不可变集合、Lambda表达式、Stream流
创建不可变集合
不能被修改的集合
应用场景
如果某个数据不能被修改,把它防御性的拷贝到不可变集合中是个很好的实践。
当集合对象被不可信的库调用时,不可变形式是安全的。

创建不可变集合
在List、Set、Map接口中,都存在静态的of方法,可以获取一个不可变的集合。
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| static<E> List<E> of(E…elements) | 创建一个具有指定元素的List集合对象 |
| static<E> Set<E> of(E…elements) | 创建一个具有指定元素的Set集合对象 |
| static<K, V> Map<K, V> of(E…elements) | 创建一个具有指定元素的Map集合对象 |
注意:这个集合不能添加、不能删除、不能修改。
示例
List
package com.louis;import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日16:41*/
public class ImmutableDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 创建不可变的List集合* 一旦创建完毕之后,是无法进行修改的,只能查询操作*/List<String> list = List.of("louis", "khan", "Alex");System.out.println("list = " + list.toString());System.out.println("--------使用迭代器的方法遍历--------");Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){String con = iterator.next();System.out.println(con);}/** louiskhanAlex* */System.out.println("---------测试是否能删除-----------");list.remove("louis");/*Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException....at com.louis.ImmutableDemo1.main(ImmutableDemo1.java:32)*/}
}
Set
package com.louis;import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日16:41*/
public class ImmutableDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 创建不可变的Set集合* 一旦创建完毕之后,是无法进行修改的,只能查询操作*/Set<String> set = Set.of("louis", "khan");Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator();while(iterator.hasNext()){String con = iterator.next();System.out.println(con);}/** louiskhan* */set.remove("louis");/** Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException* ....* at com.louis.ImmutableDemo2.main(ImmutableDemo2.java:28) * */}
}
注意:
当我们要获取一个不可变的Set集合时,里面的参数一定要保证唯一性。
Map
package com.louis;import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日16:41*/
public class ImmutableDemo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 创建不可变的Map集合* 一旦创建完毕之后,是无法进行修改的,只能查询操作*/Map<String, String> map = Map.of("1", "louis", "2", "louis", "3", "alex");Set<String> keys = map.keySet();for (String key : keys) {System.out.println(map.get(key));}/** alexlouislouis* */System.out.println("------------------");Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {String key = entry.getKey();String value = entry.getValue();System.out.println(key + "=" + value);}/** 1=louis3=alex2=louis* */}
}
注意:
1、键是不能重复的
2、Map里面的of方法,参数是有上限的,最多只能传递20个参数,即10个键值对
原因:可变参数只能存在一个且只能在最后。
static <K, V> Map<K, V> of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3, K k4, V v4, K k5, V v5,K k6, V v6, K k7, V v7, K k8, V v8, K k9, V v9, K k10, V v10) {return new ImmutableCollections.MapN<>(k1, v1, k2, v2, k3, v3, k4, v4, k5, v5,k6, v6, k7, v7, k8, v8, k9, v9, k10, v10);
}
ofEntries
如果想要创建Map的不可变集合,且键值对的数量超过了10个。
package com.louis;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日16:41*/
public class ImmutableDemo4 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 创建Map的不可变集合, 键值对的数量超过10个*///1、创建一个普通的Map集合HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("1", "a");map.put("2", "b");map.put("3", "c");map.put("4", "d");map.put("5", "e");map.put("6", "f");map.put("7", "g");map.put("8", "h");map.put("9", "i");map.put("10", "j");map.put("11", "k");//2、利用上面的数据来获取一个不可变的集合//获取到所有的键值对对象(Entry对象)Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();//把entries变成一个数组(指定类型entry)Map.Entry[] array = entries.toArray(new Map.Entry[0]);/*toArray方法会比较集合的长度和数组长度两者之间的大小如果集合的长度大于数组的长度,表示数据在数组中放不下,此时会根据实际数据的个数重新创建数组。如果集合的长度小于等于数组的长度,数据在数组中可以存放,此时不会创建新的数组而是直接使用, 剩余的会默认初始化值null*/Map m = Map.ofEntries(array);}
}
在JDK10之后,不可变集合可以使用copyOf()方法
/*** Returns an <a href="#unmodifiable">unmodifiable Map</a> containing the entries* of the given Map. The given Map must not be null, and it must not contain any* null keys or values. If the given Map is subsequently modified, the returned* Map will not reflect such modifications.** @implNote* If the given Map is an <a href="#unmodifiable">unmodifiable Map</a>,* calling copyOf will generally not create a copy.** @param <K> the {@code Map}'s key type* @param <V> the {@code Map}'s value type* @param map a {@code Map} from which entries are drawn, must be non-null* @return a {@code Map} containing the entries of the given {@code Map}* @throws NullPointerException if map is null, or if it contains any null keys or values* @since 10*/@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})static <K, V> Map<K, V> copyOf(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) {if (map instanceof ImmutableCollections.AbstractImmutableMap) {return (Map<K,V>)map;} else {return (Map<K,V>)Map.ofEntries(map.entrySet().toArray(new Entry[0]));}}
Lambda表达式
简介
什么是Lambda
Lambda是JAVA 8 添加的新特性,是一个匿名函数,使用Lambda表达式可以对一个接口进行非常简洁的实现。它是实现接口的一种方式。
示例
package com.louis;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日16:16*/
public class Program {//1、实现接口MyComparator myComparator = new MyComparator();//2、使用匿名内部类Comparator comparator = new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(int a, int b) {return a-b;}};//3、使用Lambda表达式实现接口Comparator comparator1 = (a, b)->a-b;class MyComparator implements Comparator{@Overridepublic int compare(int a, int b) {return a - b;}}interface Comparator{int compare(int a, int b);}
}
Lambda对接口的要求
虽然可以使用Lambda表达式对某些接口进行简单的实现,但并不是所有的接口都可以使用Lambda表达式实现。要求接口中定义的必须要实现的抽象方法只能是一个。
在JAVA8对接口加了一个新特性:default(可以实现也可以不实现)。
@FunctionalInterface:用来修饰函数式接口,即接口中的抽象方法只有一个。
@FunctionalInterface
interface Comparator{int compare(int a, int b);
}
Lambda基础语法
Lambda是一个匿名函数,最主要包括参数列表和方法体。
():用来描述参数列表
{}:用来描述方法体
->:Lambda运算符,读作goes to
不同类型接口
package com.louis.interfaces;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日16:34*/
public class Interfaces {@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface LambdaHaveReturnMultipleParameter {int test(int a, int b);}@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface LambdaHaveReturnNoneParameter {int test();}@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface LambdaHaveReturnSingleParameter {int test(int a);}@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface LambdaNoneReturnMultipleParameter {void test(int a, int b);}@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface LambdaNoneReturnNoneParameter {void test();}@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface LambdaNoneReturnSingleParameter {void test(int n);}
}
基础语法实现
package com.louis.syntax;import com.louis.interfaces.Interfaces;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日16:36*/
public class Syntax1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1、Lambda表达式的基础语法/*Lambda是一个匿名函数,最主要包括参数列表和方法体。():用来描述参数列表{}:用来描述方法体->:Lambda运算符,读作goes to*///无参无返回Interfaces.LambdaNoneReturnNoneParameter lambda1 = ()->{System.out.println("hello Lambda");};lambda1.test();/*hello Lambda*///无返回值单个参数Interfaces.LambdaNoneReturnSingleParameter lambda2 = (int a) -> {System.out.println(a);};lambda2.test(2);/*2*///无返回值、多个参数Interfaces.LambdaNoneReturnMultipleParameter lambda3 = (int a, int b)->{System.out.println(a-b);};lambda3.test(10, 20);/*-10*///有返回值、无参数Interfaces.LambdaHaveReturnNoneParameter lambda4 = ()->{System.out.println("lambda4");return 100;};int test = lambda4.test();System.out.println(test);/*lambda4100*///有返回值、有一个参数Interfaces.LambdaHaveReturnSingleParameter lambda5 = (int a)->{return a + 2;};int test1 = lambda5.test(10);System.out.println(test1);/*12*///有返回值、多个参数Interfaces.LambdaHaveReturnMultipleParameter lambda6 = (int a, int b)->{return a + b;};int test2 = lambda6.test(10, 20);System.out.println(test2);/*30*/}
}
Lambda语法精简
1、参数:
参数类型:由于在接口中已经定义了参数的类型和数量,所以在Lambda表达式中参数的类型可以省略。
注意:如果需要省略类型,则每一个参数的类型都要省略。千万不要出现省略一个参数,不省略一个参数类型的请况。参数小括号:如果参数列表中,参数的数量只有一个。此时小括号可以省略。
2、方法体
方法大括号:如果方法体中只有一条语句,此时大括号可以省略。
方法体有返回:如果方法体中唯一的一条语句是一个返回语句,则在省略掉大括号的同时也必须省略掉return。
package com.louis.syntax;import com.louis.interfaces.Interfaces;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日16:58*/
public class Syntax2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//语法精简//1、参数类型/*参数类型:由于在接口中已经定义了参数的类型和数量,所以在Lambda表达式中参数的类型可以省略。
` 注意:`如果需要省略类型,则每一个参数的类型都要省略。千万不要出现省略一个参数,不省略一个参数类型的请况。*/Interfaces.LambdaNoneReturnMultipleParameter lambda1 = (a, b)->{System.out.println("Hello Lambda" + (a + b));};lambda1.test(10, 11);/*Hello Lambda21*///2、参数小阔号/*如果参数列表中参数数量只有一个,可以省略小括号*/Interfaces.LambdaNoneReturnSingleParameter lambda2 = a->{System.out.println(a);};lambda2.test(10);/*10*///3、方法大括号:如果方法体中只有一条语句,此时大括号可以省略Interfaces.LambdaNoneReturnSingleParameter lambda3 = a-> System.out.println(a);lambda3.test(12);/*12*///4、方法体有返回:如果方法体中唯一的一条语句是一个返回语句,则在省略掉大括号的同时也必须省略掉return。Interfaces.LambdaHaveReturnNoneParameter lambda4 = ()->13;int test = lambda4.test();System.out.println(test);/*13*/}
}
Lambda语法进阶
方法引用
方法引用:可以将一个Lambda表达式的实现指向一个已经实现的方法。
语法:方法的隶属者::方法名,如果是静态方法,隶属者就是所在类,如果是非静态,隶属者就是所在对象。注意:
- 1、参数数量和类型必须和接口中定义的方法一致
- 2、返回值的类型也一定需要和接口中定义的方法一致
package com.louis.syntax;import com.louis.interfaces.Interfaces;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日17:19*/
public class Syntax3 {public static void main(String[] args) {//方法引用:可以将一个Lambda表达式的实现指向一个已经实现的方法。//语法:方法的隶属者::方法名,如果是静态方法,隶属者就是所在类,如果是非静态,隶属者就是所在对象。/*注意:* 1、参数数量和类型必须和接口中定义的方法一致* 2、返回值的类型也一定需要和接口中定义的方法一致* *//*Interfaces.LambdaHaveReturnSingleParameter lambda = a->a*2;*/Interfaces.LambdaHaveReturnSingleParameter lambda1 = a->change(a);//方法引用:引用了change的方法实现Interfaces.LambdaHaveReturnSingleParameter lambda2 = Syntax3::change;}private static int change(int a){return a*2;}
}
构造方法引用
Person实体类
package com.louis.data;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日17:33*/
public class Person {public String name;public Integer age;public Person(){System.out.println("Person的无参构造方法");}public Person(String name, Integer age){this.age = age;this.name = name;System.out.println("Person类的有参构造执行了");}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
构造方法引用
package com.louis.syntax;import com.louis.data.Person;
import com.louis.interfaces.Interfaces;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日16:36*/
public class Syntax4 {public static void main(String[] args) {PersonCreator creator = ()->new Person();creator.getPerson();/*Person的无参构造方法*///无参构造方法的引用PersonCreator creator1 = Person::new;creator1.getPerson();/*Person的无参构造方法*///有参构造方法的引用PersonCreator1 creator2 = Person::new;creator2.getPerson("louis", 24);/*Person类的有参构造执行了*/}//场景:interface PersonCreator{Person getPerson();}interface PersonCreator1{Person getPerson(String name, int age);}
}
实例
实例1
在一个ArrayList中有若干个Person对象,将这些Person对象按照年龄降序排序
package com.louis.exercise;import com.louis.data.Person;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日17:47*/
public class Exercise1 {//集合排序ArrayListpublic static void main(String[] args) {//场景:已知在一个ArrayList中有若干个Person对象,将这些Person对象按照年龄降序排序ArrayList<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new Person("a", 10));list.add(new Person("b", 8));list.add(new Person("c", 3));list.add(new Person("d", 9));list.add(new Person("e", 7));list.add(new Person("f", 5));list.add(new Person("g", 1));list.sort(((o1, o2) -> o2.age-o1.age));System.out.println(list);/*[Person{name='a', age=10}, Person{name='d', age=9}, Person{name='b', age=8}, Person{name='e', age=7}, Person{name='f', age=5}, Person{name='c', age=3}, Person{name='g', age=1}]*/}
}
实例2
TreeSet:它是一个set集合,但它能够对集合中的内容进行自动排序,如果两个年龄相同只会保留一个,可以添加逻辑进行保留
package com.louis.exercise;import com.louis.data.Person;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.TreeSet;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日17:47*/
public class Exercise2 {//使用Lambda表达式实现Comparator接口// TreeSet:它是一个set集合,但它能够对集合中的内容进行自动排序,如果两个年龄相同只会保留一个,可以添加逻辑进行保留public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet<Person> set = new TreeSet<>((o1, o2)->o2.age-o1.age);set.add(new Person("a", 10));set.add(new Person("b", 8));set.add(new Person("c", 3));set.add(new Person("d", 9));set.add(new Person("e", 7));set.add(new Person("f", 5));set.add(new Person("g", 1));System.out.println(set);/*[Person{name='a', age=10}, Person{name='d', age=9}, Person{name='b', age=8}, Person{name='e', age=7}, Person{name='f', age=5}, Person{name='c', age=3}, Person{name='g', age=1}]*/}
}
实例3
集合遍历
package com.louis.exercise;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日18:08*/
public class Exercise3 {//遍历结合public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8);//将集合中的每一个元素都带入到方法accept中list.forEach(System.out::print);/*12345678*///输出集合中所有的偶数list.forEach(ele->{if(ele%2==0) System.out.print(ele + " ");});/*2 4 6 8*/}
}
实例4
removeIf:移除满足条件的元素
package com.louis.exercise;import com.louis.data.Person;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日18:58*/
public class Exercise4 {public static void main(String[] args) {//需求:删除集合中满足条件的元素ArrayList<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new Person("a", 10));list.add(new Person("b", 8));list.add(new Person("c", 3));list.add(new Person("d", 9));list.add(new Person("e", 7));list.add(new Person("f", 5));list.add(new Person("g", 1));//删除集合中年龄大于5的元素//将集合中的每一个元素都带入到test方法中,如果返回值是true则删除这个元素list.removeIf(ele->ele.age>5);System.out.println(list);/*[Person{name='c', age=3}, Person{name='f', age=5}, Person{name='g', age=1}]*/}
}
实例5
package com.louis.exercise;import com.louis.data.Person;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日17:47*/
public class Exercise5 {public static void main(String[] args) {//线程实例化Thread thread = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.print(i + " ");}});thread.start();/*0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 */}
}
函数式接口
系统内置的函数式接口
1、Predicate<T> :参数T ,返回Boolean
IntPredicate<T> :参数int ,返回Boolean
LongPredicate<T> :参数long ,返回Boolean
DoublePredicate<T> :参数double ,返回Boolean
2、Consumer<T>: 参数T,返回值void
IntConsumer 参数int,返回值void
LongConsumer 参数long,返回值void
DoubleConsumer 参数double,返回值void
3、Function<T, R>:参数T,返回值R–>指定类型的参数、指定类型的返回值
IntFunction< R>:参数int,返回值R
LongFunction< R>:参数long,返回值R
DoubleFunction< R>:参数double,返回值R
IntToLongFunction:参数int,返回值long
IntToDoubleFunction:参数int,返回值double
LongToIntFunction:参数long,返回值int
LongToDoubleFunction:参数long,返回值double
DoubleToIntFunction:参数double,返回值int
DoubleToLongFunction:参数double,返回值long
4、Supplier<T>:无参,返回值T
5、UnaryOperator<T>:参数T,返回值T
6、BinaryOperator<T> :参数T,T,返回值T
7、BiFunction<T, U, R> :参数T,U,返回值R
8、BiPredicate<T, U>:参数T、U 返回值boolean
9、BiConsumer<T, U>:参数T,U返回值void
Stream流
示例
场景:创建一个集合,存储多个字符串元素,完成集合的创建和遍历。
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("张三");
list.add("王大锤");
list.add("张三三");
list.add("张二三");
list.add("李斯");
要求:
- 把所有以"张"开头的元素存储到新集合中
- 把"张"开头,长度为三的元素再存储到新集合中
- 遍历打印最终结果
package com.louis.stream;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日19:07*/
public class StreamDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** 创建集合添加元素,完成以下需求* - 把所有以"张"开头的元素存储到新集合中* - 把"张"开头,长度为三的元素再存储到新集合中* - 遍历打印最终结果*/ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("张三");list.add("王大锤");list.add("张三三");list.add("张三四");list.add("李斯");/* //1、把所有以"张"开头的元素存储到新集合中ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();for (String name : list) {if(name.startsWith("张")){list1.add(name);}}System.out.println(list1);//2、把"张"开头,长度为三的元素再存储到新集合中ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();for (String name : list1) {if(name.length() == 3){list2.add(name);}}//3、遍历打印最终结果for (String name : list2) {System.out.println(name);}*/list.stream().filter(name->name.startsWith("张")).filter(name->name.length() == 3).forEach(name->System.out.println(name));}
}
stream流
流的思想
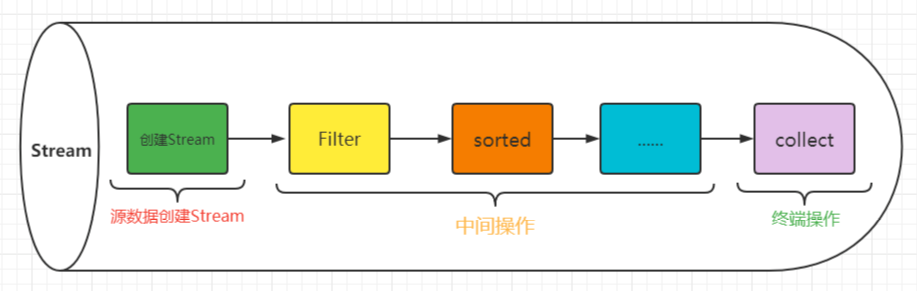
结合Lambda表达式,简化集合、数组的操作。
使用步骤
-
先得到一条stream流(流水线),并把数据放上去
获取方式 方法名 说明 单列集合 default Stream<E> stream() Collecotion中的默认方法 双列集合 无 无法直接使用stream流 数组 public static<T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array) Arrays工具类中的静态方法 一堆零散数据 public static<T> Stream<T> of(T…values) Stream接口中的静态方法 -
使用中间方法对流水线上的数据进行操作
-
使用终结方法对流水线上的数据进行操作
中间方法–>方法调用完毕后,还可以调用其他方法(如:过滤、转换)终结方法–>最后一步,调用完毕之后,不能调用其它方法(如:统计、打印)
示例
单列集合
package com.louis.stream;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.stream.Stream;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日19:07*/
public class StreamDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1、单列集合获取Stream流ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list, "a", "b", "c", "d", "e");//因为Array是Collection中的实现类,所以可以直接使用//获取到一条流水线,并把集合中的数据放到流水线上/* Stream<String> stream = list.stream();//使用终结方法打印流水线上的所有数据stream.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {@Overridepublic void accept(String s) {//s:依次表示流水线上的每一个数据System.out.println(s);}});*/list.stream().forEach(s -> {System.out.println(s);});/** abcdeProcess finished with exit code 0* */}
}
双列集合
package com.louis.stream;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日19:07*/
public class StreamDemo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {//双列集合 无 不能直接使用stream流//1、创建双列集合HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();//2、添加数据map.put(1, "a");map.put(2, "b");map.put(3, "c");map.put(4, "d");//3、获取stream流//方式一:获取键的单列集合map.keySet().stream().forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));/*1234* *///方式二:map.entrySet().stream().forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));/*1=a2=b3=c4=d* */}
}
数组
package com.louis.stream;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日19:07*/
public class StreamDemo4 {public static void main(String[] args) {//数组 public static<T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array) Arrays工具类中的静态方法//1、创建数组int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};//2、获取stream流Arrays.stream(arr).forEach(s-> System.out.print(s + " "));/*1 2 3 4 5 6 */}
}
零散数据
需要注意的是,这些数据的类型必须相同。
package com.louis.stream;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.stream.Stream;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日19:07*/
public class StreamDemo5 {public static void main(String[] args) {//零散的数据Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).forEach(re-> System.out.print(re + " "));/*1 2 3 4 5 */}
}
注意:
Stream接口中静态方法of的使用细节:
方法的形参是一个可变参数,可以传递一堆零散的数据,也可以传递数组。但是数组必须是引用类型,如果传递基本数据类型,会把整个数组当作一个元素,放到Stream当中。
stream流的中间方法
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predict) | 过滤 |
| Stream<T> limit(long maxSize) | 获取前几个元素 |
| Stream<T> skip(long n) | 跳过前几个元素 |
| Stream<T> distinct() | 元素去重,依赖(hashCode和equals方法) |
| static<T> Stream<T> concast(Stream a, Stream b) | 合并a和b两个流为一个流 |
| Stream<R> map(Function<T, R> mapper) | 转换流中的数据类型 |
注意:
- 中间方法,返回新的Stream流,原来的Stream流
只能使用一次,建议使用链式编程 - 修改Stream流中的数据,不会影响原来集合中或者数组中的数据
filter
package com.louis.stream;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.function.Predicate;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日19:07*/
public class StreamDemo6 {public static void main(String[] args) {//filter 过滤ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list,"张三", "张三三", "李斯", "王五");//把姓张的留下list.stream().filter(new Predicate<String>() {@Overridepublic boolean test(String s) {//如果返回值为true,表示当前数据留下//如果返回值为false, 表示当前数据舍弃return s.startsWith("张");}}).forEach(re-> System.out.print(re + " "));/*张三 张三三 */list.stream().filter(s->s.startsWith("张")).forEach(re->{System.out.print(re + " ");});/*张三 张三三 */}
}
limit
list.stream().limit(3).forEach(re-> System.out.print(re + " "));
/*张三 张三三 李斯 */
skip
list.stream().skip(2).forEach(re-> System.out.print(re + " "));
/*李斯 王五 */
distinct
list.add("张三");
System.out.println(list);
list.stream().distinct().forEach(re-> System.out.print(re + " "));
/*[张三, 张三三, 李斯, 王五, 张三]张三 张三三 李斯 王五 */
concat
ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list1, "louis", "khan");
Stream.concat(list.stream(), list1.stream()).forEach(re-> System.out.print(re + " "));
/*张三 张三三 李斯 王五 louis khan */
map
ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list2,"louis-21", "khan-23", "alex-24");
//获取集合中的数字//第一个类型:表示流中原来的数据类型
//第二个类型:表示要转成的之后的类型//apply的形参s:表示流中的每一个数据
//返回值:表示转换之后的数据
//当map方法执行完毕之后,流上的数据就变成了整数,所以在下面forEach当中,s依次表示流里面的每一个数据,但这个数据现在就是整数list2.stream().map(new Function<String, Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer apply(String s) {String tar = s.split("-")[1];return Integer.parseInt(tar);};
}).forEach(re -> System.out.print(re + " "));
*//*21 23 24 *//*list2.stream().map(s -> Integer.parseInt(s.split("-")[1])).forEach(re-> System.out.print(re + " "));
/*21 23 24 */
stream流的终结方法
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void forEach(Consumer action) | 遍历 |
| long count() | 统计 |
| toArray() | 收集流中的数据,放到数组中 |
| collect(Collector collector) | 收集流中的数据,放到集合中 |
forEach
package com.louis.stream;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.function.Consumer;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日8:53*/
public class StreamDemo7 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*** | void forEach(Consumer action) | 遍历 || long count() | 统计 || toArray() | 收集流中的数据,放到数组中 || collect(Collector collector) | 收集流中的数据,放到集合中 |*/ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list,"张三", "张三三", "李斯", "王五");//void forEach(Consumer action)//accept方法形参s:依次表示流里面的每一个数据//方法体:对每一个数据的处理操作(打印)list.stream().forEach(new Consumer<String>() {@Overridepublic void accept(String s) {System.out.print(s + " ");}});*//*张三 张三三 李斯 王五 *//*list.stream().forEach(s -> System.out.print(s + " "));/*张三 张三三 李斯 王五 */ }
}
count
// long count() 统计long count = list.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);
/*4*/
Array
// toArray() 收集流中的数据,放到数组中
Object[] arr1 = list.stream().toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
/*[张三, 张三三, 李斯, 王五]*///指定类型
//IntFunction的泛型:具体类型的数组
//apply的形参:流中数据的个数,要跟数组长度保持一致
//apply的返回值:具体类型的数组
//方法体:就是创建数组
String[] arr2 = list.stream().toArray(new IntFunction<String[]>() {@Overridepublic String[] apply(int value) {return new String[value];}
});System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
/*[张三, 张三三, 李斯, 王五]*/String[] arr3 = list.stream().toArray(value -> new String[value]);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr3));
/*[张三, 张三三, 李斯, 王五]*/
collect
package com.louis.stream;import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月30日19:07*/
public class StreamDemo8 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list, "louis-男-23", "khan-男-24", "alex-女-21", "jonny-女-22");//场景1:收集List集合中所有的男性List<String> newList = list.stream().filter(s -> "男".equals(s.split("-")[1])).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(newList);/*[louis-男-23, khan-男-24]*///场景2:收集Set集合中所有的男性Set<String> newList1 = list.stream().filter(s -> "男".equals(s.split("-")[1])).collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println(newList1);//场景3:收集Map集合中所有的男性,键:姓名、值:年龄Map<String, Integer> map = list.stream().filter(s -> "男".equals(s.split("-")[1]))/** toMap:包含两个参数* 参数一:表示键的生成规则* 参数二:表示值的生成规则** 参数一:* Function泛型一:表示流中每一个数据的类型* 泛型二:表示Map集合中键的数据类型* 方法apply形参:依次表示流里面的每一个数据* 方法体:生成键的代码* 返回值:已经生成的键** 参数二:* Function泛型一:表示流中每一个数据的类型* 泛型二:表示Map集合中键的数据类型* 方法apply形参:依次表示流里面的每一个数据* 方法体:生成值的代码* 返回值:已经生成的值** */.collect(Collectors.toMap(new Function<String, String>() {@Overridepublic String apply(String s) {return s.split("-")[0];}}, new Function<String, Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer apply(String s) {return Integer.parseInt(s.split("-")[2]);}}));System.out.println(map);/*{khan=24, louis=23}*///注意:收集到Map集合当中时,键不能重复,否则会报错Map<String, Integer> map1 = list.stream().filter(s -> "男".equals(s.split("-")[1])).collect(Collectors.toMap(s -> s.split("-")[0], re -> Integer.parseInt(re.split("-")[2])));System.out.println(map1);/*{khan=24, louis=23}*/}
}
实例
package com.louis.practise;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日9:50*/
public class Demo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {/** 定义一个集合,并添加一些整数1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10* 过滤基数,只留下偶数* 并将结果保存起来* */ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);List<Integer> newList = list.stream().filter(s -> s % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(newList);/*[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]*//** 创建一个ArrayList集合,并添加以下字段,字符串中前面时姓名,后面是年龄* "张三, 23"* "李四, 24"* "王五, 25"* 保留年龄大于等于24,并将集合收集到Map集合中,姓名为键,年龄为值* */ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();Collections.addAll(list1, "张三, 23", "李四, 24", "王五, 25");Map<String, String> newList1 = list1.stream().filter(s -> Integer.parseInt(s.split(", ")[1]) >= 24).collect(Collectors.toMap(s -> s.split(", ")[0], re -> re.split(", ")[1]));System.out.println(newList1);/*{李四=24, 王五=25}*//** 现在有两个ArrayList集合* 第一个集合中:存储6名男演员的名字和年龄, 第二个集合中:存储6名女演员的名字和年龄* 姓名和年龄之间使用逗号隔开。如:张三,23* 要求:* 1、男演员只要名字为三个字的前两个人* 2、女演员只要姓杨的,并且不要第一个* 3、把过滤后的男演员姓名和女演员姓名合并到一起* 4、将上面的演员信息封装成一个Actor对象* 5、将所有的演员对象都保存在List集合中* Actor类:只有:name、age* */ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList();Collections.addAll(list2,"张三,23", "李四,24", "周杰伦,30", "刘德华,50", "王宝强,50", "胡歌,45");ArrayList<String> list3 = new ArrayList();Collections.addAll(list3, "杨幂,40", "杨紫,35", "朱丹,45", "柳岩,10", "夏紫,12", "杨演员,35");List<String> newList2 = list2.stream().filter(s -> s.split(",")[0].length() == 3).limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());List<String> newList3 = list3.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("杨")).skip(1).collect(Collectors.toList());List<Actor> listAll = Stream.concat(newList2.stream(), newList3.stream()).map((String s) -> new Actor(s.split(",")[0], Integer.parseInt(s.split(",")[1]))).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(listAll);/*[Actor(name=周杰伦, age=30), Actor(name=刘德华, age=50), Actor(name=杨紫, age=35), Actor(name=杨演员, age=35)]*/}
}
Actor
package com.louis.practise;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;/*** @author XRY* @date 2023年08月31日10:30*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Actor {private String name;private Integer age;
}