1 Stream流概述
java8使用的是函数式编程模式,如同它的名字一样,它可以用来对集合或者数组进行链状流式操作,让我们更方便的对集合或者数组进行操作。
2 案例准备工作
我们首先创建2个类一个作家类,一个图书类
package com.stream.model;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;import java.util.List;/*** @author xiDi* @data 2023/8/22*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode//后期去重
public class Author implements Comparable<Author>{/*** id*/private Long id;/*** 姓名*/private String name;/*** 年龄*/private Integer age;/*** 简介*/private String intro;/*** 图书作品*/private List<Book> bookList;@Overridepublic int compareTo(Author o) {return o.getAge()-this.getAge();}
}
package com.stream.model;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;/*** @author xiDi* @data 2023/8/22*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode//后期去重
public class Book {/*** id*/private Long id;/*** 书名*/private String bookName;/*** 分类*/private String category;/*** 评分*/private Integer score;/*** 图书简介*/private String bookIntro;
}
然后我们进行数据初始化
public static List<Author> getAuthor() {//数据初始化Author author = new Author(1L, "蒙多", 33, "想去那里就去那里", null);Author author2 = new Author(2L, "亚索", 15, "唯有过往,伤人最深", null);Author author3 = new Author(3L, "易", 14, "高原血统", null);Author author4 = new Author(3L, "易", 14, "高原血统", null);List<Book> bookList = new ArrayList<>();List<Book> bookList2 = new ArrayList<>();List<Book> bookList3 = new ArrayList<>();bookList.add(new Book(1L, "英雄联盟", "爱情,游戏", 80, "双手成就梦想"));bookList.add(new Book(2L, "CF", "金钱,游戏", 60, "无兄弟,无CF"));bookList2.add(new Book(3L, "CSGO", "哲学", 85, "内格夫"));bookList2.add(new Book(3L, "CSGO", "哲学,神仙", 85, "内格夫"));bookList2.add(new Book(4L, "王者荣耀", "农药", 60, "有钱就是D"));bookList3.add(new Book(5L, "钢铁雄心4", "战争,历史", 90, "人均甲级战犯"));bookList3.add(new Book(6L, "PUBG", "开挂,神仙", 59, "会玩就是挂?"));bookList3.add(new Book(6L, "PUBG", "开挂,神仙", 59, "会玩就是挂?"));author.setBookList(bookList);author2.setBookList(bookList2);author3.setBookList(bookList3);author4.setBookList(bookList3);return Arrays.asList(author, author2, author3, author4);}3 具体方法
3.1 中间操作filter
我们要求打印姓名大于1的作家姓名,可以用到filter关键字,它的作用是过滤
我们第一步呢,就是要创建流,List创建流就是在集合后面.stream就创建了。数组创建流,使用
Arrays.stream()方法来创建
在根据我们前面学到的lambda表达式,代码就可以简写这样
//打印作家姓名大于1的作家姓名private static void test02() {List<Author> author = getAuthor();author.stream().filter(item -> item.getName().length() > 1).forEach(item -> System.out.println(item.getName()));}输出结果:

3.2 中间操作 map、distinct
map的作用是流中元素进行计算或者转换,distinctd的作用是去重
//打印所有作家姓名,去重private static void test03() {List<Author> author = getAuthor();List<String> collect = author.stream().map(Author::getName).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect);}输出结果

除了可以用map拿到我们想要的数据,我们还可以用它来对数据进行处理
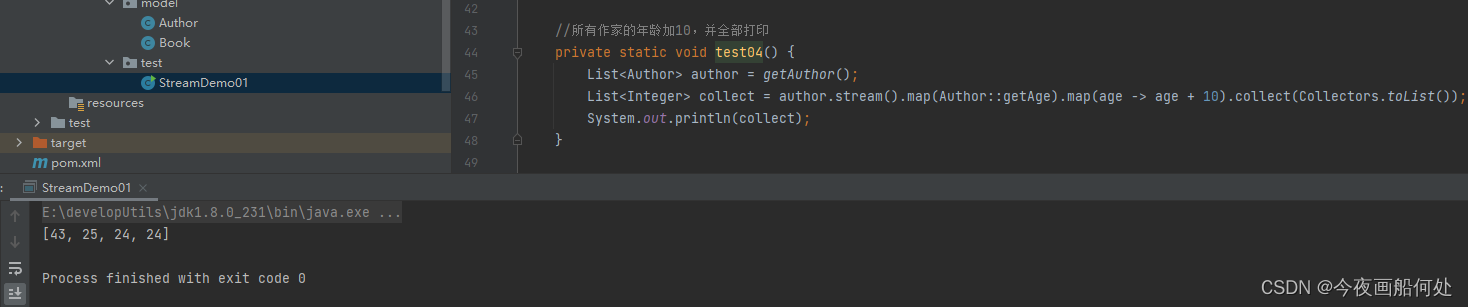
//所有作家的年龄加10,并全部打印private static void test04() {List<Author> author = getAuthor();List<Integer> collect = author.stream().map(Author::getAge).map(age -> age + 10).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect);}输出结果
3.3 中间操作 sorted
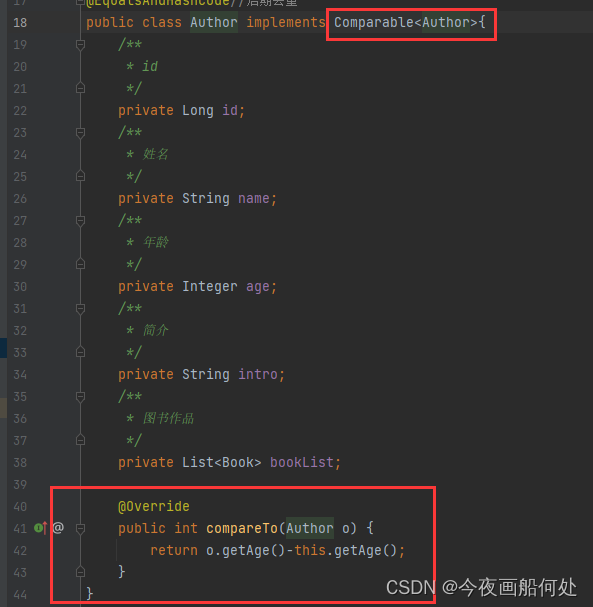
注意:调用空参的sorted方法需要流中的元素实现compareTo方法,才能实现排序,否则会报错
//按照年龄升序并输出姓名 --调用空参的sorted方法需要流中的元素实现compareTo方法,才能实现排序,否则会报错private static void test05() {List<Author> author = getAuthor();List<String> collect = author.stream().sorted().map(Author::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());for (String item : collect) {System.out.println(item);}}我们调用空参的sorted方法的话需要我们流中的元素实现Comparable,并且重写compareTo方法,重写的逻辑就是看你想要实现什么排序,比我这里实现的是根据年龄去排序
输出结果

3.4 中间操作 limit、skip
limit的作用是限制,skip的作用是跳过
//输出年龄最大的2位作家名称,并去重 --limit 限制private static void test06() {List<Author> author = getAuthor();List<String> collect = author.stream().sorted().map(Author::getName).distinct().limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());for (String item : collect) {System.out.println(item);}}这里我们用来limit来实现只要年龄前2位的作家名称
//输出年龄最大作家外的其他作家名称,并去重 --skip跳过流中前n个元素private static void test07() {List<Author> author = getAuthor();List<String> collect = author.stream().sorted().map(Author::getName).distinct().skip(1).collect(Collectors.toList());for (String item : collect) {System.out.println(item);}}我们想要输出除年龄最大外的作家名称,那么我们需要排序后,在跳过第一个即可
3.5 中间操作 faltMap
faltMap可以把一个对象转换为多个对象作为流中的元素
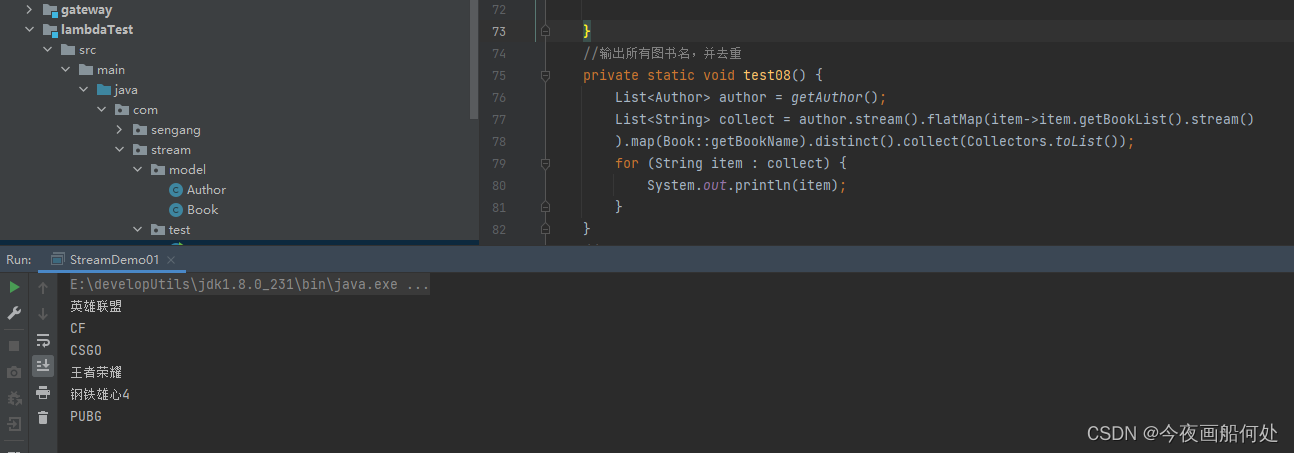
//输出所有图书名,并去重private static void test08() {List<Author> author = getAuthor();List<String> collect = author.stream().flatMap(item->item.getBookList().stream()).map(Book::getBookName).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());for (String item : collect) {System.out.println(item);}}输出结果
4 总结
Stream还是很简单和方便的,因为我也是刚学,使用比较少,所以介绍比较笼统和简单,但是只要实操一下,就能很快记住


![[NLP]深入理解 Megatron-LM](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f8384b9d4a8e483f9eb62bff34159b70.png)