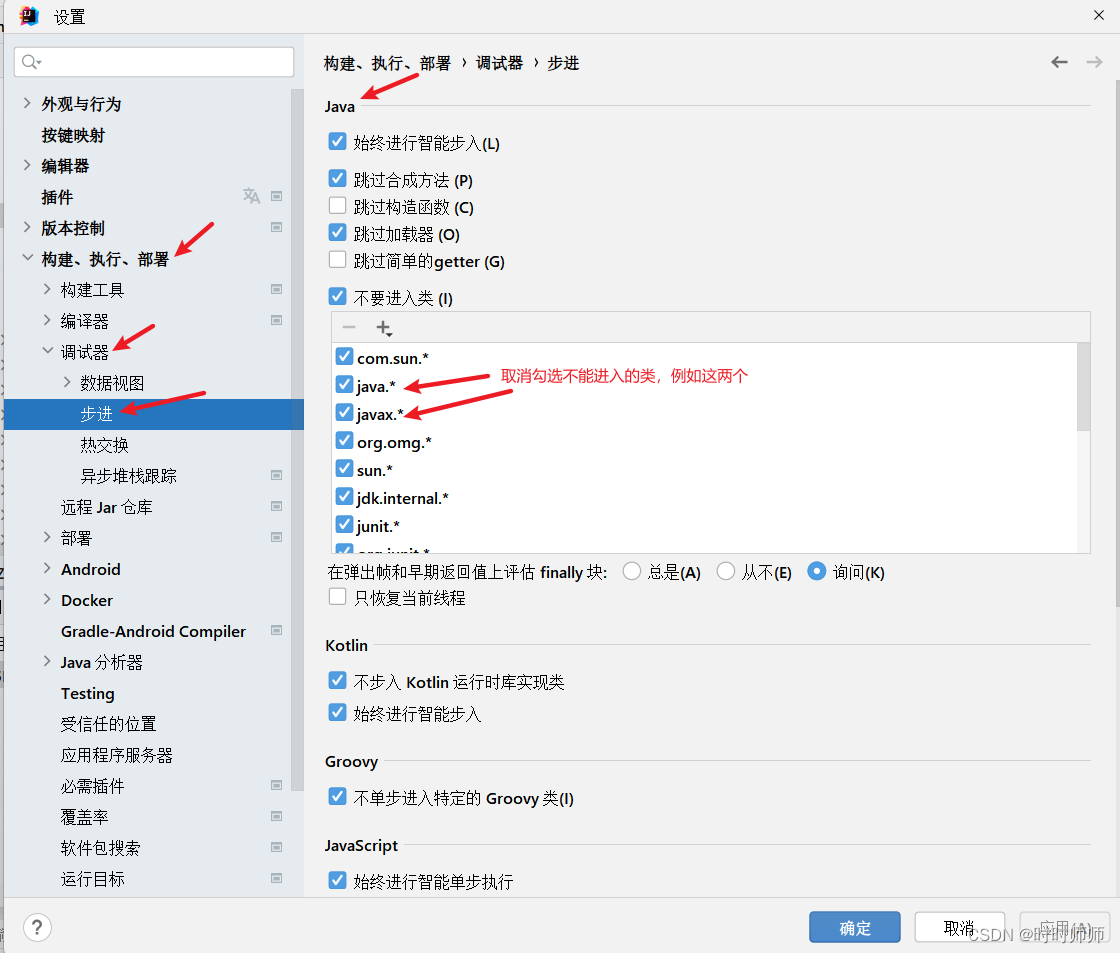
本文内容来自【黑马】Sentinel从使用到源码解读笔记,做了部分修改和补充
目录
Sentinel 基本概念
基本流程
Node
Entry
定义资源的两种方式
使用try-catch定义资源
使用注解标记资源
基于注解标记资源的实现原理
Context
什么是Context
Context的初始化
ContextUtil
ProcessorSlotChain执行流程
入口
NodeSelectorSlot
ClusterBuilderSlot
LogSlot
StatisticSlot
AuthoritySlot
SystemSlot
ParamFlowSlot
令牌桶
FlowSlot
滑动时间窗口
时间窗口请求量统计
滑动窗口QPS计算
DegradeSlot
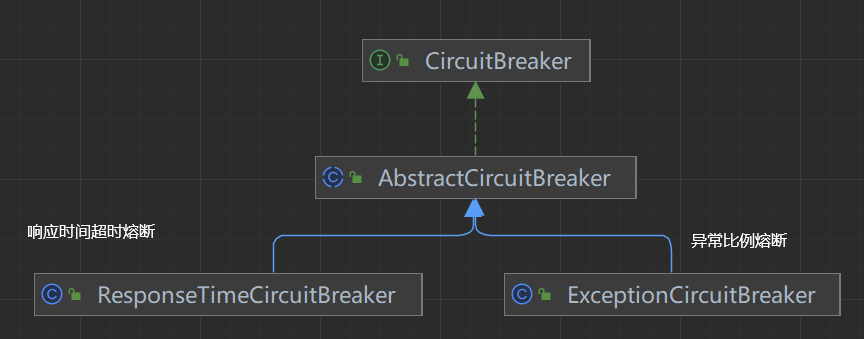
触发断路器
Sentinel 基本概念
基本流程
在 Sentinel 里面,所有的资源都对应一个资源名称以及一个 Entry。Entry 可以通过对主流框架的适配自动创建,也可以通过注解的方式或调用 API 显式创建;每一个 Entry 创建的时候,同时也会创建一系列功能插槽(slot chain)。这些插槽有不同的职责:
NodeSelectorSlot负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级;ClusterBuilderSlot用于存储资源的统计信息以及调用者信息,例如该资源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据;LogSlot用于响应日志记录块异常,以提供用于故障排除的具体日志;StatisticSlot用于记录、统计不同纬度的 runtime 指标监控信息;AuthoritySlot根据配置的黑白名单和调用来源信息,来做黑白名单控制;SystemSlot通过系统的状态,例如 load1 等,来控制总的入口流量;ParamFlowSlot负责通过频繁(“热点”)参数进行流控制的处理器插槽;FlowSlot则用于根据预设的限流规则以及前面 slot 统计的状态,来进行流量控制;DegradeSlot通过统计信息以及预设的规则,来做熔断降级;
总体的框架如下(旧版,未更新):
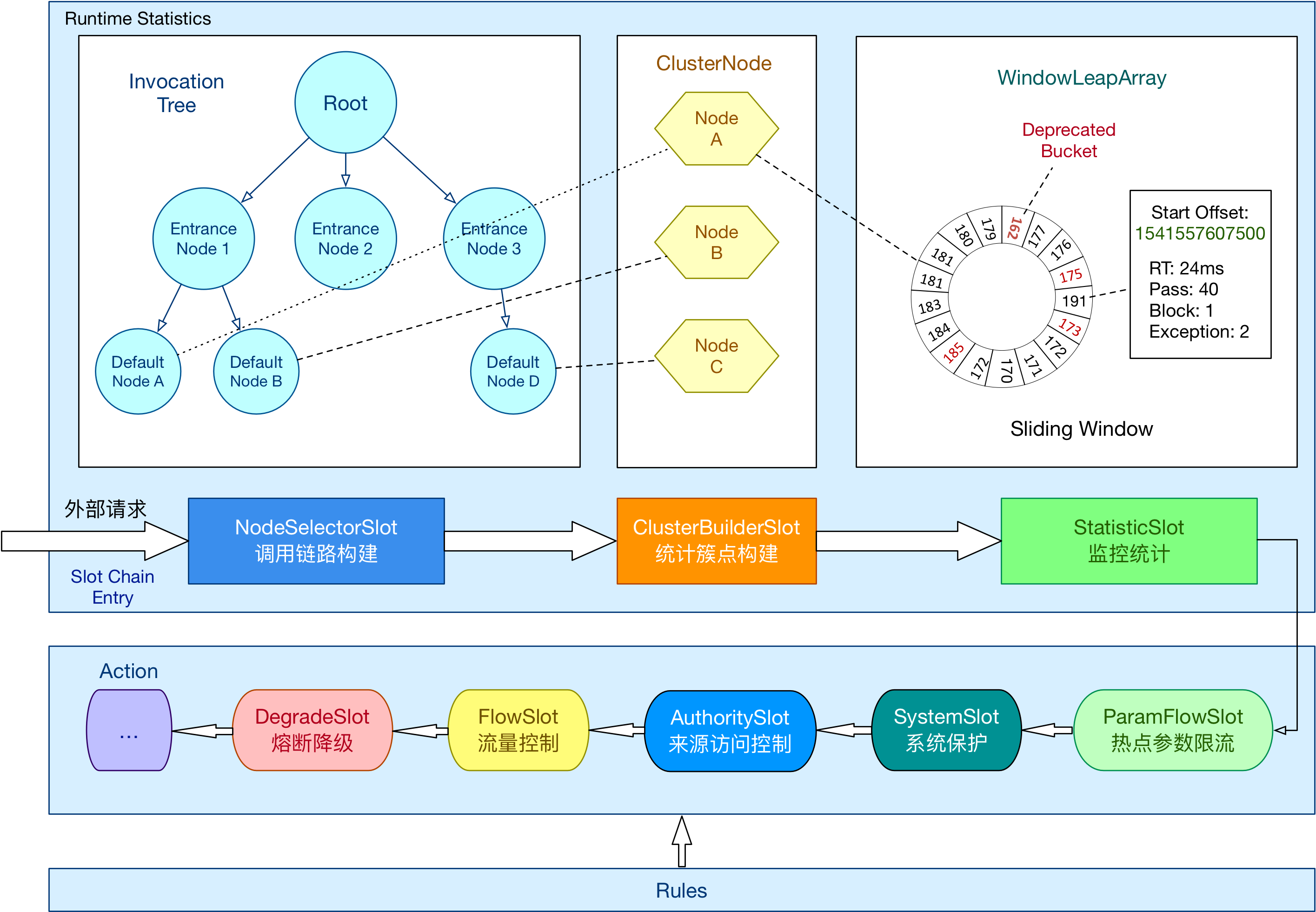
Sentinel 将 ProcessorSlot 作为 SPI 接口进行扩展(1.7.2 版本以前 SlotChainBuilder 作为 SPI),使得 Slot Chain 具备了扩展的能力。可以自行加入自定义的 slot 并编排 slot 间的顺序,从而可以给 Sentinel 添加自定义的功能。

Slot也为两大类:
- 统计数据构建部分(statistic)
-
- NodeSelectorSlot
- ClusterBuilderSlot
- LogSlot
- StatisticSlot
- 规则判断部分(rule checking)
-
- AuthoritySlot
- SystemSlot
- ParamFlowSlot
- FlowSlot
- DegradeSlot
Node
Sentinel中的簇点链路是由一个个的Node组成的,Node是一个接口,包括下面的实现:

所有的节点都可以记录对资源的访问统计数据,所以都是StatisticNode的子类。
按照作用分为两类Node:
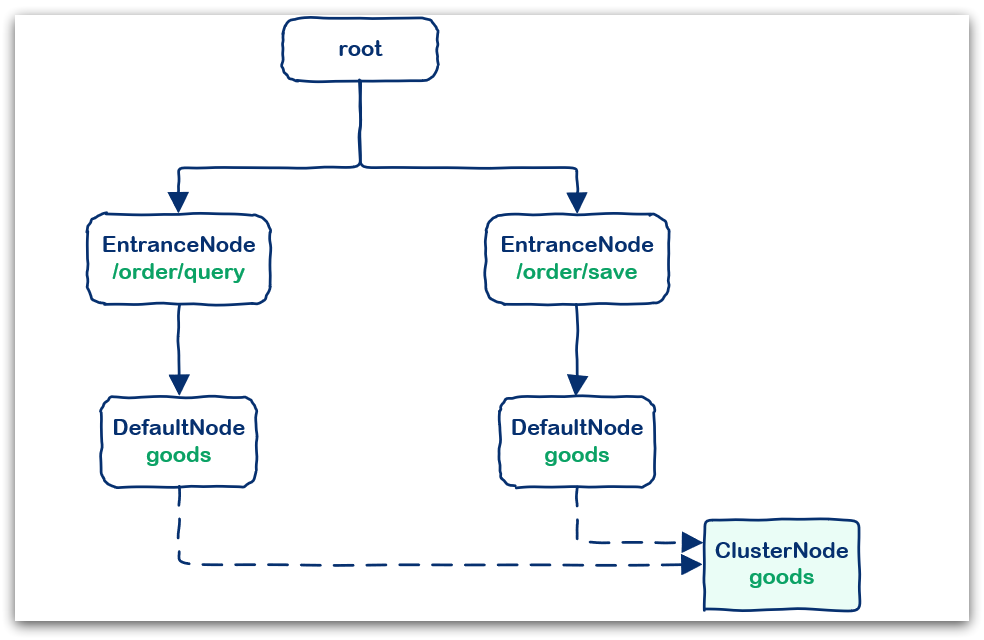
DefaultNode:代表链路树中的每一个资源,一个资源出现在不同链路中时,会创建不同的DefaultNode节点。而树的入口节点叫EntranceNode,是一种特殊的DefaultNodeClusterNode:代表资源,一个资源不管出现在多少链路中,只会有一个ClusterNode。记录的是当前资源被访问的所有统计数据之和。
DefaultNode记录的是资源在当前链路中的访问数据,用来实现基于链路模式的限流规则。
ClusterNode记录的是资源在所有链路中的访问数据,实现默认模式、关联模式的限流规则。
例如:在一个SpringMVC项目中,有两个业务:
- 业务1:controller中的资源/order/query访问了service中的资源/goods
- 业务2:controller中的资源/order/save访问了service中的资源/goods
创建的链路图如下:
Entry
默认情况下,Sentinel会将controller中的方法作为被保护资源,如果想定义自己的资源,则需显示定义。
Sentinel中的资源用Entry来表示。
定义资源的两种方式
使用try-catch定义资源
// 资源名可使用任意有业务语义的字符串,比如方法名、接口名或其它可唯一标识的字符串。
try (Entry entry = SphU.entry("resourceName")) {// 被保护的业务逻辑// do something here...
} catch (BlockException ex) {// 资源访问阻止,被限流或被降级// 在此处进行相应的处理操作
}public Order queryOrderById(Long orderId) {// 创建Entry,标记资源,资源名为resource1try (Entry entry = SphU.entry("resource1")) {// 1.查询订单,这里是假数据Order order = Order.build(101L, 4999L, "小米 MIX4", 1, 1L, null);// 2.查询用户,基于Feign的远程调用User user = userClient.findById(order.getUserId());// 3.设置order.setUser(user);// 4.返回return order;}catch (BlockException e){log.error("被限流或降级", e);return null;}
}使用注解标记资源
@SentinelResource("orderResource")
public Order queryOrderById(Long orderId) {// 1.查询订单Order order = orderMapper.findById(orderId);// 2.用Feign远程调用User user = userClient.findById(order.getUserId());// 3.封装user到Orderorder.setUser(user);// 4.返回return order;
}
基于注解标记资源的实现原理
Sentinel的stater中,spring.factories声明需要就是自动装配的配置类

在SentinelAutoConfiguration类中声明了一个SentinelResourceAspectbean
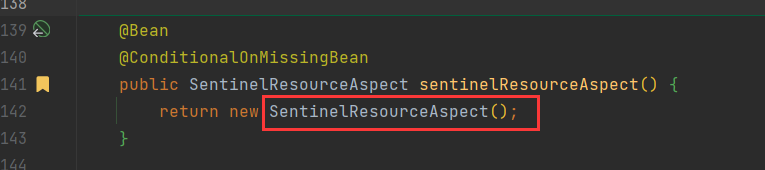
在SentinelResourceAspect中基于AOP实现了增强。
@Aspect
public class SentinelResourceAspect extends AbstractSentinelAspectSupport {// 切点是添加了 @SentinelResource注解的类@Pointcut("@annotation(com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource)")public void sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut() {}// 环绕增强@Around("sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut()")public Object invokeResourceWithSentinel(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {// 获取受保护的方法Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp);// 获取 @SentinelResource注解// @SentinelResource("resource1")SentinelResource annotation = originMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelResource.class);if (annotation == null) {// Should not go through here.throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong state for SentinelResource annotation");}// 获取注解上的资源名称String resourceName = getResourceName(annotation.value(), originMethod);EntryType entryType = annotation.entryType();int resourceType = annotation.resourceType();Entry entry = null;try {// 创建资源 Entryentry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());// 执行受保护的方法Object result = pjp.proceed();return result;} catch (BlockException ex) {return handleBlockException(pjp, annotation, ex);} catch (Throwable ex) {Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore = annotation.exceptionsToIgnore();// The ignore list will be checked first.if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && exceptionBelongsTo(ex, exceptionsToIgnore)) {throw ex;}if (exceptionBelongsTo(ex, annotation.exceptionsToTrace())) {traceException(ex);return handleFallback(pjp, annotation, ex);}// No fallback function can handle the exception, so throw it out.throw ex;} finally {if (entry != null) {entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs());}}}
}@SentinelResource注解就是一个标记,而Sentinel基于AOP思想,对被标记的方法做环绕增强,完成资源(Entry)的创建。
Context
在上面的簇点链路中除了controller方法、service方法两个资源外,还多了一个默认的入口节点:
sentinel_spring_web_context,这是一个EntranceNode类型的节点。
这个节点是在初始化Context的时候由Sentinel创建的。
什么是Context
- Context 代表调用链路上下文,贯穿一次调用链路中的所有资源(
Entry),基于ThreadLocal。 - Context 维持着入口节点(
entranceNode)、本次调用链路的curNode(当前资源节点)、调用来源(origin)等信息。 - 后续的Slot都可以通过
Context拿到DefaultNode或者ClusterNode,从而获取统计数据,完成规则判断 Context初始化的过程中,会创建EntranceNode,contextName就是EntranceNode的名称
对应的API如下:
// 创建context,包含两个参数:context名称、 来源名称
ContextUtil.enter("contextName", "originName");Context的初始化

在SentinelWebAutoConfiguration中,添加了SentinelWebInterceptor
@Autowired
private Optional<SentinelWebInterceptor> sentinelWebInterceptorOptional;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {if (!sentinelWebInterceptorOptional.isPresent()) {return;}SentinelProperties.Filter filterConfig = properties.getFilter();// 添加一个SentinelWebInterceptor拦截器registry.addInterceptor(sentinelWebInterceptorOptional.get()).order(filterConfig.getOrder()).addPathPatterns(filterConfig.getUrlPatterns());log.info("[Sentinel Starter] register SentinelWebInterceptor with urlPatterns: {}.",filterConfig.getUrlPatterns());
}SentinelWebInterceptor继承自AbstractSentinelInterceptor,而AbstractSentinelInterceptor实现了HandlerInterceptor接口,会拦截一切进入controller的方法,执行preHandle前置拦截方法,而Context的初始化就是在这里完成的。
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {try {// 获取资源名称,一般是controller方法的@RequestMapping路径,例如/order/{orderId}String resourceName = getResourceName(request);if (StringUtil.isEmpty(resourceName)) {return true;}if (increaseReferece(request, this.baseWebMvcConfig.getRequestRefName(), 1) != 1) {return true;}// Parse the request origin using registered origin parser.// 从request中获取请求来源,将来做 授权规则 判断时会用String origin = parseOrigin(request);// 获取 contextName,默认是sentinel_spring_web_contextString contextName = getContextName(request);// 创建 ContextContextUtil.enter(contextName, origin);// 创建资源,名称就是当前请求的controller方法的映射路径Entry entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON_WEB, EntryType.IN);request.setAttribute(baseWebMvcConfig.getRequestAttributeName(), entry);return true;} catch (BlockException e) {try {handleBlockException(request, response, e);} finally {ContextUtil.exit();}return false;}
}如果要关闭使用sentinel_spring_web_context作为默认的root,只需要在application.yml文件中关闭即可
spring: cloud: sentinel:web-context-unify: false # 关闭context整合ContextUtil
创建Context的方法就是ContextUtil.enter(contextName, origin);
public static Context enter(String name, String origin) {if (Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME.equals(name)) {throw new ContextNameDefineException("The " + Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME + " can't be permit to defined!");}return trueEnter(name, origin);
}protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) {// 尝试获取contextContext context = contextHolder.get();// 判空if (context == null) {// 如果为空,开始初始化Map<String, DefaultNode> localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap;// 尝试获取入口节点DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name);if (node == null) {// 判断缓存数量是否上限if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {setNullContext();return NULL_CONTEXT;} else {// 加锁,确保线程安全LOCK.lock();try {node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name);if (node == null) {if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {setNullContext();return NULL_CONTEXT;} else {node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null);// 添加入口节点到 ROOTConstants.ROOT.addChild(node);// 将入口节点放入缓存Map<String, DefaultNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1);newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap);newMap.put(name, node);contextNameNodeMap = newMap;}}} finally {LOCK.unlock();}}}// 创建Context,参数为:入口节点 和 contextNamecontext = new Context(node, name);// 设置请求来源 origincontext.setOrigin(origin);// 放入ThreadLocalcontextHolder.set(context);}// 返回return context;
}ProcessorSlotChain执行流程
入口
从上面的分析中可以知道,资源可以分为两种类型
- sentinel自己对所有的controller接口创建的资源
-
- 这种资源的创建位于
AbstractSentinelInterceptor的preHandle方法中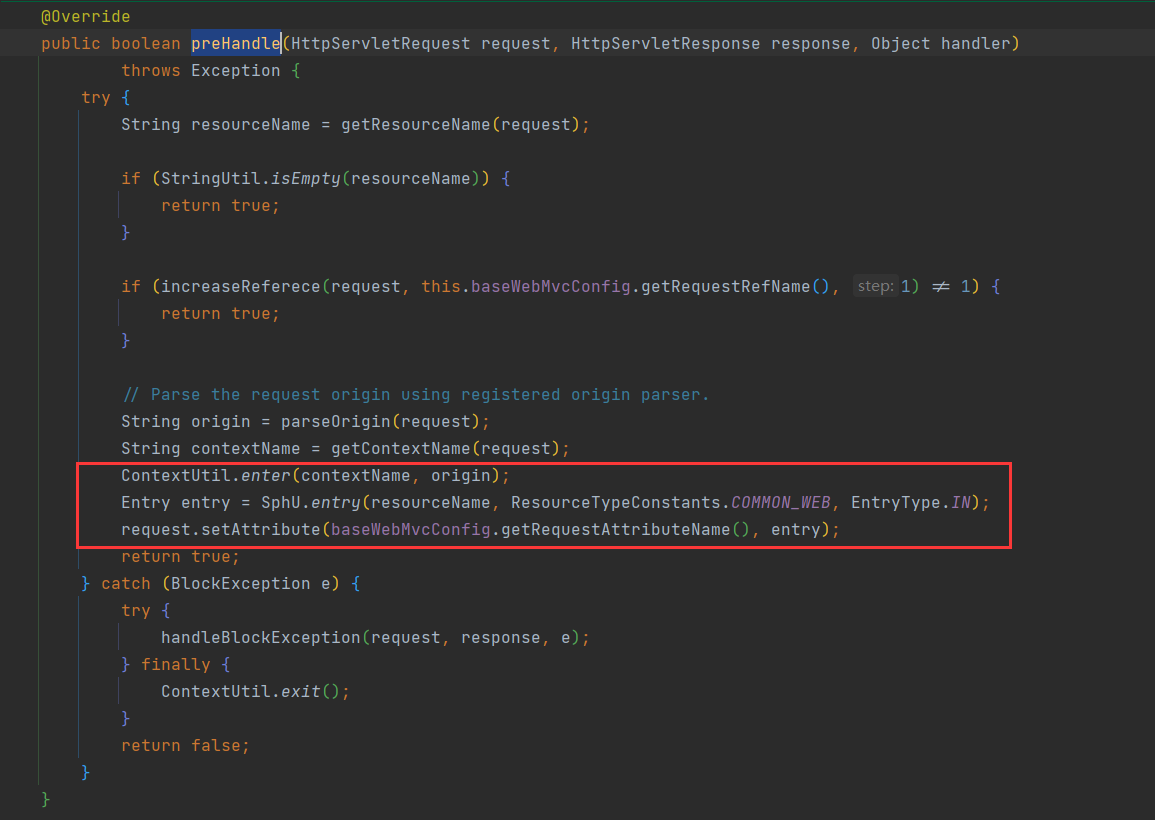
- 这种资源的创建位于
- 我们自己使用注解或者try-cache创建的声明的资源
-
- 这种资源的创建位于
SentinelResourceAspect的环绕通知中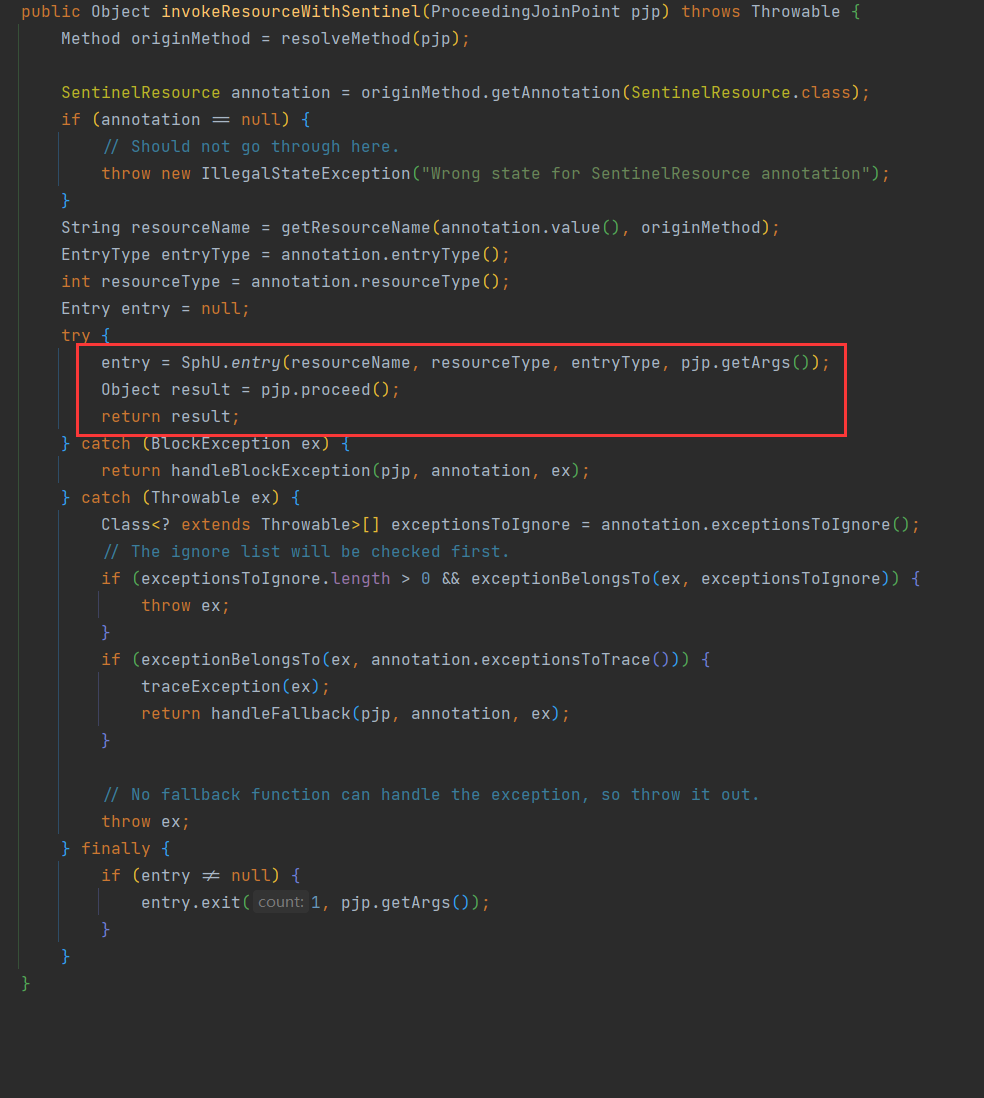
- 这种资源的创建位于
这两种方式都是用了SphU.entry();这个方法
public static Entry entry(String name, int resourceType, EntryType trafficType, Object[] args)
throws BlockException {return Env.sph.entryWithType(name, resourceType, trafficType, 1, args);
}@Override
public Entry entryWithType(String name, int resourceType, EntryType entryType, int count, Object[] args)throws BlockException {return entryWithType(name, resourceType, entryType, count, false, args);
}@Override
public Entry entryWithType(String name, int resourceType, EntryType entryType, int count, boolean prioritized,Object[] args) throws BlockException {// 将 资源名称等基本信息 封装为一个 StringResourceWrapper对象StringResourceWrapper resource = new StringResourceWrapper(name, entryType, resourceType);return entryWithPriority(resource, count, prioritized, args);
}private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws BlockException {// 获取 ContextContext context = ContextUtil.getContext();if (context instanceof NullContext) {// The {@link NullContext} indicates that the amount of context has exceeded the threshold,// so here init the entry only. No rule checking will be done.return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);}if (context == null) {// Using default context.context = InternalContextUtil.internalEnter(Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME);}// Global switch is close, no rule checking will do.if (!Constants.ON) {return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);}// 获取 Slot执行链,同一个资源,会创建一个执行链,放入缓存// 这里是创建 DefaultProcessorSlotChain子类ProcessorSlot<Object> chain = lookProcessChain(resourceWrapper);/** Means amount of resources (slot chain) exceeds {@link Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE},* so no rule checking will be done.*/if (chain == null) {return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);}// 创建 Entry,并将 resource、chain、context 记录在 Entry中Entry e = new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, chain, context);try {// 执行 slotChainchain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args);} catch (BlockException e1) {e.exit(count, args);throw e1;} catch (Throwable e1) {// This should not happen, unless there are errors existing in Sentinel internal.RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", e1);}return e;
}在这段代码中,会获取ProcessorSlotChain对象,然后基于chain.entry()开始执行slotChain中的每一个Slot。 而这里创建的是其实现类:DefaultProcessorSlotChain。
获取ProcessorSlotChain后会保存到Map中,key是ResourceWrapper,值是ProcessorSlotChain。
所以,一个资源只会有一个ProcessorSlotChain。
此时在DefaultProcessorSlotChain的entry()方法中,first是DefaultProcessorSlotChain,之后基于责任链模式,后续slot作为上一个slot的next执行。
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object t, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {first.transformEntry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
void transformEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object o, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {T t = (T)o;entry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot中的entry()方法调用顺序如下
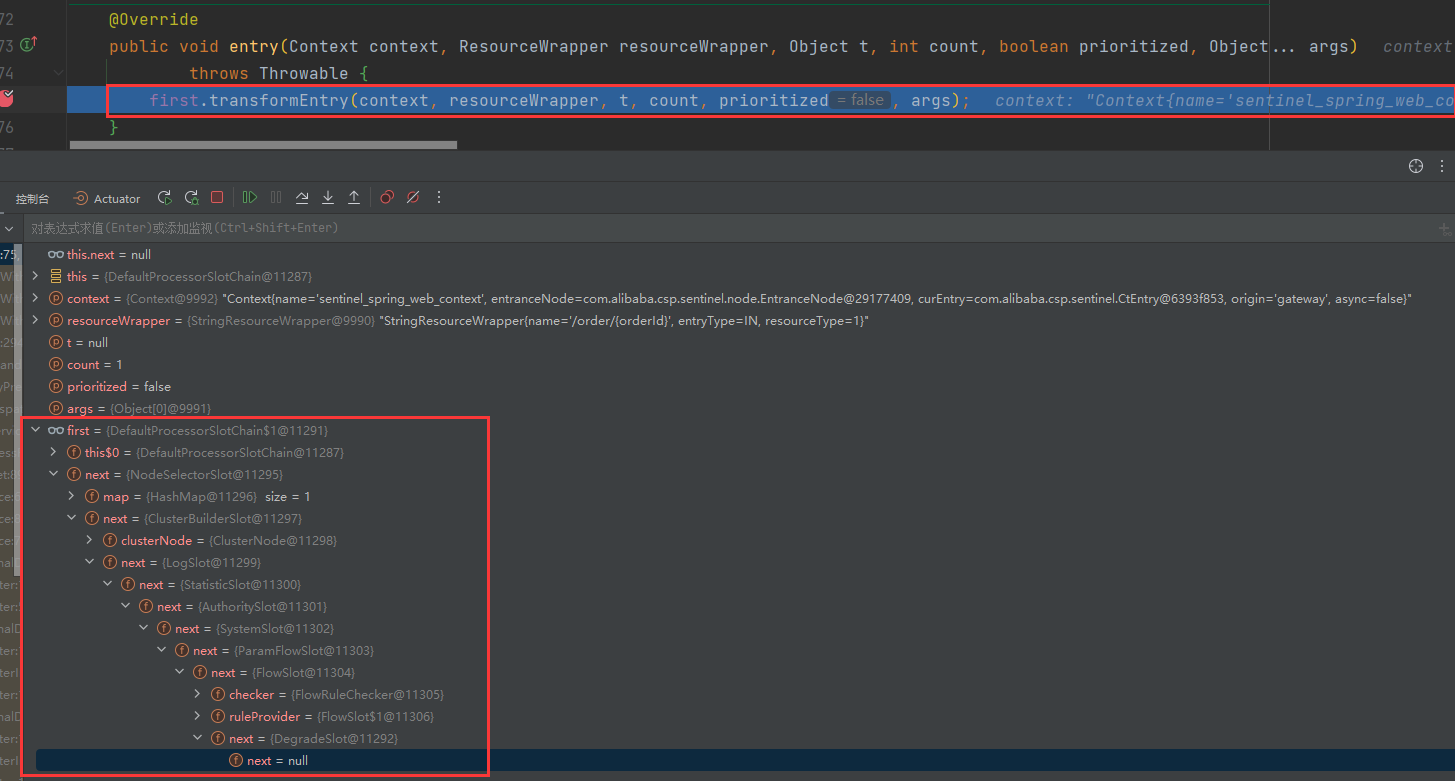
NodeSelectorSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName());if (node == null) {synchronized (this) {node = map.get(context.getName());if (node == null) {// 创建DefaultNodenode = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null);// 将DefaultNode放入缓存中,key是contextName,// 这样不同链路入口的请求,将会创建多个DefaultNode,相同链路则只有一个DefaultNodeHashMap<String, DefaultNode> cacheMap = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(map.size());cacheMap.putAll(map);cacheMap.put(context.getName(), node);map = cacheMap;// Build invocation tree// 将当前资源的DefaultNode设置为上一个资源的childNode((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node);}}}// 将当前资源的DefaultNode设置为Context中的curNode(当前节点)context.setCurNode(node);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}这个Slot完成了这么几件事情:
- 为当前资源创建 DefaultNode
- 将DefaultNode放入缓存中,key是contextName,这样不同链路入口的请求,将会创建多个DefaultNode,相同链路则只有一个DefaultNode
- 将当前资源的DefaultNode设置为上一个资源的childNode
- 将当前资源的DefaultNode设置为Context中的curNode(当前节点)
下一个slot,就是ClusterBuilderSlot
ClusterBuilderSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {// 判空,注意ClusterNode是共享的成员变量,也就是说一个资源只有一个ClusterNode,与链路无关if (clusterNode == null) {synchronized (lock) {if (clusterNode == null) {// Create the cluster node.clusterNode = new ClusterNode(resourceWrapper.getName(), resourceWrapper.getResourceType());HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(Math.max(clusterNodeMap.size(), 16));newMap.putAll(clusterNodeMap);// 放入缓存newMap.put(node.getId(), clusterNode);clusterNodeMap = newMap;}}}// 将资源的 DefaultNode与 ClusterNode关联node.setClusterNode(clusterNode);/** if context origin is set, we should get or create a new {@link Node} of the specific origin.*/if (!"".equals(context.getOrigin())) {// 记录请求来源 origin 将 origin放入 entryNode originNode = node.getClusterNode().getOrCreateOriginNode(context.getOrigin());context.getCurEntry().setOriginNode(originNode);}// 继续下一个slotfireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}LogSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {try {// 执行下一个slot,如果有异常则记录并抛出fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, obj, count, prioritized, args);} catch (BlockException e) {EagleEyeLogUtil.log(resourceWrapper.getName(), e.getClass().getSimpleName(), e.getRuleLimitApp(), context.getOrigin(), count);throw e;} catch (Throwable e) {RecordLog.warn("Unexpected entry exception", e);}}StatisticSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {try {// 执行下一个slot,做限流、降级等判断fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);// 请求通过了, 线程计数器 +1 ,用作线程隔离node.increaseThreadNum();// 请求计数器 +1 用作限流node.addPassRequest(count);if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {// 如果有 origin,来源计数器也都要 +1context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count);}if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {// 如果是入口资源,还要给全局计数器 +1.Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count);}// 请求通过后的回调.for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);}} catch (PriorityWaitException ex) {异常处理......throw e;}
}另外,需要注意的是,所有的计数+1动作都包括两部分,以node.addPassRequest(count);为例:
@Override
public void addPassRequest(int count) {// DefaultNode的计数器,代表当前链路的 计数器super.addPassRequest(count);// ClusterNode计数器,代表当前资源的 总计数器this.clusterNode.addPassRequest(count);
}AuthoritySlot
负责请求来源origin的授权规则判断,如图:
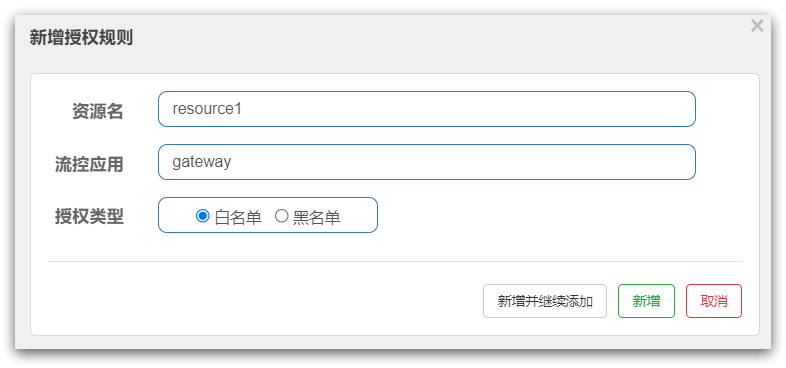
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)throws Throwable {// 校验黑白名单checkBlackWhiteAuthority(resourceWrapper, context);// 进入下一个 slotfireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}void checkBlackWhiteAuthority(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context) throws AuthorityException {// 获取授权规则Map<String, Set<AuthorityRule>> authorityRules = AuthorityRuleManager.getAuthorityRules();if (authorityRules == null) {return;}Set<AuthorityRule> rules = authorityRules.get(resource.getName());if (rules == null) {return;}// 遍历规则并判断for (AuthorityRule rule : rules) {if (!AuthorityRuleChecker.passCheck(rule, context)) {// 规则不通过,直接抛出异常throw new AuthorityException(context.getOrigin(), rule);}}
}static boolean passCheck(AuthorityRule rule, Context context) {String requester = context.getOrigin();// Empty origin or empty limitApp will pass.if (StringUtil.isEmpty(requester) || StringUtil.isEmpty(rule.getLimitApp())) {return true;}// Do exact match with origin name.int pos = rule.getLimitApp().indexOf(requester);boolean contain = pos > -1;// 如果包含,做精确匹配if (contain) {boolean exactlyMatch = false;// 使用逗号分割String[] appArray = rule.getLimitApp().split(",");for (String app : appArray) {if (requester.equals(app)) {exactlyMatch = true;break;}}contain = exactlyMatch;}// 获取校验方式。0:白名单;1:黑名单int strategy = rule.getStrategy();if (strategy == RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_BLACK && contain) {return false;}if (strategy == RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_WHITE && !contain) {return false;}return true;
}默认的请求头是空的(""),所以需要使用gateway或者重写RequestOriginParser的parseOrigin()方法对请求头进行处理,都则空的origin会直接通过
重写RequestOriginParser
@Component
public class HeaderOriginParser implements RequestOriginParser {@Overridepublic String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest request) {// 1.获取请求头String origin = request.getHeader("origin");// 2.非空判断,给空请求头附默认值if (StringUtils.isEmpty(origin)) {origin = "blank";}return origin;}
}在gateway中对请求头做处理
spring: cloud:gateway:default-filters:# 给经过网关的请求添加请求头,格式为 xxx,yyy- AddRequestHeader=Truth,Itcast is freaking awesome!- AddRequestHeader=origin,gatewaySystemSlot
SystemSlot是对系统保护的规则校验:

@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {SystemRuleManager.checkSystem(resourceWrapper);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}public static void checkSystem(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) throws BlockException {if (resourceWrapper == null) {return;}// Ensure the checking switch is on.if (!checkSystemStatus.get()) {return;}// 只针对入口资源做校验,其它直接返回if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() != EntryType.IN) {return;}// total qpsdouble currentQps = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0.0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.successQps();if (currentQps > qps) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "qps");}// total threadint currentThread = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.curThreadNum();if (currentThread > maxThread) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "thread");}// 全局平均 RT校验double rt = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.avgRt();if (rt > maxRt) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "rt");}// 全局 系统负载 校验if (highestSystemLoadIsSet && getCurrentSystemAvgLoad() > highestSystemLoad) {if (!checkBbr(currentThread)) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "load");}}// 全局 CPU使用率 校验if (highestCpuUsageIsSet && getCurrentCpuUsage() > highestCpuUsage) {throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "cpu");}
}ParamFlowSlot
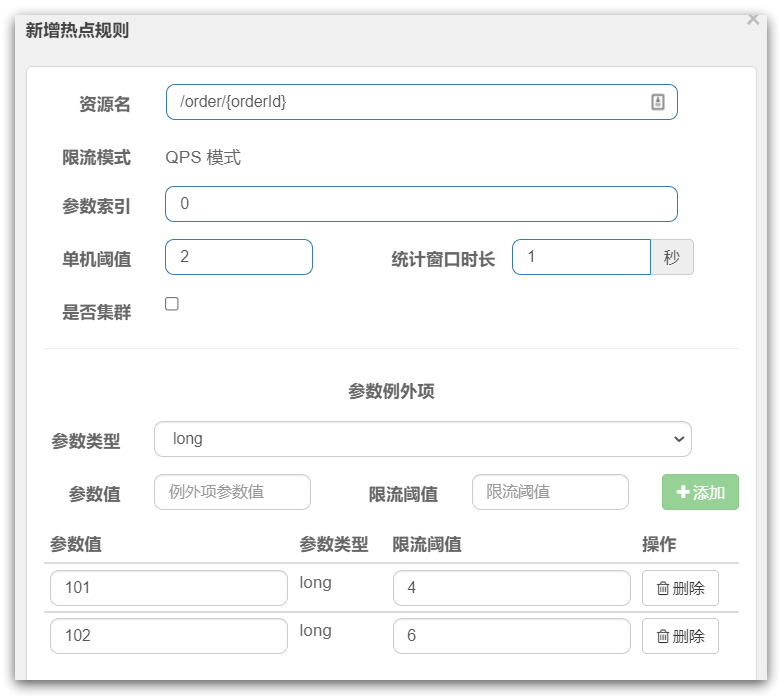
是针对进入资源的请求,针对不同的请求参数值分别统计QPS的限流方式。
- 这里的单机阈值,就是最大令牌数量:maxCount
- 这里的统计窗口时长,就是统计时长:duration
含义是每隔duration时间长度内,最多生产maxCount个令牌,上图配置的含义是每1秒钟生产2个令牌。
这里在配置资源名时,默认的controller资源是不生效的,
需要写@SentinelResource("orderResource")中的资源名。
比如对于下面的controller应该写hot而不是/order/{orderId}
@SentinelResource("hot")
@GetMapping("{orderId}")
public Order queryOrderByUserId(@PathVariable("orderId") Long orderId) {// 根据id查询订单并返回return orderService.queryOrderById(orderId);
}这是因为
// AbstractSentinelInterceptor
// 这里没有传入参数
Entry entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON_WEB, EntryType.IN);// SentinelResourceAspect
// 这里在最后传入的参数pjp.getArgs()
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());在dispatchServerlet中的doDispatch方法内部可以看到,先执行applyPreHandle(controller资源),然后执行handle(注解资源)
所以一个请求会创建两次资源(如果这个请求controller方法添加了@SentinelResource("hot"))
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);try {ModelAndView mv = null;Exception dispatchException = null;try {processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);// Determine handler for the current request.mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);if (mappedHandler == null) {noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);return;}// Determine handler adapter for the current request.HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.String method = request.getMethod();boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {return;}}// 前置处理,在这里进行controller接口的资源创建,创建的资源不支持热点参数限流if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {return;}// 执行真正的处理,在这里对添加注解的方法创建资源,支持热点参数限流// 因此,对于热点参数限流的controller方法,第一次请求进入到ParamFlowSlot的entry// 方法中时,不会进行checkFlow,因为没有传入热点参数// 第二次进入时,才会进行热点参数限流// Actually invoke the handler.mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {return;}applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);}catch (Exception ex) {异常处理。。。。。。
}核心API:
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {// 如果没有热点规则,直接放行if (!ParamFlowRuleManager.hasRules(resourceWrapper.getName())) {fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);return;}// 检查热点规则checkFlow(resourceWrapper, count, args);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException {// 检查args是否为nullif (args == null) {return;}// 检查ParamFlowRuleManager中是否定义了与给定资源名称相关的流量规则if (!ParamFlowRuleManager.hasRules(resourceWrapper.getName())) {return;}// 从ParamFlowRuleManager中获取与给定资源名称相关的所有流量规则,并将它们存储在rules列表中List<ParamFlowRule> rules = ParamFlowRuleManager.getRulesOfResource(resourceWrapper.getName());// 遍历rules列表中的每个流量规则rulefor (ParamFlowRule rule : rules) {// 应用实际的参数索引paramIdxapplyRealParamIdx(rule, args.length);// 初始化参数指标ParameterMetricStorageParameterMetricStorage.initParamMetricsFor(resourceWrapper, rule);// 使用ParamFlowChecker检查资源是否满足流量规则if (!ParamFlowChecker.passCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, args)) {// 获取触发异常的参数值和规则String triggeredParam = "";if (args.length > rule.getParamIdx()) {Object value = args[rule.getParamIdx()];triggeredParam = String.valueOf(value);}throw new ParamFlowException(resourceWrapper.getName(), triggeredParam, rule);}}
}public static boolean passCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, /*@Valid*/ ParamFlowRule rule, /*@Valid*/ int count,Object... args) {if (args == null) {return true;}int paramIdx = rule.getParamIdx();if (args.length <= paramIdx) {return true;}// Get parameter value.Object value = args[paramIdx];// Assign value with the result of paramFlowKey methodif (value instanceof ParamFlowArgument) {value = ((ParamFlowArgument) value).paramFlowKey();}// If value is null, then passif (value == null) {return true;}if (rule.isClusterMode() && rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {return passClusterCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);}return passLocalCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);
}private static boolean passLocalCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int count,Object value) {try {if (Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(value.getClass())) {for (Object param : ((Collection)value)) {if (!passSingleValueCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, param)) {return false;}}} else if (value.getClass().isArray()) {int length = Array.getLength(value);for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {Object param = Array.get(value, i);if (!passSingleValueCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, param)) {return false;}}} else {return passSingleValueCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);}} catch (Throwable e) {RecordLog.warn("[ParamFlowChecker] Unexpected error", e);}return true;
}static boolean passSingleValueCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int acquireCount,Object value) {if (rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {if (rule.getControlBehavior() == RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_RATE_LIMITER) {return passThrottleLocalCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, acquireCount, value);} else {// 走这里return passDefaultLocalCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, acquireCount, value);}} else if (rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD) {Set<Object> exclusionItems = rule.getParsedHotItems().keySet();long threadCount = getParameterMetric(resourceWrapper).getThreadCount(rule.getParamIdx(), value);if (exclusionItems.contains(value)) {int itemThreshold = rule.getParsedHotItems().get(value);return ++threadCount <= itemThreshold;}long threshold = (long)rule.getCount();return ++threadCount <= threshold;}return true;
}令牌桶
热点规则判断采用了令牌桶算法来实现参数限流,为每一个不同参数值设置令牌桶,Sentinel的令牌桶有两部分组成:

这两个Map的key都是请求的参数值,value却不同,其中:
- tokenCounters:用来记录剩余令牌数量
- timeCounters:用来记录上一个请求的时间
当一个携带参数的请求到来后,基本判断流程是这样的:
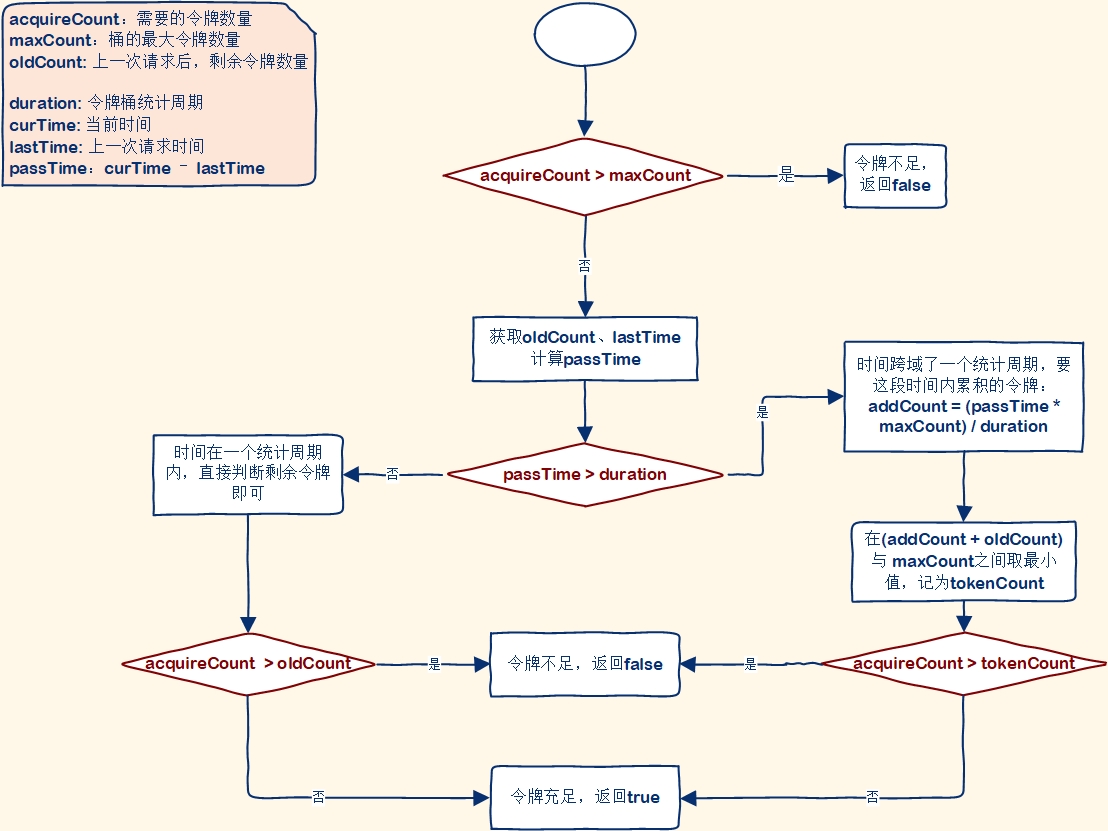
/*** 检查资源是否过载,基于给定的resourceWrapper、rule、acquireCount和value。* * @param resourceWrapper 资源包装器* @param rule 参数流规则* @param acquireCount 要获得的令牌数量* @param value 当前请求的标识符,热点参数* @return 如果资源没有过载,返回true,否则返回false*/
static boolean passDefaultLocalCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int acquireCount, Object value) {// 获取参数指标ParameterMetric metric = getParameterMetric(resourceWrapper);// 获取令牌计数器和时间计数器从指标CacheMap<Object, AtomicLong> tokenCounters = metric == null ? null : metric.getRuleTokenCounter(rule);CacheMap<Object, AtomicLong> timeCounters = metric == null ? null : metric.getRuleTimeCounter(rule);// 检查令牌计数器和时间计数器是否为空if (tokenCounters == null || timeCounters == null) {return true;}// exclusionItems存放单独配置热点限流规则的参数值,对这部分参数做自定义的限流Set<Object> exclusionItems = rule.getParsedHotItems().keySet();long tokenCount = (long)rule.getCount();if (exclusionItems.contains(value)) {tokenCount = rule.getParsedHotItems().get(value);}// 检查令牌数量是否为0if (tokenCount == 0) {return false;}// 计算最大计数(阈值),getBurstCount()允许的突发阈值,一般为0long maxCount = tokenCount + rule.getBurstCount();if (acquireCount > maxCount) {return false;}// Token bucket算法while (true) {// 获取当前时间long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();// 获取上次添加令牌的时间AtomicLong lastAddTokenTime = timeCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(currentTime));// 如果上次添加令牌的时间为空,说明令牌从未添加if (lastAddTokenTime == null) {// 令牌未添加,只需补充令牌并消耗 acquireCount 立即返回 truetokenCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(maxCount - acquireCount));return true;}// 计算自上次添加令牌以来时间间隔long passTime = currentTime - lastAddTokenTime.get();// 一个简化版的 token bucket 算法,当统计窗口已过时,才会补充令牌// 如果当前经过的时间大于一个统计窗口的时长if (passTime > rule.getDurationInSec() * 1000) {AtomicLong oldQps = tokenCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(maxCount - acquireCount));if (oldQps == null) {// Might not be accurate here.lastAddTokenTime.set(currentTime);return true;} else {long restQps = oldQps.get();// 计算累计令牌数量: 经过时间*每秒生成令牌数/(统计窗口时长*1000)long toAddCount = (passTime * tokenCount) / (rule.getDurationInSec() * 1000);// 去最大令牌数量和累计令牌数量最小值long newQps = toAddCount + restQps > maxCount ? (maxCount - acquireCount) : (restQps + toAddCount - acquireCount);// 如果没有令牌直接返回if (newQps < 0) {return false;}if (oldQps.compareAndSet(restQps, newQps)) {lastAddTokenTime.set(currentTime);return true;}Thread.yield();}} else {// 获取剩余的令牌AtomicLong oldQps = tokenCounters.get(value);// 如果剩余的令牌不为空,比较并设置旧令牌值if (oldQps != null) {long oldQpsValue = oldQps.get();if (oldQpsValue - acquireCount >= 0) {if (oldQps.compareAndSet(oldQpsValue, oldQpsValue - acquireCount)) {return true;}} else {return false;}}// 释放线程Thread.yield();}}
}FlowSlot
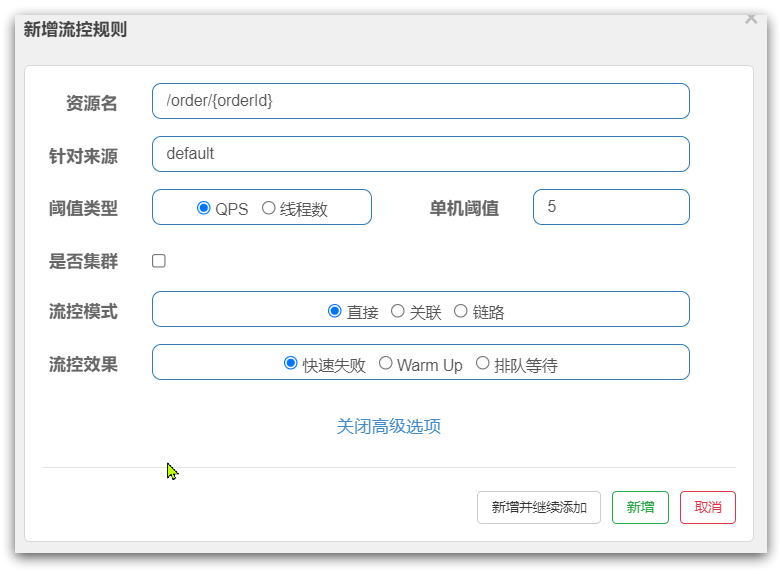
包括:
- 三种流控模式:直接模式、关联模式、链路模式
- 三种流控效果:快速失败、warm up、排队等待
三种流控模式,从底层数据统计角度,分为两类:
- 对进入资源的所有请求(ClusterNode)做限流统计:直接模式、关联模式
- 对进入资源的部分链路(DefaultNode)做限流统计:链路模式
三种流控效果,从限流算法来看,分为两类:
- 滑动时间窗口算法:快速失败、warm up
- 漏桶算法:排队等待效果
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized)
throws BlockException {checker.checkFlow(ruleProvider, resource, context, node, count, prioritized);
}public void checkFlow(Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider, ResourceWrapper resource,Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException {if (ruleProvider == null || resource == null) {return;}Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName());if (rules != null) {for (FlowRule rule : rules) {if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized)) {throw new FlowException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule);}}}
}public boolean canPassCheck(/*@NonNull*/ FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,boolean prioritized) {String limitApp = rule.getLimitApp();if (limitApp == null) {return true;}if (rule.isClusterMode()) {return passClusterCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);}return passLocalCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
}private static boolean passLocalCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,boolean prioritized) {// 根绝请求和策略选择nodeNode selectedNode = selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(rule, context, node);if (selectedNode == null) {return true;}// 这里的canPass根据不同的策略采用不同的算法实现return rule.getRater().canPass(selectedNode, acquireCount, prioritized);
}static Node selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(/*@NonNull*/ FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node) {// The limit app should not be empty.String limitApp = rule.getLimitApp();// public static final int STRATEGY_DIRECT = 0;// public static final int STRATEGY_RELATE = 1;// public static final int STRATEGY_CHAIN = 2;int strategy = rule.getStrategy(); String origin = context.getOrigin();if (limitApp.equals(origin) && filterOrigin(origin)) {if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT) {// Matches limit origin, return origin statistic node.return context.getOriginNode();}return selectReferenceNode(rule, context, node);} else if (RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_DEFAULT.equals(limitApp)) {if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT) {// Return the cluster node.// 直连模式和关联模式都采用clusterNodereturn node.getClusterNode();}return selectReferenceNode(rule, context, node);} else if (RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_OTHER.equals(limitApp)&& FlowRuleManager.isOtherOrigin(origin, rule.getResource())) {if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT) {return context.getOriginNode();}return selectReferenceNode(rule, context, node);}return null;
}static Node selectReferenceNode(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node) {String refResource = rule.getRefResource();int strategy = rule.getStrategy();if (StringUtil.isEmpty(refResource)) {return null;}// 如果是关联模式,返回clusterNodeif (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_RELATE) {return ClusterBuilderSlot.getClusterNode(refResource);}// 如果是链路模式,返回当前的node(defaultNode)if (strategy == RuleConstant.STRATEGY_CHAIN) {if (!refResource.equals(context.getName())) {return null;}return node;}// No node.return null;
}滑动时间窗口
时间窗口请求量统计
这里canPass()对规则的判断先要通过FlowRule#getRater()获取流量控制器TrafficShapingController,然后再做限流
而TrafficShapingController有3种实现:
DefaultController:快速失败,默认的方式,基于滑动时间窗口算法WarmUpController:预热模式,基于滑动时间窗口算法,只不过阈值是动态的RateLimiterController:排队等待模式,基于漏桶算法
最终的限流判断都在TrafficShapingController的canPass方法中。
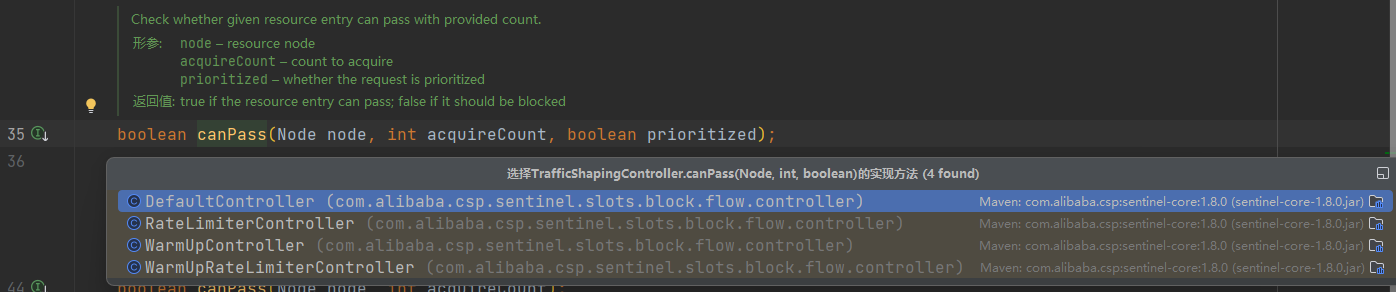

这里进入了DefaultNode内部:
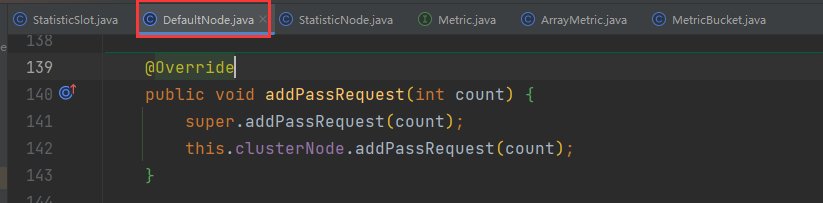
发现同时对DefaultNode和ClusterNode在做QPS统计,DefaultNode和ClusterNode都是StatisticNode的子类,这里调用addPassRequest()方法,最终都会进入StatisticNode中。随便跟入一个:
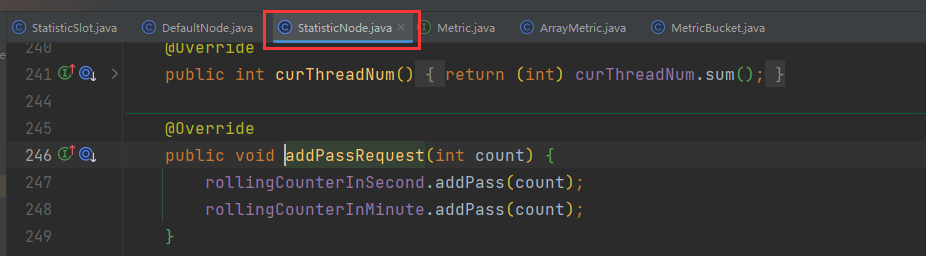
这里有秒、分两种纬度的统计,对应两个计数器。找到对应的成员变量,可以看到:

两个计数器都是ArrayMetric类型,并且传入了两个参数:
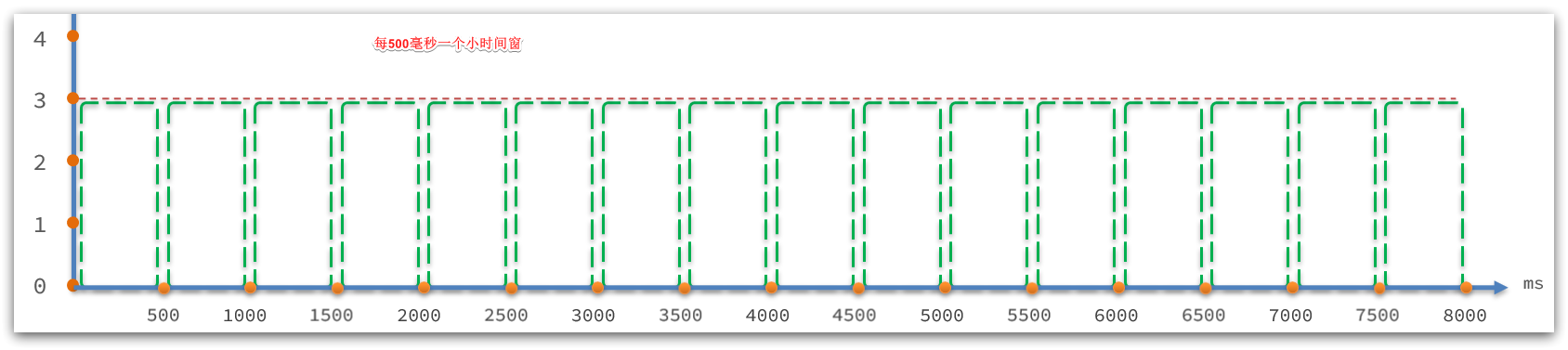
// intervalInMs:是滑动窗口的时间间隔,默认为 1 秒
// sampleCount: 时间窗口的分隔数量,默认为 2,就是把 1秒分为 2个小时间窗
public ArrayMetric(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) {this.data = new OccupiableBucketLeapArray(sampleCount, intervalInMs);
}如图:
接下来,我们进入ArrayMetric类的addPass方法:
@Override
public void addPass(int count) {// 获取当前时间所在的时间窗WindowWrap<MetricBucket> wrap = data.currentWindow();// 计数器 +1wrap.value().addPass(count);
}这里的data是一个LeapArray:
private final LeapArray<MetricBucket> data;LeapArray的四个属性:
public abstract class LeapArray<T> {// 小窗口的时间长度,默认是500ms ,值 = intervalInMs / sampleCountprotected int windowLengthInMs;// 滑动窗口内的 小窗口 数量,默认为 2protected int sampleCount;// 滑动窗口的时间间隔,默认为 1000msprotected int intervalInMs;// 滑动窗口的时间间隔,单位为秒,默认为 1private double intervalInSecond;
}LeapArray是一个环形数组,因为时间是无限的,数组长度不可能无限,因此数组中每一个格子放入一个时间窗(window),当数组放满后,角标归0,覆盖最初的window。
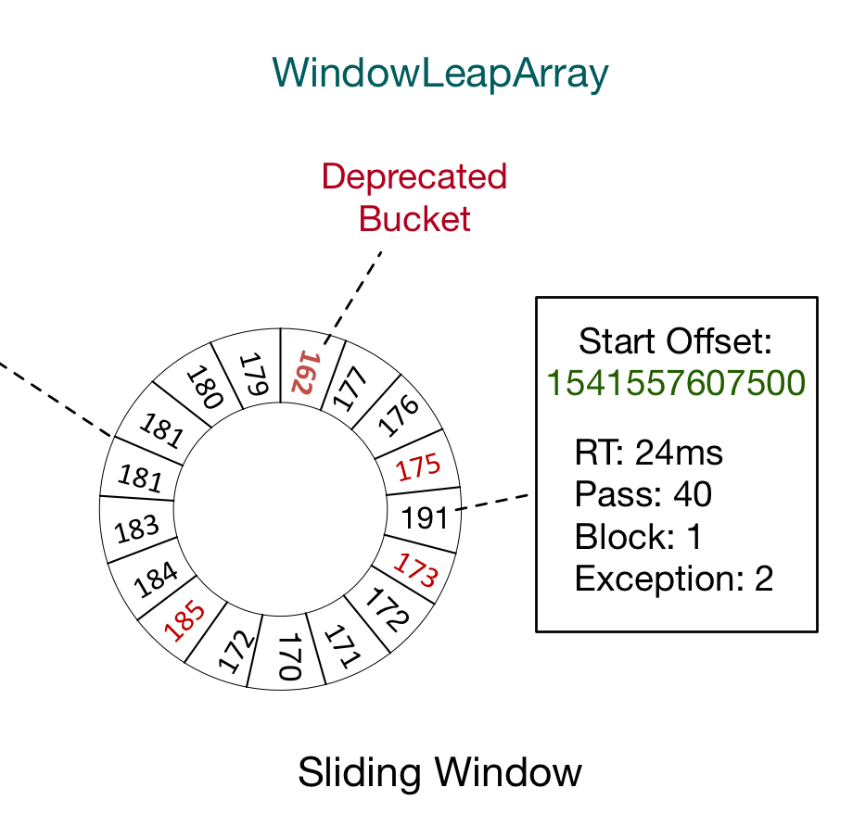
因为滑动窗口最多分成sampleCount数量的小窗口,因此数组长度只要大于sampleCount,那么最近的一个滑动窗口内的2个小窗口就永远不会被覆盖,就不用担心旧数据被覆盖的问题了。
data.currentWindow()方法:
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) {if (timeMillis < 0) {return null;}// 计算当前时间对应的数组角标int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);// 计算当前时间所在窗口的开始时间.long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);/*** 先根据角标获取数组中保存的 oldWindow 对象,可能是旧数据,需要判断.** (1) oldWindow 不存在, 说明是第一次,创建新 window并存入,然后返回即可* (2) oldWindow的 starTime = 本次请求的 windowStar, 说明正是要找的窗口,直接返回.* (3) oldWindow的 starTime < 本次请求的 windowStar, 说明是旧数据,需要被覆盖,创建 * 新窗口,覆盖旧窗口*/while (true) {WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx);if (old == null) {// 创建新 windowWindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));// 基于CAS写入数组,避免线程安全问题if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) {// 写入成功,返回新的 windowreturn window;} else {// 写入失败,说明有并发更新,等待其它人更新完成即可Thread.yield();}} else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {return old;} else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) {if (updateLock.tryLock()) {try {// 获取并发锁,覆盖旧窗口并返回return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);} finally {updateLock.unlock();}} else {// 获取锁失败,等待其它线程处理就可以了Thread.yield();}} else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) {// 这种情况不应该存在,写这里只是以防万一。return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));}}
}找到当前时间所在窗口(WindowWrap)后,只要调用WindowWrap对象中的add方法,计数器+1即可。
这里只负责统计每个窗口的请求量,不负责拦截。限流拦截要看FlowSlot中的逻辑。
滑动窗口QPS计算
FlowSlot的限流判断最终都由TrafficShapingController接口中的canPass方法来实现。该接口有三个实现类:
DefaultController:快速失败,默认的方式,基于滑动时间窗口算法WarmUpController:预热模式,基于滑动时间窗口算法,只不过阈值是动态的RateLimiterController:排队等待模式,基于漏桶算法
跟入默认的DefaultController中的canPass方法来分析:
@Override
public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) {// 计算目前为止滑动窗口内已经存在的请求量int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node);// 判断:已使用请求量 + 需要的请求量(1) 是否大于 窗口的请求阈值if (curCount + acquireCount > count) {// 大于,说明超出阈值,返回falseif (prioritized && grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {long currentTime;long waitInMs;currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();waitInMs = node.tryOccupyNext(currentTime, acquireCount, count);if (waitInMs < OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout()) {node.addWaitingRequest(currentTime + waitInMs, acquireCount);node.addOccupiedPass(acquireCount);sleep(waitInMs);// PriorityWaitException indicates that the request will pass after waiting for {@link @waitInMs}.throw new PriorityWaitException(waitInMs);}}return false;}// 小于等于,说明在阈值范围内,返回truereturn true;
}因此,判断的关键就是int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node);
private int avgUsedTokens(Node node) {if (node == null) {return DEFAULT_AVG_USED_TOKENS;}return grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD ? node.curThreadNum() : (int)(node.passQps());
}因为采用的是限流,走node.passQps()逻辑:
// 这里又进入了 StatisticNode类
@Override
public double passQps() {// 请求量 ÷ 滑动窗口时间间隔 ,得到的就是QPSreturn rollingCounterInSecond.pass() / rollingCounterInSecond.getWindowIntervalInSec();
}rollingCounterInSecond.pass()得到请求量
// rollingCounterInSecond 本质是ArrayMetric
@Override
public long pass() {// 获取当前窗口data.currentWindow();long pass = 0;// 获取当前时间的滑动窗口范围内的所有小窗口List<MetricBucket> list = data.values();// 遍历for (MetricBucket window : list) {// 累加求和pass += window.pass();}// 返回return pass;
}data.values()如何获取滑动窗口范围内的所有小窗口:
// 此处进入LeapArray类中:
public List<T> values(long timeMillis) {if (timeMillis < 0) {return new ArrayList<T>();}// 创建空集合,大小等于 LeapArray长度int size = array.length();List<T> result = new ArrayList<T>(size);// 遍历 LeapArrayfor (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {// 获取每一个小窗口WindowWrap<T> windowWrap = array.get(i);// 判断这个小窗口是否在滑动窗口时间范围内(1秒内)if (windowWrap == null || isWindowDeprecated(timeMillis, windowWrap)) {// 不在范围内,则跳过continue;}// 在范围内,则添加到集合中result.add(windowWrap.value());}// 返回集合return result;
}isWindowDeprecated(timeMillis, windowWrap)判断窗口是否符合要求
public boolean isWindowDeprecated(long time, WindowWrap<T> windowWrap) {// 当前时间 - 窗口开始时间 是否大于 滑动窗口的最大间隔(1秒)// 也就是说,我们要统计的时 距离当前时间1秒内的小窗口的 count之和return time - windowWrap.windowStart() > intervalInMs;
}DegradeSlot
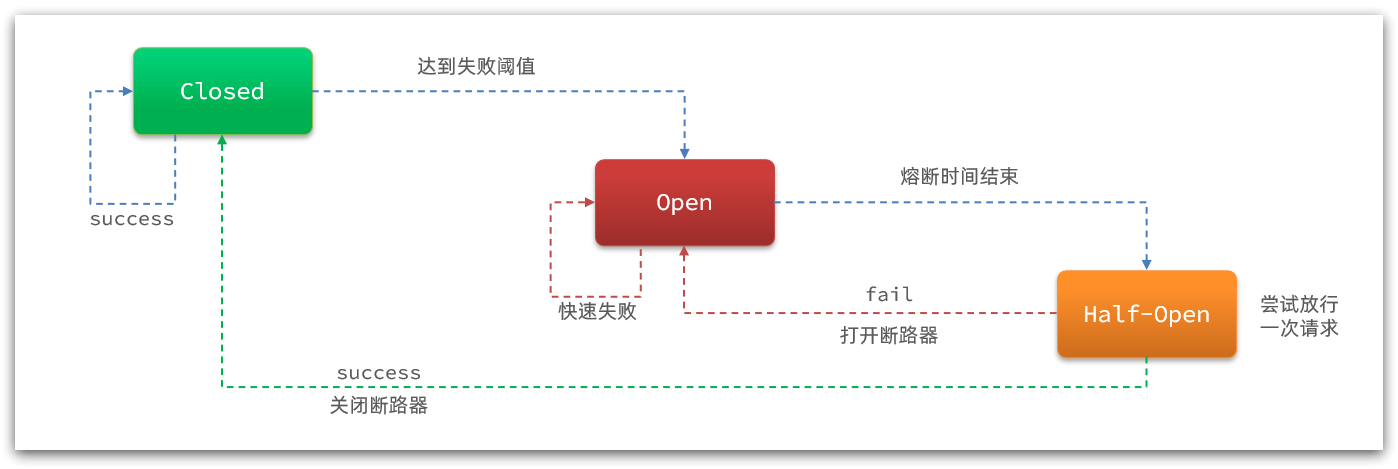
Sentinel的熔断是基于状态机实现的。当达到失败阈值时,断路器会打开,按照配置规则进行熔断。当熔断时间结束后,断路器会进入到 half-open 状态,尝试放行一次请求。当请求成功时断路器会关闭,否则重新回到打开状态。
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {performChecking(context, resourceWrapper);fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}void performChecking(Context context, ResourceWrapper r) throws BlockException {List<CircuitBreaker> circuitBreakers = DegradeRuleManager.getCircuitBreakers(r.getName());if (circuitBreakers == null || circuitBreakers.isEmpty()) {return;}for (CircuitBreaker cb : circuitBreakers) {if (!cb.tryPass(context)) {throw new DegradeException(cb.getRule().getLimitApp(), cb.getRule());}}
}
@Override
public boolean tryPass(Context context) {// 判断状态机状态if (currentState.get() == State.CLOSED) {// 如果是closed状态,直接放行return true;}if (currentState.get() == State.OPEN) {// 如果是OPEN状态,断路器打开// 继续判断OPEN时间窗是否结束,如果是则把状态从OPEN切换到 HALF_OPEN,返回truereturn retryTimeoutArrived() && fromOpenToHalfOpen(context);}// OPEN状态,并且时间窗未到,返回falsereturn false;
}protected boolean retryTimeoutArrived() {// 当前时间 大于 下一次 HalfOpen的重试时间return TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis() >= nextRetryTimestamp;
}protected boolean fromOpenToHalfOpen(Context context) {// 基于CAS修改状态,从 OPEN到 HALF_OPENif (currentState.compareAndSet(State.OPEN, State.HALF_OPEN)) {// 状态变更的事件通知notifyObservers(State.OPEN, State.HALF_OPEN, null);// 得到当前资源Entry entry = context.getCurEntry();// 给资源设置监听器,在资源Entry销毁时(资源业务执行完毕时)触发entry.whenTerminate(new BiConsumer<Context, Entry>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Context context, Entry entry) {// 判断 资源业务是否异常if (entry.getBlockError() != null) {// 如果异常,则再次进入OPEN状态currentState.compareAndSet(State.HALF_OPEN, State.OPEN);notifyObservers(State.HALF_OPEN, State.OPEN, 1.0d);}}});return true;}return false;
}这里出现了从OPEN到HALF_OPEN、从HALF_OPEN到OPEN的变化,但是还有几个没有:
- 从CLOSED到OPEN
- 从HALF_OPEN到CLOSED
触发断路器
请求经过所有插槽 后,一定会执行exit方法,而在DegradeSlot的exit方法中:

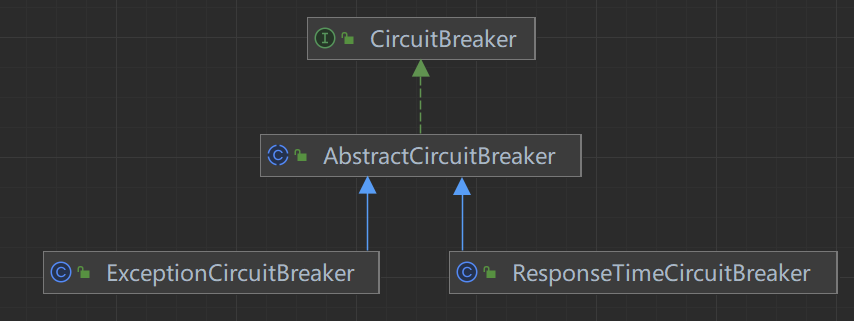
会调用CircuitBreaker的onRequestComplete()方法。而CircuitBreaker有两个实现:
@Override
public void onRequestComplete(Context context) {// 获取资源 EntryEntry entry = context.getCurEntry();if (entry == null) {return;}// 尝试获取 资源中的 异常Throwable error = entry.getError();// 获取计数器,同样采用了滑动窗口来计数SimpleErrorCounter counter = stat.currentWindow().value();if (error != null) {// 如果出现异常,则 error计数器 +1counter.getErrorCount().add(1);}// 不管是否出现异常,total计数器 +1counter.getTotalCount().add(1);// 判断异常比例是否超出阈值handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(error);
}阈值判断的方法:
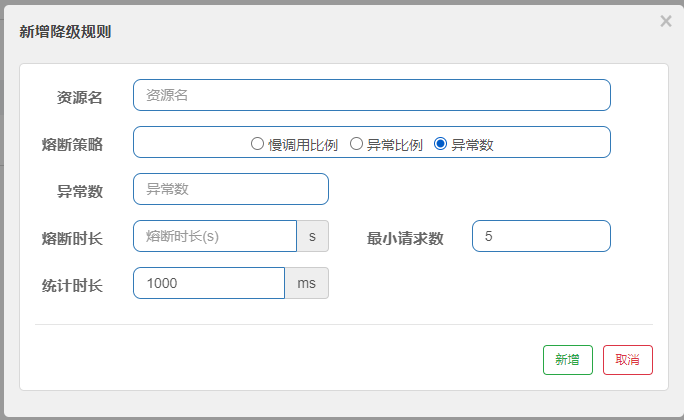
private void handleStateChangeWhenThresholdExceeded(Throwable error) {// 如果当前已经是OPEN状态,不做处理if (currentState.get() == State.OPEN) {return;}// 如果已经是 HALF_OPEN 状态,判断是否需求切换状态if (currentState.get() == State.HALF_OPEN) {if (error == null) {// 没有异常,则从 HALF_OPEN 到 CLOSEDfromHalfOpenToClose();} else {// 有一次,再次进入OPENfromHalfOpenToOpen(1.0d);}return;}// 说明当前是CLOSE状态,需要判断是否触发阈值List<SimpleErrorCounter> counters = stat.values();long errCount = 0;long totalCount = 0;// 累加计算 异常请求数量、总请求数量for (SimpleErrorCounter counter : counters) {errCount += counter.errorCount.sum();totalCount += counter.totalCount.sum();}// 如果总请求数量未达到阈值(最小请求数),什么都不做if (totalCount < minRequestAmount) {return;}double curCount = errCount;// 按照异常比例统计if (strategy == DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO) {// 计算请求的异常比例curCount = errCount * 1.0d / totalCount;}// 按照异常数统计// 如果比例超过阈值,切换到 OPENif (curCount > threshold) {transformToOpen(curCount);}
}