文章目录
- 第三课 哈希表、集合、映射
- lc1.两数之和--简单
- 题目描述
- 代码展示
- lc30.串联所有单词的子串--困难
- 题目描述
- 代码展示
- lc49.字母异位分组--中等
- 题目描述
- 代码展示
- lc874.模拟行走机器人--中等
- 题目描述
- 代码展示
- lc146.LRU缓存--中等
- 题目描述
- 相关补充
- 思路讲解
- 代码展示
- 图示理解
第三课 哈希表、集合、映射
lc1.两数之和–简单
题目描述
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
输出:[0,1]
解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6
输出:[0,1]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 104-109 <= nums[i] <= 109-109 <= target <= 109- 只会存在一个有效答案
代码展示
class Solution {
public: //HaspMap实现vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& numbers, int target) {// j < i// for i = 0 ~ n - 1:// search if (target - numbers[i]) exists in numbers[0..i-1]unordered_map<int, int> value_to_index; // 值到下标的映射for (int i = 0; i < numbers.size(); i++) {// 不等于尾部,就是找到了,存在// Java: value_to_index.containsKey(target-numbers[i])// Pythong: target-numbers[i] in value_to_indexif (value_to_index.find(target - numbers[i]) != value_to_index.end()) {return {value_to_index[target - numbers[i]], i};}// 边循环i,边插入,维护的是对于numbers[0..i-1]的映射// 本质上是在i之前查找,防止查找i本身value_to_index[numbers[i]] = i;}return {};}
};
lc30.串联所有单词的子串–困难
题目描述
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串数组 words。 words 中所有字符串 长度相同。
s 中的 串联子串 是指一个包含 words 中所有字符串以任意顺序排列连接起来的子串。
- 例如,如果
words = ["ab","cd","ef"], 那么"abcdef","abefcd","cdabef","cdefab","efabcd", 和"efcdab"都是串联子串。"acdbef"不是串联子串,因为他不是任何words排列的连接。
返回所有串联子串在 s 中的开始索引。你可以以 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"]
输出:[0,9]
解释:因为 words.length == 2 同时 words[i].length == 3,连接的子字符串的长度必须为 6。
子串 "barfoo" 开始位置是 0。它是 words 中以 ["bar","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。
子串 "foobar" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。
输出顺序无关紧要。返回 [9,0] 也是可以的。
示例 2:
输入:s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"]
输出:[]
解释:因为 words.length == 4 并且 words[i].length == 4,所以串联子串的长度必须为 16。
s 中没有子串长度为 16 并且等于 words 的任何顺序排列的连接。
所以我们返回一个空数组。
示例 3:
输入:s = "barfoofoobarthefoobarman", words = ["bar","foo","the"]
输出:[6,9,12]
解释:因为 words.length == 3 并且 words[i].length == 3,所以串联子串的长度必须为 9。
子串 "foobarthe" 开始位置是 6。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar","the"] 顺序排列的连接。
子串 "barthefoo" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["bar","the","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。
子串 "thefoobar" 开始位置是 12。它是 words 中以 ["the","foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1041 <= words.length <= 50001 <= words[i].length <= 30words[i]和s由小写英文字母组成
代码展示
class Solution {
public: //测试用例通过了,但耗时太长。vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {wordsMap = countWords(words);int tot = words.size() * words[0].size();vector<int> ans;// 枚举开始位置for (int start = 0; start + tot <= s.length(); start++) {if (isSame(s.substr(start, tot), words)) {ans.push_back(start);}}return ans;}private:unordered_map<string, int> wordsMap;// 想判断一个字符串t,是否由words拼成// 把t分解成若干个单词,然后看跟words数组是否相同(顺序无关)bool isSame(string t, vector<string>& words) {// cout << "isSame: " << t << " and words" << endl;int m = words[0].length(); // 每个单词的长度unordered_map<string, int> tMap; // 单词出现次数// 把t,每m个字符分解成一个单词// foothe 分解为 foo, thefor (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i += m) {// i开始的m个字符,组成一个单词tMap[t.substr(i, m)]++;}return equals(tMap, wordsMap);}// 判断两个map是否一样的方法// a.size() == b.size()// size: key的个数// a里面有的b里全有,且值一样bool equals(unordered_map<string, int>& a, unordered_map<string, int>& b) {if (a.size() != b.size()) return false;for (auto& key_value_pair : a) {auto& key = key_value_pair.first;auto& value = key_value_pair.second;// 如果b里面没有,或者value不相等(次数不一样)if (b.find(key) == b.end() || value != b[key]) return false;}return true;}unordered_map<string, int> countWords(vector<string>& words) {unordered_map<string, int> ans;for (string& word : words) {ans[word]++;}return ans;}
};//bar foo
//arf oot
//rfo oth
//...
优化方法:
class Solution {
public: //优化解法vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {vector<int> ans;words_map = getMap(words);int n = s.size();int m = words[0].size();int tot = m * words.size();for (int first = 0; first < m; first++) {if (first + tot > n) break;unordered_map<string, int> s_map;int curr = first;for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); i++) {s_map[s.substr(curr, m)]++;curr += m;}for (int start = first, end = curr; start + tot <= n; start += m, end += m) {if (isSame(s_map, words_map)) ans.push_back(start);s_map[s.substr(end, m)]++;s_map[s.substr(start, m)]--;}}return ans;}private:unordered_map<string, int> getMap(vector<string>& words) {unordered_map<string, int> res;for (string& word : words) {res[word]++;}return res;}bool isSame(unordered_map<string, int>& a, unordered_map<string, int>& b) {for (auto& pr : a) {if (b[pr.first] != pr.second) return false;}for (auto& pr : b) {if (a[pr.first] != pr.second) return false;}return true;}unordered_map<string, int> words_map;
};
lc49.字母异位分组–中等
题目描述
给你一个字符串数组,请你将 字母异位词 组合在一起。可以按任意顺序返回结果列表。
字母异位词 是由重新排列源单词的所有字母得到的一个新单词。
示例 1:
输入: strs = ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"]
输出: [["bat"],["nat","tan"],["ate","eat","tea"]]
示例 2:
输入: strs = [""]
输出: [[""]]
示例 3:
输入: strs = ["a"]
输出: [["a"]]
提示:
1 <= strs.length <= 1040 <= strs[i].length <= 100strs[i]仅包含小写字母
代码展示
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {// HashMap可用于分组// 从排序以后的字符串(aet)到一个数组(["ate","eat","tea"])的mapunordered_map<string, vector<string>> group;for (string& str : strs) {string copy = str;// 字符串里面的字符排序// Java: toCharArray()sort(copy.begin(), copy.end());// 分组group[copy].push_back(str);// cout << "Added " << str << " into group " << copy << endl;}vector<vector<string>> ans;// Java .keySet()// Python for .. in ...for (auto pr : group) {// pr.first == key// pr.second == valueans.push_back(pr.second);}return ans;}// 字符串长度分别是n1, n2, n3,....,总和是n// n1 log n1 + n2 log n2 + ....// <= n1 log n + n2 log n + ....// = (n1 + n2 + ...) log n// = n log n
};/*
["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"]
["aet", "aet", "ant", "aet", "ant", "abt"]
*/
lc874.模拟行走机器人–中等
题目描述
机器人在一个无限大小的 XY 网格平面上行走,从点 (0, 0) 处开始出发,面向北方。该机器人可以接收以下三种类型的命令 commands :
-2:向左转90度-1:向右转90度1 <= x <= 9:向前移动x个单位长度
在网格上有一些格子被视为障碍物 obstacles 。第 i 个障碍物位于网格点 obstacles[i] = (xi, yi) 。
机器人无法走到障碍物上,它将会停留在障碍物的前一个网格方块上,并继续执行下一个命令。
返回机器人距离原点的 最大欧式距离 的 平方 。(即,如果距离为 5 ,则返回 25 )
注意:
- 北方表示 +Y 方向。
- 东方表示 +X 方向。
- 南方表示 -Y 方向。
- 西方表示 -X 方向。
- 原点 [0,0] 可能会有障碍物。
示例 1:
输入:commands = [4,-1,3], obstacles = []
输出:25
解释:
机器人开始位于 (0, 0):
1. 向北移动 4 个单位,到达 (0, 4)
2. 右转
3. 向东移动 3 个单位,到达 (3, 4)
距离原点最远的是 (3, 4) ,距离为 32 + 42 = 25
示例 2:
输入:commands = [4,-1,4,-2,4], obstacles = [[2,4]]
输出:65
解释:机器人开始位于 (0, 0):
1. 向北移动 4 个单位,到达 (0, 4)
2. 右转
3. 向东移动 1 个单位,然后被位于 (2, 4) 的障碍物阻挡,机器人停在 (1, 4)
4. 左转
5. 向北走 4 个单位,到达 (1, 8)
距离原点最远的是 (1, 8) ,距离为 12 + 82 = 65
示例 3:
输入:commands = [6,-1,-1,6], obstacles = []
输出:36
解释:机器人开始位于 (0, 0):
1. 向北移动 6 个单位,到达 (0, 6).
2. 右转
3. 右转
4. 向南移动 6 个单位,到达 (0, 0).
机器人距离原点最远的点是 (0, 6),其距离的平方是 62 = 36 个单位。
提示:
1 <= commands.length <= 104commands[i]的值可以取-2、-1或者是范围[1, 9]内的一个整数。0 <= obstacles.length <= 104-3 * 104 <= xi, yi <= 3 * 104- 答案保证小于
231
代码展示
class Solution {
public:int robotSim(vector<int>& commands, vector<vector<int>>& obstacles) {// {(x1,y1), (x2,y2), ...}// (-200, 30000)// string: "-200,30000"// long long: (-200, 300) --> (-200+30000, 300+30000) --> (-200+30000)*60000 + 300 + 30000unordered_set<long long> blockers;for (auto& obstacle : obstacles) {blockers.insert(calcHash(obstacle[0], obstacle[1]));}// 方向数组技巧// N, E, S, Wint dx[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; // 偏移量(单位向量)int dy[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};int x = 0, y = 0;int dir = 0; // Nint ans = 0;for (int cmd : commands) {if (cmd > 0) {for (int i = 0; i < cmd; i++) {// 尝试走到nextx, nexty// 想向dir走一步,就加dir方向的偏移量int nextx = x + dx[dir];int nexty = y + dy[dir];// 有障碍物// calcHash(nextx, nexty) in blockersif (blockers.find(calcHash(nextx, nexty)) != blockers.end()) {break;}// 走一步x = nextx;y = nexty;ans = max(ans, x * x + y * y);}} else if (cmd == -1) {// 0->1->2->3->0 // N->E->S->W->N// 右转(顺时针)dir = (dir + 1) % 4;} else {// 左转,避免负数,加一个mod数dir = (dir - 1 + 4) % 4;}}return ans;}private:/*string calcHash(int x, int y) {return to_string(x) + "," + to_string(y);}*/long long calcHash(int x, int y) {return (x + 30000) * 60000ll + y + 30000; }
};
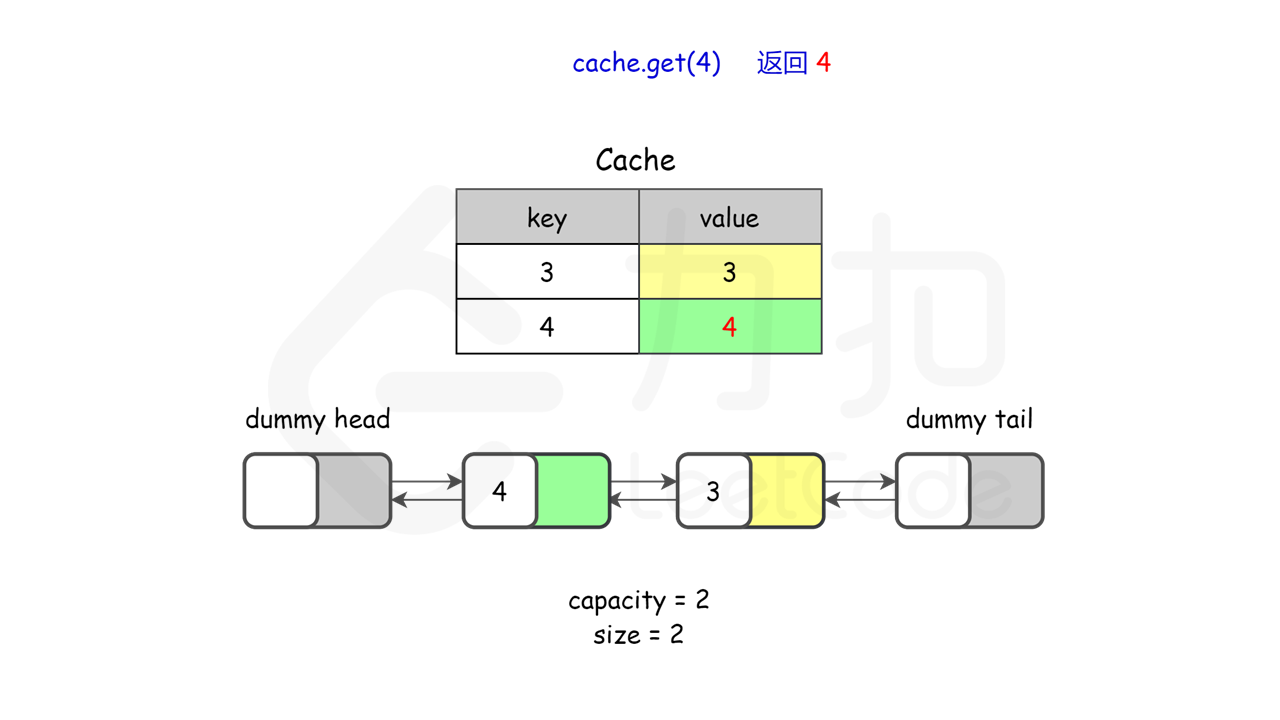
lc146.LRU缓存–中等
题目描述
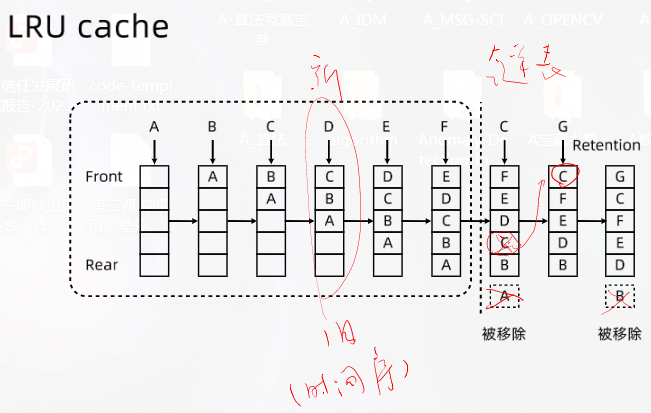
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]解释
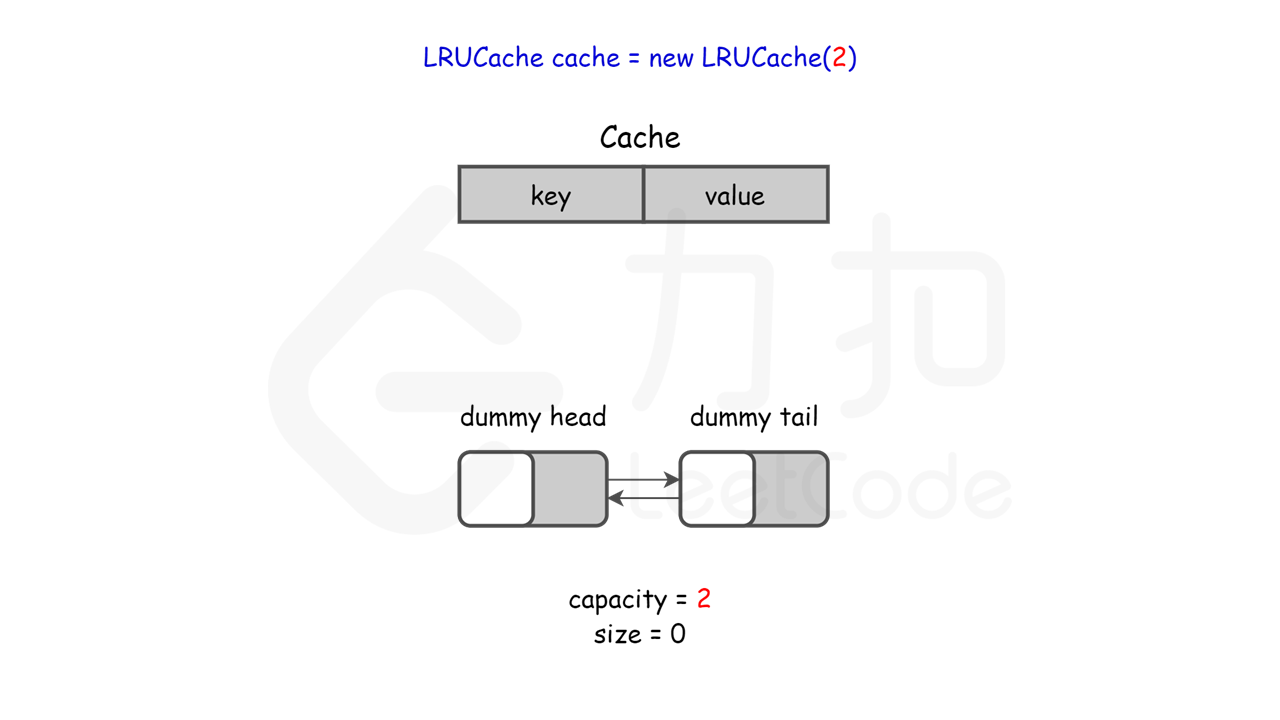
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
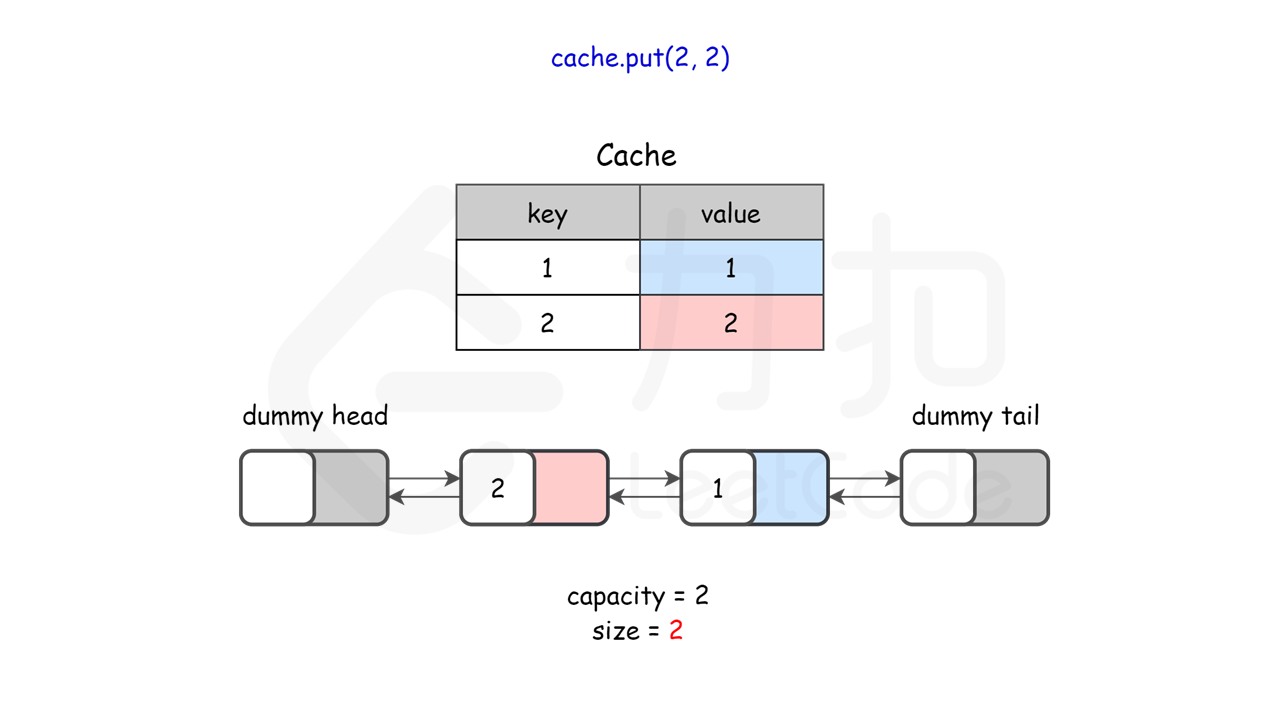
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
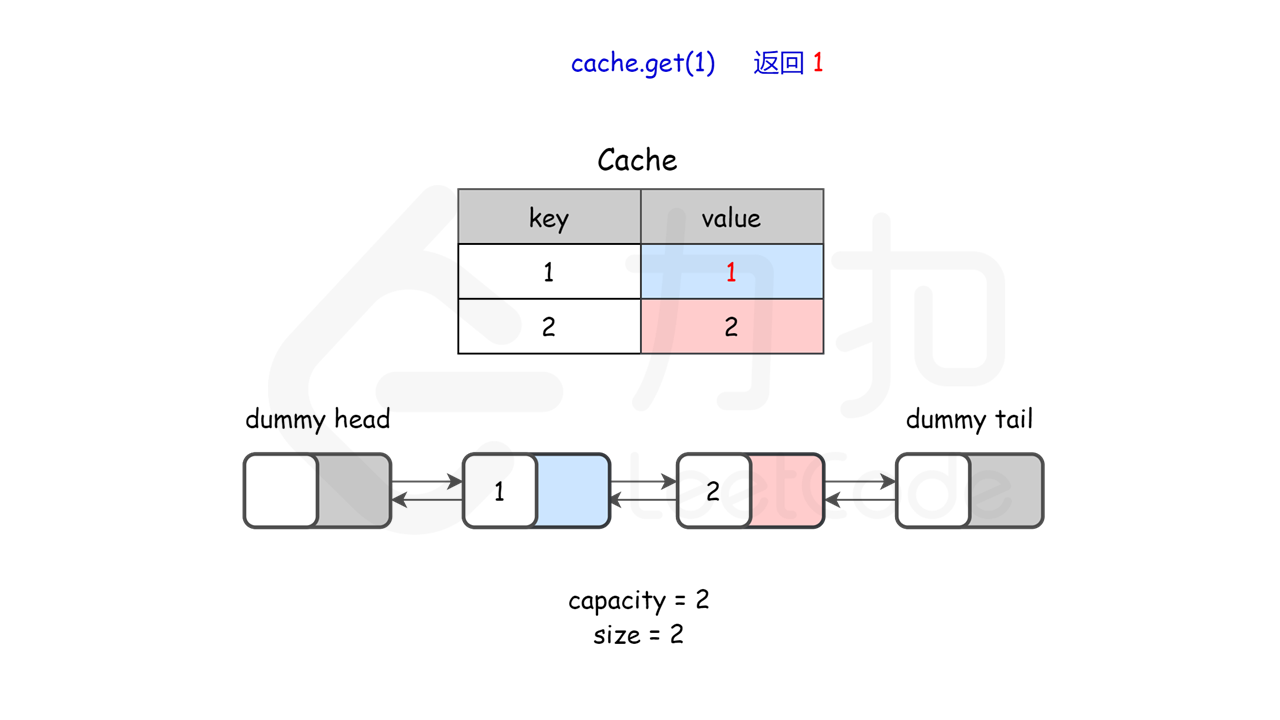
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
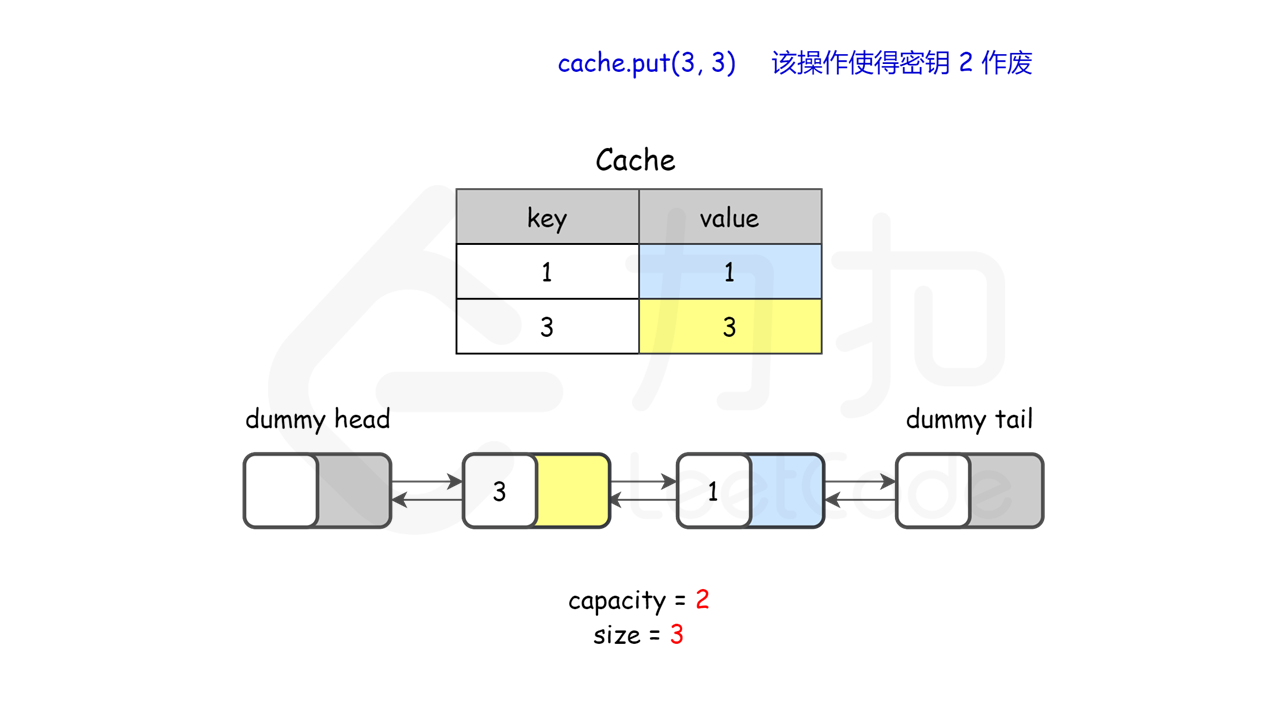
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
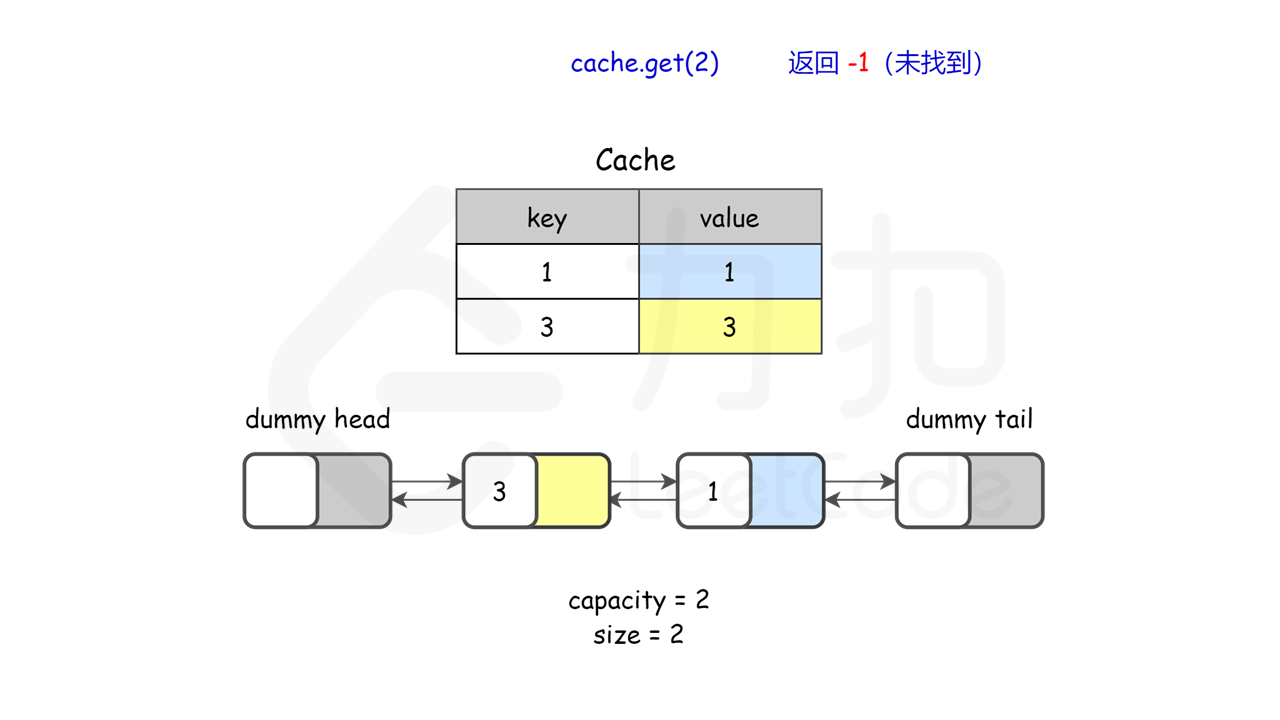
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
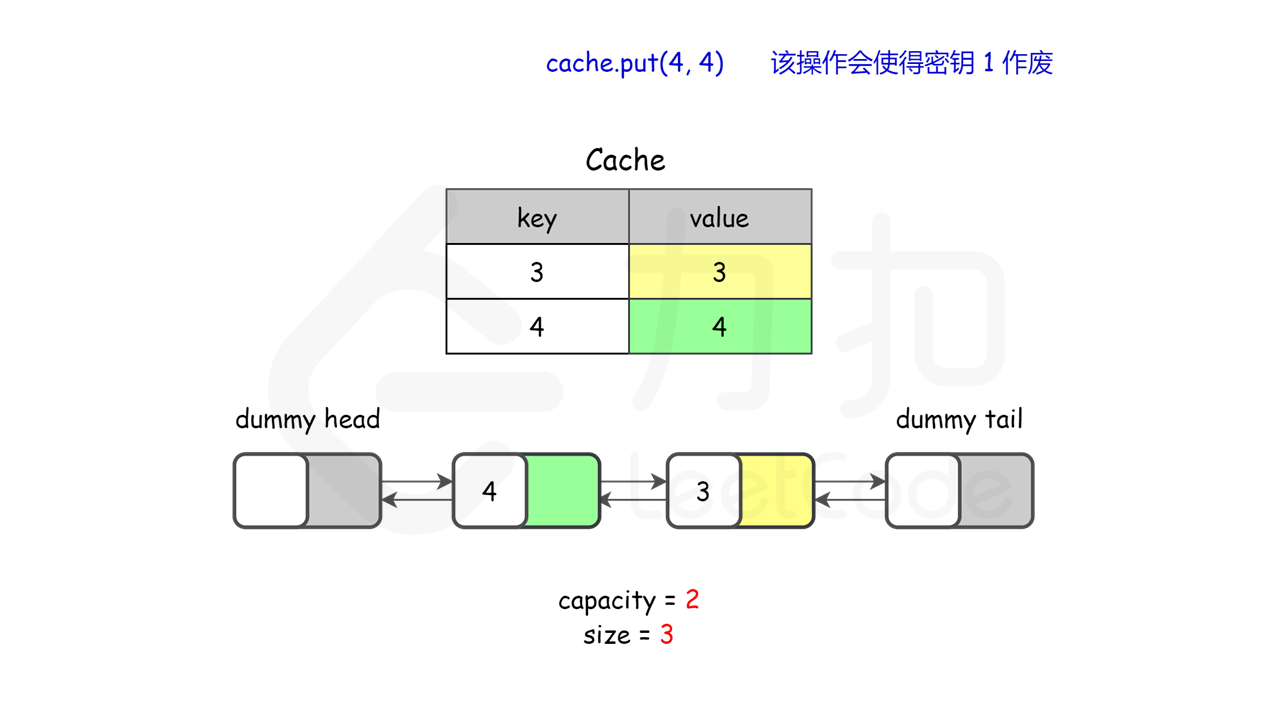
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
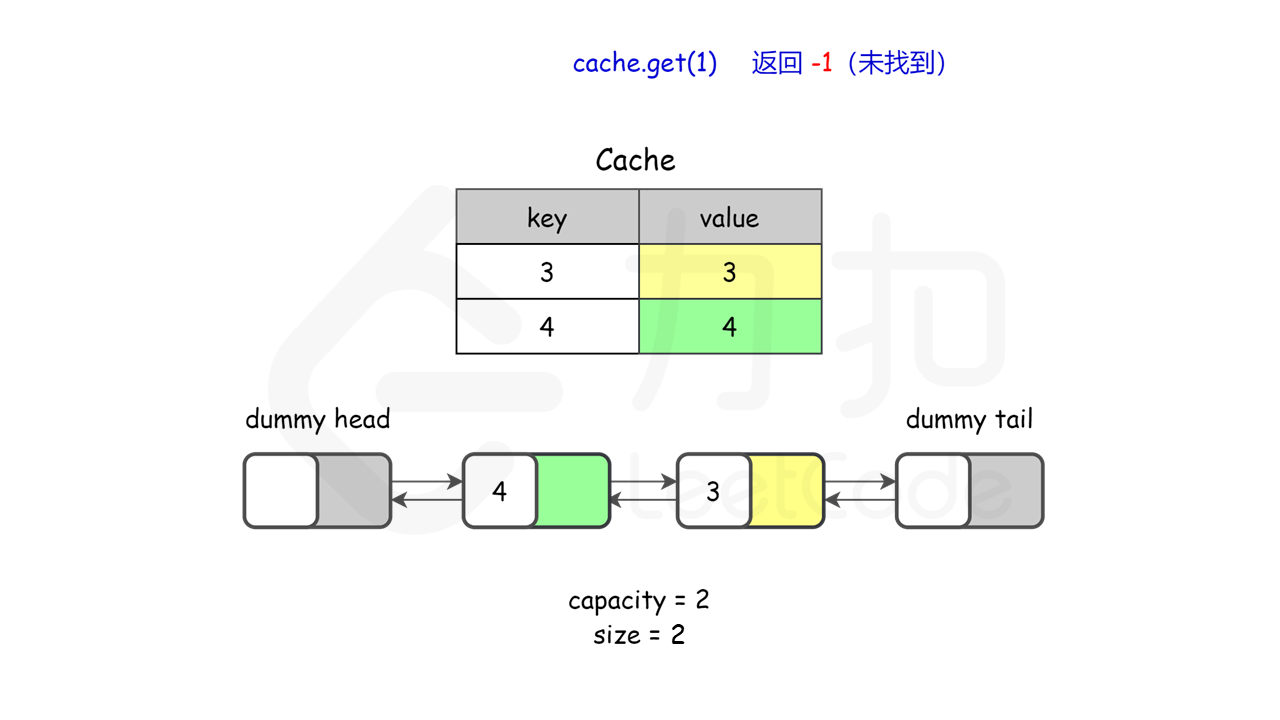
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
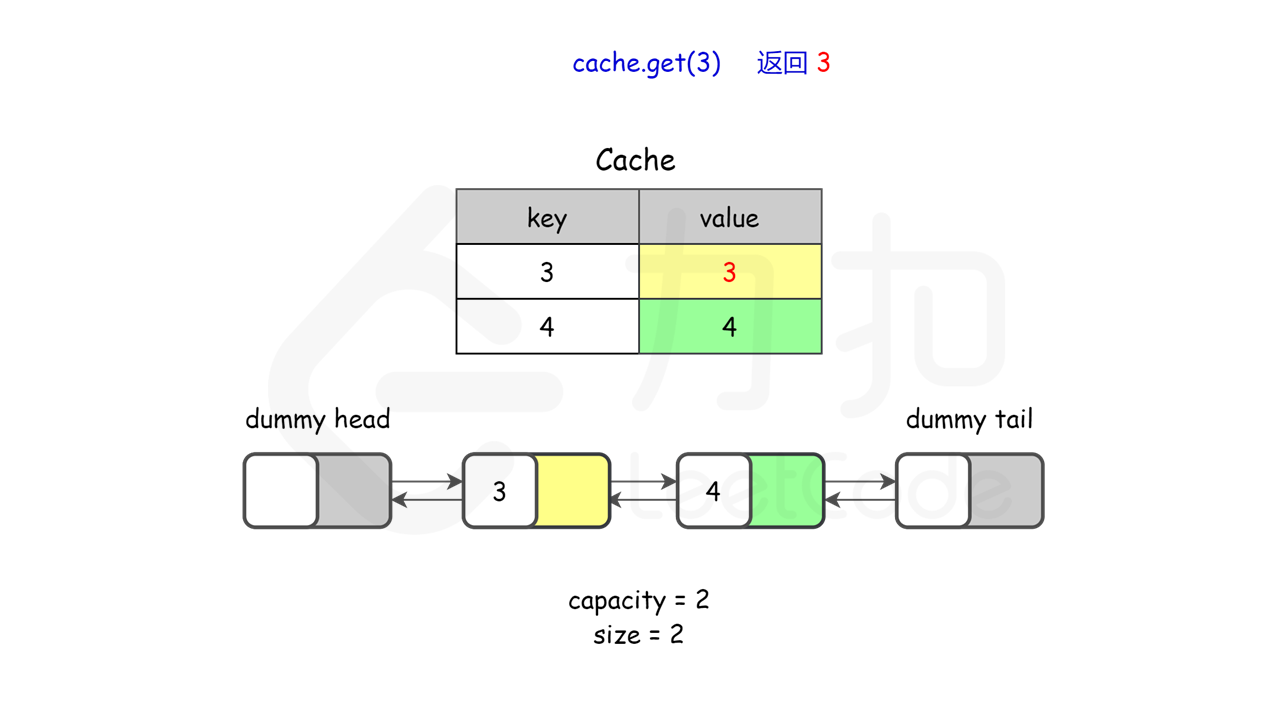
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示:
1 <= capacity <= 30000 <= key <= 100000 <= value <= 105- 最多调用
2 * 105次get和put
相关补充


思路讲解

代码展示
public class LRUCache {class DLinkedNode {int key;int value;DLinkedNode prev;DLinkedNode next;public DLinkedNode() {}public DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {key = _key; value = _value;}}private Map<Integer, DLinkedNode> cache = new HashMap<Integer, DLinkedNode>();private int size;private int capacity;private DLinkedNode head, tail;public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.size = 0;this.capacity = capacity;// 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点head = new DLinkedNode();tail = new DLinkedNode();head.next = tail;tail.prev = head;}public int get(int key) {DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);if (node == null) {return -1;}// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部moveToHead(node);return node.value;}public void put(int key, int value) {DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);if (node == null) {// 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key, value);// 添加进哈希表cache.put(key, newNode);// 添加至双向链表的头部addToHead(newNode);++size;if (size > capacity) {// 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点DLinkedNode tail = removeTail();// 删除哈希表中对应的项cache.remove(tail.key);--size;}}else {// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部node.value = value;moveToHead(node);}}private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) {node.prev = head;node.next = head.next;head.next.prev = node;head.next = node;}private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {node.prev.next = node.next;node.next.prev = node.prev;}private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) {removeNode(node);addToHead(node);}private DLinkedNode removeTail() {DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;removeNode(res);return res;}
}/*** Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);* int param_1 = obj.get(key);* obj.put(key,value);*/
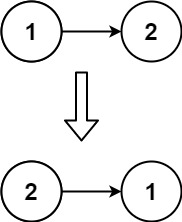
图示理解