文章
- 项目1:外星人入侵游戏
- 项目2:数据可视化
- 2.1 matplotlib
- 2.2 csv文件格式
- 2.3 json文件格式
- 2.4 使用Web API
- 2.4.1 什么是Web API?
- 2.4.2 处理API响应
- 2.5 使用Pygal可视化仓库
- 项目3:Web应用程序
- 3.1 Django入门
- 3.1.1 建立项目
- 3.1.2 创建应用程序
- 3.1.3 创建网页
- 3.2 用户账户
- 3.2.1 让用户能够输入数据
- 3.2.2 创建用户账户
- 3.2.3 让用户拥有自己的数据
- 3.3 设置应用程序的样式并对其进行部署
- 3.4 Python WEB框架之FastAPI
- 参考文献
项目1:外星人入侵游戏
- 回顾项目开发计划
- 创建第一个外星人:Alien类
import pygame
from pygame.sprite import Spriteclass Alien(Sprite):"""A class to represent a single alien in the fleet."""def __init__(self, ai_settings, screen):"""Initialize the alien, and set its starting position."""super(Alien, self).__init__()self.screen = screenself.ai_settings = ai_settings# Load the alien image, and set its rect attribute.self.image = pygame.image.load('images/alien.bmp')self.rect = self.image.get_rect()# Start each new alien near the top left of the screen.self.rect.x = self.rect.widthself.rect.y = self.rect.height# Store the alien's exact position.self.x = float(self.rect.x)def check_edges(self):"""Return True if alien is at edge of screen."""screen_rect = self.screen.get_rect()if self.rect.right >= screen_rect.right:return Trueelif self.rect.left <= 0:return Truedef update(self):"""Move the alien right or left."""self.x += (self.ai_settings.alien_speed_factor *self.ai_settings.fleet_direction)self.rect.x = self.xdef blitme(self):"""Draw the alien at its current location."""self.screen.blit(self.image, self.rect)
- 创建一群外星人
- 让外星人移动
- 射杀外星人
- 结束游戏
game_functions.py
import sys
from time import sleepimport pygamefrom bullet import Bullet
from alien import Aliendef check_keydown_events(event, ai_settings, screen, ship, bullets):"""Respond to keypresses."""if event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:ship.moving_right = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:ship.moving_left = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_SPACE:fire_bullet(ai_settings, screen, ship, bullets)elif event.key == pygame.K_q:sys.exit()def check_keyup_events(event, ship):"""Respond to key releases."""if event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:ship.moving_right = Falseelif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:ship.moving_left = Falsedef check_events(ai_settings, screen, ship, bullets):"""Respond to keypresses and mouse events."""for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:sys.exit()elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:check_keydown_events(event, ai_settings, screen, ship, bullets)elif event.type == pygame.KEYUP:check_keyup_events(event, ship)def fire_bullet(ai_settings, screen, ship, bullets):"""Fire a bullet, if limit not reached yet."""# Create a new bullet, add to bullets group.if len(bullets) < ai_settings.bullets_allowed:new_bullet = Bullet(ai_settings, screen, ship)bullets.add(new_bullet)def update_screen(ai_settings, screen, ship, aliens, bullets):"""Update images on the screen, and flip to the new screen."""# Redraw the screen, each pass through the loop.screen.fill(ai_settings.bg_color)# Redraw all bullets, behind ship and aliens.for bullet in bullets.sprites():bullet.draw_bullet()ship.blitme()aliens.draw(screen)# Make the most recently drawn screen visible.pygame.display.flip()def update_bullets(ai_settings, screen, ship, aliens, bullets):"""Update position of bullets, and get rid of old bullets."""# Update bullet positions.bullets.update()# Get rid of bullets that have disappeared.for bullet in bullets.copy():if bullet.rect.bottom <= 0:bullets.remove(bullet)check_bullet_alien_collisions(ai_settings, screen, ship, aliens, bullets)def check_bullet_alien_collisions(ai_settings, screen, ship, aliens, bullets):"""Respond to bullet-alien collisions."""# Remove any bullets and aliens that have collided.collisions = pygame.sprite.groupcollide(bullets, aliens, True, True)if len(aliens) == 0:# Destroy existing bullets, and create new fleet.bullets.empty()create_fleet(ai_settings, screen, ship, aliens)def check_fleet_edges(ai_settings, aliens):"""Respond appropriately if any aliens have reached an edge."""for alien in aliens.sprites():if alien.check_edges():change_fleet_direction(ai_settings, aliens)breakdef change_fleet_direction(ai_settings, aliens):"""Drop the entire fleet, and change the fleet's direction."""for alien in aliens.sprites():alien.rect.y += ai_settings.fleet_drop_speedai_settings.fleet_direction *= -1def ship_hit(ai_settings, stats, screen, ship, aliens, bullets):"""Respond to ship being hit by alien."""if stats.ships_left > 0:# Decrement ships_left.stats.ships_left -= 1else:stats.game_active = False# Empty the list of aliens and bullets.aliens.empty()bullets.empty()# Create a new fleet, and center the ship.create_fleet(ai_settings, screen, ship, aliens)ship.center_ship()# Pause.sleep(0.5)def check_aliens_bottom(ai_settings, stats, screen, ship, aliens, bullets):"""Check if any aliens have reached the bottom of the screen."""screen_rect = screen.get_rect()for alien in aliens.sprites():if alien.rect.bottom >= screen_rect.bottom:# Treat this the same as if the ship got hit.ship_hit(ai_settings, stats, screen, ship, aliens, bullets)breakdef update_aliens(ai_settings, stats, screen, ship, aliens, bullets):"""Check if the fleet is at an edge,then update the postions of all aliens in the fleet."""check_fleet_edges(ai_settings, aliens)aliens.update()# Look for alien-ship collisions.if pygame.sprite.spritecollideany(ship, aliens):ship_hit(ai_settings, stats, screen, ship, aliens, bullets)# Look for aliens hitting the bottom of the screen.check_aliens_bottom(ai_settings, stats, screen, ship, aliens, bullets)def get_number_aliens_x(ai_settings, alien_width):"""Determine the number of aliens that fit in a row."""available_space_x = ai_settings.screen_width - 2 * alien_widthnumber_aliens_x = int(available_space_x / (2 * alien_width))return number_aliens_xdef get_number_rows(ai_settings, ship_height, alien_height):"""Determine the number of rows of aliens that fit on the screen."""available_space_y = (ai_settings.screen_height -(3 * alien_height) - ship_height)number_rows = int(available_space_y / (2 * alien_height))return number_rowsdef create_alien(ai_settings, screen, aliens, alien_number, row_number):"""Create an alien, and place it in the row."""alien = Alien(ai_settings, screen)alien_width = alien.rect.widthalien.x = alien_width + 2 * alien_width * alien_numberalien.rect.x = alien.xalien.rect.y = alien.rect.height + 2 * alien.rect.height * row_numberaliens.add(alien)def create_fleet(ai_settings, screen, ship, aliens):"""Create a full fleet of aliens."""# Create an alien, and find number of aliens in a row.alien = Alien(ai_settings, screen)number_aliens_x = get_number_aliens_x(ai_settings, alien.rect.width)number_rows = get_number_rows(ai_settings, ship.rect.height,alien.rect.height)# Create the fleet of aliens.for row_number in range(number_rows):for alien_number in range(number_aliens_x):create_alien(ai_settings, screen, aliens, alien_number,row_number)项目2:数据可视化
2.1 matplotlib
2.2 csv文件格式
csv文件对人来说阅读起来比较麻烦,但程序可轻松提取并处理其中的值。
为什么使用csv文件格式?
CSV是纯文本文件,它使数据交换更容易,也更易于导入到电子表格或数据库存储中。例如:您可能希望将某个统计分析的数据导出到CSV文件,然后将其导入电子表格以进行进一步分析。总体而言,它使用户可以通过编程轻松地体验工作。任何支持文本文件或字符串操作的语言(例如Python)都可以直接使用CSV文件。
处理天气数据示例
数据来源:
www.wunderground.com/history
import csv
from datetime import datetimefrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt# Get dates, high, and low temperatures from file.
filename = 'your_csv_file.csv'
with open(filename) as f:reader = csv.reader(f)header_row = next(reader)dates, highs, lows = [], [], []for row in reader:try:current_date = datetime.strptime(row[0], "%Y-%m-%d")high = int(row[1])low = int(row[3])except ValueError:print(current_date, 'missing data')else:dates.append(current_date)highs.append(high)lows.append(low)# Plot data.
fig = plt.figure(dpi=128, figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(dates, highs, c='red', alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(dates, lows, c='blue', alpha=0.5)
plt.fill_between(dates, highs, lows, facecolor='blue', alpha=0.1)# Format plot.
title = "Daily high and low temperatures - 2014\nDeath Valley, CA"
plt.title(title, fontsize=20)
plt.xlabel('', fontsize=16)
fig.autofmt_xdate()
plt.ylabel("Temperature (F)", fontsize=16)
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=16)plt.show()
2.3 json文件格式
为什么使用json?
填充的数据结构需要从任何语言转换为其他语言和平台可识别的格式。JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) 是实现这一任务的数据交换格式。JSON 采用人类可读的轻量级文本,而且只需更少的编码,处理速度更快,因此成为一种深受开发人员欢迎的数据格式。
2.4 使用Web API
使用Web应用编程接口(API)自动请求网站的特定信息而不是整个网页,再对这些信息进行实时可视化。
2.4.1 什么是Web API?
Web API是网站的一部分,用于与使用非常具体的URL请求特定信息的程序交互。这种请求称为API调用。请求的数据将以易于处理的格式(如json或csv)返回。依赖于外部数据源的大多数应用程序都依赖于API调用,如集成社交媒体网站的应用程序。
2.4.2 处理API响应
$ pip install --user requests
python_repos.py
import requests# 执行API调用并存储响应
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=stars'
r = request.get(url)
print("Status code:", r.status_code)# 将API响应存储在一个变量中
response_dict = r.json()# 处理结果
print(response_dict.keys())
结果
Status code: 200
dict_key(['item','total_count','incomplete_results'])
2.5 使用Pygal可视化仓库
建立柱状图等
项目3:Web应用程序
3.1 Django入门
Django是一个Web框架 —— 一套用于帮助开发交互式网站的工具。
https://www.djangoproject.com/
3.1.1 建立项目
- 制定规范
- 建立、安装、激活虚拟环境
- 安装Django并在其中创建项目
- 创建数据库
3.1.2 创建应用程序
- 定义模型:model.py
- 激活模型:settings.py
- Django管理网站:admin.py
3.1.3 创建网页
- 映射URL:urls.py
"""Defines url patterns for users."""from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib.auth.views import loginfrom . import viewsurlpatterns = [# Login page.url(r'^login/$', login, {'template_name': 'users/login.html'},name='login'),# Logout page.url(r'^logout/$', views.logout_view, name='logout'),# Registration page. url(r'^register/$', views.register, name='register'),
]
- 编写视图:views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from django.core.urlresolvers import reverse
from django.contrib.auth import login, logout, authenticate
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationFormdef logout_view(request):"""Log the user out."""logout(request)return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('learning_logs:index'))def register(request):"""Register a new user."""if request.method != 'POST':# Display blank registration form. form = UserCreationForm()else:# Process completed form.form = UserCreationForm(data=request.POST)if form.is_valid():new_user = form.save()# Log the user in, and then redirect to home page.authenticated_user = authenticate(username=new_user.username,password=request.POST['password1'])login(request, authenticated_user)return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('learning_logs:index'))context = {'form': form}return render(request, 'users/register.html', context)
- 编写模板:index.html
创建其他网页
- 模板继承
3.2 用户账户
3.2.1 让用户能够输入数据
3.2.2 创建用户账户
- 应用程序users
- 登陆页面
- 注销
- 注册页面
3.2.3 让用户拥有自己的数据
3.3 设置应用程序的样式并对其进行部署
3.4 Python WEB框架之FastAPI
Django各种功能都糅杂在一起;Flask 框架简单,但只是单线程需要自己改造才支持多并发。
FastAPI貌似结合弥补了Flask 框架的缺陷,如果你想要快速搭建一个WEB服务,用FastAPI准没错。
pip install fastapi uvicorn python-multipart
示例
from fastapi import FastAPI
import uvicornapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/")
def index():return "Hello World"if __name__ == "__main__":uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
运行起来之后,应该会看到下面的画面:
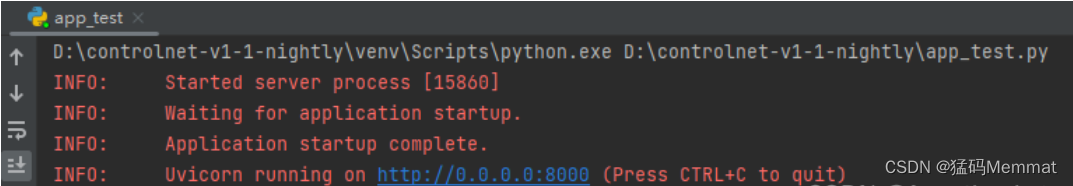
浏览器访问你的ip地址加端口号,应该就能看到“Hello World”。
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Listfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Request, UploadFile, File
import uvicorn
from starlette.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
from starlette.responses import FileResponse
from starlette.staticfiles import StaticFilesapp = FastAPI()
# 添加CORS中间件
app.add_middleware(CORSMiddleware,allow_origins=["*"],allow_credentials=True,allow_methods=["*"],allow_headers=["*"],
)app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory="static"), name="static_resources")@app.get("/")
def index():return "Hello World"@app.get("/index")
def home():return FileResponse("static/index.html")@app.get("/info")
def handle_info(name, age):return f"Hello World, {name}, {age}"@app.post("/request")
def handle_info(params: Request):return params.query_params@app.post("/request")
async def handle_info1(params: Request):form = dict(await params.form())return form# 图片批量上传
@app.post('/upload')
async def upload_file(params: Request, files: List[UploadFile] = File(...)):form = dict(await params.form())save_files = []for file in files:temp_arr = file.filename.split(".")suffix = temp_arr[len(temp_arr) - 1]file_name = f"img_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S%f')}.{suffix}"with open(file_name, "wb") as f:content = await file.read() # 读取上传文件的内容f.write(content) # 将内容写入文件save_files.append(file_name)return {"code": 200,"data": {"params": form,"save_files": save_files}}if __name__ == "__main__":uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
本节参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36991535/article/details/132522146
参考文献
《Python编程:从入门到实践》【美】Eric Matthes 著 袁国忠 译 : https://www.ituring.com.cn/book/1861
Dive Into Python: https://diveintopython.org/learn