本文介绍Embeddings的基本概念,并使用最少但完整的代码讲解Embeddings是如何使用的,帮你打造专属AI聊天机器人(智能客服),你可以拿到该代码进行修改以满足实际需求。
ChatGPT的Embeddings解决了什么问题?
如果直接问ChatGPT:What is langchain? If you do not know please do not answer.,由于ChatGPT不知道2021年9月份之后的事情,而langchain比较新,是在那之后才有的,所以ChatGPT会回答不知道:
I’m sorry, but I don’t have any information on “langchain.” It appears to be a term that is not widely recognized or used in general knowledge.
如果我们用上Embeddings,用上面的问题提问,它可以给出答案:
LangChain is a framework for developing applications powered by language models.
有了这个技术,我们就可以对自己的文档进行提问,从而拓展ChatGPT的知识范围,打造定制化的AI智能客服。例如在官网接入ChatGPT,根据网站的文档让他回答用户的问题。
Embeddings相关基本概念介绍
什么是Embeddings?
在跳进代码之前,先简要介绍一下什么是Embeddings。在介绍Embeddings之前我们需要先学习一下「向量」这个概念。
我们可以将一个事物从多个维度来描述,例如声音可以从「时域」和「频域」来描述(傅里叶变换可能很多人都听过),维度拆分的越多就越能描述一个事物,在向量空间上的接近往往意味着这两个事物有更多的联系,而向量空间又是比较好计算的,于是我们可以通过计算向量来判断事物的相似程度。
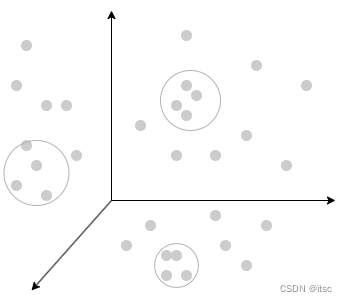
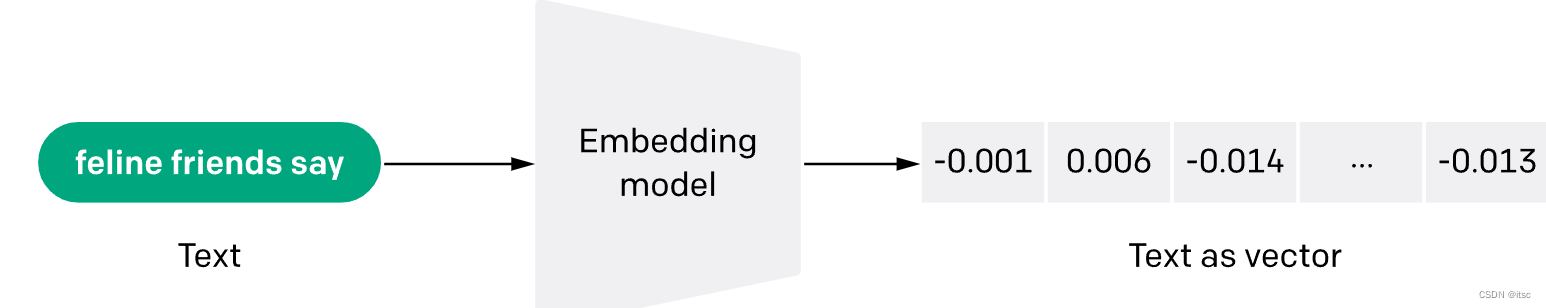
在自然语言处理 (NLP) 的中,Embeddings是将单词或句子转换为数值向量的一种方法。这些向量捕获单词或句子的语义,使我们能够对它们执行数学运算。例如,我们可以计算两个向量之间的余弦相似度来衡量它们在语义上的相似程度。
Embeddings使用流程讲解
如何让ChatGPT回答没有训练过的内容?流程如下,一图胜千言。
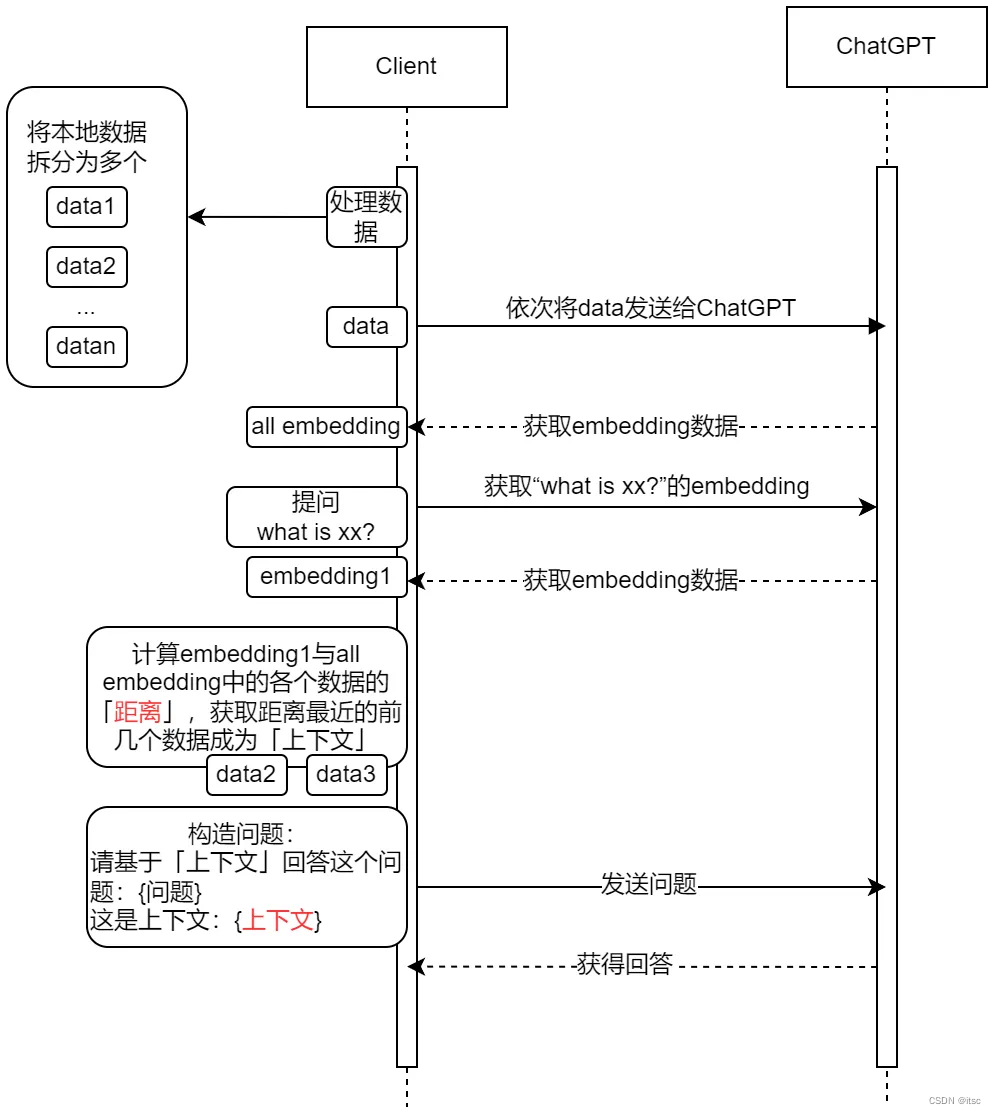
分步解释:
- 首先是获取本地数据的embeddings结果,由于一次embeddings调用的token数量是有限制的,先将数据进行分段然后以依次行调用获得所有数据的embeddings结果。
- 然后我们开始提问,同样的,将提问的内容也做一次embedding,得到一个结果。
- 再将提问的intending结果和之前所有数据的embedded结果进行距离的计算,这里的距离就是指向量之间的距离,然后我们获取距离最近的几段段数据来作为我们提问的「上下文」(例如这里找到data2/data3是和问题最相关的内容)。
- 获得上下文之后我们开始构造真正的问题,问题会将上下文也附属在后面一并发送给chat gpt,这样它就可以回答之前不知道的问题了。
总结来说:
之所以能够让ChatGPT回答他不知道的内容,其实是因为我们把相关的上下文传递给了他,他从上下文中获取的答案。如何确定要发送哪些上下文给他,就是通过计算向量距离得到的。
embedding实战代码(python)
让我来看看实际的代码。
前置条件
- Python 3.6 或更高版本。
- OpenAI API 密钥,或者其他提供API服务的也可以。
- 安装了以下 Python 软件包:
requests、beautifulsoup4、pandas、tiktoken、openai、numpy。 - 私有文本数据集。在这个示例中,使用名为
langchainintro.txt的文本文件,这里面是langchain官网的一些文档说明,文档比较新所以ChatGPT肯定不知道,以此来测试效果。
代码:
代码来自于OpenAI官网,我做了一些改动和精简。
import os
import numpy as np
import openai
import pandas as pd
import tiktoken
from ast import literal_eval
from openai.embeddings_utils import distances_from_embeddings
import tracebacktokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("cl100k_base")def get_api_key():return os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY')def set_openai_config():openai.api_key = get_api_key()openai.api_base = "https://openai.api2d.net/v1"def remove_newlines(serie):serie = serie.str.replace('\n', ' ')serie = serie.str.replace('\\n', ' ')serie = serie.str.replace(' ', ' ')serie = serie.str.replace(' ', ' ')return seriedef load_text_files(file_name):with open(file_name, "r", encoding="UTF-8") as f:text = f.read()return textdef prepare_directory(dir_name="processed"):if not os.path.exists(dir_name):os.mkdir(dir_name)def split_into_many(text, max_tokens):# Split the text into sentencessentences = text.split('. ')# Get the number of tokens for each sentencen_tokens = [len(tokenizer.encode(" " + sentence)) for sentence in sentences]chunks = []tokens_so_far = 0chunk = []# Loop through the sentences and tokens joined together in a tuplefor sentence, token in zip(sentences, n_tokens):# If the number of tokens so far plus the number of tokens in the current sentence is greater# than the max number of tokens, then add the chunk to the list of chunks and reset# the chunk and tokens so farif tokens_so_far + token > max_tokens:chunks.append(". ".join(chunk) + ".")chunk = []tokens_so_far = 0# If the number of tokens in the current sentence is greater than the max number of# tokens, split the sentence into smaller parts and add them to the chunkwhile token > max_tokens:part = sentence[:max_tokens]chunk.append(part)sentence = sentence[max_tokens:]token = len(tokenizer.encode(" " + sentence))# Otherwise, add the sentence to the chunk and add the number of tokens to the totalchunk.append(sentence)tokens_so_far += token + 1# Add the last chunk to the list of chunksif chunk:chunks.append(". ".join(chunk) + ".")return chunksdef shorten_texts(df, max_tokens):shortened = []# Loop through the dataframefor row in df.iterrows():# If the text is None, go to the next rowif row[1]['text'] is None:continue# If the number of tokens is greater than the max number of tokens, split the text into chunksif row[1]['n_tokens'] > max_tokens:shortened += split_into_many(row[1]['text'], max_tokens)# Otherwise, add the text to the list of shortened textselse:shortened.append(row[1]['text'])df = pd.DataFrame(shortened, columns=['text'])df['n_tokens'] = df.text.apply(lambda x: len(tokenizer.encode(x)))return dfdef create_embeddings(df):df['embeddings'] = df.text.apply(lambda x: openai.Embedding.create(input=x, engine='text-embedding-ada-002')['data'][0]['embedding'])df.to_csv('processed/embeddings.csv')return dfdef load_embeddings():df = pd.read_csv('processed/embeddings.csv', index_col=0)df['embeddings'] = df['embeddings'].apply(literal_eval).apply(np.array)return dfdef create_context(question, df, max_len=1800, size="ada"
):"""Create a context for a question by finding the most similar context from the dataframe"""# print(f'start create_context')# Get the embeddings for the questionq_embeddings = openai.Embedding.create(input=question, engine='text-embedding-ada-002')['data'][0]['embedding']# print(f'q_embeddings:{q_embeddings}')# Get the distances from the embeddingsdf['distances'] = distances_from_embeddings(q_embeddings, df['embeddings'].values, distance_metric='cosine')# print(f'df[distances]:{df["distances"]}')returns = []cur_len = 0# Sort by distance and add the text to the context until the context is too longfor i, row in df.sort_values('distances', ascending=True).iterrows():# print(f'i:{i}, row:{row}')# Add the length of the text to the current lengthcur_len += row['n_tokens'] + 4# If the context is too long, breakif cur_len > max_len:break# Else add it to the text that is being returnedreturns.append(row["text"])# Return the contextreturn "\n\n###\n\n".join(returns)def answer_question(df,model="text-davinci-003",question="Am I allowed to publish model outputs to Twitter, without a human review?",max_len=1800,size="ada",debug=False,max_tokens=150,stop_sequence=None
):"""Answer a question based on the most similar context from the dataframe texts"""context = create_context(question,df,max_len=max_len,size=size,)# If debug, print the raw model responseif debug:print("Context:\n" + context)print("\n\n")prompt = f"Answer the question based on the context below, \n\nContext: {context}\n\n---\n\nQuestion: {question}\nAnswer:"messages = [{'role': 'user','content': prompt}]try:# Create a completions using the questin and contextresponse = openai.ChatCompletion.create(messages=messages,temperature=0,max_tokens=max_tokens,stop=stop_sequence,model=model,)return response["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]except Exception as e:# print stacktraceback.print_exc()print(e)return ""def main():# 设置API keyset_openai_config()# 载入本地数据texts = []text = load_text_files("langchainintro.txt")texts.append(('langchainintro', text))prepare_directory("processed")# 创建一个dataframe,包含fname和text两列df = pd.DataFrame(texts, columns=['fname', 'text'])df['text'] = df.fname + ". " + remove_newlines(df.text)df.to_csv('processed/scraped.csv')# 计算token数量df.columns = ['title', 'text']df['n_tokens'] = df.text.apply(lambda x: len(tokenizer.encode(x)))# print(f'{df}')df = shorten_texts(df, 500)# 如果processed/embeddings.csv已经存在,直接load,不存在则createif os.path.exists('processed/embeddings.csv'):df = load_embeddings()else:df = create_embeddings(df)print(f"What is langchain? If you do not know please do not answer.")ans = answer_question(df, model='gpt-3.5-turbo', question="What is langchain? If you do not know please do not answer.", debug=False)print(f'ans:{ans}')if __name__ == '__main__':main()代码流程与时序图的流程基本一致,注意api_key需要放入环境变量,也可以自己改动。
如果直接问ChatGPT:What is langchain? If you do not know please do not answer.,ChatGPT会回答不知道:
I’m sorry, but I don’t have any information on “langchain.” It appears to be a term that is not widely recognized or used in general knowledge.
运行上面的代码,它可以给出答案:
LangChain is a framework for developing applications powered by language models.
可以看到它使用了我们提供的文档来回答。
拓展
- 注意token消耗,如果你的本地数据非常多,embedding阶段将会消耗非常多的token,请注意使用。
- embedding阶段仍然会将本地数据传给ChatGPT,如果你有隐私需求,需要注意。
- 一般生产环境会将向量结果存入「向量数据库」而不是本地文件,此处为了演示直接使用的文本文件存放。




![[npm]脚手架本地全局安装1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4f644e247d664a5a9deedc89a76118ba.png)