在之前的两篇文章中,我介绍了GPT 1和2的模型,并分别用Tensorflow和Pytorch来实现了模型的训练。具体可以见以下文章链接:
1. 基于Tensorflow来重现GPT v1模型_gzroy的博客-CSDN博客
2. 花费7元训练自己的GPT 2模型_gzroy的博客-CSDN博客
有了GPT模型,我们自然会想更进一步来训练自己的ChatGPT,让模型能和我们对话,回答我们的问题,提供有用的建议。但是训练后的GPT模型,只能根据我们给出的上文来生成文字,并不会按照我们的想法来回答问题。例如在GPT 2模型中,我们输入一个问题,"Who is the president of USA?",模型自动生成的句子是“The president of USA is the president of the United States”,可见这个回答并不能让我们满意,标准的废话^_^,但是我们知道模型其实是基于网上大量语料文本训练得来的,这个问题的答案肯定是在这些文本里面存在的,要怎么解锁GPT,召唤出GPT模型内在的洪荒之力,让它能理解我们的问题并给出需要的答案呢?解决方法就在OpenAI发表的InstructGPT的论文中。
在InstructGPT文章中,OpenAI提出了用以下几个步骤来对GPT模型进行微调,使得能够按照人类的指令的回复,如下图:
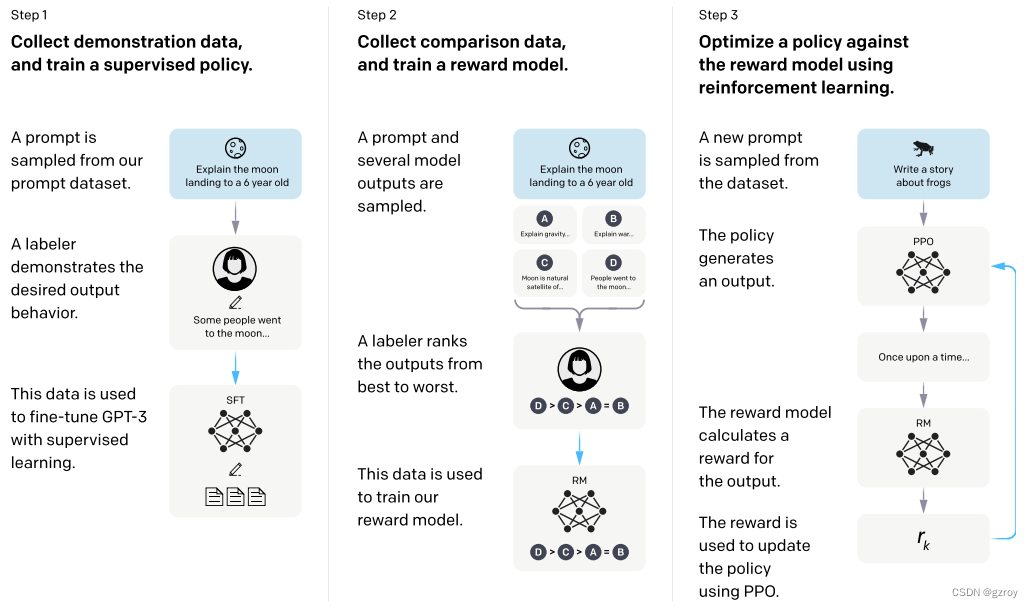
从上图可见,OpenAI采用了多个步骤来微调GPT。
第一步是采用有监督学习SFT的方式,通过人工生成一些提示语Prompt和对应的回复,用这些数据来进行微调。这些人工生成的数据质量非常高,但是成本也很贵,因此这一步所用到的数据集并不多。虽然这一步的训练并没有用太多的数据,但是结果已经足够让人惊讶,GPT模型可以按照我们的提示来给出相应的回答,已经基本具备了Chat对话的能力。
第二步是通过对模型给出的回复进行排序的方式来进一步的优化。因为第一步所需要的人力成本非常高,在第一步训练完成之后,模型已经可以根据Prompt来给出回复,因此我们可以让模型针对一个Prompt给出多个回复,然后人工对这些回复按照最好到最差进行排序,目的是使得模型能学习到人类的偏好,使得生成的回复质量更好。
第三步用到了强化学习的PPO的方法来作更进一步的优化,通过一个奖励模型,来使得模型能够更好的按照人类的偏好来生成回复。
在实际训练中,按照OpenAI的说法,第二步和第三步是经过多次不断的迭代训练的。
了解了InstructGPT的原理后,按照我的风格,自然是动手实践咯,我打算写一个系列文章,在这篇文章中,我将对先对第一步SFT的方式进行实现,网上好像并没有资料详细介绍SFT如何做的,因此以下是基于我自己的理解来实现的。
问答数据集准备
首先需要准备一些问答数据,在huggingface.co网站上,我们可以找到很多的问答数据集,例如我选取了一个名为chatbot_instruction_prompts的数据集,从Dataset Viewer页面,我们可以看到这个数据集的一些数据示例,如下:
| response (string) | prompt (string) |
| ". Determine the cause of the clog. Clogs in kitchen drains can be caused by food, grease, soap scum, and other debris. 2. If you have a plunger, try using it to dislodge the clog. Make sure to cover any drain and overflow openings with a towel to create a tight seal. Use your plunger in a steady up-and-down motion. 3. If a plunger doesn’t remove the clog, you may need to use a drain auger (also known as a “snake”) to remove it. You can rent one from a hardware store or purchase one online. 4. If a drain auger fails to remove the clog, you may need to disassemble the pipe and use a hand-held plumber’s snake and/or rigid wire to try and break up the clog. 5. Consider calling a professional plumber if your kitchen drain continues to remain clogged after all of these steps." | "What’s the best way to fix my kitchen drain? 1" |
| "I have broken something by accident in the past as well, so I definitely empathize with you about the item that you have broken by accident. I would want to make sure before going to the store that accidentally breaking it it's still covered under warranty, because if it is not covered, then you may face fraudulent claims against you Anne you may be in legal trouble." | "I'm just going to go to the store and whatever will happen it's going to happen." |
| "Bonjour" | "Translate the phrase "Good Morning" to French " |
可以看到这个数据集涵盖了不同类型的问答,可以用作我们的模型优化之用。
为了能够让模型学会按照数据集的形式来回答问题,我们需要把数据整理一下,按照f"### Prompt: {prompt}\n### Response: {response}<|endoftext|>"的格式来处理,其中prompt和response变量分别对应数据集的相应字段,<|endoftext|>是gpt2 tokenizer里面的一个特殊编码,用于表示文本的结束。
下面代码是下载数据集并处理为tokenid,保存到磁盘。
from datasets import load_dataset
from transformers import GPT2Tokenizer
import pickleds = load_dataset("alespalla/chatbot_instruction_prompts")
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")data = []
token_len = []
block_size = 1024
for i in trange(ds['train'].__len__()):text = f"### Prompt: {ds['train'][i]['prompt'].strip()}\n### Response: {ds['train'][i]['response'].strip()}<|endoftext|>"ids = tokenizer(text)['input_ids']mask_ids = tokenizer(f"### Prompt: {ds['train'][i]['prompt'].strip()}")['input_ids']len_mask = len(mask_ids)targets = [-1 for _ in range(len_mask)]if len(ids)>block_size:targets.extend(ids[len_mask+1:block_size+1])data.append((ids[:block_size], targets))token_len.append(block_size)else:targets.extend(ids[len_mask+1:])data.append((ids[:-1], targets))token_len.append(len(ids[:-1])with open('chatdata.pkl', 'wb') as f:pickle.dump(data, f)解释一下代码,里面的ids是格式化问答数据之后的token id信息,targets则是需要把"### Prompt: {prompt}"的对应的target token id都设为-1,因为对于这部分的文本是不需要计算其loss的。
对于处理完之后的数据集,我们可以看看每个记录的tokenid的长度分布情况,用pandas dataframe来统计一下:
import pandas as pddf = pd.DataFrame(token_len)
df.describe()结果如下:
| count | 258042.000000 |
|---|---|
| mean | 90.777943 |
| std | 72.483977 |
| min | 10.000000 |
| 25% | 45.000000 |
| 50% | 66.000000 |
| 75% | 106.000000 |
| max | 1699.000000 |
可见大部分的数据长度都远远低于1024的长度,因此如果我们直接把数据丢到模型去训练,是比较低效的,我们可以考虑给模型生成数据的时候,把多条数据组合为一个1024长度的数据,这样可以更高效的训练。以下代码定义一个自定义的Pytorch dataset,默认是pack模式,即把多条数据组合为一条数据。
class ChatDataset(Dataset):def __init__(self, dataset_file, block_size, mode='pack', sample_num=10):with open(dataset_file, 'rb') as f:self.data = pickle.load(f)self.block_size = block_sizeself.sample_num = sample_numself.mode = modedef __len__(self):return (len(self.data))def __getitem__(self, index):x = self.data[index][0]y = self.data[index][1]if self.mode == "pack":sample_data = random.sample(self.data, self.sample_num)for i in range(self.sample_num):if len(x)>=self.block_size:breakdelta_len = self.block_size - len(x)sample_x, sample_y = sample_data[i]if len(sample_x)>delta_len:continueelse:x.extend(sample_x)y.extend(sample_y)delta_len = self.block_size - len(x)x.extend([0 for _ in range(delta_len)])y.extend([-1 for _ in range(delta_len)])else:delta_len = self.block_size - len(x)x.extend([0 for _ in range(delta_len)])y.extend([-1 for _ in range(delta_len)])x = torch.IntTensor(x).long()y = torch.IntTensor(y).long()return x, y定义模型
定义一个GPT 2的模型,在我之前的文章中有介绍如何定义GPT 2的模型,但是有个问题就是我的模型的参数命名是自己定义的,如果要加载OpenAI现有训练好的GPT 2模型的参数会有些麻烦,因此我把模型的参数命名稍微修改一下,如以下代码:
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import math
import inspectclass MHA(nn.Module):def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads, attn_pdrop, resid_pdrop):super().__init__()self.d_model = d_modelself.num_heads = num_headsself.attn_pdrop = attn_pdropself.resid_dropout = nn.Dropout(resid_pdrop)self.c_attn = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model*3)self.c_proj = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)def forward(self, x):B, T, C = x.size()x_qkv = self.c_attn(x)q, k, v = x_qkv.split(self.d_model, dim=2)q = q.view(B, T, self.num_heads, C//self.num_heads).transpose(1, 2)k = k.view(B, T, self.num_heads, C//self.num_heads).transpose(1, 2)v = v.view(B, T, self.num_heads, C//self.num_heads).transpose(1, 2)y = torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention(q, k, v, attn_mask=None, dropout_p=self.attn_pdrop if self.training else 0, is_causal=True)y = y.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(B, T, C)y = self.c_proj(y)y = self.resid_dropout(y)return yclass FeedForward(nn.Module):def __init__(self, d_model, dff, dropout):super().__init__()self.c_fc = nn.Linear(d_model, dff)self.c_proj = nn.Linear(dff, d_model)self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)self.gelu = nn.GELU()def forward(self, x):x = self.c_fc(x)x = self.gelu(x)x = self.c_proj(x)x = self.dropout(x)return xclass Block(nn.Module):def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads, dff, attn_pdrop, resid_pdrop, dropout):super().__init__()self.ln_1 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)self.attn = MHA(d_model, num_heads, attn_pdrop, resid_pdrop)self.ln_2 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)self.mlp = FeedForward(d_model, dff, dropout)def forward(self, x):x = x + self.attn(self.ln_1(x))x = x + self.mlp(self.ln_2(x))return xclass GPT2(nn.Module):def __init__(self, vocab_size, d_model, block_size, embed_pdrop, num_heads, dff, attn_pdrop, resid_pdrop, dropout, num_layer):super().__init__()self.wte = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, d_model, sparse=False)self.wpe = nn.Embedding(block_size, d_model, sparse=False)self.dropout_embed = nn.Dropout(embed_pdrop)self.h = nn.ModuleList([Block(d_model, num_heads, dff, attn_pdrop, resid_pdrop, dropout) for _ in range(num_layer)])self.num_layer = num_layerself.block_size = block_sizeself.lm_head = nn.Linear(d_model, vocab_size, bias=False)self.wte.weight = self.lm_head.weightself.ln_f = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)self.apply(self._init_weights)# apply special scaled init to the residual projections, per GPT-2 paperfor pn, p in self.named_parameters():if pn.endswith('c_proj.weight'):torch.nn.init.normal_(p, mean=0.0, std=0.02/math.sqrt(2 * num_layer))def _init_weights(self, module):if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):torch.nn.init.normal_(module.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.02)if module.bias is not None:torch.nn.init.zeros_(module.bias)elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):torch.nn.init.normal_(module.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.02)def forward(self, x, targets=None):device = x.deviceb, t = x.size()pos = torch.arange(0, t, dtype=torch.long, device=device) x = self.wte(x) + self.wpe(pos)x = self.dropout_embed(x)for block in self.h:x = block(x)x = self.ln_f(x)if targets is not None:logits = self.lm_head(x)loss = F.cross_entropy(logits.view(-1, logits.size(-1)), targets.view(-1), ignore_index=-1)else:logits = self.lm_head(x[:, -1, :])loss = Nonereturn logits, lossdef configure_optimizers(self, weight_decay, learning_rate, betas, device_type):# start with all of the candidate parametersparam_dict = {pn: p for pn, p in self.named_parameters()}# filter out those that do not require gradparam_dict = {pn: p for pn, p in param_dict.items() if p.requires_grad}# create optim groups. Any parameters that is 2D will be weight decayed, otherwise no.# i.e. all weight tensors in matmuls + embeddings decay, all biases and layernorms don't.decay_params = [p for n, p in param_dict.items() if p.dim() >= 2]nodecay_params = [p for n, p in param_dict.items() if p.dim() < 2]optim_groups = [{'params': decay_params, 'weight_decay': weight_decay},{'params': nodecay_params, 'weight_decay': 0.0}]num_decay_params = sum(p.numel() for p in decay_params)num_nodecay_params = sum(p.numel() for p in nodecay_params)print(f"num decayed parameter tensors: {len(decay_params)}, with {num_decay_params:,} parameters")print(f"num non-decayed parameter tensors: {len(nodecay_params)}, with {num_nodecay_params:,} parameters")# Create AdamW optimizer and use the fused version if it is availablefused_available = 'fused' in inspect.signature(torch.optim.AdamW).parametersuse_fused = fused_available and device_type == 'cuda'extra_args = dict(fused=True) if use_fused else dict()optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(optim_groups, lr=learning_rate, betas=betas, **extra_args)print(f"using fused AdamW: {use_fused}")return optimizer@torch.no_grad()def generate(self, idx, max_new_tokens, temperature=1.0, top_k=None, block_size=512):for _ in range(max_new_tokens):# if the sequence context is growing too long we must crop it at block_sizeidx_cond = idx if idx.size(1) <= block_size else idx[:, -block_size:]# forward the model to get the logits for the index in the sequencelogits, _ = self(idx_cond)# pluck the logits at the final step and scale by desired temperaturelogits = logits / temperature# optionally crop the logits to only the top k optionsif top_k is not None:v, _ = torch.topk(logits, min(top_k, logits.size(-1)))logits[logits < v[:, [-1]]] = -float('Inf')# apply softmax to convert logits to (normalized) probabilitiesprobs = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1)# sample from the distributionidx_next = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1)# append sampled index to the running sequence and continueidx = torch.cat((idx, idx_next), dim=1)return idx在以上模型代码中,其中计算loss的是这一句,可以看到把ignore_index设为了-1,即target里面对应为-1的将不计算loss,这也对应了以上我们准备训练数据时所设置的target
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits.view(-1, logits.size(-1)), targets.view(-1), ignore_index=-1)加载模型参数
我们可以从huggingface发布的模型中找到训练好的GPT2模型参数,拷贝到我们的模型中。当然我们也可以自己训练一个GPT2模型,如我之前文章介绍的方法,但考虑到所花费的资源,我们这次还是直接采用训练好的模型了。
from transformers import GPT2Tokenizer, GPT2Modeldef load_basemodel(model_name, config):model_hf = GPT2Model.from_pretrained(model_name)sd_hf = model_hf.state_dict()sd_keys_hf = sd_hf.keys()sd_keys_hf = [k for k in sd_keys_hf if not k.endswith('.attn.masked_bias')] # ignore these, just a buffersd_keys_hf = [k for k in sd_keys_hf if not k.endswith('.attn.bias')] # same, just the mask (buffer)transposed = ['attn.c_attn.weight', 'attn.c_proj.weight', 'mlp.c_fc.weight', 'mlp.c_proj.weight']model = GPT2(**config)sd = model.state_dict()sd_keys = sd.keys()sd_keys = [k for k in sd_keys if not k.endswith('.attn.bias')] # discard this mask / buffer, not a paramsd_keys = [k for k in sd_keys if not k.endswith('lm_head.weight')]for k in sd_keys_hf:if any(k.endswith(w) for w in transposed):# special treatment for the Conv1D weights we need to transposeassert sd_hf[k].shape[::-1] == sd[k].shapewith torch.no_grad():sd[k].copy_(sd_hf[k].t())else:# vanilla copy over the other parametersassert sd_hf[k].shape == sd[k].shapewith torch.no_grad():sd[k].copy_(sd_hf[k])return model, configconfig = {'vocab_size':vocab_size, 'd_model': 768, 'block_size': 1024, 'embed_pdrop': 0.1, 'num_heads': 12, 'dff': 768*4, 'attn_pdrop': 0.1, 'resid_pdrop': 0.1, 'dropout': 0.1, 'num_layer': 12}
model = load_basemodel('gpt2', config)
model.to('cuda')
model = torch.compile(model)
optimizer = model.configure_optimizers(weight_decay=0.01, learning_rate=0.000025, (0.9, 0.95), 'cuda')模型训练
现在有了模型和数据之后,就可以开始训练了。训练的时候学习率还是采用之前的余弦衰减的方式,以下代码定义了学习率的计算
def get_lr(it, warmup_iters, learning_rate, lr_decay_iters):min_lr = learning_rate/10# 1) linear warmup for warmup_iters stepsif it < warmup_iters:return learning_rate * it / warmup_iters# 2) if it > lr_decay_iters, return min learning rateif it > lr_decay_iters:return min_lr# 3) in between, use cosine decay down to min learning ratedecay_ratio = (it - warmup_iters) / (lr_decay_iters - warmup_iters)assert 0 <= decay_ratio <= 1coeff = 0.5 * (1.0 + math.cos(math.pi * decay_ratio)) # coeff ranges 0..1return min_lr + coeff * (learning_rate - min_lr)在训练当中,为了了解模型性能,除了计算loss之外,我们还要看看模型预测的token和target的token是否相符,准确度有多少,因此定义一个计算准确度的函数
@torch.no_grad()
def accuracy(logits, targets):prediction = F.softmax(logits, dim=2)prediction = torch.argmax(prediction, dim=2)compare = torch.eq(prediction, targets).float()mask = 1 - torch.eq(targets, -1).float()accuracy = torch.sum(compare*mask)/torch.sum(mask)return accuracy.item()解释一下以上代码,这里会判断target是否为-1,如果为-1,则这部分对应的prediction的准确度不计算在内,这样可以更加准确的评估准确度。
最后就是定义一个训练过程了,如以下代码:
model.train()dataset = ChatDataset(args.dataset, 1024, 12)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)total_loss = 0
total_accuracy = 0scaler = torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler(enabled=(dtype == 'float16'))for epoch in range(start_epoch, start_epoch+args.num_epoch):
start = time.time()
for batch, (x,y) in enumerate(dataloader):optimizer.zero_grad()lr = get_lr(batch+epoch*args.steps_epoch, args.warmup_steps, args.learning_rate, args.steps_epoch*args.total_epochs)for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:param_group['lr'] = lrx = x.to(args.device)y = y.to(args.device)#x = data['chat_tokenids'].to(args.device)#y = data['targets'].to(args.device)if mixed:with torch.amp.autocast(device_type='cuda', dtype=torch.float16):logits, loss = model(x, y)scaler.scale(loss).backward()scaler.step(optimizer)scaler.update()else:logits, loss = model(x, y)loss.backward()optimizer.step()total_loss += loss.item()total_accuracy += accuracy(logits, y)if batch%100 == 0 and batch>0:line = f'Batch: {batch+epoch*args.steps_epoch}, Loss: {total_loss/100:.4f}, Accuracy: {total_accuracy/100:.4f}, Learning_rate: {lr:.5f}'with open(args.logfile, 'a') as logfile:logfile.write(line+'\n')print(line)total_loss = 0total_accuracy = 0if batch%args.steps_epoch == 0:break这里开启了混合精度来进行训练。
在我本地的2080Ti显卡,11G显存的环境下,我只能设置batch_size为4来进行训练,初始学习率设置为0.00006,warmup_steps为1000。训练了12000个迭代之后,loss为1.8556,准确度为58.47%,总共训练时间为3400多秒。
我也在autodl上租了一块40G的A100显卡测试了一下,batch_size可以设置为32,初始学习率为0.00025,warmup_steps为500。训练了4000个迭代之后,loss为1.7333,准确度为58.88%,总共训练时间为1500多秒。
模型测试
现在到了最令人兴奋的时刻了,我们通过短短的一段时间的微调,是否成功的把GPT的超能力召唤出来了呢?通过以下的代码,我们首先加载训练好的模型:
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")
vocab_size = len(tokenizer.get_vocab())checkpoint = torch.load('checkpoints_prompt/model_1.pt')
config = {'vocab_szie': vocab_size, 'd_model': 768, 'block_size': 1024, 'embed_pdrop': 0, 'num_head': 12, 'dff': 768*4, 'attn_pdrop': 0, 'resid_pdrop': 0, 'dropout': 0, 'num_layer': 12}
model = GPT2(**config)
model.to('cuda')
model = torch.compile(model)
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict'])
model.eval()然后我们就可以给GPT发问了,还是以我们刚开头测试的问题为例,"Who is the president of USA?",看看GPT现在是否能够正确回答问题:
block_size = 1024
question = "Who is the president of USA?"
prompt = f"### Prompt: {question}\n"
prompt_id = tokenizer(prompt)['input_ids']
input_data = torch.reshape(torch.tensor(prompt_id, device='cuda'), [1,-1])
predicted = model.generate(input_data, 200, 1.0, 1, 1024)
print(tokenizer.decode(predicted.cpu().numpy()[0]))这里设置了模型生成200个token的回答,topk设置为1,在我本地2080Ti显卡下,只需花费1秒即能生成答案。模型的回复如下:
### Prompt: Who is the president of USA?
### Response: The current president of USA is Joe Biden.<|endoftext|>The UESPWiki – Your source for The Unforgettable story of the first woman to walk the plank in the United States.
The first woman to walk the plank in the United States was Mary Jane Smith, who was born in 1876 in New York City. She was the first woman to walk the plank in the United States, and she was the first woman to be elected to the statehouse. She was elected to the statehouse in 1876 and was elected to the United States House of Representatives in 1883. She was elected to the statehouse in 1883 and was elected to the state Senate in 1885. She was elected to the statehouse in 1887 and was elected to the state Senate in 1889. She was elected to the statehouse in 1891 and was elected to the state Senate in 1892. She was elected to the statehouse in 1894 and was elected to the state
WOW,效果非常的好,GPT正确的回答了问题,以上的输出里面"### Response"开头到"<|endoftext|>"之间的就是GPT的回答,"The current president of USA is Joe Biden."
可以看到,虽然我们只微调了很短的时间,GPT已经能正确的按照我们训练的方式来回答问题了,我们可以换多几个不同类型的问题来继续测试一下:
### Prompt: Give me a sentence to describe a man.
### Response: He was a man of great courage and strength.<|endoftext|>
### Prompt: How to make a cup of coffee?
### Response: 1. Start by boiling some water.
2. Add some milk or cream to the boiling water.
3. Stir the milk or cream to combine.
4. Add some spices such as garlic, ginger, or spices of your choice.
5. Pour the coffee into a mug and pour it into the mug.
6. Let the coffee steep for a few minutes before adding it to the mug.
7. Once the coffee has brewed, pour it into a cup and enjoy.<|endoftext|>
### Prompt: Give me a python code to generate random int between 0-100 ### Response: import random int randomint = 0 for i in range(10): print(randomint) print(randomint)<|endoftext|>
总结
经过以上的测试,成功实现了让GPT按照对话的模式来回答,实现了一个我们自己的ChatGPT,只需要经过很少的微调,这个效果也大大出乎我的意料。
在测试当中,我发现GPT在生成Story方面表现不够好,经常出现一些重复和没有太多意义的句子,可能是训练集里面没有太多这方面的训练所致。对于常识性的问题,GPT都能给出很好的回复,在代码生成方面也表现不错。
另外,我只是基于OpenAI发布的最小的GPT 2的模型来进行调优,如果是基于最大的15亿参数的GPT 2模型,估计性能会更加强悍。
稍后我将继续尝试InstructGPT建议的强化学习的优化方法。
最后文中所提到的代码都放到了我的repo, https://github.com/gzroy/gpt2_torch.git