1.通过多项式拟合交互探索概念
import math
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l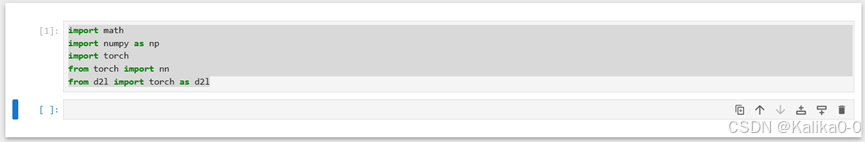
2.使用三阶多项式来生成训练和测试数据的标签
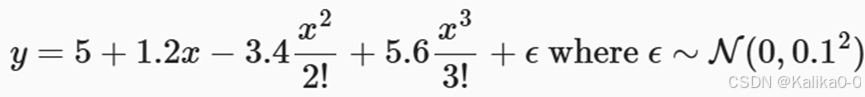
max_degree = 20 # 多项式的最大阶数
n_train, n_test = 100, 100 # 训练和测试数据集大小
true_w = np.zeros(max_degree) # 分配大量的空间
true_w[0:4] = np.array([5, 1.2, -3.4, 5.6])features = np.random.normal(size=(n_train + n_test, 1))
np.random.shuffle(features)
poly_features = np.power(features, np.arange(max_degree).reshape(1, -1))
for i in range(max_degree):poly_features[:, i] /= math.gamma(i + 1) # gamma(n)=(n-1)!
# labels的维度:(n_train+n_test,)
labels = np.dot(poly_features, true_w)
labels += np.random.normal(scale=0.1, size=labels.shape)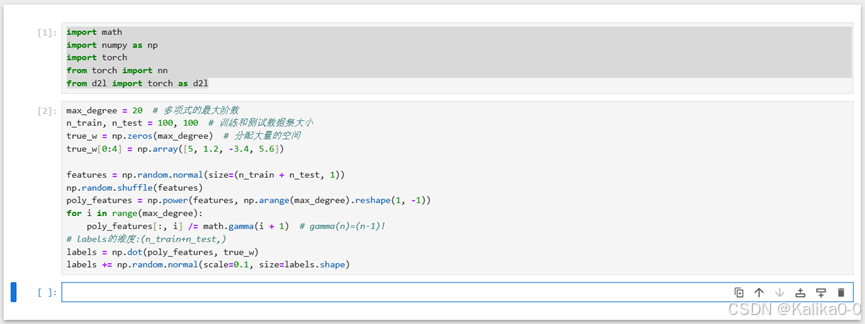
3.查看样本
true_w, features, poly_features, labels = [torch.tensor(x, dtype=torch.float32) for x in [true_w, features, poly_features, labels]]features[:2], poly_features[:2, :], labels[:2]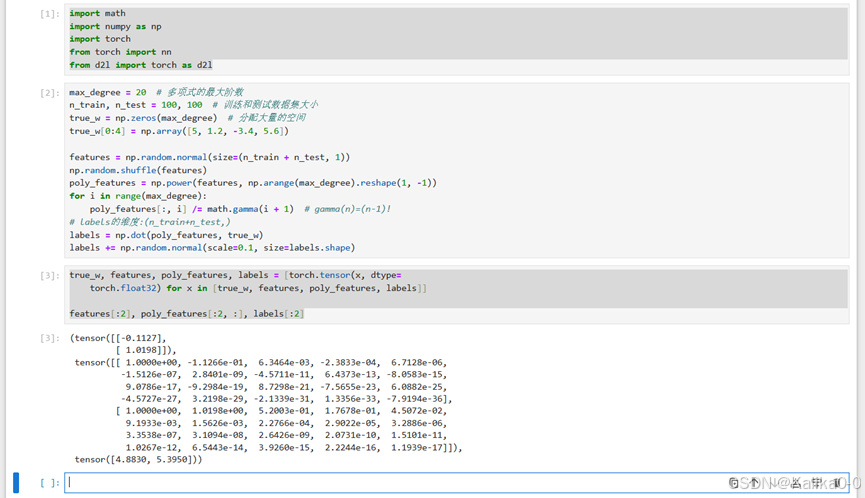
4.实现函数来评估模型在给定数据集的损失
def evaluate_loss(net, data_iter, loss):"""评估给定数据集上模型的损失"""metric = d2l.Accumulator(2)for X, y in data_iter:out = net(X)y = y.reshape(out.shape)l = loss(out, y)metric.add(l.sum(), l.numel())return metric[0] / metric[1]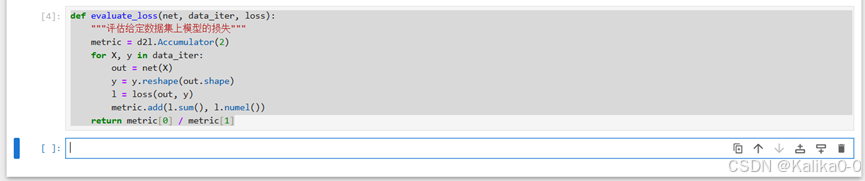
5.定义训练函数
def train(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels,num_epochs=400):loss = nn.MSELoss()input_shape = train_features.shape[-1]net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_shape, 1, bias=False))batch_size = min(10, train_labels.shape[0])train_iter = d2l.load_array((train_features, train_labels.reshape(-1,1)),batch_size)test_iter = d2l.load_array((test_features, test_labels.reshape(-1,1)),batch_size, is_train=False)trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01)animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[1e-3, 1e2],legend=['train', 'test'])for epoch in range(num_epochs):d2l.train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, trainer)if epoch == 0 or (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0:animator.add(epoch + 1, (evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))print('weight:', net[0].weight.data.numpy())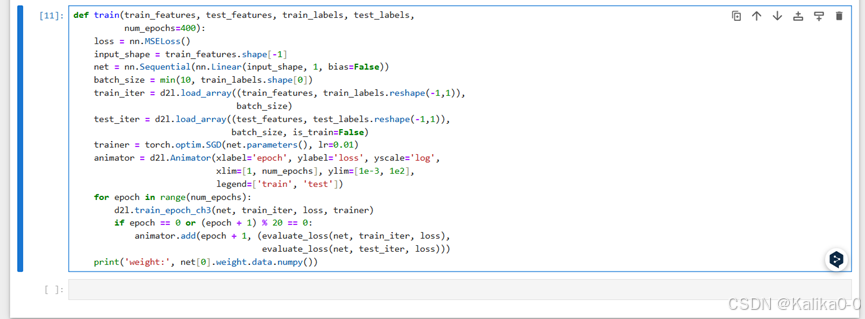













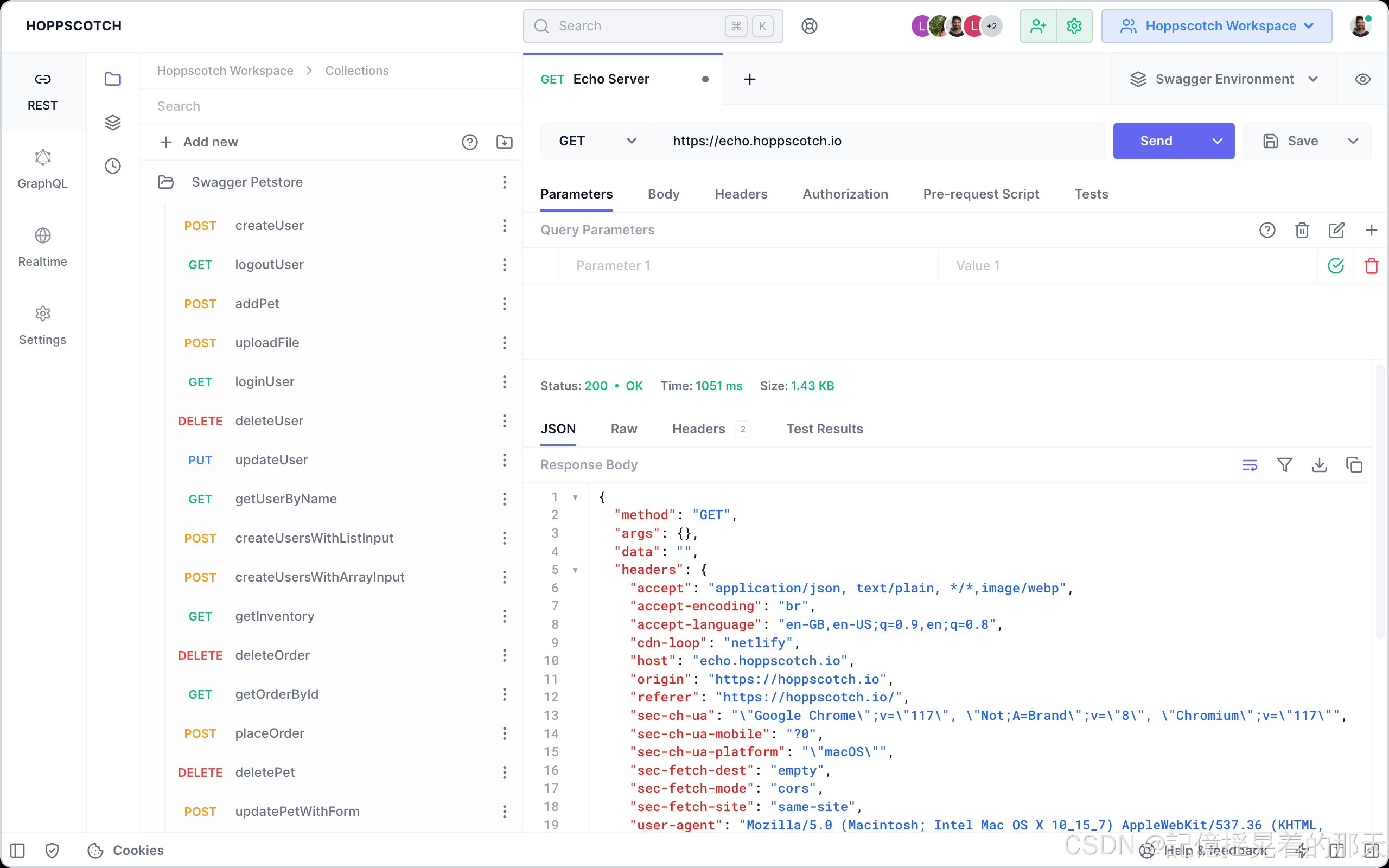
![[bug] vllm 0.6.1 RuntimeError: operator torchvision::nms does not exist](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9158c39dc86e44e2a11ce5366fbfc8cb.png)