文章目录
- 需求
- 示例数据
- 代码实现
需求
输入数据表(矩阵),绘制无向图。
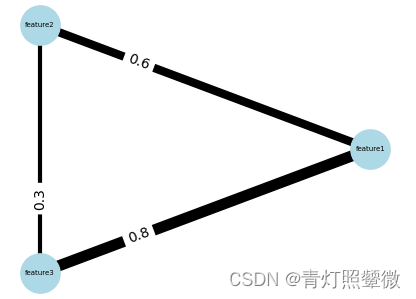
示例数据
**示例数据1:**3个特征之间的关系数据 (data1.txt)
| features | feature1 | feature2 | feature3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| feature1 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| feature2 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.3 |
| feature3 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 1 |
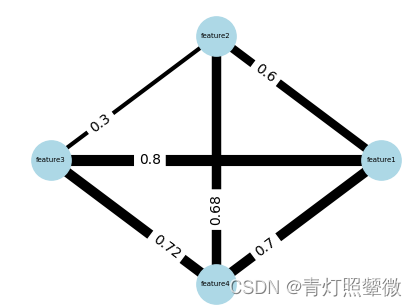
**示例数据2:**4个特征之间的关系数据 (data2.txt)
| features | feature1 | feature2 | feature3 | feature4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| feature1 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| feature2 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.68 |
| feature3 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 1 | 0.72 |
| feature4 | 0.7 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 1 |
代码实现
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom collections import OrderedDict
import mathdef calculate_circle_points(n, r=1, center=(0, 0)):"""将圆按弧线等分后, 分割点的坐标=========================Parameters----------n: int等分的份数r: float, int, optional[1]圆的半径, 默认[1]center: tuple, optional [(0, 0)]圆的中心, 默认(0, 0)Returns-------points: list划分后的点坐标list"""points = []circumference = 2 * math.pi * r # 圆的周长for i in range(n):theta = (i / n) * circumference # 当前等分点所对应的弧长x = center[0] + math.cos(theta) # x 坐标y = center[1] + math.sin(theta) # y 坐标points.append((x, y))return pointsdef list2dict_tuple(lst):"""根据list的元素个数, 定义字典的布局===============================布局为一个圆形Paramters---------lst: list输入listRetures-------odict:根据list元素个数 返回每个元素位置字典"""n = len(lst) # 节点数# 圈上的点坐标circle_points = calculate_circle_points(n)# 坐标和点构成字典odict = OrderedDict()for node_i, point in zip(lst, circle_points):odict[node_i] = pointreturn odictdef draw_nx_graph(matrix, outfig=None, fixed_node=False):"""输入矩阵数据,绘制无向图Parameters----------matrix: DataFrame矩阵数据比如, 多个特征间的相关性矩阵outfig: str, optional [None]默认None, 不输出绘图, 否则设置绘图路径fixed_node: bool, optional [False]固定节点位置- 特征较少时, 可设置为True- 特征较多时, 建议设置为False因为设置固定节点位置, 可能会影响节点之间的边连线或出现边的标签覆盖问题Returns-------None"""# 画布大小plt.figure(figsize=(4, 3))# 创建空的无向图G = nx.Graph()# 添加节点for node in matrix.columns:G.add_node(node)# 添加边for row, col in zip(*matrix.where(pd.np.triu(pd.np.ones(matrix.shape), k=1).astype(bool)).stack().reset_index().drop(columns=0).values.T):value = matrix.loc[row, col]G.add_edge(row, col, weight=value)# 绘制无向图edges = G.edges()weights = [G[u][v]['weight'] for u, v in edges]if fixed_node:# 固定节点位置 (特征较少时)nodelst = G.nodes() # 获取节点名称listposdict = list2dict_tuple(nodelst) # 根据list元素个数布局节点位置# posdict = {'feature1': (0, 0), 'feature2': (0, 1), 'feature3': (1, 0)}else: # 特征较多时posdict = None# print(posdict)nx.draw(G, pos=posdict,with_labels=True, font_size=5, # 节点标签字体 node_color="lightblue", # 节点颜色node_size=800, width=np.array(weights)*10,)if fixed_node:labels = nx.get_edge_attributes(G, 'weight')nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G, posdict, edge_labels=labels,label_pos=0.3,)# nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G, pos=nx.spring_layout(G), edge_labels=labels)else:print("NOTE: not fixed note pos, will not add labels of edges. ""And network graph will be changed, every time this script is executed.")# 输出绘图if outfig:plt.savefig(outfig)plt.show(block=False)plt.pause(1)plt.close()def main(datafile, outfig=None, fixed_node=False):# 读取数据matrix = pd.read_csv(datafile, sep='\t', index_col=0)# 调用函数绘制无向图draw_nx_graph(matrix, outfig, fixed_node)
使用示例1:
datafile = './data1.txt'
# outfig = './data1.nx_grpaph.pdf'
main(datafile, fixed_node=True, outfig=None)

示例2:
datafile = './data2.txt'
# outfig = './data2.nx_grpaph.pdf'
main(datafile, fixed_node=True, outfig=None)
![2023年中国汽车座舱行业发展现状及趋势分析:高级人机交互(HMI)系统将逐步提升[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f637b1b5c70af2b2cc3a0748a2d95bfd.png)