前置加加:返回的是加加之前的node,所以得先记录下数据(拷贝构造一份),再加加,然后返回之前记录下的节点。
Self& operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}
4.2 后置减减和前置减减
后置减减和后置加加类似:
Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}前置减减和前置加加类似:
Self& operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}
4.3 解引用
这里*it返回的是什么值?
要返回的时节点里面的data
T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}
4.4 !=和==
比较两个迭代器相不相等,比较的是节点的指针
bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}
重载==:
bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}
4.5 begin 和 end
begin执行第一个节点,也就是head的next
iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}
这里是用来匿名对象来构造迭代器:

还可以写成:
单参数的构造,支持隐私类型转换
iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}

end指向的是head
iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}
4.6 const迭代器
不能直接在原来的迭代器上面加上const,会导致普通迭代器就不能修改了。
const迭代器,需要是迭代器不能修改,还是迭代器指向的内容?
迭代器指向的内容不能修改!const iterator不是我们需要const迭代器,所以不能在普通迭代器的前面加const。
使用就增加一个重载的const迭代器:
const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;
那么就得单独搞一个类ListConstIterator,让const迭代器*it不能修改:再把相同的操作符重载一下
template<class T>struct ListConstIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;Node* _node;ListConstIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// *itconst T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}// it->const T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};
4.7 迭代器优化
发现普通迭代器和const迭代器里面很多运算符都是一样的,而const迭代器里面就直是不能修改指向的内容,代码显得冗余。就可以用模板来修改这两个类,把他们两个融成一个类。
就是返回值的类型不同,就用模板变,用一个模板参数:template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// *it//T& operator*()Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}// it->//T* operator->()Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};
本质上相当于我们写了一个类模板,编译器实例化生成两个类。
从而在list类里面就修改为:
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
5. Modifiers
5.1 insert
insert实现在某一个位置之前插入一个节点
先搞一个节点,然后记录原链表pos位置的指针,然后一前一后改指向
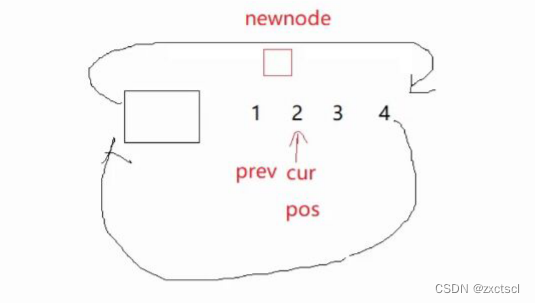
void insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* prev = cur->_prev;prev->_next = cur;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->prev = newnode;}
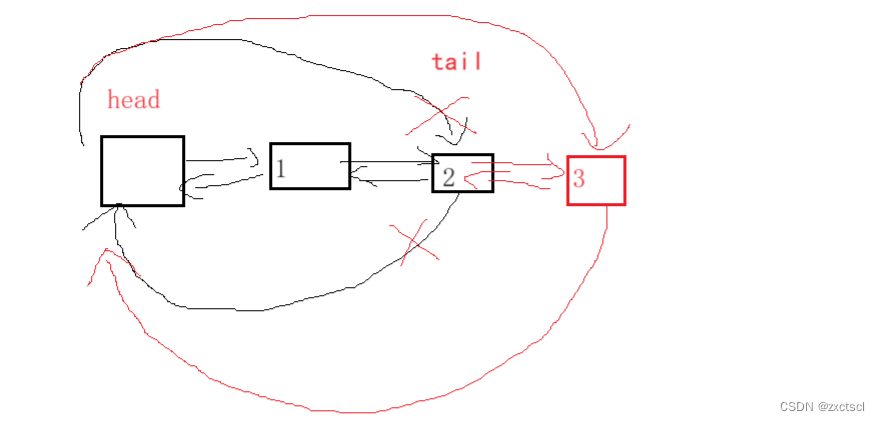
5.2 push_back
新开一个节点,然后让原链表的tail指向新节点,让新节点的prev指向tail,再把head的prev改为新节点,新节点的next改为head。
代码实现:
void push_back(const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;}
来测试一下:
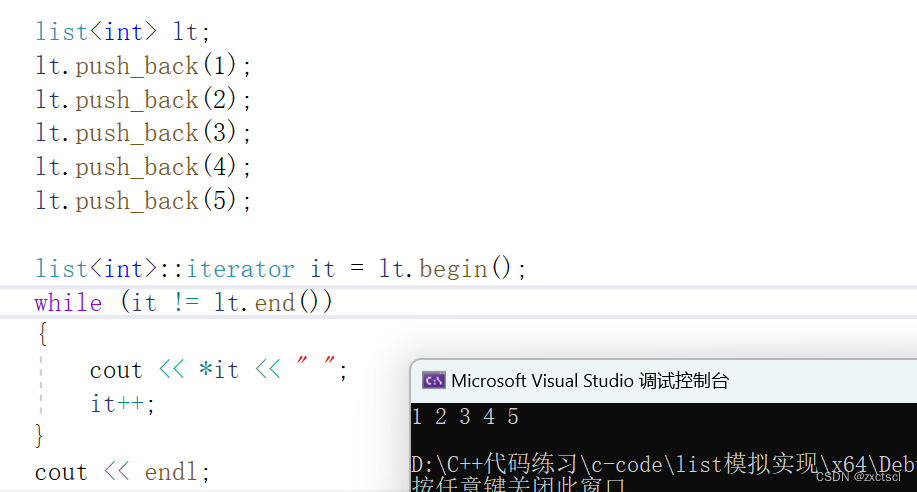
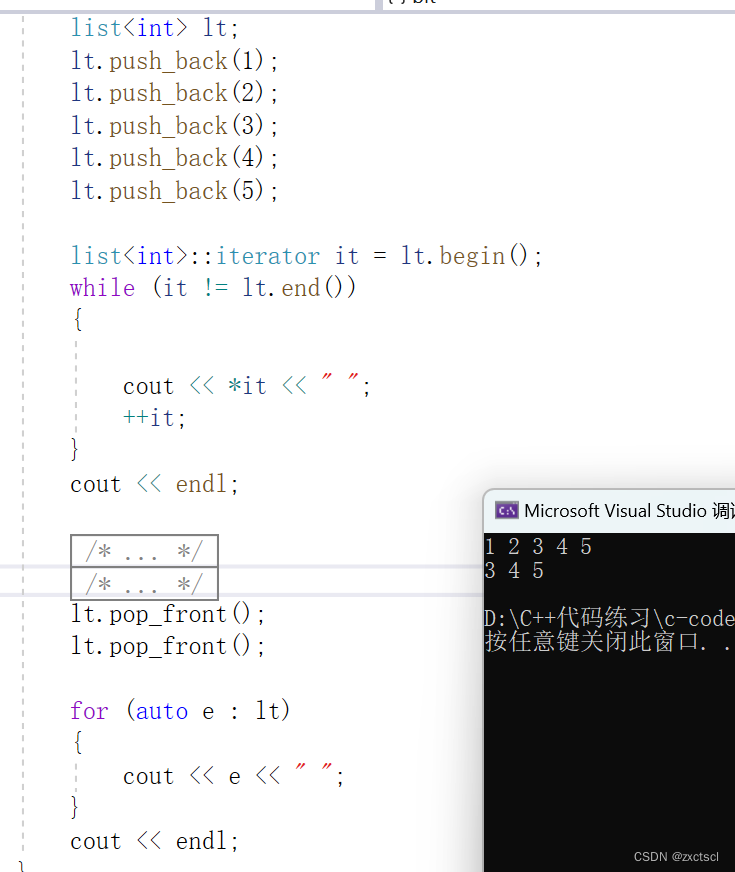
void test_list1(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";it++;}cout << endl;}

push_back用erase来实现会更简单:在end位置插入一个数
void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}
5.3 push_front
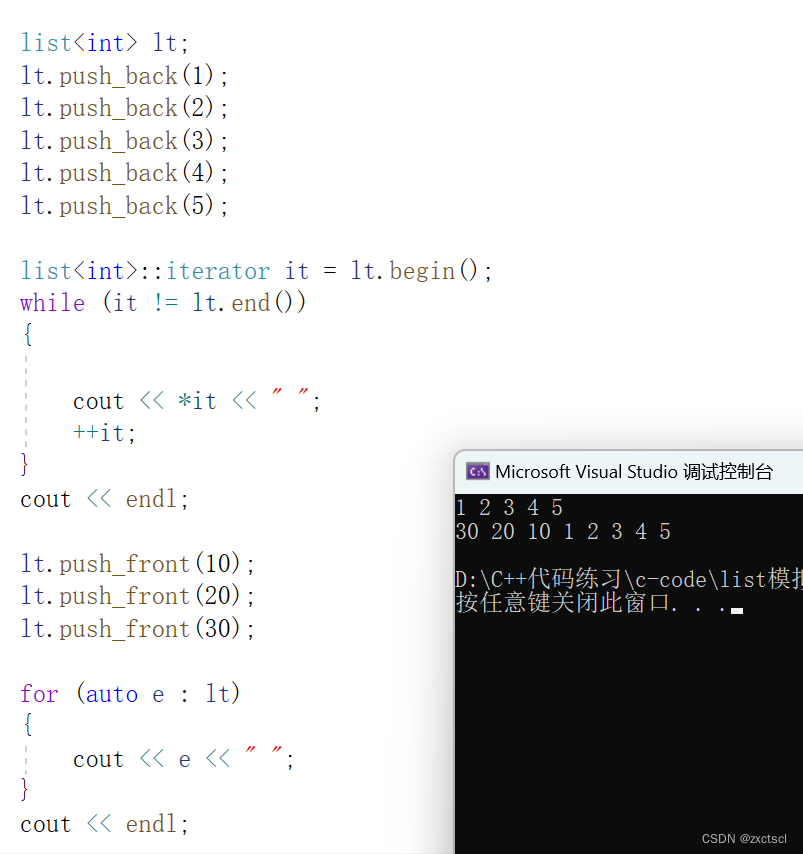
头插就是在begin插入一个数:
void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}
测试一下:
5.4 erase
先记录下要删除的节点,和它前一个节点prev 还有它的后一个节点next。然后让prev的_next 指向next;next的_prev 指向 prev。
删除会导致迭代器失效的问题,为了避免,就返回删除节点的下一个位置。
iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);}
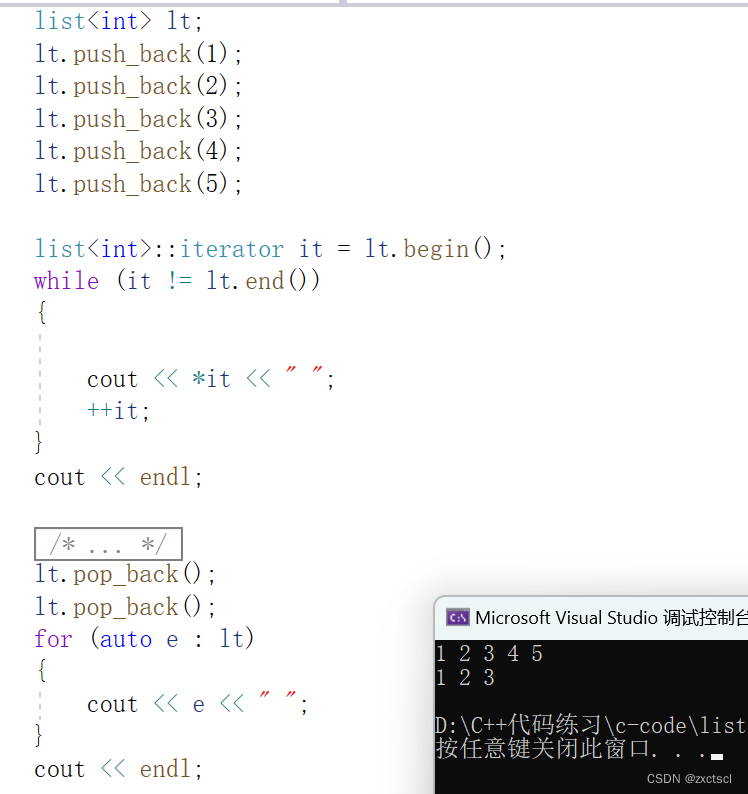
5.5 pop_back
尾删复用erase,而尾是在end前面的一个位置,所以先减减end再删除
void pop_back(){erase(--end());}
5.6 pop_front
因为begin所在的位置就是头节点,所以直接删除begin就可以:
void pop_front(){erase(begin());}
5.7 重载operator->
用户自定义一个类型:
struct A{int _a1;int _a2;A(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0):_a1(a1), _a2(a2){}};
调用push_back插入数据,可以是匿名对象,也可以多参数进行隐式类型转换:
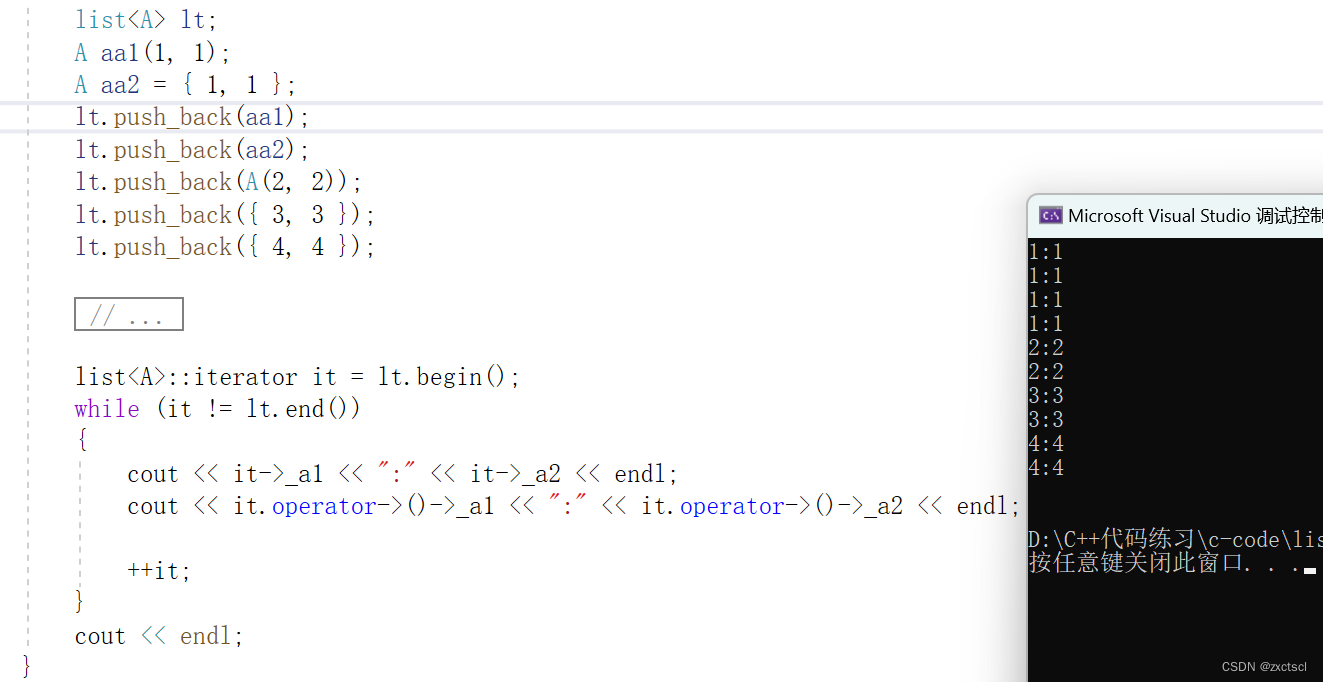
list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 1, 1 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa2);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3, 3 });lt.push_back({ 4, 4 });
但是要把数据输出到屏幕上,使用*it是不可以的:
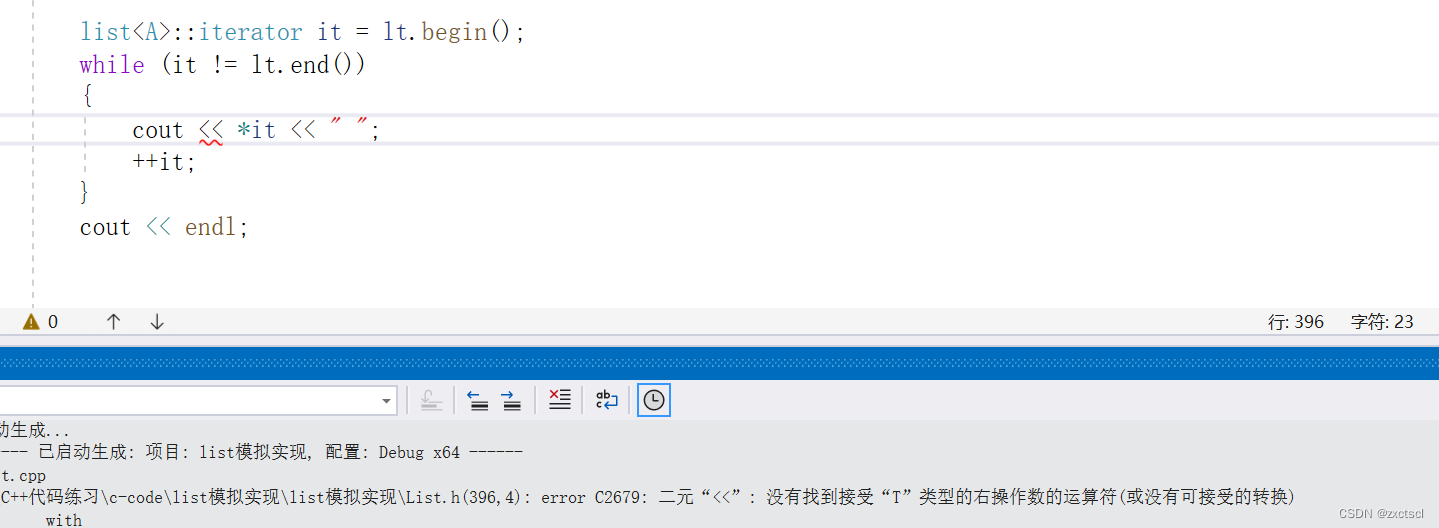
A是一个自定义类型,A不支持流插入,要想指出就得自己写一个重载一个。如果不想写,可以换个方式,这里的数据是公有的可以直接访问。
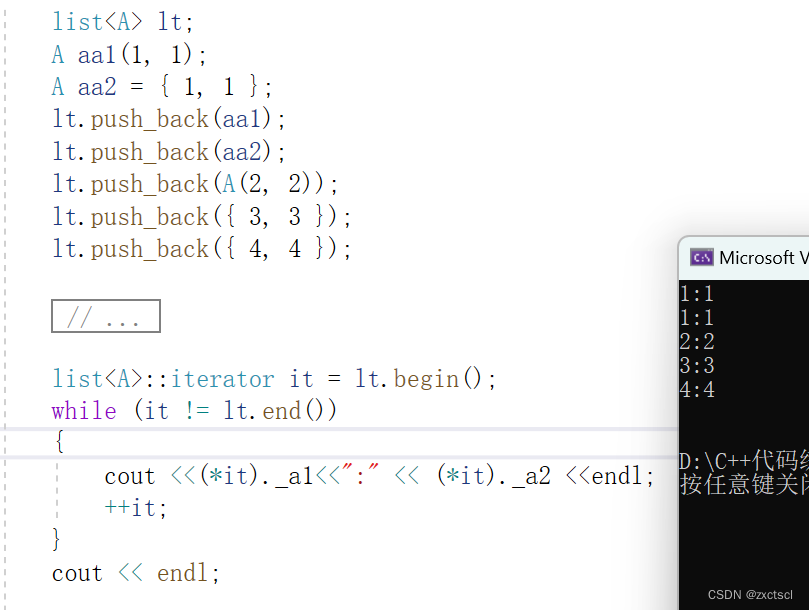
就直接*it返回的是A,再拿到a1和a2的数据就可以:
list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout <<(*it)._a1<<":" << (*it)._a2 <<endl;++it;}cout << endl;

这里A*的一个指针访问数据是先解引用,返回A对象,再来.对象里面的成员变量:
A* ptr = &aa1;(*ptr)._a1;
迭代器就是想要模仿A*的行为,所以迭代器就重载了一个->:it->,它返回的是data的地址。
T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}
访问它里面的就是这样:
cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl;
其实是编译器为了可读性,省略了一个箭头:第一个箭头是运算符重载,就返回data里面的地址也就是A*,第二个箭头就能访问A里面的数据了。
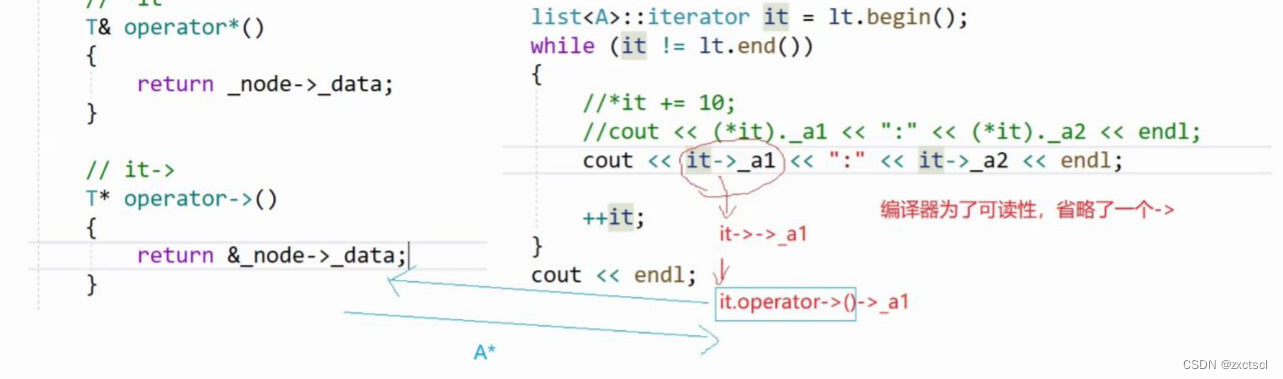
原生指针的行为就是:
cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a2 << endl;
测试一下都能使用:
void test_list2(){list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 1, 1 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa2);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3, 3 });lt.push_back({ 4, 4 });list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl;cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a2 << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}
5.8 swap
直接调用库里面的swap来交换:
void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}
5.9 clear
clear清理掉所有数据,直接复用迭代器来把数据全部删除,但是没有清理掉哨兵位head
void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}
6. 附代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<assert.h>namespace bit
{template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _data;ListNode(const T& x = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(x){}};// typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;// typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// *it//T& operator*()Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}// it->//T* operator->()Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};//template<class T>//struct ListConstIterator//{// typedef ListNode<T> Node;// typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;// Node* _node;// ListConstIterator(Node* node)// :_node(node)// {}// // *it// const T& operator*()// {// return _node->_data;// }// // it->// const T* operator->()// {// return &_node->_data;// }// // ++it// Self& operator++()// {// _node = _node->_next;// return *this;// }// Self operator++(int)// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_next;// return tmp;// }// Self& operator--()// {// _node = _node->_prev;// return *this;// }// Self operator--(int)// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_prev;// return tmp;// }// bool operator!=(const Self& it)// {// return _node != it._node;// }// bool operator==(const Self& it)// {// return _node == it._node;// }//};template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;public://typedef ListIterator<T> iterator;//typedef ListConstIterator<T> const_iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//iterator begin()//{// //return iterator(_head->_next);// iterator it(_head->_next);// return it;//}iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(){empty_init();}// lt2(lt1)list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}// lt1 = lt3list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}/*void push_back(const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;}*/void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(val);Node* prev = cur->_prev;// prev newnode cur;prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;_size++;}iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;_size--;return iterator(next);}size_t size() const{return _size;}bool empty(){return _size == 0;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};void test_list1(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;/*lt.push_front(10);lt.push_front(20);lt.push_front(30);*//*lt.pop_back();lt.pop_back();for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;*/lt.pop_front();lt.pop_front();for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}struct A{int _a1;int _a2;A(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0):_a1(a1), _a2(a2){}};void test_list2(){list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 1, 1 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa2);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3, 3 });lt.push_back({ 4, 4 });//A* ptr = &aa1;//(*ptr)._a1;//ptr->_a1;//list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();//while (it != lt.end())//{// cout <<(*it)._a1<<":" << (*it)._a2 <<endl;// ++it;//}//cout << endl;list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl;cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << it.operator->()->_a2 << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}void PrintList(const list<int>& clt){list<int>::const_iterator it = clt.begin();while (it != clt.end()){//*it += 10;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}void test_list3(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);PrintList(lt);list<int> lt1(lt);PrintList(lt1);}}