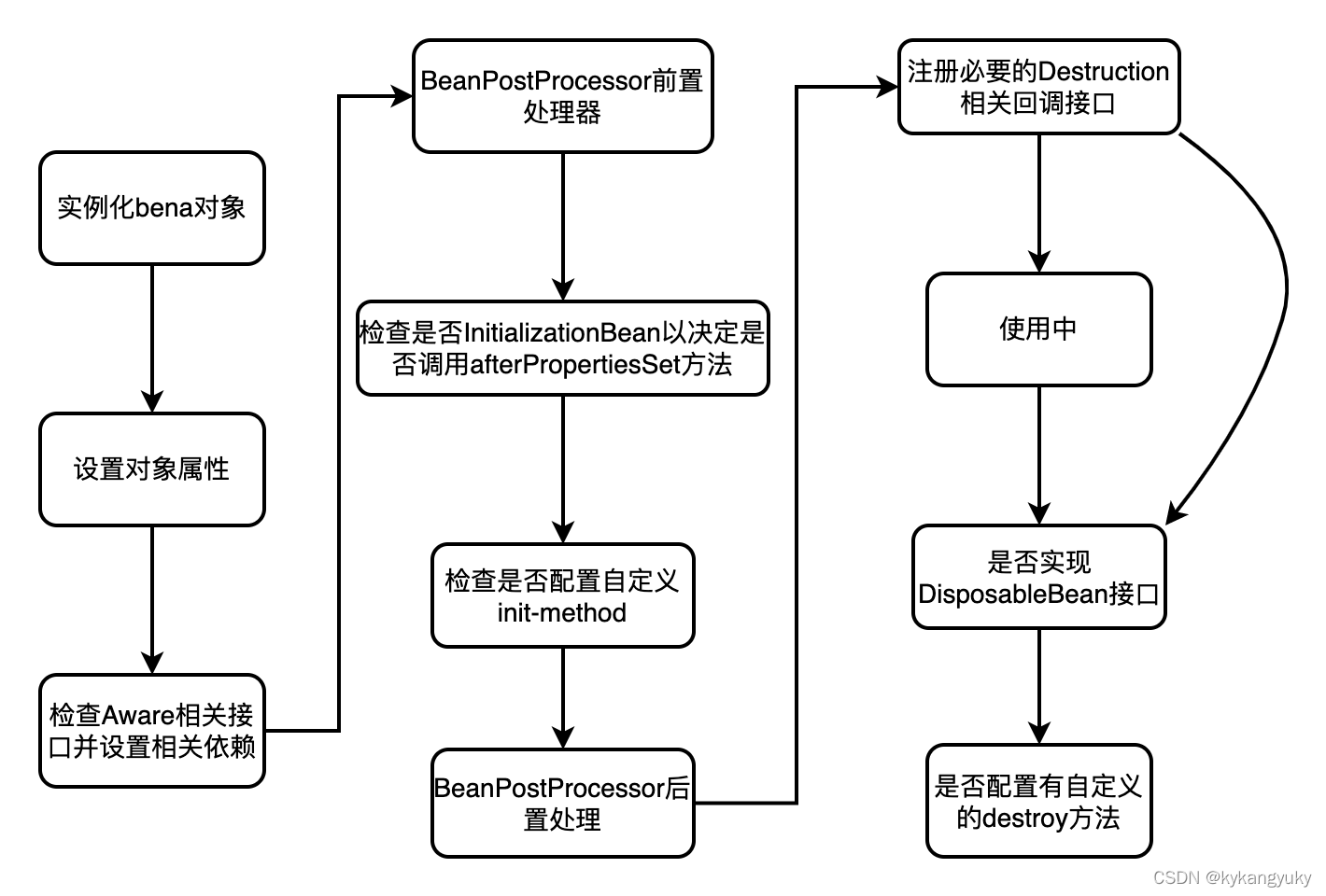
MLIR TOY Language
文章目录
- MLIR TOY Language
- 如何编译该项目
- ch1: MLIR 前端IR解析
- ch2: 定义方言和算子 (ODS)
- 1. 定义方言
- 2. 定义OP
- 3. OP相关操作
- 4. 定义OP ODS (Operation Definition Specification)
- 1. 基本定义
- 2. 添加文档
- 3. 验证OP
- 4. 新增构造函数
- 5. 定义打印OP的格式
- ch3: 高级语言特定分析和转换 (patter-rewrite) (DRR)
- 1. c++ code实现图匹配和转化
- 2. 声明式 DRR 实现图匹配和转化
- ch4: 通过接口实现通用转化(pass)
- 1. 背景
- 2. shape推断,为代码生成做准备
- 1. 通过C++ 代码
- 2. 通过ODS声明interface
- ch5:部分IR降低到低级别IR
- 1. 方言转换
- 1. 转换目标
- 2. 重写模式
- ch6: 降低到LLVM和代码生成
- ch7: 像IR中添加复合数据类型
- 如何学习MLIR
$(nproc) # linux下返回CPU的核心数,可以用来编译项目
cmake报错后如何排查:
make n指令可以打印出所有执行的指令,cmake --build . --target <target>可以分模块编译,查看是哪个模块导致的报错。
如何编译该项目
参考自: MLIR Unix-like编译
git clone https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project.git
mkdir llvm-project/build
cd llvm-project/build
# 编译
cmake -G "Unix Makefiles" ../llvm \-DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS=mlir \-DLLVM_BUILD_EXAMPLES=ON \-DLLVM_TARGETS_TO_BUILD="Native" \-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \-DLLVM_ENABLE_ASSERTIONS=ON \-DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=clang -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=clang++ -DLLVM_ENABLE_LLD=ON \ # 加速编译-DLLVM_CCACHE_BUILD=ON # 缓存,加速下一次重新编译# 编译
cmake --build . --target check-mlir使用Cmake编译LLVM的官网教程
ch1: MLIR 前端IR解析
- 官网toy-1 文档
官方将会新建一个名为toy的语言,来介绍 MLIR 的相关概念.
ch2: 定义方言和算子 (ODS)
%t_tensor = "toy.transpose"(%tensor) {inplace = true} : (tensor<2x3xf64>) -> tensor<3x2xf64> loc("example/file/path":12:1)
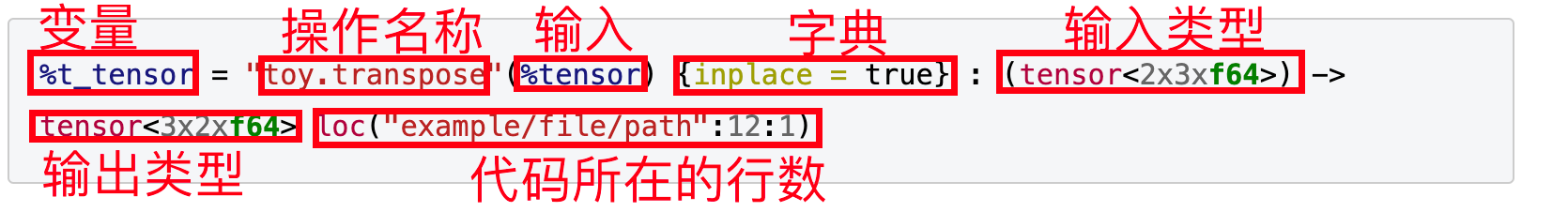
LOC:source loaction for debuggging purposes
MLIR 中,每一个operation都与代码位置强相关,不像LLVM,可以随意删除。
MLIR可以自定义IR的所有属性,operation,type,同时IR总是可以简化为上述途中的格式。
这样统一的格式,就方便了MLIR解析和重新表示任何IR。
1. 定义方言
- 定义方言
- 代码形势
- tablegen
2. 定义OP
通过代码操作,略
3. OP相关操作
定义一个OP后,我们就可以访问和转换它,在MLIR中,有2个主要相关的类, Operation 和 OP
-
Opration: op的具体实现子类,具体的OP类,用于对所有数据进行操作。 -
OP: op的基类,MLIR总是值传递,MLIR一般不通过指针或者引用传递。void processConstantOp(mlir::Operation *operation) {// 将op进行类型转换。ConstantOp op = llvm::dyn_cast<ConstantOp>(operation);
4. 定义OP ODS (Operation Definition Specification)
1. 基本定义
- 定义OP
- 定义参数和结果
def ConstantOp : Toy_Op<"constant"> {// 文档let summary = "constant operation";let description = [{Constant operation turns a literal into an SSA value. The data is attachedto the operation as an attribute. For example:%0 = "toy.constant"(){ value = dense<[[1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]]> : tensor<2x3xf64> }: () -> tensor<2x3xf64>}];// The constant operation takes an attribute as the only input.// `F64ElementsAttr` corresponds to a 64-bit floating-point ElementsAttr.// 输入let arguments = (ins F64ElementsAttr:$value);// The constant operation returns a single value of TensorType.// F64Tensor corresponds to a 64-bit floating-point TensorType.// 输出let results = (outs F64Tensor);// 验证器,设置为1是为了生成1个默认的验证方法,该方法会在该OP的构造器完成后调用。// 验证器,用于验证OP的合法性let hasVerifier = 1;// 构造器// ODS会自动生成一些简单的构造方法let builders = [// Build a constant with a given constant tensor value.OpBuilder<(ins "DenseElementsAttr":$value), [{// Call into an autogenerated `build` method.build(builder, result, value.getType(), value);}]>,// Build a constant with a given constant floating-point value. This builder// creates a declaration for `ConstantOp::build` with the given parameters.OpBuilder<(ins "double":$value)>];
}
2. 添加文档
let description = [{Constant operation turns a literal into an SSA value. The data is attachedto the operation as an attribute. For example:%0 = "toy.constant"(){ value = dense<[[1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]]> : tensor<2x3xf64> }: () -> tensor<2x3xf64>}];
3. 验证OP
let hasVerifier = 1;
4. 新增构造函数
// Add custom build methods for the constant operation. These methods populate// the `state` that MLIR uses to create operations, i.e. these are used when// using `builder.create<ConstantOp>(...)`.let builders = [// Build a constant with a given constant tensor value.OpBuilder<(ins "DenseElementsAttr":$value), [{// Call into an autogenerated `build` method.build(builder, result, value.getType(), value);}]>,// Build a constant with a given constant floating-point value. This builder// creates a declaration for `ConstantOp::build` with the given parameters.OpBuilder<(ins "double":$value)>];
5. 定义打印OP的格式
// Divert the printer and parser to `parse` and `print` methods on our operation,// to be implemented in the .cpp file. More details on these methods is shown below.let hasCustomAssemblyFormat = 1;// In the following format we have two directives, `attr-dict` and `type`.// These correspond to the attribute dictionary and the type of a given// variable represectively.let assemblyFormat = "$input attr-dict `:` type($input)";
ch3: 高级语言特定分析和转换 (patter-rewrite) (DRR)
官方toy-3
PDLL
方言之间的转换分为:
- 局部转换
- 全局转换
MLIR中使用DAG 重写器来优化转换方案。
有2种方法可以实现模式匹配转换。
- 命令行 c++模式匹配和重写
- 表驱动的声明性重写规则(DRR)
1. c++ code实现图匹配和转化
匹配IR中树状模式并替换为一组不同的操作,我们以通过实现MLIR的 Canonicalizer (规范化器) 传递 RewritePattern 来进行。
对于简单的 C++ 重写方法,涉及匹配 IR 中的树状模式并将其替换为一组不同的操作,我们可以通过实现 RewritePattern
比如对一个变量,进行二次转置其实就是变量自身,我们可以通过以下操作 transpose(transpose(X)) -> X
/// Fold transpose(transpose(x)) -> x
struct SimplifyRedundantTranspose : public mlir::OpRewritePattern<TransposeOp> {/// We register this pattern to match every toy.transpose in the IR./// The "benefit" is used by the framework to order the patterns and process/// them in order of profitability.// 将该重写器进行注册 (针对Transpose OP)SimplifyRedundantTranspose(mlir::MLIRContext *context): OpRewritePattern<TransposeOp>(context, /*benefit=*/1) {}/// This method is attempting to match a pattern and rewrite it. The rewriter/// argument is the orchestrator of the sequence of rewrites. It is expected/// to interact with it to perform any changes to the IR from here.mlir::LogicalResultmatchAndRewrite(TransposeOp op,mlir::PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {// Look through the input of the current transpose.// 拿到transpose操作的变量mlir::Value transposeInput = op.getOperand();// 拿到该变量定义的地方的OP,TransposeOp transposeInputOp = transposeInput.getDefiningOp<TransposeOp>();// Input defined by another transpose? If not, no match.if (!transposeInputOp)return failure();// Otherwise, we have a redundant transpose. Use the rewriter.rewriter.replaceOp(op, {transposeInputOp.getOperand()});return success();}
};// 为了确保该patten工作,我们需要在该OP的ODS定义声明以下字段hasCanonicalizer = 1 // 同时我们需要注册该OP// Register our patterns for rewrite by the Canonicalization framework.
void TransposeOp::getCanonicalizationPatterns(RewritePatternSet &results, MLIRContext *context) {results.add<SimplifyRedundantTranspose>(context);
}// 我们还需要开启这个passmlir::PassManager pm(module->getName());pm.addNestedPass<mlir::toy::FuncOp>(mlir::createCanonicalizerPass());
2. 声明式 DRR 实现图匹配和转化
DRR Decalarative-rule-based pattern-match and rewrite
- DRR的官方文档
声明性、基于规则的模式匹配和重写 (DRR) 是一种基于操作 DAG 的声明性重写器,为模式匹配和重写规则提供基于表的语法:
class Pattern<dag sourcePattern, list<dag> resultPatterns,list<dag> additionalConstraints = [],dag benefitsAdded = (addBenefit 0)>;
比如上面的c++代码就可以:
// Reshape(Reshape(x)) = Reshape(x)
def ReshapeReshapeOptPattern : Pat<(ReshapeOp(ReshapeOp $arg)),(ReshapeOp $arg)>;
DRR 还提供了一种方法,用于在转换以参数和结果的某些属性为条件时添加参数约束。例如,当重整形冗余时(即当输入和输出形状相同时),该转换会消除reshape。
·def TypesAreIdentical : Constraint<CPred<"$0.getType() == $1.getType()">>;
def RedundantReshapeOptPattern : Pat<(ReshapeOp:$res $arg), (replaceWithValue $arg),[(TypesAreIdentical $res, $arg)]>;
ch4: 通过接口实现通用转化(pass)
1. 背景
-
对不同的方言.我们通常希望执行一组常见的转换和分析,
-
为了避免每种方言实现每个转换会导致大量代码重复.
-
设计了一种更通用的解决方案,以接口的形式,使 MLIR 基础设施与表示一样可扩展。接口为方言和操作提供了通用机制,以便为转换或分析提供信息。
2. shape推断,为代码生成做准备
1. 通过C++ 代码
// This class defines the interface for handling inlining with Toy operations.
/// We simplify inherit from the base interface class and override
/// the necessary methods.
struct ToyInlinerInterface : public DialectInlinerInterface {using DialectInlinerInterface::DialectInlinerInterface;/// This hook checks to see if the given callable operation is legal to inline/// into the given call. For Toy this hook can simply return true, as the Toy/// Call operation is always inlinable.bool isLegalToInline(Operation *call, Operation *callable,bool wouldBeCloned) const final {return true;}/// This hook checks to see if the given operation is legal to inline into the/// given region. For Toy this hook can simply return true, as all Toy/// operations are inlinable.bool isLegalToInline(Operation *, Region *, bool,IRMapping &) const final {return true;}/// This hook cheks if the given 'src' region can be inlined into the 'dest'/// region. The regions here are the bodies of the callable functions. For/// Toy, any function can be inlined, so we simply return true.bool isLegalToInline(Region *dest, Region *src, bool wouldBeCloned,IRMapping &valueMapping) const final {return true;}/// This hook is called when a terminator operation has been inlined. The only/// terminator that we have in the Toy dialect is the return/// operation(toy.return). We handle the return by replacing the values/// previously returned by the call operation with the operands of the/// return.void handleTerminator(Operation *op,MutableArrayRef<Value> valuesToRepl) const final {// Only "toy.return" needs to be handled here.auto returnOp = cast<ReturnOp>(op);// Replace the values directly with the return operands.assert(returnOp.getNumOperands() == valuesToRepl.size());for (const auto &it : llvm::enumerate(returnOp.getOperands()))valuesToRepl[it.index()].replaceAllUsesWith(it.value());}
};
在 toy 方言上注册该接口
void ToyDialect::initialize() {addInterfaces<ToyInlinerInterface>();
}
2. 通过ODS声明interface
- 添加ODS声明
def ShapeInferenceOpInterface : OpInterface<"ShapeInference"> {// 接口描述let description = [{Interface to access a registered method to infer the return types for anoperation that can be used during type inference.}];// 我们定义操作需要提供的接口方法。接口方法由以下部分组成:描述;字符串形式的 C++ 返回类型;字符串形式的方法名称;以及一些可选组件,let methods = [InterfaceMethod<"Infer and set the output shape for the current operation.","void", "inferShapes">];
}
- 将声明添加到OP中
def MulOp : Toy_Op<"mul",[..., DeclareOpInterfaceMethods<ShapeInferenceOpInterface>]> {...
}
每个OP 都需要为 inferShapes() 方法提供定义。例如,对于乘法,结果形状被推断为输入的形状。
/// Infer the output shape of the MulOp, this is required by the shape inference
/// interface.
void MulOp::inferShapes() { getResult().setType(getLhs().getType()); }
- 实现pass
// 实现pass
class ShapeInferencePass: public mlir::PassWrapper<ShapeInferencePass, OperationPass<FuncOp>> {void runOnOperation() override {FuncOp function = getOperation();...}
};// 实例化pass
std::unique_ptr<mlir::Pass> mlir::toy::createShapeInferencePass() {return std::make_unique<ShapeInferencePass>();
}// 注册passpm.addPass(mlir::createShapeInferencePass());
ch5:部分IR降低到低级别IR
通过在同一函数中共存的多种方言来执行渐进式降低。
1. 方言转换
MLIR 有许多不同的方言,因此有一个统一的框架在它们之间进行转换非常重要。这就是 DialectConversion 框架发挥作用的地方。该框架允许将一组非法操作转换为一组合法操作。要使用这个框架,我们需要提供两件事(以及可选的第三件事):
- 转化目标
- 一组重写模式
- (可选)类型转化器
1. 转换目标
我们希望将计算密集型 Toy 操作转换为 Affine 、 Arith 、 Func 操作的组合和 MemRef 方言以进行进一步优化。为了开始降低,我们首先定义我们的转换目标:
void ToyToAffineLoweringPass::runOnOperation() {// The first thing to define is the conversion target. This will define the// final target for this lowering.mlir::ConversionTarget target(getContext());// We define the specific operations, or dialects, that are legal targets for// this lowering. In our case, we are lowering to a combination of the// `Affine`, `Arith`, `Func`, and `MemRef` dialects.target.addLegalDialect<affine::AffineDialect, arith::ArithDialect,func::FuncDialect, memref::MemRefDialect>();// We also define the Toy dialect as Illegal so that the conversion will fail// if any of these operations are *not* converted. Given that we actually want// a partial lowering, we explicitly mark the Toy operations that don't want// to lower, `toy.print`, as *legal*. `toy.print` will still need its operands// to be updated though (as we convert from TensorType to MemRefType), so we// only treat it as `legal` if its operands are legal.target.addIllegalDialect<ToyDialect>();target.addDynamicallyLegalOp<toy::PrintOp>([](toy::PrintOp op) {return llvm::none_of(op->getOperandTypes(),[](Type type) { return type.isa<TensorType>(); });});...
}
上面,我们首先将玩具方言设置为非法,然后将打印操作设置为合法。我们也可以反过来做。各个操作始终优先于(更通用的)方言定义,因此顺序并不重要。详情请参阅 ConversionTarget::getOpInfo 。
2. 重写模式
定义了转换目标后,我们就可以定义如何将非法操作转换为合法操作。
DialectConversion框架也使用RewritePatterns来执行转换逻辑。- 这些模式可能是之前看到的
RewritePatterns, - 也可能是特定于转换框架
ConversionPattern的新型模式。
- 这些模式可能是之前看到的
ConversionPatterns 与传统的 RewritePatterns 不同,因为它们接受附加的 operands 参数,其中包含已重新映射/替换的操作数。这在处理类型转换时使用,因为模式希望对新类型的值进行操作,但与旧类型的值进行匹配。对于我们的降低,这个不变量将很有用,因为它从当前正在操作的 TensorType 转换为 MemRefType。
我们来看一段降低 toy.transpose 操作的片段:
/// Lower the `toy.transpose` operation to an affine loop nest.
struct TransposeOpLowering : public mlir::ConversionPattern {TransposeOpLowering(mlir::MLIRContext *ctx): mlir::ConversionPattern(TransposeOp::getOperationName(), 1, ctx) {}/// Match and rewrite the given `toy.transpose` operation, with the given/// operands that have been remapped from `tensor<...>` to `memref<...>`.mlir::LogicalResultmatchAndRewrite(mlir::Operation *op, ArrayRef<mlir::Value> operands,mlir::ConversionPatternRewriter &rewriter) const final {auto loc = op->getLoc();// Call to a helper function that will lower the current operation to a set// of affine loops. We provide a functor that operates on the remapped// operands, as well as the loop induction variables for the inner most// loop body.lowerOpToLoops(op, operands, rewriter,[loc](mlir::PatternRewriter &rewriter,ArrayRef<mlir::Value> memRefOperands,ArrayRef<mlir::Value> loopIvs) {// Generate an adaptor for the remapped operands of the TransposeOp.// This allows for using the nice named accessors that are generated// by the ODS. This adaptor is automatically provided by the ODS// framework.TransposeOpAdaptor transposeAdaptor(memRefOperands);mlir::Value input = transposeAdaptor.input();// Transpose the elements by generating a load from the reverse// indices.SmallVector<mlir::Value, 2> reverseIvs(llvm::reverse(loopIvs));return rewriter.create<mlir::AffineLoadOp>(loc, input, reverseIvs);});return success();}
};
注册该pattern
void ToyToAffineLoweringPass::runOnOperation() {...// Now that the conversion target has been defined, we just need to provide// the set of patterns that will lower the Toy operations.mlir::RewritePatternSet patterns(&getContext());patterns.add<..., TransposeOpLowering>(&getContext());
ch6: 降低到LLVM和代码生成
跳过~没看
ch7: 像IR中添加复合数据类型
跳过~没看
如何学习MLIR
1. 对接不同的软件框架;
2. 对接软件框架和硬件芯片。
Dialect 和 DialectConversion
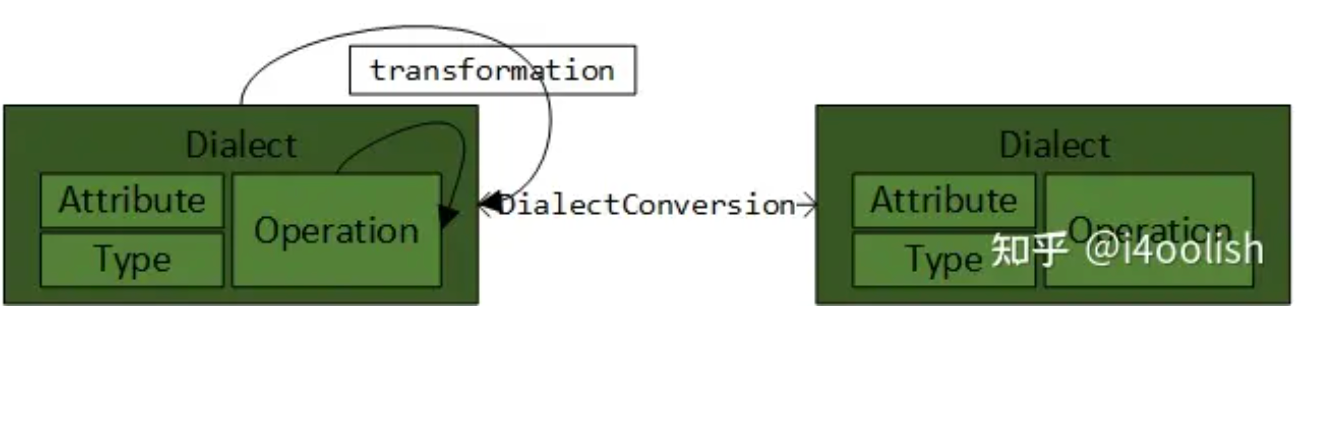
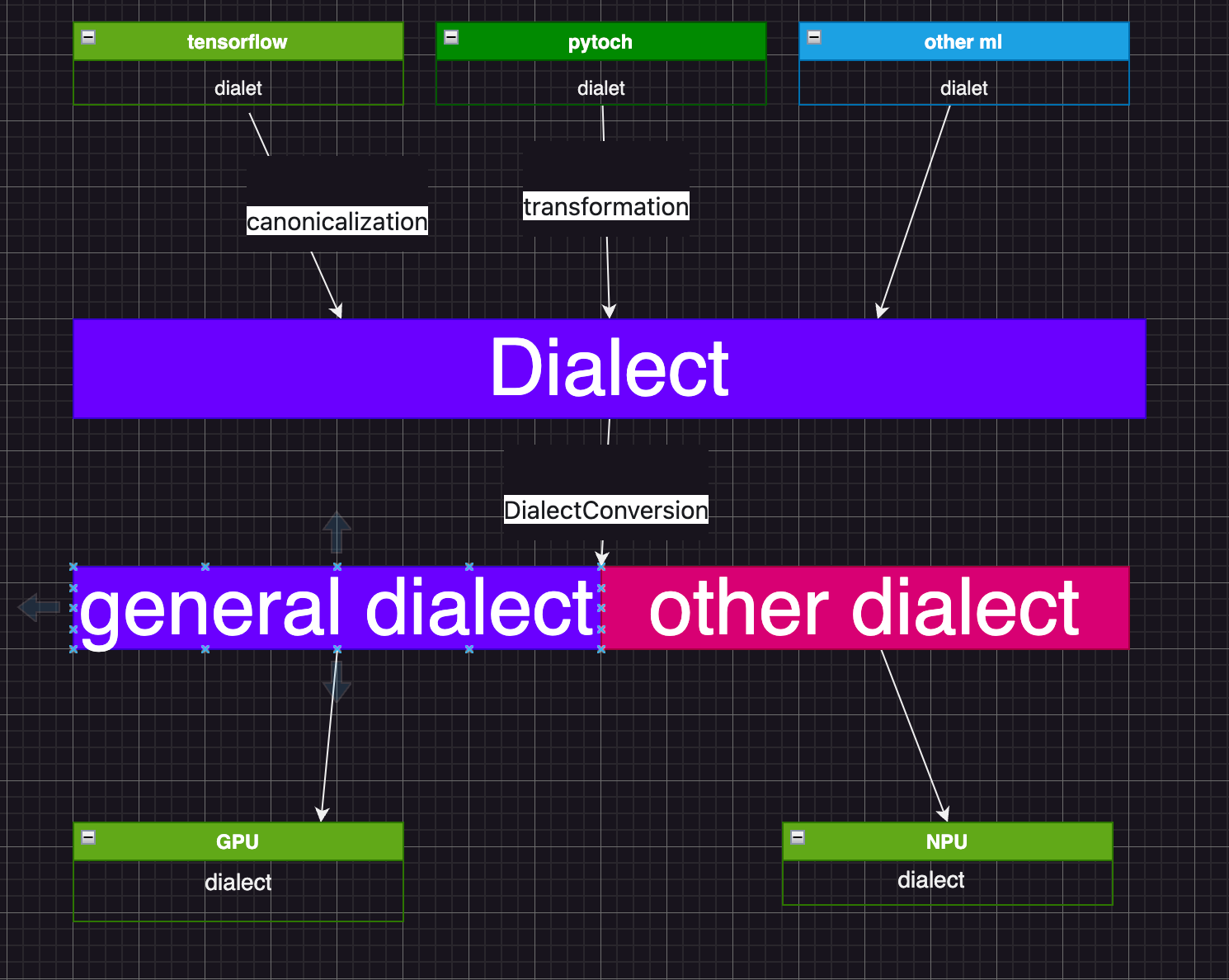
- 学习MLIR基本模块;
- 学习MLIR提供的
Dialects,各个Dialects的定位,以及为弥补软硬件gap,提供的这些gap的分类和关联。
关于MLIR基本模块学习过程如下:
-
Dialect, Attribute, Type, Operation;想象如果自己去实现,该怎么设计类; -
DialectConversion;想象在自己实现的前四个模块上,如何实现DialectConversion; -
Interface, Constraint, Trait;同样,想象自己会怎么增加这些功能; -
Transformation,Concalization; -
Region, Block:- 基于1. 设计的Operation,
- 以及4. 增加的Transformation,想象如何对Operation进行抽象,提取出Region和Block的概念;
-
Pass;
-
最后才是
ODS和DRR。
ps: 这部分借鉴自知乎:
作者:i4oolish
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/435109274/answer/2290343429。
- IREE 的代码结构
以 IREE 的 FLOW方言为例, 看一下IREE的代码结构.
(iree) (base) ➜ Flow git:(20240609) ✗ tree -L 1
.
├── BUILD.bazel
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── ConversionPatterns.h 和 cpp 文件, 声明各类rewirte Pattern和实现,并提供一个接口,可以注册所有pattern
├── IR定义方言,OP,和interface,
├── TransformExtensions没看懂
└── Transforms 声明pass,并且调用tablegen,然后将实现和声明编译为MLIR动态库.Passes.td实现各类pass
MLIR官网的这个教程我觉得有点抽象,整个社区的反馈也是觉得写的并不简易入门.
我比较推荐另一个博主的一篇入门博客: mlir-入门教程
该教程代码开源在GitHub, 使用的是Bazel编译工具.除此之外没有槽点.