已知 f ( x ) = ln x x f\left(x\right) = \frac{\ln x}{x} f(x)=xlnx,若 f ( x ) = a f\left(x\right) = a f(x)=a有两个不用的零点 x 1 , x 2 x_1, x_2 x1,x2,且 x 1 < x 2 x_1<x_2 x1<x2,求证:
(1)求 a a a的范围
f ( x ) = ln x x f\left(x\right)=\frac{\ln x}{x} f(x)=xlnx
f ′ = 1 − ln x x 2 f^{\prime} = \frac{1-\ln x}{x^2} f′=x21−lnx
极值点为 x = e x=e x=e
x ∈ ( 0 , e ) x\in\left(0,e\right) x∈(0,e), f f f单调递增
x ∈ ( e , + ∞ ) x\in\left(e,+\infty\right) x∈(e,+∞), f f f单调递减
lim x → 0 + f ( x ) = − ∞ \lim\limits_{x\to 0^+} f\left(x\right) = -\infty x→0+limf(x)=−∞
lim x → + ∞ f ( x ) = 0 \lim\limits_{x\to +\infty} f\left(x\right) = 0 x→+∞limf(x)=0
f ( e ) = 1 e f\left(e\right) = \frac{1}{e} f(e)=e1
因此 0 < a < 1 e 0<a<\frac{1}{e} 0<a<e1
ALG不等式
x 1 x 2 < x 1 − x 2 ln x 1 − ln x 2 < x 1 + x 2 2 \sqrt{x_1x_2} <\frac{x_1- x_2}{\ln x_1 - \ln x_2}<\frac{x_1+x_2}{2} x1x2<lnx1−lnx2x1−x2<2x1+x2
x 1 < e < x 2 x_1<e<x_2 x1<e<x2
ln x 1 = a x 1 \ln x_1 = a x_1 lnx1=ax1
ln x 2 = a x 2 \ln x_2 = a x_2 lnx2=ax2
(2) x 1 + x 2 > 2 a x_1+x_2 >\frac{2}{a} x1+x2>a2
x 1 + x 2 > 2 x 1 − x 2 ln x 1 + ln x 2 = 2 a x_1+x_2 > 2 \frac{x_1 - x_2}{\ln x_1 +\ln x_2}=\frac{2}{a} x1+x2>2lnx1+lnx2x1−x2=a2
(3) x 1 + x 2 > 2 e x_1+x_2 > 2e x1+x2>2e
由(2)
x 1 + x 2 > 2 a > 2 e x_1+x_2 >\frac{2}{a}> 2e x1+x2>a2>2e
(4) x 1 + x 2 > 2 a \sqrt{x_1} + \sqrt{x_2} > \frac{2}{\sqrt{a}} x1+x2>a2
x 1 + x 2 > 2 x 1 − x 2 ln x 1 − ln x 2 = 4 a 1 x 1 + x 2 \sqrt{x_1} + \sqrt{x_2}>2\frac{\sqrt{x_1} - \sqrt{x_2}}{\ln\sqrt{x_1}-\ln\sqrt{x_2}}=\frac{4}{a}\frac{1}{\sqrt{x_1} + \sqrt{x_2}} x1+x2>2lnx1−lnx2x1−x2=a4x1+x21
因此
x 1 + x 2 > 4 a = 2 a \sqrt{x_1} + \sqrt{x_2}>\sqrt{\frac{4}{a}}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{a}} x1+x2>a4=a2
(7) x 1 x 2 < 1 a 2 x_1x_2<\frac{1}{a^2} x1x2<a21
x 1 x 2 < x 1 − x 2 ln x 1 − ln x 2 = 1 a \sqrt{x1x_2} < \frac{x_1 - x_2}{\ln x_1 - \ln x_2} = \frac{1}{a} x1x2<lnx1−lnx2x1−x2=a1
因此
x 1 x 2 < 1 a 2 x_1x_2<\frac{1}{a^2} x1x2<a21
(5) 1 x 1 + 1 x 2 > 2 a \frac{1}{x_1}+\frac{1}{x_2} >2a x11+x21>2a
由(2)和(7)
1 x 1 + 1 x 2 = x 1 + x 2 x 1 x 2 > 2 a a 2 = 2 a \frac{1}{x_1}+\frac{1}{x_2} = \frac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}>\frac{2}{a}a^2=2a x11+x21=x1x2x1+x2>a2a2=2a
(6) e 2 < x 1 x 2 e^2<x_1x_2 e2<x1x2
由(2)
x 1 x 2 = e ln x 1 + ln x 2 = e a ( x 1 + x 2 ) > e a 2 a = e 2 x_1x_2 = e^{\ln x_1 + \ln x_2}=e^{a\left(x_1+x_2\right)}>e^{a\frac{2}{a}}=e^2 x1x2=elnx1+lnx2=ea(x1+x2)>eaa2=e2
(9) x 1 + x 2 < − 2 ln a a x_1 +x_2 < \frac{-2\ln a}{a} x1+x2<a−2lna
由(7)
x 1 + x 2 = ln x 1 + ln x 2 a = ln x 1 x 2 a < ln 1 a 2 a = − 2 ln a a x_1+x_2 = \frac{\ln x_1 + \ln x_2}{a}=\frac{\ln x1_x2}{a}<\frac{\ln \frac{1}{a^2}}{a}=\frac{-2\ln a}{a} x1+x2=alnx1+lnx2=alnx1x2<alna21=a−2lna
(16) ( x 1 + 1 ) ( x 2 + 1 ) < 3 a 2 − 2 a + 1 \left(x_1+1\right)\left(x_2+1\right) <\frac{3}{a^2} -\frac{2}{a}+1 (x1+1)(x2+1)<a23−a2+1
即证明
x 1 + x 2 + x 1 x 2 < 3 a 2 − 2 a = 3 − 2 a a 2 x_1+x_2 +x_1x_2 < \frac{3}{a^2} -\frac{2}{a}=\frac{3-2a}{a^2} x1+x2+x1x2<a23−a2=a23−2a
由(9)和(7)
x 1 + x 2 + x 1 x 2 < − 2 ln a a + 1 a 2 = 1 − 2 a ln a a 2 x_1+x_2 +x_1x_2 < \frac{-2\ln a}{a} + \frac{1}{a^2} = \frac{1-2a\ln a}{a^2} x1+x2+x1x2<a−2lna+a21=a21−2alna
即证明 1 − 2 a ln a < 3 − 2 a 1-2a\ln a <3-2a 1−2alna<3−2a
设 g ( a ) = 2 a ln a − 2 a + 2 ( 0 < a < 1 e ) g\left(a\right)=2a\ln a-2a+2\left(0<a<\frac{1}{e}\right) g(a)=2alna−2a+2(0<a<e1)
g ′ ( a ) = 2 ln a + 2 − 2 = 2 ln a < 0 g^{\prime}\left(a\right)=2 \ln a+2-2=2\ln a <0 g′(a)=2lna+2−2=2lna<0
g ( a ) > g ( 1 e ) = 0 g\left(a\right)>g\left(\frac{1}{e}\right)=0 g(a)>g(e1)=0
因此成立
(25) f ′ ( x 1 ) + f ′ ( x 2 ) > 0 f^{\prime}\left(x_1\right) +f^{\prime}\left(x_2\right)>0 f′(x1)+f′(x2)>0
由(5)
f ′ ( x 1 ) + f ′ ( x 2 ) = 1 − ln x 1 x 1 2 + 1 − ln x 2 x 2 2 = 1 − a x 1 x 1 2 + 1 − a x 2 x 2 2 = 1 x 1 2 x 2 2 ( x 1 2 + x 2 2 − a x 1 x 2 ( x 1 + x 2 ) ) > 1 x 1 2 x 2 2 ( x 1 2 − x 2 2 ln x 1 − ln x 2 − a x 1 x 2 ( x 1 + x 2 ) ) > 1 x 1 2 x 2 2 ( x 1 2 − x 2 2 a x 1 − a x 2 − a 1 a 2 ( x 1 + x 2 ) ) = 0 \begin{aligned} f^{\prime}\left(x_1\right) +f^{\prime}\left(x_2\right)&=\frac{1-\ln x_1}{x_1^2}+\frac{1-\ln x_2}{x_2^2}\\ &=\frac{1-a x_1}{x_1^2}+\frac{1-a x_2}{x_2^2}\\ &=\frac{1}{x_1^2x_2^2}\left(x_1^2+x_2^2-ax_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)\right)\\ &>\frac{1}{x_1^2x_2^2}\left(\frac{x_1^2-x_2^2}{\ln x_1-\ln x_2}-ax_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)\right)\\ &>\frac{1}{x_1^2x_2^2}\left(\frac{x_1^2-x_2^2}{a x_1-a x_2}-a\frac{1}{a^2}\left(x_1+x_2\right)\right)\\ &=0 \end{aligned} f′(x1)+f′(x2)=x121−lnx1+x221−lnx2=x121−ax1+x221−ax2=x12x221(x12+x22−ax1x2(x1+x2))>x12x221(lnx1−lnx2x12−x22−ax1x2(x1+x2))>x12x221(ax1−ax2x12−x22−aa21(x1+x2))=0
(29)证明:当 m ≥ 1 m\ge 1 m≥1时, x 1 x 2 m > e m + 1 x_1x_2^m >e^{m+1} x1x2m>em+1
由(6)
x 1 x 2 m = x 1 x 2 x 2 m − 2 > e 2 e m − 2 = e m + 1 x_1 x_2^m =x_1x_2 x_2^{m-2}>e^2 e^{m-2}=e^{m+1} x1x2m=x1x2x2m−2>e2em−2=em+1
构造函数放缩型[同小]
g ( x ) = ln x − 3 x − e x + e g\left(x\right) = \ln x - \frac{3x-e}{x+e} g(x)=lnx−x+e3x−e
g ′ ( x ) = ( x − e ) 2 ( x + e ) 2 > 0 g^{\prime}\left(x\right) = \frac{\left(x-e\right)^2}{\left(x+e\right)^2}>0 g′(x)=(x+e)2(x−e)2>0
g ( e ) = 0 g\left(e\right) = 0 g(e)=0
因此 x < e x<e x<e时, ln x < 3 x − e x + e \ln x < \frac{3x-e}{x+e} lnx<x+e3x−e
x > e x>e x>e时, ln x > 3 x − e x + e \ln x > \frac{3x-e}{x+e} lnx>x+e3x−e
(12)
3 x − e x + e = a x ⇒ a x 2 + ( a e − 3 ) x + e = 0 \frac{3x-e}{x+e}=ax\Rightarrow ax^2+\left(ae-3\right)x+e=0 x+e3x−e=ax⇒ax2+(ae−3)x+e=0
Δ = ( a e − 1 ) ( a e − 9 ) > 0 \Delta = \left(ae-1\right)\left(ae-9\right)>0 Δ=(ae−1)(ae−9)>0
设 x 3 , x 4 x_3,x_4 x3,x4为 3 x − e x + e = a x \frac{3x-e}{x+e}=ax x+e3x−e=ax的两个根
x 3 x 4 = e a x_3x_4 = \frac{e}{a} x3x4=ae
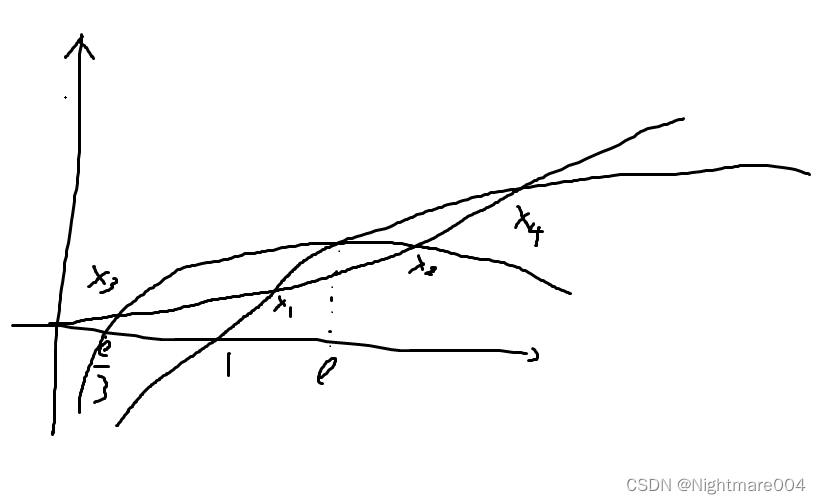
根据图像 x 3 < x 1 < e < x 2 < x 4 x_3 < x_1 < e < x_2 < x4 x3<x1<e<x2<x4
因此
x 1 x 2 > x 3 x 4 = e a x_1 x_2 > x_3 x_4 = \frac{e}{a} x1x2>x3x4=ae
(11) ln x 1 + ln x 2 > 1 − ln a \ln x_1 + \ln x_2 >1-\ln a lnx1+lnx2>1−lna
由(12)
ln x 1 + ln x 2 = ln x 1 x 2 > 1 − ln a \ln x_1 +\ln x_2=\ln x_1 x_2 >1-\ln a lnx1+lnx2=lnx1x2>1−lna
(10) x 1 + x 2 > 1 − ln a a x_1 + x_2 >\frac{1-\ln a}{a} x1+x2>a1−lna
x 1 + x 2 = ln x 1 + ln x 2 a > 1 − ln a a x_1 + x_2 =\frac{\ln x_1 +\ln x_2}{a}>\frac{1-\ln a}{a} x1+x2=alnx1+lnx2>a1−lna
(8) x 1 + x 2 > 3 a − e x_1 + x_2 > \frac{3}{a}-e x1+x2>a3−e
g ( a ) = − 2 − ln a + e a g\left(a\right) = -2-\ln a +ea g(a)=−2−lna+ea
g ′ ( a ) = − 1 a + e < 0 g^{\prime}\left(a\right)=-\frac{1}{a}+e<0 g′(a)=−a1+e<0
g ( a ) > g ( 1 a ) = 0 g\left(a\right)>g\left(\frac{1}{a}\right)=0 g(a)>g(a1)=0
由(10)
x 1 + x 2 > 1 − ln a a > 3 a − e x_1 + x_2 >\frac{1-\ln a}{a}> \frac{3}{a}-e x1+x2>a1−lna>a3−e
(17) x 1 2 x 2 + x 2 2 x 1 > 2 e a 2 x_1^2 x_2 +x_2^2 x_1 >\frac{2e}{a^2} x12x2+x22x1>a22e
由(2),(12)
x 1 2 x 2 + x 2 2 x 1 = x 1 x 2 ( x 1 + x 2 ) > e a 2 a = 2 e a 2 x_1^2 x_2 +x_2^2 x_1=x_1 x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)>\frac{e}{a}\frac{2}{a}=\frac{2e}{a^2} x12x2+x22x1=x1x2(x1+x2)>aea2=a22e
构造函数放缩型[同大]
g ( x ) = ln x − x 2 e + e 2 x − 1 g\left(x\right) = \ln x -\frac{x}{2e}+\frac{e}{2x}-1 g(x)=lnx−2ex+2xe−1
g ′ ( x ) = − ( x − e ) 2 2 e x 2 < 0 g^{\prime}\left(x\right) = -\frac{\left(x-e\right)^2}{2ex^2}<0 g′(x)=−2ex2(x−e)2<0
x < e x<e x<e时, ln x > x 2 e − e 2 x + 1 \ln x> \frac{x}{2e}-\frac{e}{2x}+1 lnx>2ex−2xe+1
x > e x>e x>e时, ln x < x 2 e − e 2 x + 1 \ln x< \frac{x}{2e}-\frac{e}{2x}+1 lnx<2ex−2xe+1
(13) 1 x 1 + 1 x 2 > 2 e \frac{1}{x_1}+\frac{1}{x_2} > \frac{2}{e} x11+x21>e2
x 2 e − e 2 x + 1 = a x ⇒ ( 2 a e − 1 ) x 2 − 2 e x + e 2 = 0 \frac{x}{2e}-\frac{e}{2x}+1 = ax \Rightarrow \left(2ae -1\right)x^2-2ex+e^2=0 2ex−2xe+1=ax⇒(2ae−1)x2−2ex+e2=0
Δ = 8 e 2 ( 1 − a e ) > 0 \Delta=8e^2\left(1-ae\right)>0 Δ=8e2(1−ae)>0
设 x 2 e − e 2 x + 1 = a x \frac{x}{2e}-\frac{e}{2x}+1 = ax 2ex−2xe+1=ax两个根为 x 5 , x 6 x_5, x_6 x5,x6
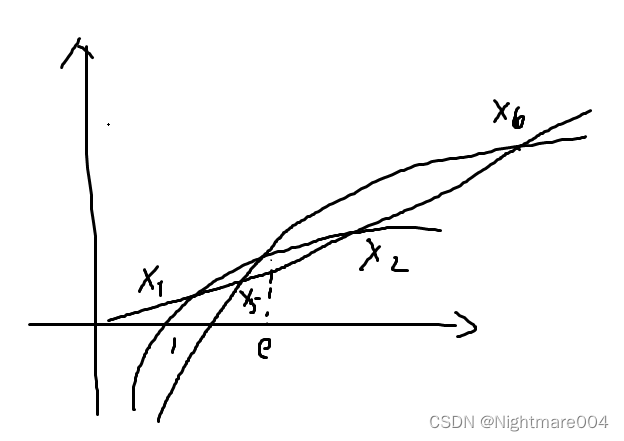
x 1 < x 5 < e < x 2 < x 6 x_1 <x_5 < e<x_2 < x_6 x1<x5<e<x2<x6
x 5 + x 6 = 2 e 2 a e − 1 x_5+x_6 = \frac{2e}{2ae-1} x5+x6=2ae−12e
x 5 x 6 = e 2 2 a e − 1 x_5x_6 = \frac{e^2}{2ae-1} x5x6=2ae−1e2
1 x 1 + 1 x 2 > 1 x 5 + 1 x 6 = x 5 + x 6 x 5 x 6 = 2 e \frac{1}{x_1}+\frac{1}{x_2} >\frac{1}{x_5}+\frac{1}{x_6}=\frac{x_5+x_6}{x_5x_6}=\frac{2}{e} x11+x21>x51+x61=x5x6x5+x6=e2
(15) 1 ln x 1 + 1 ln x 2 > 2 a e \frac{1}{\ln x_1} + \frac{1}{\ln x_2} > 2ae lnx11+lnx21>2ae
由(13)
1 ln x 1 + 1 ln x 2 = 1 a ( 1 x 1 + 1 x 2 ) = 2 a e > 2 a e \frac{1}{\ln x_1} + \frac{1}{\ln x_2}=\frac{1}{a}\left(\frac{1}{x_1}+\frac{1}{x_2}\right)=\frac{2}{ae}>2ae lnx11+lnx21=a1(x11+x21)=ae2>2ae
构造函数放缩型[间距减小]
g ( x ) = ln x − 2 + e x g\left(x\right)=\ln x - 2 +\frac{e}{x} g(x)=lnx−2+xe
g ′ ( x ) = x − e x 2 g^{\prime}\left(x\right)=\frac{x-e}{x^2} g′(x)=x2x−e
g ( x ) ≥ g ( e ) = 0 g\left(x\right)\ge g\left(e\right)=0 g(x)≥g(e)=0
当且仅当 x = e x=e x=e时 g ( x ) = 0 g\left(x\right)=0 g(x)=0
(19) x 1 < 1 − 1 − a e a x_1 < \frac{1-\sqrt{1-ae}}{a} x1<a1−1−ae
2 − e x = a x ⇒ a x 2 − 2 x + e = 0 2-\frac{e}{x}=ax\Rightarrow ax^2-2x+e=0 2−xe=ax⇒ax2−2x+e=0
Δ = 4 ( 1 − a e ) > 0 \Delta = 4\left(1-ae\right)>0 Δ=4(1−ae)>0
设 2 − e x = a x 2-\frac{e}{x}=ax 2−xe=ax的根为 x 7 , x 8 x_7,x_8 x7,x8
x 7 = 1 − 1 − a e a , x 8 = 1 + 1 − a e a x_7=\frac{1-\sqrt{1-ae}}{a},x_8=\frac{1+\sqrt{1-ae}}{a} x7=a1−1−ae,x8=a1+1−ae
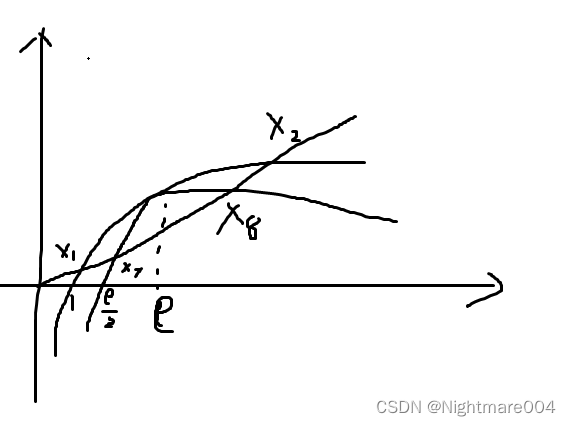
x 1 < x 7 < x 8 < x 2 x_1<x_7<x_8<x_2 x1<x7<x8<x2
因此
x 1 < 1 − 1 − a e a x_1 < \frac{1-\sqrt{1-ae}}{a} x1<a1−1−ae
(20) x 2 > 1 + 1 − a e a x_2>\frac{1+\sqrt{1-ae}}{a} x2>a1+1−ae
由(19)成立
(18) x 1 x 2 < a e \frac{x_1}{x_2}<ae x2x1<ae
x 1 x 2 < 1 − 1 − a e a a 1 + 1 − a e = 1 − 1 − a e 1 + 1 − a e = a e ( 1 + 1 − a e ) 2 < a e \frac{x_1}{x_2}<\frac{1-\sqrt{1-ae}}{a}\frac{a}{1+\sqrt{1-ae}}=\frac{1-\sqrt{1-ae}}{1+\sqrt{1-ae}}=\frac{ae}{\left(1+\sqrt{1-ae}\right)^2}<ae x2x1<a1−1−ae1+1−aea=1+1−ae1−1−ae=(1+1−ae)2ae<ae
(21) x 2 − x 1 > 2 1 − a e a x_2-x_1>\frac{2\sqrt{1-ae}}{a} x2−x1>a21−ae
由(19),(20)显然
(22) x 2 − x 1 > 1 − a e a x_2-x_1>\frac{\sqrt{1-ae}}{a} x2−x1>a1−ae
由(21)显然
(23) x 2 − x 1 > 1 − a e x_2-x_1>\sqrt{1-ae} x2−x1>1−ae
由(22)显然
(24) x 2 − x 1 > 2 e a − e 2 x_2-x_1>2\sqrt{\frac{e}{a}-e^2} x2−x1>2ae−e2
由(21)
x 2 − x 1 > 2 1 − a e a > 2 e a − e 2 = 2 e a 1 − a e x_2-x_1>\frac{2\sqrt{1-ae}}{a}>2\sqrt{\frac{e}{a}-e^2}=2\sqrt{\frac{e}{a}}\sqrt{1-ae} x2−x1>a21−ae>2ae−e2=2ae1−ae
(26) x 2 − x 1 > ( e 2 − 2 ) ( 1 − a e ) x_2-x_1>\left(e^2-2\right)\left(1-ae\right) x2−x1>(e2−2)(1−ae)
e ≈ 2.718 e \approx 2.718 e≈2.718
3 ≈ 1.73 \sqrt{3}\approx 1.73 3≈1.73
因此 e < 3 + 1 e<\sqrt{3}+1 e<3+1
e 2 − 2 − 2 e = ( e + 3 − 1 ) ( e − 3 − 1 ) < 0 e^2-2-2e=\left(e+\sqrt{3}-1\right)\left(e-\sqrt{3}-1\right)<0 e2−2−2e=(e+3−1)(e−3−1)<0
由(21)
x 2 − x 1 > 2 1 − a e a > 2 e 1 − a e > ( e 2 − 2 ) 1 − a e > ( e 2 − 2 ) ( 1 − a e ) x_2-x_1>\frac{2\sqrt{1-ae}}{a}>2e\sqrt{1-ae}>\left(e^2-2\right)\sqrt{1-ae}>\left(e^2-2\right)\left(1-ae\right) x2−x1>a21−ae>2e1−ae>(e2−2)1−ae>(e2−2)(1−ae)
(27) x 2 − x 1 > 2 ( e − 2 ) 1 − a e x_2-x_1>2\left(e-2\right)\sqrt{1-ae} x2−x1>2(e−2)1−ae
由(21)
x 2 − x 1 > 2 1 − a e a > 2 e 1 − a e > 2 ( e − 2 ) 1 − a e x_2-x_1>\frac{2\sqrt{1-ae}}{a}>2e\sqrt{1-ae}>2\left(e-2\right)\sqrt{1-ae} x2−x1>a21−ae>2e1−ae>2(e−2)1−ae
切线放缩[间距增大]及特殊非对称式
(28) x 2 − x 1 < 4 e 3 2 − 1 − ( 2 e 2 + 1 ) a ( 3 2 e 3 2 < a < 1 e ) x_2-x_1 < 4e^{\frac{3}{2}}-1-\left(2e^2+1\right)a\left(\frac{3}{2e^{\frac{3}{2}}}<a<\frac{1}{e}\right) x2−x1<4e23−1−(2e2+1)a(2e233<a<e1)
(30)若 1 a < ( 1 − m ) x 1 + m x 2 \frac{1}{a}<\left(1-m\right)x_1+m x_2 a1<(1−m)x1+mx2恒成立,求 m m m的取值范围
即 m > 1 a − x 1 x 2 − x 1 m>\frac{\frac{1}{a}-x_1}{x_2-x_1} m>x2−x1a1−x1
令 s = x 2 − 1 a s=x_2-\frac{1}{a} s=x2−a1
t = 1 a − x 1 t=\frac{1}{a}-x_1 t=a1−x1
1 a − x 1 x 2 − x 1 = t s + t = 1 1 + s t \frac{\frac{1}{a}-x_1}{x_2-x_1}=\frac{t}{s+t}=\frac{1}{1+\frac{s}{t}} x2−x1a1−x1=s+tt=1+ts1
由(19),(20)
s t > 1 + 1 − a e a − 1 a 1 a − 1 − 1 − a e a = 1 \frac{s}{t}>\frac{\frac{1+\sqrt{1-ae}}{a}-\frac{1}{a}}{\frac{1}{a}-\frac{1-\sqrt{1-ae}}{a}}=1 ts>a1−a1−1−aea1+1−ae−a1=1
因此
1 1 + s t < 1 2 \frac{1}{1+\frac{s}{t}}<\frac{1}{2} 1+ts1<21
因此
m ∈ [ 1 2 , + ∞ ] m\in\left[\frac{1}{2},+\infty\right] m∈[21,+∞]
(14) 2 ln x 1 + ln x 2 > e 2\ln x_1 + \ln x_2 >e 2lnx1+lnx2>e
参考:
https://www.zhihu.com/question/442349127/answer/1711515692