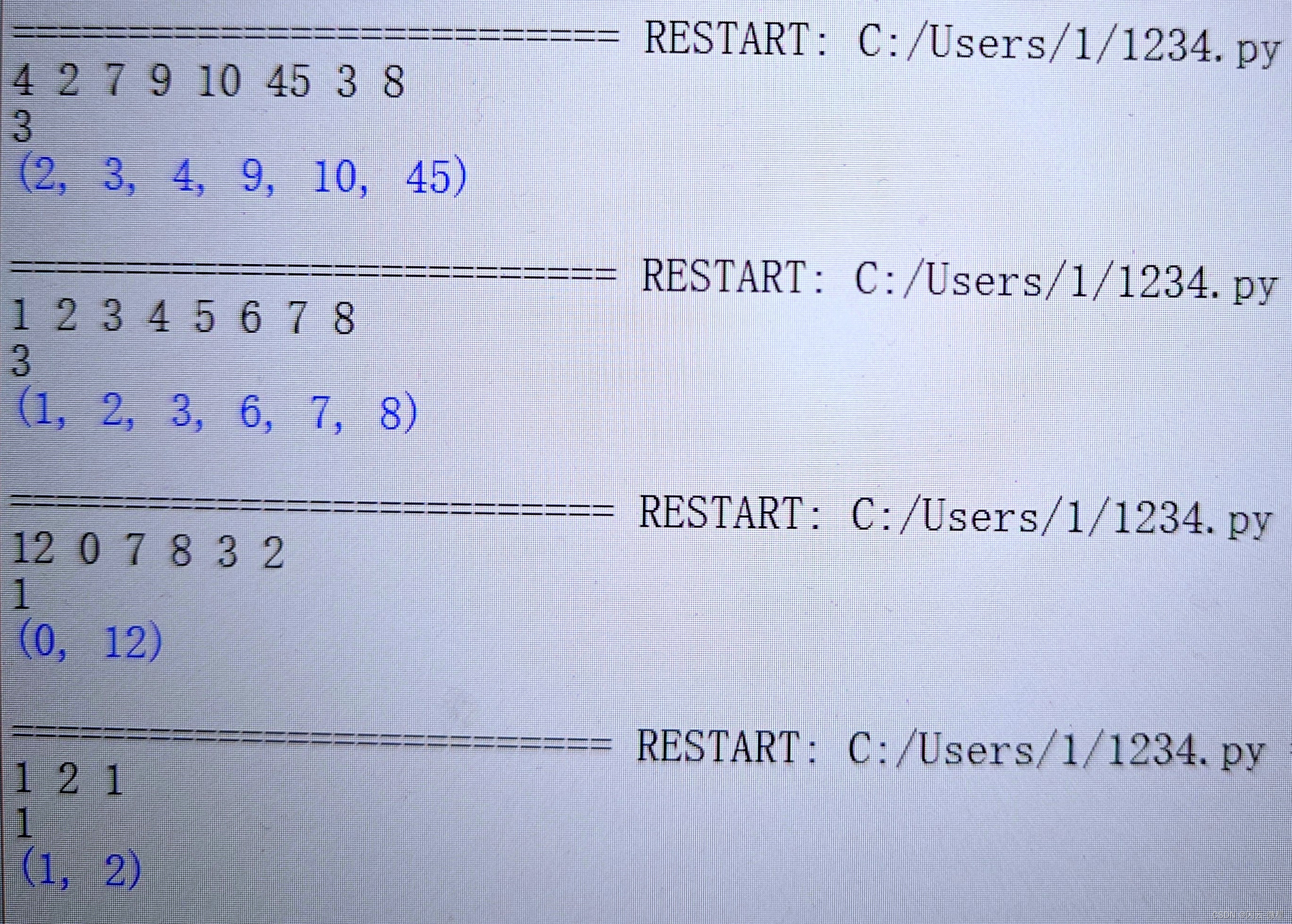
目录
一、Mysql对数据的增删改
1. 增加数据
2. 修改数据(UPDATE语句)
3. 删除
3.1 delete、truncate、drop区别
二、DQL语言(重点)
1. 单表查询
1.1 最简单的查询
1.2 从表中获取数据
1.3 字段名起别名
1.4 添加字段
1.5 distinct 去重
1.6 带条件的查询
1.7 in 表示在某个特定的范围内
1.8 like 模糊查询
1.9 null
1.10 聚合函数(重点)
1.11 group by(重重点)
1.12 where和having区别
1.13 order by 排序
1.14 limit 分页 0开始 (页码-1)*步长,步长
1.15 扩展
1.16 小结
2. 多表查询
2.1 内联查询
2.2 外联查询
2.3 子查询(内部查询)
2.4 结果集控制语句
2.5 case when then end语句
三、Sql执行顺序
1. Sql语句在数据库中的执行流程
2. Sql查询语句的执行顺序
一、Mysql对数据的增删改
1. 增加数据
-- insert into 表名(字段名,字段名,...,字段名)values/value (值,值...值)
-- 日期使用字符串的形式进行书写日期格式(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss)
(1)全字段的插入
方式一:insert into student(sid,sname,birthday,ssex,classid)
values(9,'张三','2007-1-1','男',1);
方式二:
1)null
insert into student values(null,'齐韬尊','1789-1-1','女',2);
2)default
insert into student values(default,'齐韬尊','1789-1-1','女',2);
(2)部分字段插入
insert into student(sname,ssex) values('齐同学','女');
alter student modify ssex varchar(10) not null default '保密'; -- 非空,默认保密
insert into student(sname) values('陈博远');
(3)一次性添加多条数据
1)方式一 (最常用的方式)
insert into 表名(字段名...) values(值..),(值..)...
insert into student(sname,ssex) values('杨文琦','男'),('杨博海','男'),('杨坤','男');
2)方式二 (不常用)
insert into select
插入和被插入的表都必须存在。
create table newstu(
xingming varcahr(10),
xingbie varchar(10),
classid int
);
insert into newstu(xingming,xingbie,classid) select sname,ssex,classid from student;
3)方式三(不常用)I/O高,容易锁表
create table select
被插入表(stu1)不能能存在,被插入表没有任何约束。
create table stu1 select sid,sname,birthday from student;
2. 修改数据(UPDATE语句)
-- update 表名 set 字段名=值,字段名=值,...,字段名=值
-- 【where子句条件】
-- where 子句中的条件是对表中每一条数据进行判断,判断成立该数据的父句执行,判断不成立该数据的父句不执行
update stu1 set birthday='1678-2-2';
update stu1 set birthday='1888-1-1' where sname='陈博远';
update newstu set classid = 200 where xingbie != '男'; -- null是类型,不是值,性别为null,不会受影响
update newstu set classid = 300 where xingbie <> '女'; -- <> 不等于
update newstu set xingbie = '保密' where classid < 260;
update newstu xingbie = '外星人' where classid >=30 and classid <=90;
-- 30 50 70 性别变为地球人
update newstu set xingbie='地球人' where classid=30 or classid=50 or classid=70;
update newstu set xingbie='火星人' where classid>=30 and classid<=90;
update newstu set xingbie='水星人' where classid between 30 and 90;
3. 删除
-- delete from 表名 【where 子句】
delete from newstu;
delete from stu1 where sid=1;
-- 清空表/截断表
-- truncate 表名
truncate stu1;
3.1 delete、truncate、drop区别
-- delete只删数据
-- truncate不仅把数据删掉,还删除了索引
-- drop 不仅把数据删掉,还删除了索引,表结构也删了
二、DQL语言(重点)
DQL(Data Query Language 数据查询语言)。用途是查询数据库数据,如SELECT语句。是SQL语句中最核心、最重要的语句,也是使用频率最高的语句。其中,可以根据表的结构和关系分为单表查询和多表联查。
单表查询
针对数据库中的一张数据表进行查询,可以通过各种查询条件和方式去做相关的优化。
多表联查
针对数据库中两张或者两张以上的表同时进行查询,依赖的手段有复杂查询和嵌套查询
1. 单表查询
-- 所有的查询都会得到一张虚拟表
1.1 最简单的查询
select 123;
select 'abc';
select 1+1;
1.2 从表中获取数据
-- select 字段名,字段名... from 表名
(1)全字段查询
select sid,sname,birthday,ssex,classid from student;
select * from student; -- 效率慢,不推荐使用
(2)部分字段查询
select sname,ssex from student;
1.3 字段名起别名
select sname as '姓名' from student;
select sname as '姓名',birthday '生日' from student;
select sname as '姓名',birthday '生日',ssex 性别 from student;
select sname 姓名 from student;
1.4 添加字段
select sname,'猿究院' from student;
select sname,'猿究院' 学校 from student; -- 字段猿究院别名为学校
1.5 distinct 去重
-- 所有的字段的数据都一致才会去重
select ssex from student;
select distinct ssex from student;
select distinct sname,ssex from student;
1.6 带条件的查询
-- 【where子句】
select * from student where sid = 5
select * from student where sid <> 5;
select * from student where sid > 5;
select * from student where sid between 3 and 6;
-- 查找1班的女同学
select * from student where classid=1 and ssex='女';
-- 面试题
-- 查询年龄大于1990-1-1 的同学
select * from student where birthday < '1990-1-1'; -- 日期比大小,逻辑反的
1.7 in 表示在某个特定的范围内
-- 3 5 7 9
-- or 会让索引失效
select * from student where sid=3 or sid=5 or sid=7 or sid=9;
-- 推荐
-- in 可以使用索引
select * from student where sid in(3,5,7,9,20,100);
1.8 like 模糊查询
-- 模糊符号
(1)% 任意多的字符
(2)_ 一个任意字符
insert into student(sname) values('杨文齐'),('小小杨'),('杨帅哥'),('帅气的杨同学');
select * from student where sname like '%杨%';
select * from student where sname like '%杨';
select * from student where sname like '杨%';
select * from student where sname like '杨__'; -- 两个下划线
1.9 null
-- is:是一个什么
select * from student where birthday is null;
select * from student where birthday is not null;
1.10 聚合函数(重点)
-- 把多个值变为一个值
-- count() 统计个数
-- max() 求最大值
-- min() 求最小值
-- sum() 总和
-- avg() 平均值
(1)count 任何类型 不统计null
-- select count(字段、常量、*) from 表名
select count(sid) from student; -- 主键
select count(classid) from student; -- 不统计null
select count('a') from student; -- 不推荐
select count(123) from student; -- 推荐
select count(*) from student; -- 推荐
(2) sum avg min max 数值类型
select sum(score) from sc;
select avg(score) from sc;
select max(score) from sc;
select min(score) from sc;
-- 统计出成绩表中一共有多少次考试,总成绩,平均分,最高分,最低分
select count(*),sum(score),avg(score),max(score),min(score) from sc;
1.11 group by(重重点)
对所有的数据进行分组统计;
分组的依据字段可以有多个,并依次分组。
-- 分组之后必然有聚合
-- 男女同学个有多少人
select ssex,count(1) from student group by ssex;
-- 统计出各班有多少人
select classid,count(1) from student group by classid;
-- 统计成绩表中每个同学的总分和平均分
select sid,sum(score),avg(score) from sc group by sid;
1.12 where和having区别
-- having 对数据表中单个数据进行判断,与group by结合使用,进行分组后的数据筛选。
-- 查询出平均分不及格的同学
select sid,sum(score),avg(score) from sc
group by sid
having avg(score) < 60;
select sid,sum(score),avg(score) from sc
where score < 60
group by sid
having avg(score) < 60;
1.13 order by 排序
-- 先写先排
-- 升序 asc 不写(默认)
-- 降序 desc 必须声明
select * from student order by classid;
select * from student order by classid asc;
select * from sc order by score desc,cid desc; -- score降序,分数相同,按cid降序
1.14 limit 分页 0开始 (页码-1)*步长,步长
-- select * from 表名 limit 位置,步长
select * from student limit 6,3
-- 应用层解决
-- select * from student limit (3-1)*3,3 错误的
-- 找到成绩及格的总分数排名第二的:sid总成绩
select sid,sum(score) from sc
where score >60
group by sid
order by sum(score) desc
limit 1,1
1.15 扩展

1.16 小结
• DML语句内容
• INSERT语句,UPDATE语句和DELETE语句;
• 新增语句如何实现多记录同时新增?
• INSERT INTO `表名` (`字段1`,`字段n`) VALUES (值1,值n),(值1,值n),(值1,值n);
• WHERE子句的功能?
• 依赖逻辑条件对数据库的记录修改,删除或者查询;
• TRUNCATE语句和DELETE语句的异同?
• 相同点:都能删除数据,都不能修改表结构;
• 不同点:1、前者会重置自增计数器,后者不会;
2、前者无条件约束,速度快效率高。
• DQL语句内容
• SELECT语句。
2. 多表查询
2.1 内联查询
(1)非等值查询 -- 笛卡尔积 两个结果集相乘 逻辑上有错误
-- 查询出学生和班级信息
select * from student,class;
(2)等值查询
-- 查询出学生和班级信息 student class
select * from student,class
where student.classid=class.classid;
-- 5张表联查
select * from student,class,course,teacher,sc
where student.classid=class.classid and course.cid=sc.cid and class.classid=student.classid and teacher.Tid=course.Tid;
-- 查询出学过张三老师课程的学生信息
select * from student,class,course,teacher,sc
where student.sid=sc.sid and course.cid=sc.cid and teacher.Tid=course.Tid and teacher.tname='张三';
-- 多表最终跟单表一致
-- 查询每个学生的平均成绩 学生姓名,班级名称,平均成绩
select sname,classname,avg(score) from student,sc,class
where student.sid=sc.sid and class.classid=student.classid
group by student.sid;
(3)inner join on
-- 笛卡尔积
-- 表的个数多,每个表的数据量不大,吃内存,IO小
select * from student,class
where student.classid = class.classid and ssex='男';
-- 通过第一张表的结果集进行on条件匹配
-- 表少,每张表的数据量很大,内存占用小,但IO高
select * from student
inner join class on student.classid = class.classid
where ssex='男';
-- 3表查询
select * from studentinner join class on student.classid=class.classidinner join sc on student.sid=sc.sid;-- 5表联查
select * from studentinner join class on student.classid=class.classidinner join sc on student.sid=sc.sidinner join course on sc.cid=course.Cidinner join teacher on course.tid=teacher.Tid;-- 每门课程的平均成绩 课程名称 代课老师姓名 平均成绩
select cname,tname,avg(score) from course,teacher,scwhere course.cid=sc.cid and teacher.tid=course.tidgroup by course.cid;select cname,tname,avg(score) from scinner join course on sc.cid=course.Cidinner join teacher on course.tid=teacher.Tidgroup by course.cid;2.2 外联查询
(1)主查表
-- 查询出主表所有信息
-- 所有学生的数据和对应的班级信息 主查学生
-- left join on 左外联 主查表在join左
select * from student
left join class on student.classid=class.classid;
-- right join on 右外联 主查表在join右
select * from class
right join student on student.classid=class.classid;
-- 查询出所有学生都学过多少门课程 学生姓名 课程数 *含null

-- 没有班级的学生 绿色
select * from studentleft join class on student.classid=class.classidwhere class.classid is null;-- 没有学生的班级 橙色
select * from student right join class on class.classid= student.classidwhere student.sid is null;select * from class left join student on class.classid= student.classidwhere student.sid is null(2) union 两个结果集的并集
-- 去除重复 distinct一样
-- 不同类型的字段是可以合并的
-- 不同列数量的结果集是不允许合并的
-- 取别名给第一个结果集才有用
-- 库中的所有人的名字
select sname,ssex from student
UNION
select tname,tsex from teacher;
select sname,ssex,classid from student
UNION
select tname,tsex,temail from teacher;
select sname 姓名,ssex 性别,classid from student
UNION
select tname,tsex,temail from teacher;
-- 获取没有学生的班级和没有班级的学生 紫色
select * from studentleft join class on student.classid=class.classidwhere class.classid is nullunionselect * from student right join class on class.classid= student.classidwhere student.sid is null-- 获取没有班级的学生和 班级和学生都有的 还要获取没有学生的班级 -- 绿紫橙
1)全连接 去重
select * from studentleft join class on student.classid=class.classidunionselect * from student right join class on class.classid=student.classid2)不去重的并集 union all
select * from studentleft join class on student.classid=class.classidunion allselect * from student right join class on class.classid= student.classid2.3 子查询(内部查询)
(1)where子查询 效率低
-- 查询id最大的一名同学
select * from student order by student.sid desc limit 0,1;
-- 查询id最大的一名同学(子查询)
select max(sid) from student;
select * from student where sid =16; -- 魔术
select * from student where sid =(select max(sid) from student);
-- 查询每个班下id最大的同学(子查询)
select max(sid) from student
group by student.classid;
select * from student
where sid in(select max(sid) from student group by student.classid);
select * from student,class
where sid in(select max(sid) from student group by student.classid) and student.classid=class.classid;
select * from student
left join class on student.classid=class.classid
where sid in(select max(sid) from student group by student.classid);
select * from student
inner join class on student.classid=class.classid
where sid in(select max(sid) from student group by student.classid);
-- 查询学过张三老师课程的学生
select * from student where sid in -- in 查询多条记录(select sid from sc where cid=(select cid from course where tid=(select tid from teacher where tname='张三')));-- 查询大于5人的班级名称和人数(不适用子查询)
select classname,count(*) from classleft join student on class.classid=student.classidgroup by class.classidhaving count(*) > 5 ;(2)from子查询
-- 查询大于5人的班级名称和人数(子查询)
select classname,人数 from class left join
(select classid,count(*) 人数 from student group by classid) t1 -- t1是别名
on class.classid=t1.classid
where 人数>5;
(3)exists 子查询 子句有结果,父句执行,子句没结果,父句不执行
select * from teacher
where exists (select * from student where classid=1);
(4)any,some,all
1)any
-- 查询出一班成绩比二班最低成绩高的学生
select distinct student.* from scleft join student on sc.sid=student.Sidwhere student.classid=1 and score > any(select min(score) from scleft join student on sc.sid=student.sidwhere student.classid=2)2)some
select DISTINCT student.* from scleft join student on sc.sid = student.sidwhere student.classid = 1 and score > some (select score from scleft join student on sc.sid = student.sidwhere student.classid = 2)3)all
-- 查询出一班成绩比二班最高成绩高的学生
select DISTINCT student.* from scleft join student on sc.sid = student.sidwhere student.classid = 1 and score > (select max(score) from scleft join student on sc.sid = student.sidwhere student.classid = 2)select DISTINCT student.* from scleft join student on sc.sid = student.sidwhere student.classid = 1 and (score > 70.0 and score > 60.0and score >80.0 and score >50.0 and score > 30.0 and score > 20.0and score > 31.0 and score > 34.0)select distinct student.* from scleft join student on sc.sid=student.Sidwhere student.classid=1 and score > all(select min(score) from scleft join student on sc.sid=student.sidwhere student.classid=2)2.4 结果集控制语句
-- IF(expr1,expr2,expr3)
-- expr1 条件
-- expr2 条件成立 显示数据
-- expr3 条件不成立 显示数据
select * from teacher;
-- 1 女
-- 0 男
select tid,tname,if(tsex=1,'女','男') tsex,tbirthday,taddress from teacher;
-- IFNULL(expr1,expr2)
-- expr1 字段
-- expr2 当字段为null 默认值
select sid,sname,ifnull(birthday,'这个学生没有生日,很可怜') bir,ssex from student;
2.5 case when then end语句
-- 没有在选项的为null
select tid,tname,case tsexwhen 0 then'男'when 1 then'女'end tsex,tbirthday,taddress from teacher;select tid,tname,case tsexwhen 0 then '男'when 1 then '女'else '保密'end tsex,tbirthday,taddress from teacher;select tid,tname,casewhen tsex >1 then '男'when tsex =1 then '女'when tsex <1 then '保密'end tsex,tbirthday,taddress from teacher;-- 查询学生成绩
select score,casewhen score >=90 then 'A'when score >=80 then 'B'when score >=70 then 'C'when score >=60 then 'D'when score <60 then '不及格'endfrom sc;select sname,score,casewhen score >=90 then 'A'when score >=80 then 'B'when score >=70 then 'C'when score >=60 then 'D'when score <60 then '不及格'endfrom scinner join student on sc.sid=student.sid;-- 面试题
-- 行专列 列转行
-- 统计各分数段人数
(1)
-- 分数段 人数
-- 100-90
-- 90-80
-- 80-70
-- 70-60
-- 不及格
select '100-90' 分数段,count(*) 人数 from sc where score <=100 and score >=90unionselect '90-80', count(*) from sc where score <90 and score >=80unionselect '80-70', count(*) from sc where score <80 and score >=70unionselect '70-60', count(*) from sc where score <70 and score >=60unionselect '不及格', count(*) from sc where score <60;
(2)
-- 分数段 100-90 90-80 80-70 70-60 不及格
-- 人数
select '人数' 分数段,count(case when score>=90 and score<=100 then score end) '100-90',count(case when score>=80 then score end) '90-80',count(case when score>=70 then score end) '80-70',count(case when score>=60 then score end) '70-60',count(case when score<60 then score end) '不及格'
from sc;
三、Sql执行顺序
1. Sql语句在数据库中的执行流程

2. Sql查询语句的执行顺序