前言
本文从 U-Net 入手熟悉分割的简单方法,再看 YOLOv8 的方法。主要梳理 YOLOv8 的网络结构,以及 Predict 过程的后处理方法。
U-Net 代码地址:https://github.com/milesial/Pytorch-UNet
YOLOv8 代码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
YOLOv8 官方文档:https://docs.ultralytics.com/
1. U-Net
1.1 网络结构

CBR
Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
ReLU(inplace=True)
1.2 转置卷积
torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None
)
H o u t = ( H i n − 1 ) × stride [ 0 ] − 2 × padding [ 0 ] + dilation [ 0 ] × ( kernel_size [ 0 ] − 1 ) + output_padding [ 0 ] + 1 H_{out} = (H_{in} - 1) \times \text{stride}[0] - 2 \times \text{padding}[0] + \text{dilation}[0] \times (\text{kernel\_size}[0] - 1) + \text{output\_padding}[0] + 1 Hout=(Hin−1)×stride[0]−2×padding[0]+dilation[0]×(kernel_size[0]−1)+output_padding[0]+1
W o u t = ( W i n − 1 ) × stride [ 1 ] − 2 × padding [ 1 ] + dilation [ 1 ] × ( kernel_size [ 1 ] − 1 ) + output_padding [ 1 ] + 1 W_{out} = (W_{in} - 1) \times \text{stride}[1] - 2 \times \text{padding}[1] + \text{dilation}[1] \times (\text{kernel\_size}[1] - 1) + \text{output\_padding}[1] + 1 Wout=(Win−1)×stride[1]−2×padding[1]+dilation[1]×(kernel_size[1]−1)+output_padding[1]+1
- stride
控制原图像素之间的填充量,数值为 stride − 1 \text{stride}-1 stride−1 - kernel_size,padding
kernel_size 为转置卷积核大小,并且和 padding 一同决定原图四周填充量,数值为 kernel_size − padding − 1 \text{kernel\_size}-\text{padding}-1 kernel_size−padding−1 - dilation
控制卷积核采样点的间距(空洞卷积),默认为1,即最普通的卷积
注:转置卷积在卷积时的 stride 固定为1,output_padding 固定为0;而参数中设置的 stride、padding 用于控制卷积之前对输入的填充
以 kernel_size = 2 , stride = 2 , padding = 0 , H i n = 640 , W i n = 640 \text{kernel\_size}=2,\text{stride}=2,\text{padding}=0,H_{in}=640,W_{in}=640 kernel_size=2,stride=2,padding=0,Hin=640,Win=640 为例
- 像素间填充 2-1=1, 640 × 640 → 1279 × 1279 640\times640\to1279\times1279 640×640→1279×1279
- 四周填充 2-0-1=1, 1279 × 1279 → 1281 × 1281 1279\times1279\to1281\times1281 1279×1279→1281×1281
- 2x2卷积, 1281 × 1281 → 1280 × 1280 1281\times1281\to1280\times1280 1281×1281→1280×1280
查看不同卷积的可视化:https://github.com/vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic/blob/master/README.md
1.3 Loss
单分类
loss = BCEWithLogitsLoss(P, Y) + dice_loss(sigmoid(P), Y)
多分类
loss = CrossEntropyLoss(P, Y) + dice_loss(softmax(P), one_hot(Y))
(1)BCEWithLogitsLoss
对于每个样本 l = − [ y l o g σ ( x ) + ( 1 − y ) l o g ( 1 − σ ( x ) ) ] l=-[ylog\sigma (x)+(1-y)log(1-\sigma (x))] l=−[ylogσ(x)+(1−y)log(1−σ(x))],最后求均值
(2)dice_loss
l = 1 − sum ( 2 × P × Y ) sum ( P ) + sum ( Y ) l = 1-\frac{\text{sum}(2\times P\times Y)}{\text{sum}(P)+\text{sum}(Y)} l=1−sum(P)+sum(Y)sum(2×P×Y)
这里的 Y Y Y 作为标签是固定的, P P P 通过让目标区域值靠近1提高分子值,背景区域靠近0降低分母值,即 P → Y P\to Y P→Y,从而降低loss
1.4 Predict
单分类
mask = sigmoid(P) > threshold
多分类
mask = P.argmax(dim=1)
2. YOLOv8-seg
2.1 网络结构
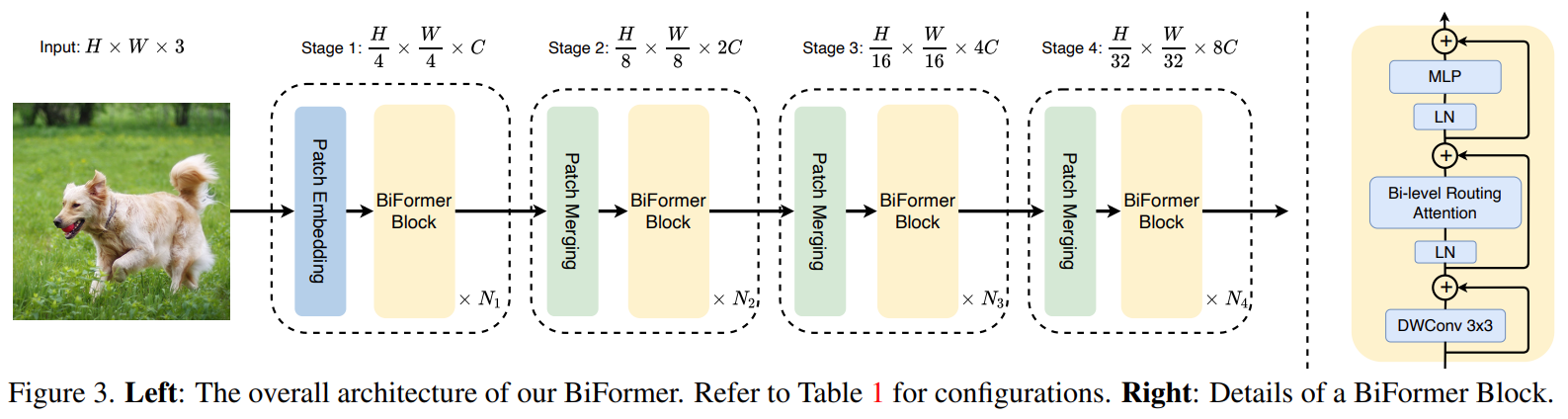
结构图中数据按 yolov8m-seg 的 predict 过程绘制,输入图像为 1280x720,预处理时通过 LetterBox 对图像进行保长宽比缩放和 padding,使其长宽都能被最大下采样倍率32整除。在 train 过程中,输入大小统一为 640x640。
主干

CBS
Conv2d(3, 48, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
BatchNorm2d(48, eps=0.001, momentum=0.03, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
SiLU(inplace=True)
C2f 模块

SPPF

Segment-head
分割

检测

注:DLF层中的卷积层参数是固定的,在这里是 torch.arange(16)。
Anchor
Anchor坐标是把特征图看做一个网格,每个像素边长为1,把每个格子的中心点坐标取出来。以 x0 (h=48,w=80) 为例,左上角坐标为 (0.5,0.5),右下角点为 (79.5,47.5)。
DLF的输出对应目标框左上角坐标和右下角坐标到Anchor坐标的距离,与Anchor融合并乘上对应的下采样倍率得到 dbox。
lt, rb = dfl(box).chunk(2, dim=1)
x1y1 = anchor_points - lt
x2y2 = anchor_points + rb
2.2 预测
模型推理输出
Y: [b,4,5040]
mc: [b,32,5040]
p: [b,32,96,160]Y为检测结果,4对应检测框坐标
mc为分割结果,32对应分割的特征向量,通过和p做矩阵乘法可以转化成mask形式模型最终推理的输出preds包含两项
(1)torch.cat(y, mc], 1), 即检测和分割的结果, shape:[b,37,5040]
(2)包含3项的元组a. [x0, x1, x2], 即detect层的中间输出b. mc [b,32,5040]c. p [b,32,96,160]
NMS
p = nms((20,37,5040), conf=0.25, iou=0.7, agnostic=False, max_det=300, nc=1)(1) 分类得分阈值筛选 class_scores > conf=0.25
[5040,37] --> [n1,37]
(2) 提取类别
[n1,37] --> [n1,38] (xyxy, cls_score, cls, 32)
(3) 若此时box数量大于 max_nms=30000, 选取 cls_score 较大的30000个
(4) 调库 torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres), 选取前 max_det=300 项
[n1,38] --> [n2,38]
(5) nms-merge, 默认跳过
mask
masks = process_mask(protos, 模型输出p [b,32,96,160]masks_in=pred[:, 6:], nms结果的mask部分bboxes=pred[:, :4], nms结果的box部分shape=img.shape[2:], 输入图像大小(384,640)upsample=True
)def process_mask(protos, masks_in, bboxes, shape, upsample=False):c, mh, mw = protos.shapeih, iw = shape"""矩阵乘法+sigmoid得到mask"""masks = (masks_in @ protos.float().view(c, -1)).sigmoid().view(-1, mh, mw)"""比例变换"""downsampled_bboxes = bboxes.clone()downsampled_bboxes[:, 0] *= mw / iwdownsampled_bboxes[:, 2] *= mw / iwdownsampled_bboxes[:, 3] *= mh / ihdownsampled_bboxes[:, 1] *= mh / ih"""裁减掉box范围以外的值"""masks = crop_mask(masks, downsampled_bboxes) # CHWif upsample:masks = F.interpolate(masks[None], shape, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)[0] # CHW"""按阈值0.5转为二值图mask"""return masks.gt_(0.5)



![[答疑]校长出轨主任流程的业务建模](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d6dbd6e595594db3908d549c4ed817f3.png)