题目:Always if
An if statement usually creates a 2-to-1 multiplexer, selecting one input if the condition is true, and the other input if the condition is false.
if语句通常创建一个2- to -1多路复用器,如果条件为真,则选择其中一个输入,如果条件为假,则选择另一个输入。

This is equivalent to using a continuous assignment with a conditional operator:
这相当于使用带有条件运算符的连续赋值:
assign out = (condition) ? x : y;
However, the procedural if statement provides a new way to make mistakes. The circuit is combinational only if out is always assigned a value.
但是,过程if语句提供了一种新的方式来犯错误。电路只有在out总是被赋值时才是组合的。
A bit of practice
一些实践
Build a 2-to-1 mux that chooses between a and b. Choose b if both sel_b1 and sel_b2 are true. Otherwise, choose a. Do the same twice, once using assign statements and once using a procedural if statement.
构建一个2-to-1的多路复用器,在sel_b1和sel_b2都为真时选择b,否则选择a。使用assign语句和过程if语句各做一次。
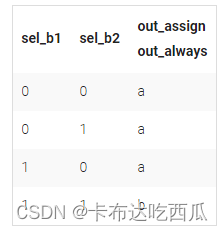
上面给出了如何通过assign利用 ? : 和always利用i =f语句实现多路复用器,
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module(input clk,input a,input b,output wire out_assign,output reg out_always_comb,output reg out_always_ff );//assign语句assign out_assign = a ^ b;//组合型always块always@(*)beginout_always_comb = a ^ b;end//时钟型always块always@(posedge clk)beginout_always_ff <= a ^ b;end
endmodule

![[LeetCode]-138. 随机链表的复制](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4bd101c1a6b74dff9549ac49db197b49.png)