文章目录
- 1.RepLoss 设计思想
- 2.RepLoss 主要工作
- 2.1 吸引项
- 2.2 排斥项(RepGT)
- 2.3 排斥项(RepBox)
- 2.4 总结
- 3. yolov5+Repulsion
- 3.1 rep_loss.py
- 3.2 loss.py
- 3.3 hyp.scratch.yaml
- 4. 总结
1.RepLoss 设计思想
物体遮挡问题可以分为类内遮挡和类间遮挡两种情况。类间遮挡产生于扎堆的同类物体,也被称为密集遮挡(crowd occlusion)。
原文连接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.07752
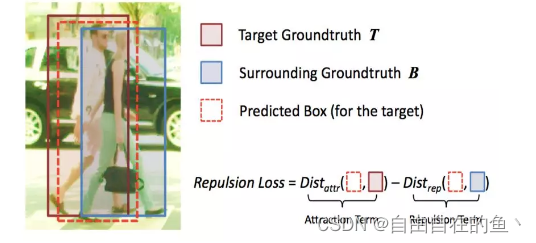
密集遮挡的主要影响表现在显著增加了行人定位的难度。比如,当目标行人 T 被行人 B 遮挡之时,由于两者外观特征相似,检测器很可能无法进行定位。从而本应该框定 T 的边界框转而框定 B,导致定位不准确。更糟糕的是,由于非极大值抑制(non-maximum suppression/NMS)需要进一步处理主要的检测结果,从 T 移走的边界框可能会被 B 的预测框抑制,进而造成 T 漏检。即,人群遮挡使得检测器对 NMS 阈值很敏感:较高的阈值会带来更多的误检(false positives),较低的阈值则造成更多的漏检(missed detection)。这会让大多数实例分割框架失效,因为它们也需要精确的检测结果。因此,如何精确地定位人群之中的每个行人是检测器最为关键的问题之一。
2.RepLoss 主要工作
Reulsion loss完整公式如下:
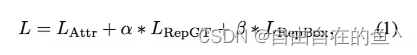
其中 L_Attr 是吸引项,需要预测框靠近其指定目标;L_RepGT 和 L_RepBox 是排斥项,分别需要预测框远离周遭其他的 groundtruth 物体和其他指定目标不同的预测框。系数 α 和 β 充当权重以平衡辅助损失。
第一部分为预测框与真实目标框所产生的损失值(attraction term)
第二部分为预测框与相邻真实目标框所产生的损失值(repulsion term(RepGT))
第三部分为预测框与相邻不是预测同一真实目标的预测框所产生的损失值(repulsion Box(RepBox))
通过两个相关系数alpha和beta来平衡两部分repulsion损失值。
2.1 吸引项
本文沿用 Smooth_L1 构造吸引项。给定一个 proposal P ∈ P_+,把具有极大值 IoU 的 groundtruth box 作为其指定目标:G^P_Attr = arg max_G∈G IoU(G,P)。B^P 是回归自 proposal P 的预测框。由此吸引损失可计算为:

2.2 排斥项(RepGT)
RepGT 损失旨在使 proposal 受到相邻的非目标 groundtruth 物体的排斥。给定一个 proposal P ∈ P_+,它的排斥 groundtruth 物体被定义为除了其指定目标之外带有最大 IoU 区域的 groundtruth 物体。受 IoU 损失的启发,RepGT 损失被计算以惩罚 B^P 和 G^P_Rep 之间的重叠(由 IoG 定义)。IoG(B, G) ∈ [0, 1],从而 RepGT 损失可写为:

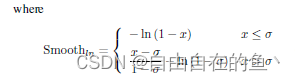
其中 Smooth_ln 是一个在区间 (0, 1) 连续可微分的平滑 ln 函数,σ ∈ [0, 1) 是调节 RepLoss 对异常值的敏感度的平滑参数。由此可见,proposal 越倾向于与非目标 groundtruth 物体重叠,RepGT 损失对边界框回归器的惩罚就越大,从而有效防止边界框移向相邻的非目标物体。
2.3 排斥项(RepBox)
NMS 是绝大多数检测框架中不可或缺的后处理步骤,为降低检测器对 NMS 的敏感度,作者接着提出 RepBox 损失,意在排斥来自不同指定目标的 proposal。RepBox 损失可计算为:
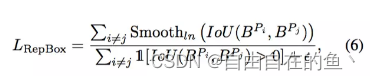
从上式可以看到,为最小化 RepBox 损失,指定目标不同的两个预测框之间的 IoU 区域需要较小。这意味着 RepBox 损失可以降低 NMS 之后不同回归目标的边界框合并为一的概率,使得检测器在密集场景中更鲁棒。
2.4 总结
Repulsion损失函数由三个部分构成,
第一部分主要作用:预测目标框吸引IOU最大的真实目标框,使得预测更加准确;
第二部分主要作用:远离除IOU最大值之外的最大的IOU目标框
第三部分主要作用:预测框之间互相远离;
3. yolov5+Repulsion
在yolov5中使用Repulsion损失函数解决密集且遮挡的物体,亲测可用
3.1 rep_loss.py
在utils下面创建rep_loss.py文件,rep_loss.py内容如下:
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as npclass RepLoss(nn.Module):def __init__(self, alpha=1, beta=1, sigma=0.5):super(RepLoss, self).__init__()self.alpha = alphaself.beta = betaself.sigma = sigmaself.eps = 1e-7def forward(self, gt_boxes, pre_boxes):box_iou = self.bbox_iou(gt_boxes, pre_boxes)proposal_overlaps = self.bbox_iou(pre_boxes, pre_boxes, xywh=False)max_attr, max_attr_index = box_iou.max(dim=0)GT_attr = gt_boxes[max_attr_index]box_iou[max_attr_index, range(pre_boxes.shape[0])] = 0# 判断是否有多个预测目标,若只有一个预测目标和真实目标匹配,则第二项不开启if not box_iou.sum == 0:max_rep, max_rep_index = box_iou.max(dim=0)GT_rep = gt_boxes[max_rep_index]rep_loss = self.Attr(pre_boxes, GT_attr, max_attr) + \self.alpha * self.RepGT(pre_boxes, GT_rep, max_attr) + \self.beta * self.RepBox(proposal_overlaps)else:rep_loss = self.Attr(GT_attr, pre_boxes, max_attr) + self.beta*self.RepBox(proposal_overlaps)return rep_lossdef Attr(self, gt_boxes, pre_boxes, max_iou):Attr_loss = 0for index, (gt_box, pre_box) in enumerate(zip(gt_boxes, pre_boxes)):# if max_iou[index] > self.sigma:Attr_loss += self.SmoothL1(gt_box, pre_box)Attr_loss = Attr_loss.sum() / len(gt_boxes)return Attr_lossdef RepGT(self, gt_boxes, pre_boxes, max_iou):RepGT_loss = 0count = 0for index, (gt_box, pre_box) in enumerate(zip(gt_boxes, pre_boxes)):# if max_iou[index] > self.sigma:count += 1IOG = self.RepGT_iog(gt_box, pre_box)if IOG > self.sigma:RepGT_loss += ((IOG - self.sigma) / ((1 - self.sigma) - math.log(1 - self.sigma))).sum()else:RepGT_loss += -(1 - IOG).clamp(min=self.eps).log().sum()RepGT_loss = RepGT_loss.sum() / countreturn RepGT_lossdef RepBox(self, overlaps):RepBox_loss = 0overlap_loss =0count = 0#result = overlaps.triu(1)for i in range(0, overlaps.shape[0]):for j in range(1 + i, overlaps.shape[0]):count += 1if overlaps[i][j] > self.sigma:RepBox_loss += ((overlaps[i][j] - self.sigma) / ((1 - self.sigma) - math.log(1 - self.sigma))).sum()else:RepBox_loss += -(1 - overlaps[i][j]).clamp(min=self.eps).log().sum()RepBox_loss = RepBox_loss / countreturn RepBox_lossdef SmoothL1(self, pred, target, beta=1.0):diff = torch.abs(pred - target)cond = torch.lt(diff, beta)loss = torch.where(cond, 0.5 * diff ** 2 / beta, diff - 0.5 * beta)return lossdef RepGT_iog(self, box1, box2, List=True):if List: # transform from xywh to xyxyb1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]else: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[:, 0], box1[:, 1], box1[:, 2], box1[:, 3]b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[:, 0], box2[:, 1], box2[:, 2], box2[:, 3]# Intersection areainter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)# g_area Areag_area = torch.abs(b2_x2 - b2_x1) * torch.abs(b2_y2 - b2_y1)# IoUiog = inter / g_areareturn iogdef bbox_iou(self, bboxes1, bboxes2, xywh=True, eps=1e-7):if xywh:# chunk(4, -1)表示在最后一个维度上切块(x1, y1, w1, h1), (x2, y2, w2, h2) = bboxes1.chunk(4, -1), bboxes2.chunk(4, -1)bboxes1[:, 0:1], bboxes1[:, 1:2], bboxes1[:, 2:3], bboxes1[:,3:4] = x1 - w1 / 2, y1 - h1 / 2, x1 + w1 / 2, y1 + h1 / 2bboxes2[:, 0:1], bboxes2[:, 1:2], bboxes2[:, 2:3], bboxes2[:,3:4] = x2 - w2 / 2, y2 - h2 / 2, x2 + w2 / 2, y2 + h2 / 2lt = torch.max(bboxes1[:, None, :2], bboxes2[:, :2]) # [rows, cols, 2]rb = torch.min(bboxes1[:, None, 2:], bboxes2[:, 2:]) # [rows, cols, 2]wh = (rb - lt + 1).clamp(min=0) # [rows, cols, 2]overlap = wh[:, :, 0] * wh[:, :, 1]area1 = (bboxes1[:, 2] - bboxes1[:, 0] + 1) * (bboxes1[:, 3] - bboxes1[:, 1] + 1)area2 = (bboxes2[:, 2] - bboxes2[:, 0] + 1) * (bboxes2[:, 3] - bboxes2[:, 1] + 1)ious = overlap / (area1[:, None] + area2 - overlap).clamp(min=eps) # 会产生大于1的值???return ious.clamp(min=eps, max=1)3.2 loss.py
需要在loss.py中修改代码,调用rep_loss.py中的Repulsion损失函数,找到class ComputeLoss修改如下:
class ComputeLoss:sort_obj_iou = False# Compute lossesdef __init__(self, model, autobalance=False):device = next(model.parameters()).device # get model deviceh = model.hyp # hyperparameters# Define criteriaBCEcls = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.tensor([h['cls_pw']], device=device))BCEobj = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=torch.tensor([h['obj_pw']], device=device))# Class label smoothing https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.04103.pdf eqn 3self.cp, self.cn = smooth_BCE(eps=h.get('label_smoothing', 0.0)) # positive, negative BCE targets# Focal lossg = h['fl_gamma'] # focal loss gammaif g > 0:BCEcls, BCEobj = FocalLoss(BCEcls, g), FocalLoss(BCEobj, g)m = de_parallel(model).model[-1] # Detect() moduleself.balance = {3: [4.0, 1.0, 0.4]}.get(m.nl, [4.0, 1.0, 0.25, 0.06, 0.02]) # P3-P7self.ssi = list(m.stride).index(16) if autobalance else 0 # stride 16 indexself.BCEcls, self.BCEobj, self.gr, self.hyp, self.autobalance = BCEcls, BCEobj, 1.0, h, autobalanceself.na = m.na # number of anchorsself.nc = m.nc # number of classesself.nl = m.nl # number of layersself.anchors = m.anchorsself.device = deviceself.rep_loss = RepLoss(alpha=0.5, beta=0.5, sigma=0.5)def __call__(self, p, targets): # predictions, targetslcls = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device) # class losslbox = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device) # box losslobj = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device) # object losstcls, tbox, indices, anchors = self.build_targets(p, targets) # targetspre_boxes = []bs = p[0].shape[0]if self.hyp['Reploss']:lrep = torch.zeros(1, device=self.device)gt_boxes = targets# Lossesfor i, pi in enumerate(p): # layer index, layer predictionsb, a, gj, gi = indices[i] # image, anchor, gridy, gridxtobj = torch.zeros(pi.shape[:4], dtype=pi.dtype, device=self.device) # target objn = b.shape[0] # number of targetsif n:# pxy, pwh, _, pcls = pi[b, a, gj, gi].tensor_split((2, 4, 5), dim=1) # faster, requires torch 1.8.0# 将pi的内部信息划分为cx,cy,wh,_,clspxy, pwh, _, pcls = pi[b, a, gj, gi].split((2, 2, 1, self.nc), 1) # target-subset of predictions# Regressionpxy = pxy.sigmoid() * 2 - 0.5pwh = (pwh.sigmoid() * 2) ** 2 * anchors[i]pbox = torch.cat((pxy, pwh), 1) # predicted boxiou = bbox_iou(pbox, tbox[i], EIoU=True).squeeze() # iou(prediction, target)lbox += (1.0 - iou).mean() # iou lossif self.hyp['Reploss']:pre_box = torch.cat((b[:, None],(pbox[:, 0] + gi)[:, None] / pi.shape[3], (pbox[:, 1] + gj)[:, None] / pi.shape[2],(pbox[:, 2])[:, None] / pi.shape[3], (pbox[:, 3])[:, None] / pi.shape[2]), 1)pre_boxes.append(pre_box)# Objectnessiou = iou.detach().clamp(0).type(tobj.dtype)if self.sort_obj_iou:j = iou.argsort()b, a, gj, gi, iou = b[j], a[j], gj[j], gi[j], iou[j]if self.gr < 1:iou = (1.0 - self.gr) + self.gr * ioutobj[b, a, gj, gi] = iou # iou ratio# Classificationif self.nc > 1: # cls loss (only if multiple classes)t = torch.full_like(pcls, self.cn, device=self.device) # targetst[range(n), tcls[i]] = self.cplcls += self.BCEcls(pcls, t) # BCE# Append targets to text file# with open('targets.txt', 'a') as file:# [file.write('%11.5g ' * 4 % tuple(x) + '\n') for x in torch.cat((txy[i], twh[i]), 1)]obji = self.BCEobj(pi[..., 4], tobj)lobj += obji * self.balance[i] # obj lossif self.autobalance:self.balance[i] = self.balance[i] * 0.9999 + 0.0001 / obji.detach().item()if self.hyp['Reploss'] and len(pre_boxes) != 0:pre_boxes = torch.cat(pre_boxes)for i in range(bs):gt_index = gt_boxes[:, 0] == igt_batch_boxes = gt_boxes[gt_index, 2:]pre_index = pre_boxes[:, 0] == iprd_batch_boxes = pre_boxes[pre_index, 1:]if len(prd_batch_boxes) != 0 and len(prd_batch_boxes) != 0:lrep += self.rep_loss(gt_batch_boxes, prd_batch_boxes)lrep = lrep / bslrep *= self.hyp['rep']if self.autobalance:self.balance = [x / self.balance[self.ssi] for x in self.balance]lbox *= self.hyp['box']lobj *= self.hyp['obj']lcls *= self.hyp['cls']bs = tobj.shape[0] # batch sizeif self.hyp['Reploss']:return (lbox + lobj + lcls + lrep) * bs, torch.cat((lbox, lobj, lcls, lrep)).detach()else:return (lbox + lobj + lcls) * bs, torch.cat((lbox, lobj, lcls)).detach()def build_targets(self, p, targets):# Build targets for compute_loss(), input targets(image,class,x,y,w,h)na, nt = self.na, targets.shape[0] # number of anchors, targetstcls, tbox, indices, anch = [], [], [], []gain = torch.ones(7, device=self.device) # normalized to gridspace gainai = torch.arange(na, device=self.device).float().view(na, 1).repeat(1, nt) # same as .repeat_interleave(nt)targets = torch.cat((targets.repeat(na, 1, 1), ai[..., None]), 2) # append anchor indicesg = 0.5 # biasoff = torch.tensor([[0, 0],[1, 0],[0, 1],[-1, 0],[0, -1], # j,k,l,m# [1, 1], [1, -1], [-1, 1], [-1, -1], # jk,jm,lk,lm],device=self.device).float() * g # offsetsfor i in range(self.nl):anchors, shape = self.anchors[i], p[i].shapegain[2:6] = torch.tensor(shape)[[3, 2, 3, 2]] # xyxy gain# Match targets to anchorst = targets * gain # shape(3,n,7)if nt:# Matchesr = t[..., 4:6] / anchors[:, None] # wh ratioj = torch.max(r, 1 / r).max(2)[0] < self.hyp['anchor_t'] # compare# j = wh_iou(anchors, t[:, 4:6]) > model.hyp['iou_t'] # iou(3,n)=wh_iou(anchors(3,2), gwh(n,2))t = t[j] # filter# Offsetsgxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xygxi = gain[[2, 3]] - gxy # inversej, k = ((gxy % 1 < g) & (gxy > 1)).Tl, m = ((gxi % 1 < g) & (gxi > 1)).Tj = torch.stack((torch.ones_like(j), j, k, l, m))t = t.repeat((5, 1, 1))[j]offsets = (torch.zeros_like(gxy)[None] + off[:, None])[j]else:t = targets[0]offsets = 0# Definebc, gxy, gwh, a = t.chunk(4, 1) # (image, class), grid xy, grid wh, anchorsa, (b, c) = a.long().view(-1), bc.long().T # anchors, image, classgij = (gxy - offsets).long()gi, gj = gij.T # grid indices# Appendindices.append((b, a, gj.clamp_(0, shape[2] - 1), gi.clamp_(0, shape[3] - 1))) # image, anchor, gridtbox.append(torch.cat((gxy - gij, gwh), 1)) # boxanch.append(anchors[a]) # anchorstcls.append(c) # classreturn tcls, tbox, indices, anch
3.3 hyp.scratch.yaml
在配置文件中引入超参:
Reploss: True# True开启Reploss,False关闭Reploss
rep: 2 # Reploss权重
4. 总结
上述代码经测试可以正常使用,本人在测试时只开启前两项吸引项+排斥项(RepGT),训练速度非常慢,需要一直计算IOU。
没有使用第三项排斥项(RepBox)原因:当物体非常密集时,所有预测框之间非常接近,若开启第三项则所有的预测框互相远离,会导致预测结果与真是目标框位置偏差,并且第三项计算量很大。