v10出了就想看看它的loss设计有什么不同,看下来由于v8和v10的loss部分基本一致就放一起了。
v10的论文笔记,还没看的可以看看,初步尝试耗时确实有提升
好记性不如烂笔头,还是得记录一下,以免忘了,废话结束!!!
代码地址:GitHub - THU-MIG/yolov10: YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.14458
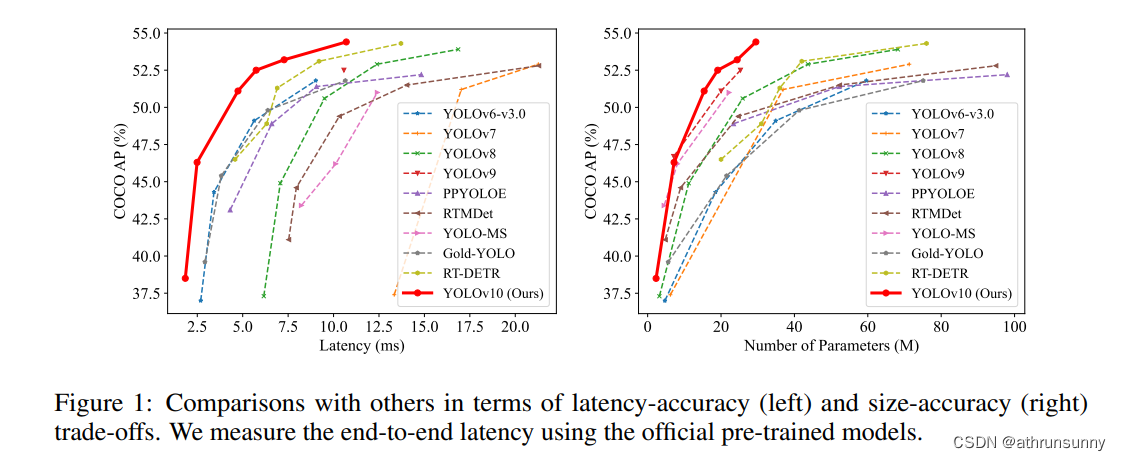
YOLOv10/8从Anchor-Based(box anchor)换成了Anchor-Free(point anchor),检测头也换成了Decoupled Head,这一结构具有提高收敛速度的好处,(在box anchor 方案中试过精度也有提升,但耗时增加了一些)但另一方面讲,也会遇到分类与回归不对齐的问题。在一些网络中,会通过将feature map中的cell(point anchor中心点所编码的box)与ground truth进行IOU计算以分配预测所用cell,但用来分类和回归的最佳cell通常不一致。为了解决这一问题,引入了TAL(Task Alignment Learning)来负责正负样本分配,使得分类和回归任务之间具有较高的对齐一致性。
yolov10/v8中的loss主要分为2部分3个loss:
一、回归分支的损失函数:
1、DFL(Distribution Focal Loss),计算anchor point的中心点到左上角和右下角的偏移量
2、IoU Loss,定位损失,采用CIoU loss,只计算正样本的定位损失
二、分类损失:
1、分类损失,采用BCE loss,只计算正样本的分类损失。
v8DetectionLoss
v8和v10的loss最大的不同在于,v10有两个解耦头,一个计算one2one head,一个计算one2many head,但是两个head的loss函数一样,就是超参数有一些不同
class v10DetectLoss:def __init__(self, model):self.one2many = v8DetectionLoss(model, tal_topk=10)self.one2one = v8DetectionLoss(model, tal_topk=1)def __call__(self, preds, batch):one2many = preds["one2many"]loss_one2many = self.one2many(one2many, batch)one2one = preds["one2one"]loss_one2one = self.one2one(one2one, batch)return loss_one2many[0] + loss_one2one[0], torch.cat((loss_one2many[1], loss_one2one[1]))one2many的topk为10,one2one的topk为1。(这部分代码和我写辅助监督的方式一样)
class v8DetectionLoss:"""Criterion class for computing training losses."""def __init__(self, model, tal_topk=10): # model must be de-paralleled"""Initializes v8DetectionLoss with the model, defining model-related properties and BCE loss function."""device = next(model.parameters()).device # get model deviceh = model.args # hyperparametersm = model.model[-1] # Detect() moduleself.bce = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(reduction="none")self.hyp = hself.stride = m.stride # model stridesself.nc = m.nc # number of classesself.no = m.noself.reg_max = m.reg_maxself.device = deviceself.use_dfl = m.reg_max > 1self.assigner = TaskAlignedAssigner(topk=tal_topk, num_classes=self.nc, alpha=0.5, beta=6.0)self.bbox_loss = BboxLoss(m.reg_max - 1, use_dfl=self.use_dfl).to(device)self.proj = torch.arange(m.reg_max, dtype=torch.float, device=device)def preprocess(self, targets, batch_size, scale_tensor):"""Preprocesses the target counts and matches with the input batch size to output a tensor."""if targets.shape[0] == 0:out = torch.zeros(batch_size, 0, 5, device=self.device)else:i = targets[:, 0] # image index_, counts = i.unique(return_counts=True)counts = counts.to(dtype=torch.int32)out = torch.zeros(batch_size, counts.max(), 5, device=self.device)for j in range(batch_size):matches = i == jn = matches.sum()if n:out[j, :n] = targets[matches, 1:]out[..., 1:5] = xywh2xyxy(out[..., 1:5].mul_(scale_tensor))return outdef bbox_decode(self, anchor_points, pred_dist):"""Decode predicted object bounding box coordinates from anchor points and distribution."""if self.use_dfl:b, a, c = pred_dist.shape # batch, anchors, channelspred_dist = pred_dist.view(b, a, 4, c // 4).softmax(3).matmul(self.proj.type(pred_dist.dtype))# pred_dist = pred_dist.view(b, a, c // 4, 4).transpose(2,3).softmax(3).matmul(self.proj.type(pred_dist.dtype))# pred_dist = (pred_dist.view(b, a, c // 4, 4).softmax(2) * self.proj.type(pred_dist.dtype).view(1, 1, -1, 1)).sum(2)return dist2bbox(pred_dist, anchor_points, xywh=False)def __call__(self, preds, batch):"""Calculate the sum of the loss for box, cls and dfl multiplied by batch size."""loss = torch.zeros(3, device=self.device) # box, cls, dflfeats = preds[1] if isinstance(preds, tuple) else predspred_distri, pred_scores = torch.cat([xi.view(feats[0].shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in feats], 2).split((self.reg_max * 4, self.nc), 1)pred_scores = pred_scores.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()pred_distri = pred_distri.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()dtype = pred_scores.dtypebatch_size = pred_scores.shape[0]imgsz = torch.tensor(feats[0].shape[2:], device=self.device, dtype=dtype) * self.stride[0] # image size (h,w)anchor_points, stride_tensor = make_anchors(feats, self.stride, 0.5)# Targetstargets = torch.cat((batch["batch_idx"].view(-1, 1), batch["cls"].view(-1, 1), batch["bboxes"]), 1)targets = self.preprocess(targets.to(self.device), batch_size, scale_tensor=imgsz[[1, 0, 1, 0]])gt_labels, gt_bboxes = targets.split((1, 4), 2) # cls, xyxymask_gt = gt_bboxes.sum(2, keepdim=True).gt_(0)# Pboxespred_bboxes = self.bbox_decode(anchor_points, pred_distri) # xyxy, (b, h*w, 4)_, target_bboxes, target_scores, fg_mask, _ = self.assigner(pred_scores.detach().sigmoid(),(pred_bboxes.detach() * stride_tensor).type(gt_bboxes.dtype),anchor_points * stride_tensor,gt_labels,gt_bboxes,mask_gt,)target_scores_sum = max(target_scores.sum(), 1)# Cls loss# loss[1] = self.varifocal_loss(pred_scores, target_scores, target_labels) / target_scores_sum # VFL wayloss[1] = self.bce(pred_scores, target_scores.to(dtype)).sum() / target_scores_sum # BCE# Bbox lossif fg_mask.sum():target_bboxes /= stride_tensorloss[0], loss[2] = self.bbox_loss(pred_distri, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, target_bboxes, target_scores, target_scores_sum, fg_mask)loss[0] *= self.hyp.box # box gainloss[1] *= self.hyp.cls # cls gainloss[2] *= self.hyp.dfl # dfl gainreturn loss.sum() * batch_size, loss.detach() # loss(box, cls, dfl)v8DetectionLoss中preprocess
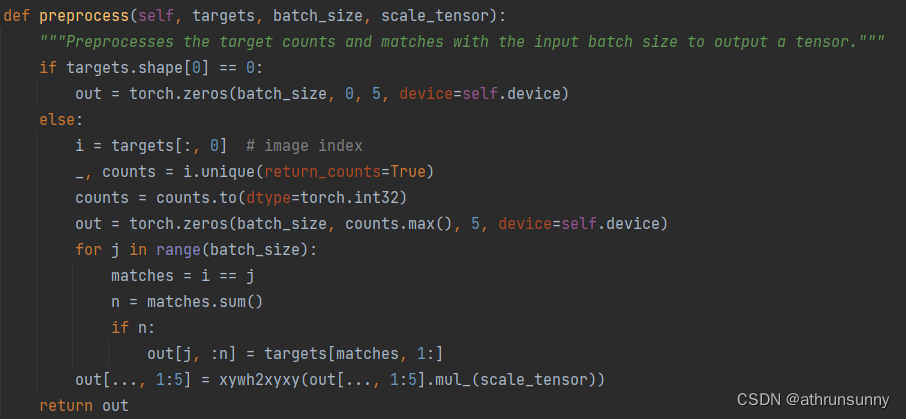
该函数主要是用来处理gt,将同一batch中不同长度的gt(cls + boxes)做对齐,短的gt用全0补齐。假设一个batch为2,其中image1的gt是[4,5],image2的gt是[7,5],那么取该batch中最长的7创建一个batch为2的张量[2,7,5],batch1的前四维为gt信息,为全0。下面用一组实际数据为例:

对应的gt_labels,gt_bboxes,mask_gt(之后会提到)

v8DetectionLoss中bbox_decode
该函数主要是将每一个anchor point和预测的回归参数通过dist2bbox做解码,生成anchor box与gt计算iou
def dist2bbox(distance, anchor_points, xywh=True, dim=-1):"""Transform distance(ltrb) to box(xywh or xyxy)."""assert(distance.shape[dim] == 4)lt, rb = distance.split([2, 2], dim)x1y1 = anchor_points - ltx2y2 = anchor_points + rbif xywh:c_xy = (x1y1 + x2y2) / 2wh = x2y2 - x1y1return torch.cat((c_xy, wh), dim) # xywh bboxreturn torch.cat((x1y1, x2y2), dim) # xyxy bboxloss[1] bce loss对应类别损失
loss[1] = self.bce(pred_scores, target_scores.to(dtype)).sum() / target_scores_sum # BCEloss[0] 对应iou loss
loss[2] 对应dfl loss
loss[0], loss[2] = self.bbox_loss(pred_distri, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, target_bboxes, target_scores, target_scores_sum, fg_mask)bbox loss的实现如下:
class BboxLoss(nn.Module):"""Criterion class for computing training losses during training."""def __init__(self, reg_max, use_dfl=False):"""Initialize the BboxLoss module with regularization maximum and DFL settings."""super().__init__()self.reg_max = reg_maxself.use_dfl = use_dfldef forward(self, pred_dist, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, target_bboxes, target_scores, target_scores_sum, fg_mask):"""IoU loss."""weight = target_scores.sum(-1)[fg_mask].unsqueeze(-1)iou = bbox_iou(pred_bboxes[fg_mask], target_bboxes[fg_mask], xywh=False, CIoU=True)loss_iou = ((1.0 - iou) * weight).sum() / target_scores_sum# DFL lossif self.use_dfl:target_ltrb = bbox2dist(anchor_points, target_bboxes, self.reg_max)loss_dfl = self._df_loss(pred_dist[fg_mask].view(-1, self.reg_max + 1), target_ltrb[fg_mask]) * weightloss_dfl = loss_dfl.sum() / target_scores_sumelse:loss_dfl = torch.tensor(0.0).to(pred_dist.device)return loss_iou, loss_dfl@staticmethoddef _df_loss(pred_dist, target):"""Return sum of left and right DFL losses.Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) proposed in Generalized Focal Losshttps://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9792391"""tl = target.long() # target lefttr = tl + 1 # target rightwl = tr - target # weight leftwr = 1 - wl # weight rightreturn (F.cross_entropy(pred_dist, tl.view(-1), reduction="none").view(tl.shape) * wl+ F.cross_entropy(pred_dist, tr.view(-1), reduction="none").view(tl.shape) * wr).mean(-1, keepdim=True)TaskAlignedAssigner
这个我认为是整个loss设计中的重头戏
因为整个loss中不像anchor base算法中需要计算前背景的obj loss,所以在TaskAlignedAssigner中需要确定哪些anchor属于前景哪些anchor属于背景,所以TaskAlignedAssigner得到target_labels, target_bboxes, target_scores的同时还需要得到前景的mask--fg_mask.bool()
class TaskAlignedAssigner(nn.Module):"""A task-aligned assigner for object detection.This class assigns ground-truth (gt) objects to anchors based on the task-aligned metric, which combines bothclassification and localization information.Attributes:topk (int): The number of top candidates to consider.num_classes (int): The number of object classes.alpha (float): The alpha parameter for the classification component of the task-aligned metric.beta (float): The beta parameter for the localization component of the task-aligned metric.eps (float): A small value to prevent division by zero."""def __init__(self, topk=13, num_classes=80, alpha=1.0, beta=6.0, eps=1e-9):"""Initialize a TaskAlignedAssigner object with customizable hyperparameters."""super().__init__()self.topk = topkself.num_classes = num_classesself.bg_idx = num_classesself.alpha = alphaself.beta = betaself.eps = eps@torch.no_grad()def forward(self, pd_scores, pd_bboxes, anc_points, gt_labels, gt_bboxes, mask_gt):"""Compute the task-aligned assignment. Reference code is available athttps://github.com/Nioolek/PPYOLOE_pytorch/blob/master/ppyoloe/assigner/tal_assigner.py.Args:pd_scores (Tensor): shape(bs, num_total_anchors, num_classes)pd_bboxes (Tensor): shape(bs, num_total_anchors, 4)anc_points (Tensor): shape(num_total_anchors, 2)gt_labels (Tensor): shape(bs, n_max_boxes, 1)gt_bboxes (Tensor): shape(bs, n_max_boxes, 4)mask_gt (Tensor): shape(bs, n_max_boxes, 1)Returns:target_labels (Tensor): shape(bs, num_total_anchors)target_bboxes (Tensor): shape(bs, num_total_anchors, 4)target_scores (Tensor): shape(bs, num_total_anchors, num_classes)fg_mask (Tensor): shape(bs, num_total_anchors)target_gt_idx (Tensor): shape(bs, num_total_anchors)"""self.bs = pd_scores.shape[0]self.n_max_boxes = gt_bboxes.shape[1]if self.n_max_boxes == 0:device = gt_bboxes.devicereturn (torch.full_like(pd_scores[..., 0], self.bg_idx).to(device),torch.zeros_like(pd_bboxes).to(device),torch.zeros_like(pd_scores).to(device),torch.zeros_like(pd_scores[..., 0]).to(device),torch.zeros_like(pd_scores[..., 0]).to(device),)mask_pos, align_metric, overlaps = self.get_pos_mask(pd_scores, pd_bboxes, gt_labels, gt_bboxes, anc_points, mask_gt)target_gt_idx, fg_mask, mask_pos = self.select_highest_overlaps(mask_pos, overlaps, self.n_max_boxes)# Assigned targettarget_labels, target_bboxes, target_scores = self.get_targets(gt_labels, gt_bboxes, target_gt_idx, fg_mask)# Normalizealign_metric *= mask_pospos_align_metrics = align_metric.amax(dim=-1, keepdim=True) # b, max_num_objpos_overlaps = (overlaps * mask_pos).amax(dim=-1, keepdim=True) # b, max_num_objnorm_align_metric = (align_metric * pos_overlaps / (pos_align_metrics + self.eps)).amax(-2).unsqueeze(-1)target_scores = target_scores * norm_align_metricreturn target_labels, target_bboxes, target_scores, fg_mask.bool(), target_gt_idx
get_pos_mask
def get_pos_mask(self, pd_scores, pd_bboxes, gt_labels, gt_bboxes, anc_points, mask_gt):"""Get in_gts mask, (b, max_num_obj, h*w)."""mask_in_gts = self.select_candidates_in_gts(anc_points, gt_bboxes) # 表示anchor中心是否位于对应的ground truth bounding box内# Get anchor_align metric, (b, max_num_obj, h*w)align_metric, overlaps = self.get_box_metrics(pd_scores, pd_bboxes, gt_labels, gt_bboxes, mask_in_gts * mask_gt)# Get topk_metric mask, (b, max_num_obj, h*w)mask_topk = self.select_topk_candidates(align_metric, topk_mask=mask_gt.expand(-1, -1, self.topk).bool())# Merge all mask to a final mask, (b, max_num_obj, h*w)mask_pos = mask_topk * mask_in_gts * mask_gt # 一个anchor point 负责一个gt object的预测return mask_pos, align_metric, overlaps其中包含select_candidates_in_gts,get_box_metrics,select_topk_candidates,由这三个函数共同选择正样本anchor point的位置
def select_candidates_in_gts(xy_centers, gt_bboxes, eps=1e-9):"""Select the positive anchor center in gt.Args:xy_centers (Tensor): shape(h*w, 2)gt_bboxes (Tensor): shape(b, n_boxes, 4)Returns:(Tensor): shape(b, n_boxes, h*w)"""n_anchors = xy_centers.shape[0] # 表示anchor中心的数量bs, n_boxes, _ = gt_bboxes.shapelt, rb = gt_bboxes.view(-1, 1, 4).chunk(2, 2) # left-top, right-bottom# 通过计算每个anchor中心与每个gt_bboxes的左上角和右下角之间的差值,以及右下角和左上角之间的差值,并将结果拼接为形状为 (bs, n_boxes, n_anchors, -1) 的张量。bbox_deltas = torch.cat((xy_centers[None] - lt, rb - xy_centers[None]), dim=2).view(bs, n_boxes, n_anchors, -1) # return (bbox_deltas.min(3)[0] > eps).to(gt_bboxes.dtype)# 计算 bbox_deltas 张量沿着第3个维度的最小值,形状为 (b, n_boxes, h*w) 的布尔型张量,表示anchor中心是否位于对应的ground truth bounding box内(最小值都为正数)return bbox_deltas.amin(3).gt_(eps) 实现思想很简单就是,将anchor point的坐标与gt box的左上角坐标相减,得到一个差值,同时gt box右下角的坐标与anchor point的坐标相减,同样得到一个差值,如果anchor point位于gt box内,那么这两组差值的数值都应该是大于0的数。
select_candidates_in_gts用于初步筛选位于gt box中的anchor points
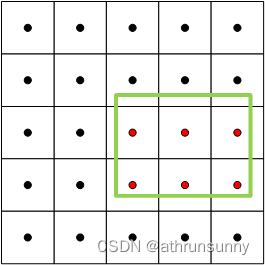
如上图,假设绿色的为gt box,红色的anchor points就是通过 select_candidates_in_gts筛选出来用于预测该gt box表示的object的可能的anchor point,最后返回的是关于这些anchor point的位置mask
get_box_metrics
它具有如下参数:
pd_scores:就是分类head输出的结果,shape一般为[bs, 8400, 80](以coco数据集,输入640*640为例)
pd_bboxes:回归head输出的结果,shape一般为[bs, 8400, 4]
gt_labels,gt_bboxes,mask_gt为gt所包含的信息,由于gt有做过数据用0补齐,mask_gt表示实际上非零的数据
mask_in_gts * mask_gt:表示实际上有gt标签位置上的候选anchor的位置的mask
def get_box_metrics(self, pd_scores, pd_bboxes, gt_labels, gt_bboxes, mask_gt):"""Compute alignment metric given predicted and ground truth bounding boxes."""na = pd_bboxes.shape[-2]mask_gt = mask_gt.bool() # b, max_num_obj, h*woverlaps = torch.zeros([self.bs, self.n_max_boxes, na], dtype=pd_bboxes.dtype, device=pd_bboxes.device) # 存储ioubbox_scores = torch.zeros([self.bs, self.n_max_boxes, na], dtype=pd_scores.dtype, device=pd_scores.device) # 存储边界框的分数ind = torch.zeros([2, self.bs, self.n_max_boxes], dtype=torch.long) # torch.Size([2, 2, 7]) * 0 # 2, b, max_num_objind[0] = torch.arange(end=self.bs).view(-1, 1).expand(-1, self.n_max_boxes) # b, max_num_obj # 批次信息 为从0到 self.bs-1 的序列,将其展开为形状为 (self.bs, self.n_max_boxes)ind[1] = gt_labels.squeeze(-1) # b, max_num_obj # 类别信息 为 gt_labels 的挤压操作(squeeze(-1)),将其形状变为 (self.bs, self.n_max_boxes)# Get the scores of each grid for each gt clsbbox_scores[mask_gt] = pd_scores[ind[0], :, ind[1]][mask_gt] # b, max_num_obj, h*w 根据实际边界框的掩码来获取每个网格单元的预测分数,并存储在 bbox_scores 中# (b, max_num_obj, 1, 4), (b, 1, h*w, 4)pd_boxes = pd_bboxes.unsqueeze(1).expand(-1, self.n_max_boxes, -1, -1)[mask_gt]gt_boxes = gt_bboxes.unsqueeze(2).expand(-1, -1, na, -1)[mask_gt]overlaps[mask_gt] = self.iou_calculation(gt_boxes, pd_boxes)# 对于满足实际边界框掩码的每个位置,从 pd_bboxes 中获取预测边界框(pd_boxes)和实际边界框(gt_boxes)计算iou,并将结果存储在 overlaps 中align_metric = bbox_scores.pow(self.alpha) * overlaps.pow(self.beta) # align_metric = bbox_scores^alpha * overlaps^beta 计算对齐度量,其中 alpha 和 beta 是超参数return align_metric, overlaps通过iou计算预测框(解码后的)与gt box之间的iou得到overlap;由于每个anchor point都有80个类别的预测得分,通过该处gt box对应的类别标签得到预测得分,得到bbox_scores,通过align_metric = bbox_scores^alpha * overlaps^beta 计算对齐度量。该度量同时考虑得分和框的重叠度。
select_topk_candidates
就是通过get_box_metrics中得到的align_metric来确定所有与gt有重叠的anchor中align_metric最高的前十(或前一)
def select_topk_candidates(self, metrics, largest=True, topk_mask=None):"""Select the top-k candidates based on the given metrics.Args:metrics (Tensor): A tensor of shape (b, max_num_obj, h*w), where b is the batch size,max_num_obj is the maximum number of objects, and h*w represents thetotal number of anchor points.largest (bool): If True, select the largest values; otherwise, select the smallest values.topk_mask (Tensor): An optional boolean tensor of shape (b, max_num_obj, topk), wheretopk is the number of top candidates to consider. If not provided,the top-k values are automatically computed based on the given metrics.Returns:(Tensor): A tensor of shape (b, max_num_obj, h*w) containing the selected top-k candidates."""# (b, max_num_obj, topk)# 使用 torch.topk 函数在给定的度量指标张量 metrics 的最后一个维度上选择前 k 个最大。# 这将返回两个张量:topk_metrics (形状为 (b, max_num_obj, topk)) 包含了选定的度量指标,以及 topk_idxs (形状为 (b, max_num_obj, topk)) 包含了相应的索引topk_metrics, topk_idxs = torch.topk(metrics, self.topk, dim=-1, largest=largest)if topk_mask is None:topk_mask = (topk_metrics.max(-1, keepdim=True)[0] > self.eps).expand_as(topk_idxs)# (b, max_num_obj, topk)topk_idxs.masked_fill_(~topk_mask, 0) # 使用 topk_mask 将 topk_idxs 张量中未选中的索引位置(~topk_mask)用零进行填充# (b, max_num_obj, topk, h*w) -> (b, max_num_obj, h*w)count_tensor = torch.zeros(metrics.shape, dtype=torch.int8, device=topk_idxs.device)ones = torch.ones_like(topk_idxs[:, :, :1], dtype=torch.int8, device=topk_idxs.device)for k in range(self.topk):# Expand topk_idxs for each value of k and add 1 at the specified positionscount_tensor.scatter_add_(-1, topk_idxs[:, :, k : k + 1], ones) # 使用 scatter_add_ 函数根据索引 topk_idxs[:, :, k : k + 1],将 ones 张量的值相加到 count_tensor 张量的相应位置上# count_tensor.scatter_add_(-1, topk_idxs, torch.ones_like(topk_idxs, dtype=torch.int8, device=topk_idxs.device))# Filter invalid bboxescount_tensor.masked_fill_(count_tensor > 1, 0) # 将 count_tensor 中大于 1 的值用零进行填充,以过滤掉超过一个的边界框return count_tensor.to(metrics.dtype)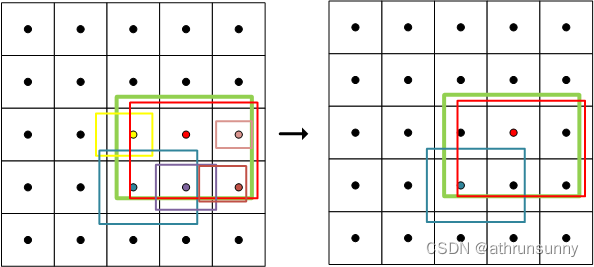
比如上图,由于这里只是作为示例,只表示其中一个特征图上gt样例,其他层的gt位置可能有更多的anchor point满足 align_metric的条件被保留下来(不必太纠结这里是不是有10个),因为PAN输出了三层特征图,anchor对应每层特征图的中心,而实践中将每层的anchor展平之后合并在一起得到8400的长度,而最终是在这8400中取前十的anchor,所以每层特征图上保留的anchor可能数量不等。
此时被保留下来的anchor point的位置用1表示,其余位置为0,仅保留了指标前十的样本作为正样本
select_highest_overlaps
def select_highest_overlaps(mask_pos, overlaps, n_max_boxes):"""If an anchor box is assigned to multiple gts, the one with the highest IoU will be selected.Args:mask_pos (Tensor): shape(b, n_max_boxes, h*w)overlaps (Tensor): shape(b, n_max_boxes, h*w)Returns:target_gt_idx (Tensor): shape(b, h*w)fg_mask (Tensor): shape(b, h*w)mask_pos (Tensor): shape(b, n_max_boxes, h*w)"""# (b, n_max_boxes, h*w) -> (b, h*w)fg_mask = mask_pos.sum(-2) # 对 mask_pos 沿着倒数第二个维度求和,得到形状为 (b, h*w) 的张量 fg_mask,表示每个网格单元上非背景anchor box的数量if fg_mask.max() > 1: # one anchor is assigned to multiple gt_bboxes# 创建一个布尔型张量 mask_multi_gts,形状为 (b, n_max_boxes, h*w),用于指示哪些网格单元拥有多个ground truth bounding boxesmask_multi_gts = (fg_mask.unsqueeze(1) > 1).expand(-1, n_max_boxes, -1) # (b, n_max_boxes, h*w)# 获取每个网格单元上具有最高IoU的ground truth bounding box的索引,并创建一个张量 is_max_overlaps,形状与 mask_pos 相同,# 其中最高IoU的ground truth bounding box对应的位置上为1,其余位置为0。max_overlaps_idx = overlaps.argmax(1) # (b, h*w)is_max_overlaps = torch.zeros(mask_pos.shape, dtype=mask_pos.dtype, device=mask_pos.device)is_max_overlaps.scatter_(1, max_overlaps_idx.unsqueeze(1), 1) # max_overlaps_idx表示具有最大iou的索引,将具有最大iou的位置设置为1# 根据 mask_multi_gts 来更新 mask_pos。对于存在多个ground truth bounding box的网格单元,将 is_max_overlaps 中# 对应位置的值赋给 mask_pos,以保留具有最高IoU的ground truth bounding box的匹配情况mask_pos = torch.where(mask_multi_gts, is_max_overlaps, mask_pos).float() # (b, n_max_boxes, h*w)fg_mask = mask_pos.sum(-2)# Find each grid serve which gt(index)target_gt_idx = mask_pos.argmax(-2) # (b, h*w) # 得到每个网格单元上具有最高IoU的ground truth bounding box的索引 target_gt_idxreturn target_gt_idx, fg_mask, mask_pos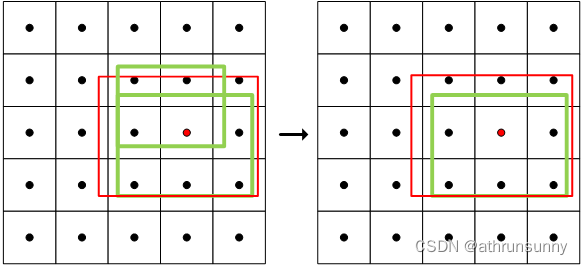
对被分配了多个gt的anchor去重,得到前景的mask以及anchor point上具有最高IoU的ground truth bounding box的索引。假设上图中红色的anchor被分配给了两个gt,通select_highest_overlaps后会保留gt与该anchor的iou最大的那个,并用该anchor来预测该gt,另一个gt则可能会被周围的其他anchor所负责。此时也要更新mask_pos,毕竟重新对anchor做了处理。
因为每个anchor负责一个类别的检测,mask_pos表示最终确定的anchor的mask,如下图所示为其中一个batch中数据形式
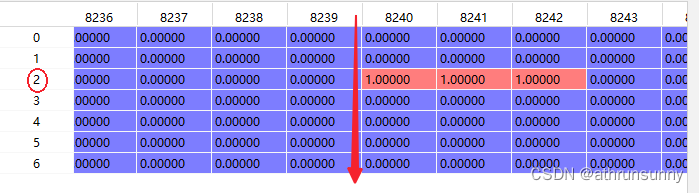
该batch中8240,8241,8242为最终确定的anchor,其在红色箭头所示维度上对应的索引为2,target_gt_idx在该batch上的最终表示为:

get_targets
有了以上的信息之后就获取gt了
def get_targets(self, gt_labels, gt_bboxes, target_gt_idx, fg_mask):"""Compute target labels, target bounding boxes, and target scores for the positive anchor points.Args:gt_labels (Tensor): Ground truth labels of shape (b, max_num_obj, 1), where b is thebatch size and max_num_obj is the maximum number of objects.gt_bboxes (Tensor): Ground truth bounding boxes of shape (b, max_num_obj, 4).target_gt_idx (Tensor): Indices of the assigned ground truth objects for positiveanchor points, with shape (b, h*w), where h*w is the totalnumber of anchor points.fg_mask (Tensor): A boolean tensor of shape (b, h*w) indicating the positive(foreground) anchor points.Returns:(Tuple[Tensor, Tensor, Tensor]): A tuple containing the following tensors:- target_labels (Tensor): Shape (b, h*w), containing the target labels forpositive anchor points.- target_bboxes (Tensor): Shape (b, h*w, 4), containing the target bounding boxesfor positive anchor points.- target_scores (Tensor): Shape (b, h*w, num_classes), containing the target scoresfor positive anchor points, where num_classes is the numberof object classes."""# Assigned target labels, (b, 1)batch_ind = torch.arange(end=self.bs, dtype=torch.int64, device=gt_labels.device)[..., None]# 使用 target_gt_idx 加上偏移量,得到形状为 (b, h*w) 的 target_gt_idx 张量,表示正样本anchor point的真实类别索引target_gt_idx = target_gt_idx + batch_ind * self.n_max_boxes # (b, h*w)# 使用 flatten 函数将 gt_labels 张量展平为形状为 (b * max_num_obj) 的张量,然后使用 target_gt_idx 进行索引,# 得到形状为 (b, h*w) 的 target_labels 张量,表示正样本anchor point的目标标签target_labels = gt_labels.long().flatten()[target_gt_idx] # (b, h*w)# Assigned target boxes, (b, max_num_obj, 4) -> (b, h*w, 4)target_bboxes = gt_bboxes.view(-1, gt_bboxes.shape[-1])[target_gt_idx] # 表示正样本anchor point的目标边界框# Assigned target scorestarget_labels.clamp_(0)# 10x faster than F.one_hot()target_scores = torch.zeros((target_labels.shape[0], target_labels.shape[1], self.num_classes),dtype=torch.int64,device=target_labels.device,) # (b, h*w, 80)target_scores.scatter_(2, target_labels.unsqueeze(-1), 1) # 使用 scatter_ 函数将 target_labels 的值进行 one-hot 编码,将张量中每个位置上的目标类别置为 1fg_scores_mask = fg_mask[:, :, None].repeat(1, 1, self.num_classes) # (b, h*w, 80)target_scores = torch.where(fg_scores_mask > 0, target_scores, 0) # 根据 fg_scores_mask 的值,将 target_scores 张量中的非正样本位置(值小于等于 0)即背景类置为零return target_labels, target_bboxes, target_scores该函数的要点基本都在代码里注释了
得到target后还要对target_scores做一些归一化操作