记录一下常见的工业协议数据读取方法
目录
- 前言
- Modbus协议说明
- Netty 读取测试
- 使用plc4x 读取测试
- 结束语
前言
Modbus 是一种通讯协议,用于在工业控制系统中进行数据通信和控制。Modbus 协议主要分为两种常用的变体:Modbus RTU 和 Modbus TCP/IP
-
Modbus RTU:Modbus RTU 是一种基于串行通信的协议。
-
Modbus TCP/IP:Modbus TCP/IP 是一种基于 TCP/IP 网络的协议。
本次使用TCP协议,一般常见使用这种协议。
Modbus 协议一般工业设备例如光电信号,各类传感器和执行器等。
一些电力设备(如变压器、开关设备、仪表等)
Modbus协议说明
如果要使用netty读取modbus协议数据必须了解一下协议报文格式。
参考: https://neugates.io/docs/zh/latest/appendix/protocol/modbus_tcp.html
如果设备数量< 30个可以尝试使用 Neuro 产品读取,里面包含配置监控SDK等。
Modbus=MBAP(报文头)+PDU(帧结构)
Netty 读取测试
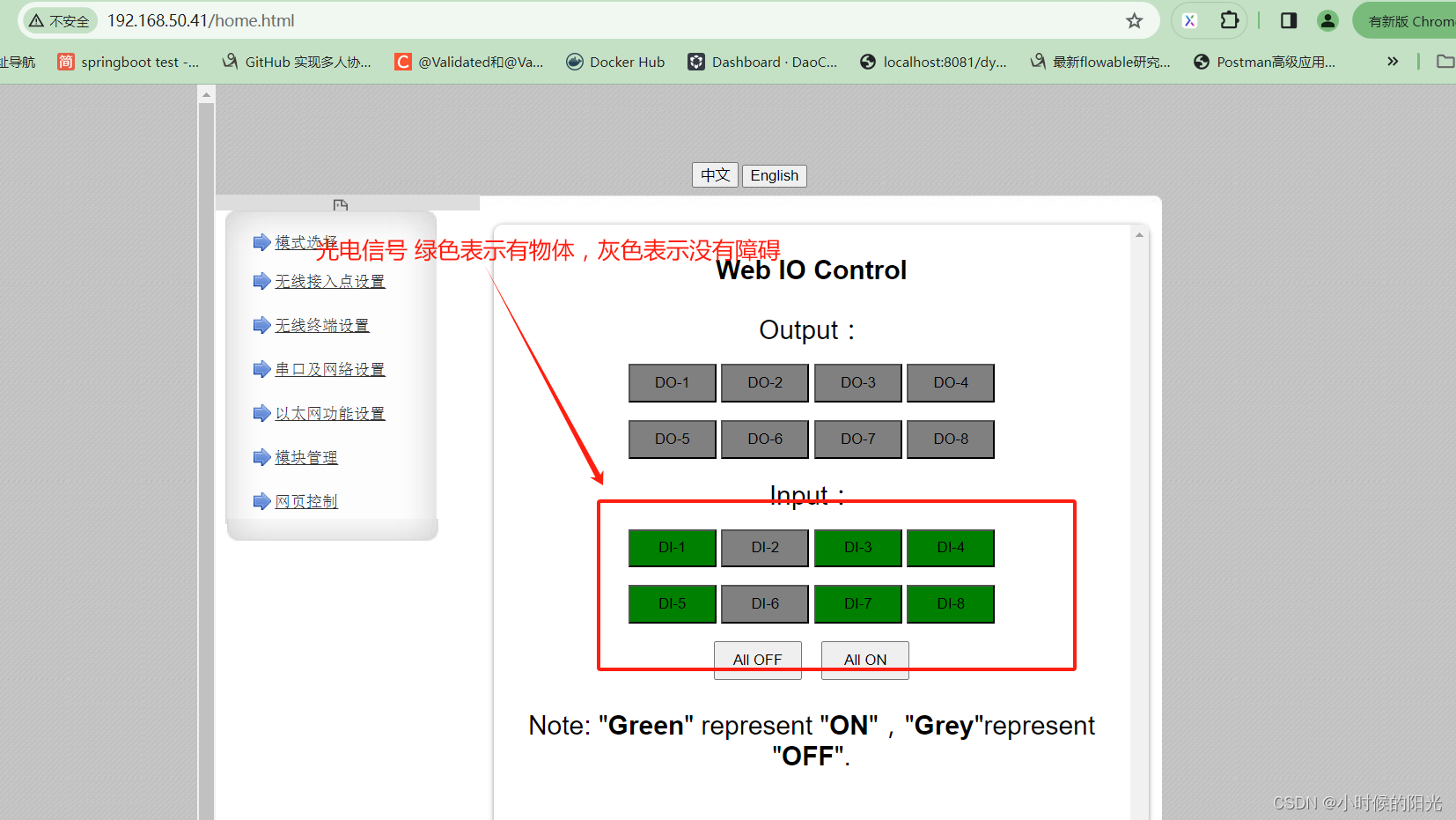
假设有一个光电IO模块对接了8个激光设备,激光扫描到障碍物为1 没有扫到位0,先通过厂家自带的web端管理界面查看目前的实际信号情况:
这边测试的Netty代码如下:
package org.example.modbus;import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;public class ModbusClient {private final String host;private final int port;public ModbusClient(String host, int port) {this.host = host;this.port = port;}public void start() throws InterruptedException {EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true).handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(Channel ch) {ch.pipeline().addLast(new ModbusClientHandler());}});ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();f.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {group.shutdownGracefully();}}private static class ModbusClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {// writeShort 一次写2个字节 writeByte 一次写1个字节ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.buffer();// >>>>>>>>>>>>构造 M B A P Header(报文头)<<<<<<<<<<<<<// 事务标识符 占用2个字节// 可以解释为报文的序列号,例如测试使用的 Modbus Poll 客户端一直发送数据,// 所以每发送一次数据标识符就加一。服务器接收时会把这个数据原封返回。buffer.writeShort(1);// 协议类型 占用2个字节, 十六进制格式"00 00" 表示Modbus TCP 协议buffer.writeShort(0);// 长度 占用2个字节, 6 表示报文长度(后面有6个字节),包括 M B A P Header 和 PDU// 表示从单元标识符开始后面数据的长度。如:00 06 表示后面有 0X06 个字节长度的数据。buffer.writeShort(6);// 单元标识符 占用1个字节, 17 表示设备存储单元编号buffer.writeByte(17);// >>>>>>>>>>>>构造 PDU PDU=功能码+数据<<<<<<<<<<<<<// 功能码 占用1个字节, 02 表示读离散量输入buffer.writeByte(2);// 开始读的数据的地址。从 00 32 开始读数据。buffer.writeShort(32);// 读取的寄存器数量。从开始位置读 00 08 个寄存器数据。buffer.writeShort(8);ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);}@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {ByteBuf buffer = (ByteBuf) msg;byte[] response = new byte[buffer.readableBytes()];buffer.readBytes(response);System.out.println("Response: " + bytesToHex(response));}@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {cause.printStackTrace();ctx.close();}}private static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {// 这个 bytesToHex 方法用于将一个 byte 数组转换为十六进制格式的字符串。// 每个字节被转换为两个十六进制字符,并用空格分隔,// 最终返回一个表示十六进制表示形式的字符串StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (byte b : bytes) {sb.append(String.format("%02X ", b));}return sb.toString();}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {String host = "192.168.50.41";int port = 28899;new ModbusClient(host, port).start();}
}光电IO设备模块IP地址为 192.168.50.41 端口使用 28899,上面代码是使用netty 向IO模块发送读取 8个光电的离散量信号报文,地址从32开始,然后获得modbus协议的结果报文,最终获得的结果报文解析成十六进制的字符串形式如下:
Response: 00 01 00 00 00 04 11 02 01 CD
还是建议参考上面推荐的文档,这里截取主要信息:

根据上面的样例说明,我们其实想要得到的结果是最后2位16进制数据 DD,占据1个字节,因为我们读取的是离散值(类似true或fase 一般是1或者0),因此我们将 CD转换为二进制数据:
1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1
从低位开始(从右 至 左) 对应厂家web管理界面中的 DI-1 DI-2 …
绿色=1 灰色=0
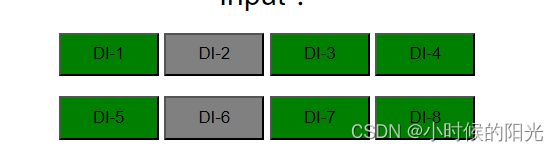
可以发现netty读取到的信号和厂家web管理界面显示的数据一致。
使用plc4x 读取测试
apache旗下工业协议适配工具库,具体文档查看官网:
链接: https://plc4x.apache.org/users/protocols/modbus.html
pom.xml文件引入maven依赖包:
<properties><plc4x.version>0.12.0</plc4x.version></properties><dependency><groupId>org.apache.plc4x</groupId><artifactId>plc4j-api</artifactId><version>${plc4x.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.plc4x</groupId><artifactId>plc4j-driver-modbus</artifactId><version>${plc4x.version}</version></dependency>代码如下:
package cn.guzt.modbustest;import cn.hutool.core.util.ArrayUtil;
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
import org.apache.plc4x.java.api.PlcConnection;
import org.apache.plc4x.java.api.PlcDriverManager;
import org.apache.plc4x.java.api.messages.PlcReadRequest;
import org.apache.plc4x.java.api.messages.PlcReadResponse;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;/*** apache PLX modbus测试用例** @author guzt*/
public class ModbusExample {protected static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ModbusExample.class);public static void main(String[] args) {String ip = "192.168.50.41";String port = "28899";// 单元标识符:相当于设备的地址String unitIdentifier = "17";String timeout = "5000";String urlFormat = "modbus-tcp:tcp://{}:{}?unit-identifier={}&request-timeout={}";// try里面会自动关闭连接try (PlcConnection plcConnection = PlcDriverManager.getDefault().getConnectionManager().getConnection(StrUtil.format(urlFormat, ip, port, unitIdentifier, timeout))) {// Check if this connection support reading of data.if (!plcConnection.getMetadata().isReadSupported()) {logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>This connection doesn't support reading.");return;}// Check if this connection support writing of data.if (!plcConnection.getMetadata().isWriteSupported()) {logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>This connection doesn't support writing.");return;}if (plcConnection.isConnected()) {logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>Modbus已经连上..............");}// Create a new read request:// You will need to pass the reference you are asking forPlcReadRequest.Builder builder = plcConnection.readRequestBuilder();// 一次性读取几个寄存器里面的内容int count = 8;// 这里面的起始地址为实际为 32,传递参数时候加1int startAddress = 33;for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {// 功能码 (tagAddress) Modbus 的操作对象有四种:线圈、离散输入、输入寄存器、保持寄存器。// 1. 线圈:相当于开关,在 Modbus 中可读可写,数据只有 00 和 01。// 2. 离散量:输入位,开关量,在 Modbus 中只读。// 3. 输入寄存器:只能从模拟量输入端改变的寄存器,在 Modbus 中只读。// 4. 保持寄存器:用于输出模拟量信号的寄存器,在 Modbus 中可读可写。// 查看参考:https://neugates.io/docs/zh/latest/appendix/protocol/modbus_tcp.html// 不同功能码对应不同的地址格式:参看 org.apache.plc4x.java.modbus.base.tag.ModbusTagHandlerbuilder.addTagAddress("第" + (i + 1) + "个光电信号:", "discrete-input:" + (startAddress + i));}// 这种方式一次性读取8个:builder.addTagAddress("DI-count8N", "discrete-input:33:BOOL[8]")PlcReadRequest readRequest = builder.build();logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>开始读取");// Execute the requestPlcReadResponse response = readRequest.execute().get();// Handle the response// 创建了一个写请求,尝试将地址1的线圈设置为truefor (String fieldName : response.getTagNames()) {if (response.getObject(fieldName) instanceof Boolean) {logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>Boolean[" + fieldName + "]: " + response.getBoolean(fieldName));} else if (ArrayUtil.isArray(response.getObject(fieldName))) {logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>Array[" + fieldName + "]: " + response.getObject(fieldName));} else {logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>Object[" + fieldName + "]: " + response.getObject(fieldName));}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
执行打印结果如下:
...
16:20:25.378 [main] INFO cn.guzt.modbustest.ModbusExample - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>Boolean[第1个光电信号:]: true
16:20:25.378 [main] INFO cn.guzt.modbustest.ModbusExample - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>Boolean[第2个光电信号:]: false
16:20:25.378 [main] INFO cn.guzt.modbustest.ModbusExample - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>Boolean[第3个光电信号:]: true
16:20:25.378 [main] INFO cn.guzt.modbustest.ModbusExample - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>Boolean[第4个光电信号:]: true
16:20:25.378 [main] INFO cn.guzt.modbustest.ModbusExample - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>Boolean[第5个光电信号:]: true
16:20:25.378 [main] INFO cn.guzt.modbustest.ModbusExample - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>Boolean[第6个光电信号:]: false
16:20:25.378 [main] INFO cn.guzt.modbustest.ModbusExample - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>Boolean[第7个光电信号:]: true
16:20:25.378 [main] INFO cn.guzt.modbustest.ModbusExample - >>>>>>>>>>>>>>Boolean[第8个光电信号:]: true...
从第1行至第8行记录值 对应厂家web管理界面中的 DI-1 DI-2 …
绿色=true 灰色=fase

可以发现plc4x读取到的信号和厂家web管理界面显示的数据一致。
结束语
读取Modbus的开源库有很多,这里列举常见的使用库,尤其是 Plc4x 这个适配了主流的工业协议,值得我们去研究。
使用netty的话对基本功要求比较高,如果对modbus工业协议包括TCP/IP协议一知半解估计应该是写不出成功案例。