文章目录
- 1.线程的创建方式
- 1.1继承Thread类,重写run方法
- 1.2实现Runnable接口,重写run方法。
- 1.3实现Callable接口,重新call方法
- 1.4以上三种总结
- 1.5使用线程池创建线程
- 1.5.1线程池创建线程的方式
- 1.5.2线程池的七大参数含义
- 1.5.3线程池的工作流程
- 1.5.4一个线程池core:7,max:20,queue:50。100个并发进来,怎么分配。
- 2.CompletableFuture异步编排
- 2.1创建异步对象方式
- 2.2计算完成时回调方法
- 2.1.1方法完成时的感知(方法一)
- 2.1.2方法完成时的处理(方法二)
- 2.3线程的串行化的方法
- 2.3.1不能接收值且没有返回值
- 2.3.2可以接收值但是没有返回值
- 2.3.3可以接收值也可以返回值
- 2.4两任务组合-一个完成即可
- 2.5两任务组合-两个都要完成
- 2.6多任务组合
- 2.7查看商品详情实战
1.线程的创建方式
1.1继承Thread类,重写run方法
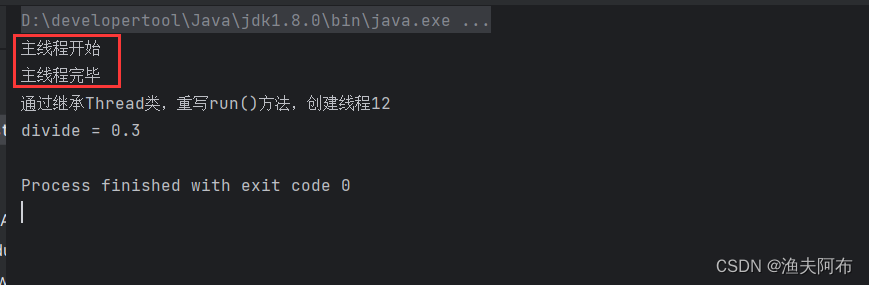
package com.atguigu.gmall.product.thread;import java.math.BigDecimal;public class ThreadTest {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 线程的创建方式* 1.继承Thread类*///开启线程System.out.println("主线程开始");Thread thread = new Thread01();thread.start();System.out.println("主线程完毕");}public static class Thread01 extends Thread{//创建线程方法一//通过继承Thread类重写run()方法,在run()方法中编写业务类@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("通过继承Thread类,重写run()方法,创建线程"+Thread.currentThread().getId());BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal(3);BigDecimal divide = bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal);System.out.println("divide = " + divide);}}
}结果
1.2实现Runnable接口,重写run方法。
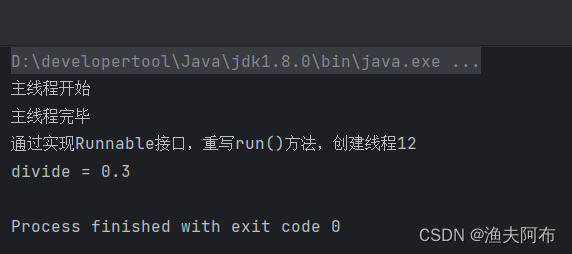
package com.atguigu.gmall.product.thread;import java.math.BigDecimal;public class RunableTest {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 创建线程的方法二:* 通过实现Runable接口,重新run方法,创建线程。*///开启线程System.out.println("主线程开始");Runable01 runable01 = new Runable01();Thread thread = new Thread(runable01);thread.start();System.out.println("主线程完毕");}public static class Runable01 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("通过实现Runnable接口,重写run()方法,创建线程"+Thread.currentThread().getId());BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal(3);BigDecimal divide = bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal);System.out.println("divide = " + divide);}}
}
1.3实现Callable接口,重新call方法
package com.atguigu.gmall.product.thread;import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
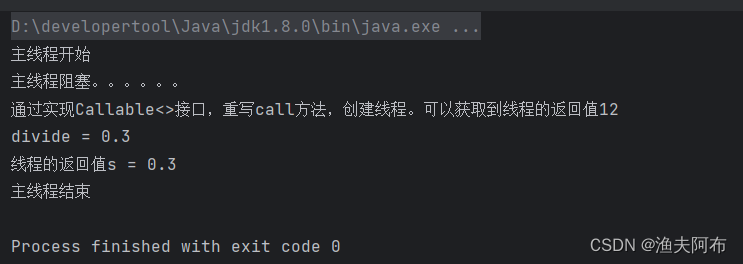
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;public class CallableTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {/*** 创建线程的方法三* 通过实现Callable<>接口,重写call方法,创建线程。可以获取到线程的返回值*/System.out.println("主线程开始");FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<String>(new Callable01());//开启线程new Thread(futureTask).start();//获取线程的返回值,会阻塞主线程System.out.println("主线程阻塞。。。。。。");String s = futureTask.get();System.out.println("线程的返回值s = " + s);System.out.println("主线程结束");}public static class Callable01 implements Callable<String>{@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {System.out.println("通过实现Callable<>接口,重写call方法,创建线程。可以获取到线程的返回值"+Thread.currentThread().getId());BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal(3);BigDecimal divide = bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal);System.out.println("divide = " + divide);return divide.toString();}}
}
1.4以上三种总结
1.开启线程的方式,Thread对象调用start方法。
2.以上三种只有第三种可以接收线程的返回值。
1.5使用线程池创建线程
1.5.1线程池创建线程的方式
/*** 使用线程池创建线程*/ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10,20,10,TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1000),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
1.5.2线程池的七大参数含义
/*** Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial* parameters.** @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the* pool* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads* will wait for new tasks before terminating.* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable}* tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.* @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor* creates a new thread* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached*/public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,ThreadFactory threadFactory,RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
- corePoolSize:核心的线程池数。也就是线程池一创建就有的。
- maximumPoolSize:最大的线程池数。这个线程池可以创建的最大的线程池数。
- keepAliveTime:当线程池中的线程数大于核心的线程池时,这些线程池执行完任务保持存活的时间。
- unit:时间单位
- workQueue:阻塞队列,当任务大于核心线程数时,任务就会放在阻塞队列中。
- threadFactory:创建工厂。指定线程名。
- handler:拒绝策略。当线程池中所有的线程都在执行任务,而且阻塞队列已经满了。那么来了任务就需要执行拒绝策略了。
1.5.3线程池的工作流程
1、创建线程池,会创建core线程。
2、当任务来了,core线程进行处理,若core不够,那么就会将任务放在workQueue中,当核心线程空闲下来,去workQueue阻塞队列中去任务。
3、若阻塞队列满了,线程池就去开启新的线程,直至线程池中的线程数达到maximumPoolSize最大线程池数。若新的线程空闲下来,过了过期时间,就会自动销毁。
4、若线程池中的线程池数达到了最大线程池数,而且还来了任务,那么就会使用拒绝策略进行处理。
5、所有的线程都是由指定的factory工厂创建的。
1.5.4一个线程池core:7,max:20,queue:50。100个并发进来,怎么分配。
首先:7个线程直接进行处理。
然后:进入队列50个。
再次:开启13个线程进行处理。
最后:70个被安排,30个交给阻塞队列。
2.CompletableFuture异步编排
2.1创建异步对象方式
//方法一:public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {return asyncRunStage(asyncPool, runnable);}//方法二public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor) {return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable);}//方法三public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U>supplier) {return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);}//方法四public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,Executor executor) {return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier);}
1.runXxx方法没有返回值,supplyXxx方法有返回值。
2.可以传入自定义的线程池,否则默认的线程池。
3.都不会接收返回值。
代码
package com.atguigu.gmall.product.completableFuture;import rx.Completable;import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.concurrent.*;public class Test {public static ExecutorService executors = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {/*** 1.创建异步对象*///CompletableFuture类中的静态方法long startMain = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("主线程--开始");CompletableFuture<Void> future01 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(new Runnable01());CompletableFuture<Void> future02 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {long start02 = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("id============================");long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();System.out.println("当前线程的id = " + id);BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(2);BigDecimal divide = a.divide(b);System.out.println("运行结果divide = " + divide+"02-"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start02));}, executors);CompletableFuture<String> future03 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {long start03 = System.currentTimeMillis();long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();System.out.println("id============================");System.out.println("当前线程的id = " + id);BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(2);BigDecimal divide = a.divide(b);System.out.println("运行结果divide = " + divide+"03-"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start03));return divide.toString();});System.out.println("获取返回结果future03.get() = " + future03.get());CompletableFuture<String> future04 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {long start04 = System.currentTimeMillis();long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();System.out.println("id============================");System.out.println("当前线程的id = " + id);BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(2);BigDecimal divide = a.divide(b);System.out.println("运行结果divide = " + divide+"04-"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start04));return divide.toString();},executors);System.out.println("获取返回结果future04 = " + future04.get());System.out.println("主线程--结束"+"Main用时"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - startMain));}public static class Runnable01 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {long start01 = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("id============================");long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();System.out.println("当前线程的id = " + id);BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(2);BigDecimal divide = a.divide(b);System.out.println("运行结果divide = " + divide+"01-"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start01));}}public static class Callable01 implements Callable<String> {@Overridepublic String call() {System.out.println("id============================");long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();System.out.println("当前线程的id = " + id);BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(2);BigDecimal divide = a.divide(b);System.out.println("运行结果divide = " + divide);return divide.toString();}}
}2.2计算完成时回调方法
2.1.1方法完成时的感知(方法一)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action);}public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(asyncPool, action);}public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action, Executor executor) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);}public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn) {return uniExceptionallyStage(fn);}
whenComplete 可以处理正常结果但是不能返回结果、感知异常但是不能处理异常。这个方法不可以进行返回值
exceptionally可以感知异常并且修改返回值进行返回。
whenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 的区别:
whenComplete:是执行当前任务的线程执行继续执行 whenComplete 的任务。
whenCompleteAsync:是执行把 whenCompleteAsync 这个任务继续提交给线程池来进行执行。
方法不以 Async 结尾,意味着 Action 使用相同的线程执行,而 Async 可能会使用其他线程执行(如果是使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)
代码示例
package com.atguigu.gmall.product.completableFuture;import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.concurrent.*;public class Test02 {public static ExecutorService executors = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> exceptionally = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int i = 10/0;return "a";}).whenCompleteAsync((res, exception) -> {//尽可以感到异常,不可以修改返回结果System.out.println("输出返回结果" + res);}, executors).exceptionally((exception -> {//可以感到异常,并且修改返回结果return "b";}));System.out.println("获取返回结果:" + exceptionally.get());}public static class Runnable01 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {long start01 = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("id============================");long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();System.out.println("当前线程的id = " + id);BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(2);BigDecimal divide = a.divide(b);System.out.println("运行结果divide = " + divide+"01-"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start01));}}public static class Callable01 implements Callable<String> {@Overridepublic String call() {System.out.println("id============================");long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();System.out.println("当前线程的id = " + id);BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(2);BigDecimal divide = a.divide(b);System.out.println("运行结果divide = " + divide);return divide.toString();}}
}2.1.2方法完成时的处理(方法二)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) {return uniHandleStage(null, fn);}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) {return uniHandleStage(asyncPool, fn);}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn, Executor executor) {return uniHandleStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);}不仅可以处理正常结果而且可以处理异常
不仅可以接收值,而且可以返回处理结果
代码实例
package com.atguigu.gmall.product.completableFuture;import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.concurrent.*;public class Test02 {public static ExecutorService executors = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> exceptionally = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int i = 10/0;return "a";}).handleAsync((res,exception) -> {//不仅可以接收参数,而且可以返回结果if (res != null){return "值"+res;}if (exception != null){return "异常"+exception.getMessage();}return "0";},executors);System.out.println("获取返回结果:" + exceptionally.get());}public static class Runnable01 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {long start01 = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("id============================");long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();System.out.println("当前线程的id = " + id);BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(2);BigDecimal divide = a.divide(b);System.out.println("运行结果divide = " + divide+"01-"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start01));}}public static class Callable01 implements Callable<String> {@Overridepublic String call() {System.out.println("id============================");long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();System.out.println("当前线程的id = " + id);BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal(10);BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(2);BigDecimal divide = a.divide(b);System.out.println("运行结果divide = " + divide);return divide.toString();}}
}2.3线程的串行化的方法
2.3.1不能接收值且没有返回值
thenRun方法:只要上面的任务执行完成,就开始执行thenRun,只是处理完任务后,执行 thenRun的后续操作
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {return uniRunStage(null, action);}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor) {return uniRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);}
代码示例
package com.atguigu.gmall.product.completableFuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class Test03 {public static ExecutorService excutor =Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Void> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int i = 0;System.out.println("i = " + i);return i;}).thenRunAsync(() -> {int j = 0;System.out.println("j = " + j);});Void unused = future01.get();System.out.println("unused = " + unused);}
}2.3.2可以接收值但是没有返回值
thenAccept方法:消费处理结果。接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果。
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) {return uniAcceptStage(null, action);}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action) {return uniAcceptStage(asyncPool, action);}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor) {return uniAcceptStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);}
2.3.3可以接收值也可以返回值
thenApply 方法:当一个线程依赖另一个线程时,获取上一个任务返回的结果,并返回当前任务的返回值。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(null, fn);}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(asyncPool, fn);}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor) {return uniApplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);}
代码示例
package com.atguigu.gmall.product.completableFuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class Test03 {public static ExecutorService excutor =Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> future03 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int i = 0;System.out.println("i = " + i);return i;}).thenApplyAsync((res) -> {res++;return res;});Integer integer = future03.get();System.out.println("integer = " + integer);}
}带有Async默认是异步执行的。这里所谓的异步指的是不在当前线程内执行。
Function<? super T,? extends U>
T:上一个任务返回结果的类型
U:当前任务的返回值类型
2.4两任务组合-一个完成即可
2.5两任务组合-两个都要完成
2.6多任务组合
2.7查看商品详情实战
@Autowiredprivate ThreadPoolExecutor executor;public Map<String, Object> getBySkuId(Long skuId) {Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();//添加布隆过滤器 每次添加skuinfo信息的时候,都会把skuid放在布隆过滤器中,这样查询skuinfo时,// 首先进行检查是否通过布隆过滤器,通过说明在数据库中存在该数据。不通过说明数据库不存在该数据。// 布隆过滤器可以解决缓存穿透的问题。RBloomFilter<Object> bloomFilter = redissonClient.getBloomFilter(RedisConst.SKU_BLOOM_FILTER);if (!bloomFilter.contains(skuId)) return result;//添加异步任务 查询skuInfoCompletableFuture<SkuInfo> skuInfoCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {SkuInfo skuInfo = productFeignClient.getSkuInfo(skuId);if (skuInfo == null){return skuInfo;}result.put("skuInfo",skuInfo);return skuInfo;}, executor);// 获取分类数据CompletableFuture<Void> categoryViewCompletableFuture = skuInfoCompletableFuture.thenAcceptAsync((skuInfo) -> {BaseCategoryView categoryView = productFeignClient.getCategoryView(skuInfo.getCategory3Id());result.put("categoryView", categoryView);});// 获取销售属性+销售属性值CompletableFuture<Void> spuSaleAttrListCompletableFuture = skuInfoCompletableFuture.thenAcceptAsync((skuInfo -> {List<SpuSaleAttr> spuSaleAttrListCheckBySku = productFeignClient.getSpuSaleAttrListCheckBySku(skuId, skuInfo.getSpuId());result.put("spuSaleAttrList", spuSaleAttrListCheckBySku);}));// 查询销售属性值Id 与skuId 组合的mapCompletableFuture<Void> valuesSkuJsonCompletableFuture = skuInfoCompletableFuture.thenAcceptAsync(skuInfo -> {Map skuValueIdsMap = productFeignClient.getSkuValueIdsMap(skuInfo.getSpuId());// 将这个map 转换为页面需要的Json 对象String valueJson = JSON.toJSONString(skuValueIdsMap);result.put("valuesSkuJson", valueJson);});// spu海报数据CompletableFuture<Void> spuPosterListCompletableFuture = skuInfoCompletableFuture.thenAcceptAsync(skuInfo -> {// 返回map 集合 Thymeleaf 渲染:能用map 存储数据!List<SpuPoster> spuPosterList = productFeignClient.getSpuPosterBySpuId(skuInfo.getSpuId());result.put("spuPosterList", spuPosterList);});// 获取价格CompletableFuture<Void> skuPriceCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {BigDecimal skuPrice = productFeignClient.getSkuPrice(skuId);// map 中 key 对应的谁? Thymeleaf 获取数据的时候 ${skuInfo.skuName}result.put("price", skuPrice);});CompletableFuture<Void> skuAttrListCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {List<BaseAttrInfo> attrList = productFeignClient.getAttrList(skuId);// 使用拉姆达表示List<Map<String, String>> skuAttrList = attrList.stream().map((baseAttrInfo) -> {Map<String, String> attrMap = new HashMap<>();attrMap.put("attrName", baseAttrInfo.getAttrName());attrMap.put("attrValue", baseAttrInfo.getAttrValueList().get(0).getValueName());return attrMap;}).collect(Collectors.toList());result.put("skuAttrList", skuAttrList);});//阻塞主线程等待总的结果CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.allOf(skuInfoCompletableFuture, categoryViewCompletableFuture,spuSaleAttrListCompletableFuture, valuesSkuJsonCompletableFuture,spuPosterListCompletableFuture, skuPriceCompletableFuture,skuAttrListCompletableFuture);future.join();return result;}修改之前

修改之后