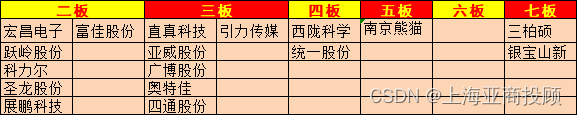
✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅
✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨
🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿
🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
🌟🌟 追风赶月莫停留 🌟🌟
🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀
🌟🌟 平芜尽处是春山🌟🌟
🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿
✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨
✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅
🍋单链表
- 🍌单链表的定义
- 🍌单链表的结构
- 🍍循环的单链表
- 🍍不循环单链表
- 🍌单链表增删查改(无头+单向+非循环链表增删查改实现)
- 🍍其它接口
- 🍍动态申请一个节点
- 🍍单链表打印
- 🍍单链表尾插
- 🍍单链表的头插
- 🍍单链表的尾删
- 🍍单链表头删
- 🍍单链表查找
- 🍍单链表在pos位置之后插入x
- 🍍 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
- 🍌单链表整体代码的实现
🍌单链表的定义
单链表:一种链式存取的数据结构,用一组地址任意的存储单元存放线性表中的数据元素。链表中的数据是以结点来表示的,每个结点的构成:元素(数据元素的映象) + 指针(指示后继元素存储位置),元素就是存储数据的存储单元,指针就是连接每个结点的地址数据。

上图就是一个简单的空的(没有装数据)单链表
🍌单链表的结构
🍍循环的单链表
typedef int SLDatatype;
typedef struct SListNode
{SLDatatype val;struct SListNode* next;}SListNode;
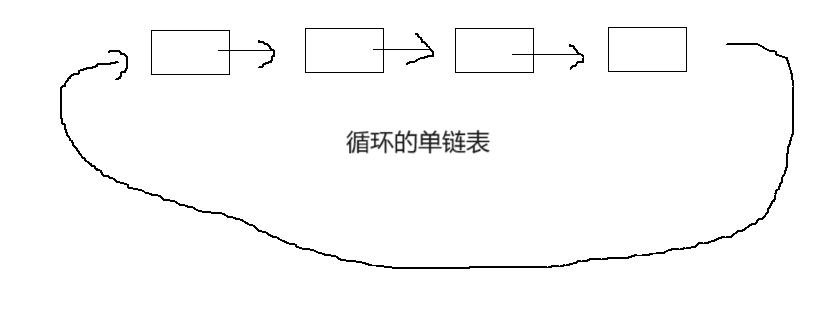
这就是循环的单链表
🍍不循环单链表
typedef int SLDatatype;
typedef struct SListNode
{SLDatatype val;struct SListNode* next;}SListNode;
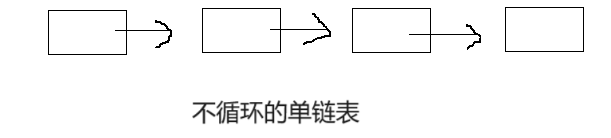
这就是不循环的单链表,而且没有装入数据
循环单链表和不循环的单链表创建是一样的只不过是在结尾的时候,循环的单链表中最后一个也就是尾指向了头,而不循环的单链表中的尾指向了空(NULL)
🍌单链表增删查改(无头+单向+非循环链表增删查改实现)
🍍其它接口
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int SLDatatype;
typedef struct SListNode
{SLDatatype val;struct SListNode* next;}SListNode;
🍍动态申请一个节点
// 动态申请一个节点
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLDatatype x)
{SListNode* cur = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));if (cur == NULL){perror("malloc faild");exit(-1);}cur->val = x;cur->next = NULL;return cur;
}
大家如果对于malloc和realloc以及空间的创建的用法有些遗忘,可以看我这篇博客:动态内存管理(这是一个链接,有需要的朋友可以直接点进去)
🍍单链表打印
// 单链表打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* ps)
{//为保存头指针的位置//需要重新定义一个指针来移动SListNode* cur = ps; while (cur){printf("%d->", cur->val);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}
因为在链表这里,都是指针移动,所以我们需要保存头指针的位置不变,故需要重新定义一个指针来移动。
🍍单链表尾插
// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SListNode** ps, SLDatatype x)
{SListNode* new = BuySListNode(x);//尾插要分两种情况//第一种是链表里是为空的,而为空,就需要用到二级指针来改变结构体的指针//第二种是链表里数据不为空的
if (*ps == NULL){*ps = new;}else{SListNode* cur = *ps;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = new;}
}
注意:
尾插要分两种情况
(1)第一种是链表里是为空的,而为空,就需要用到二级指针来改变结构体的指针
(2)第二种是链表里数据不为空的

大家可能对于这个没有头的头指针还是难以理解,尽可能去理解吧,我刚开始学习这个也是这样,不过单链表题写多了以及学了后面带头的头指针就会好很多。

第二种情况还是很好理解的
🍍单链表的头插
// 单链表的头插第一种方法:
void SListPushFront(SListNode** ps, SLDatatype x)
{SListNode* new = BuySListNode(x);if (*ps == NULL){*ps = new;}else{SListNode* cur = *ps;*ps = new;new->next = cur;}
}
// 单链表的头插第二种方法:
void SListPushFront(SListNode** ps, SLDatatype x)
{SListNode* new = BuySListNode(x);new->next = *ps;*ps = new;}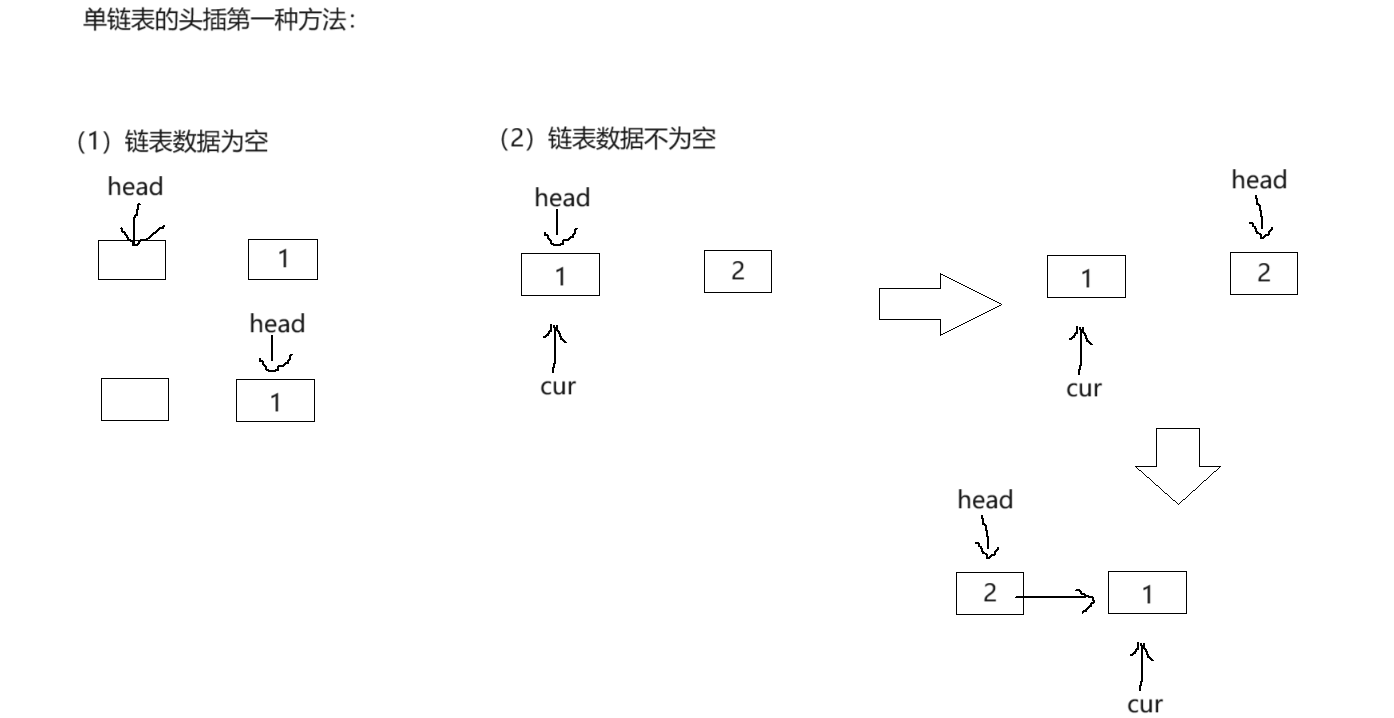
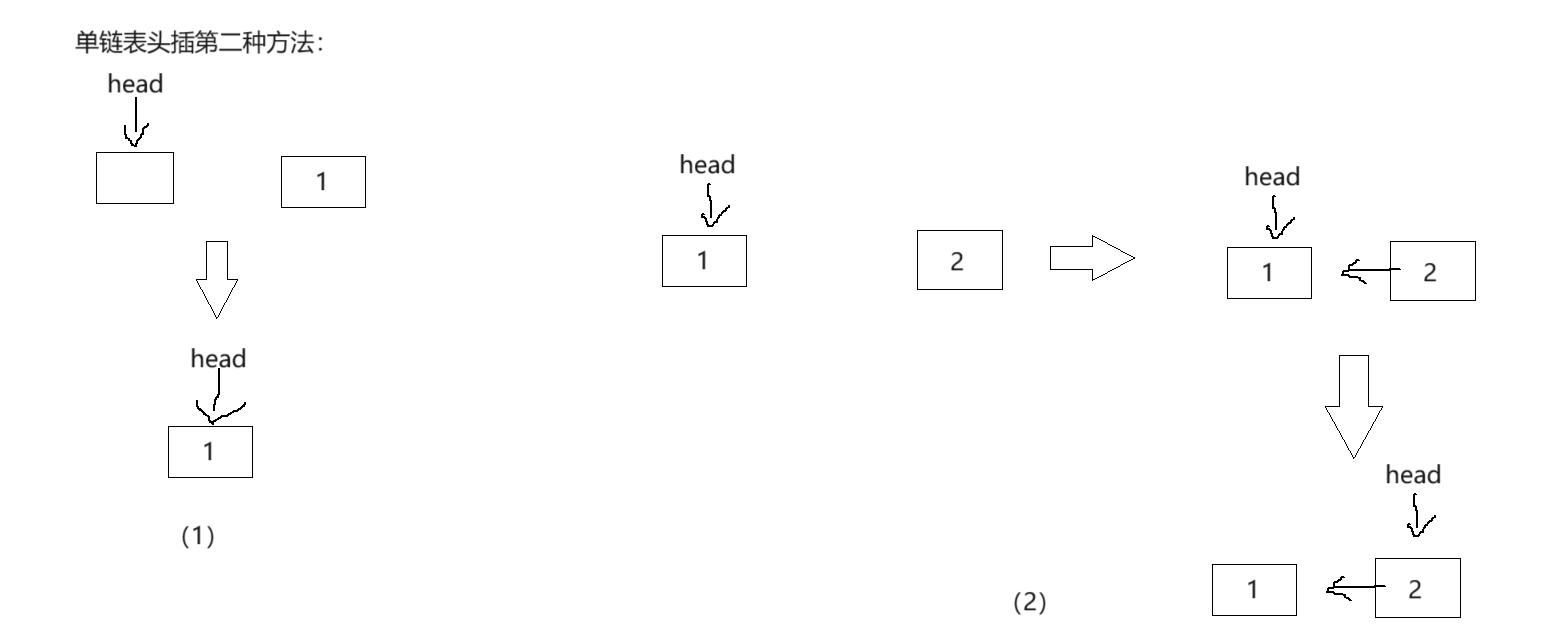
这两种方法都挺好理解的
🍍单链表的尾删
// 单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode** ps)
{assert(*ps);//防止链表为空if ((*ps)->next == NULL)//只有一个节点{free(*ps);*ps = NULL;}else //两个节点及以上{SListNode* cur = *ps;while (cur->next->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}free(cur->next); cur->next = NULL;}
}
注意节点个数
在尾删就得看节点个数了,然后分为三种情况,0节点和一个节点、两个节点及以上

🍍单链表头删
// 单链表头删
void SListPopFront(SListNode** ps)
{assert(*ps);//防止链表为空//链表不为空SListNode* cur = *ps;*ps = cur->next;free(cur);cur->next = NULL;
}
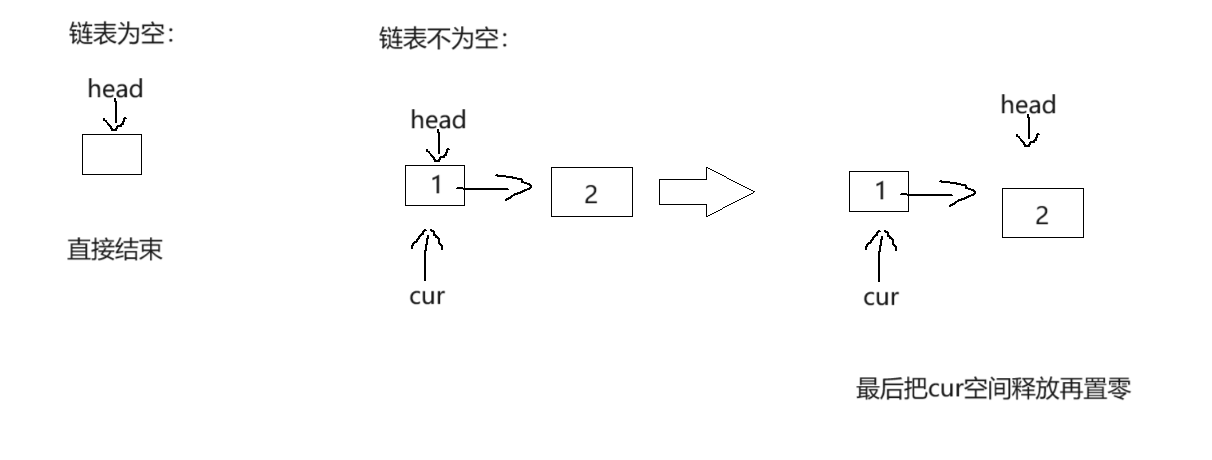
上面的尾插,头插,尾删,了解后,这里应该都能很好的理解了
🍍单链表查找
// 单链表查找
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* ps, SLDatatype x)
{assert(ps);SListNode* cur = ps;while (cur->next != NULL){if (cur->val == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}
这个查找就很简单了,直接遍历一遍就可以了,注意一下循环停止的时间
🍍单链表在pos位置之后插入x
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLDatatype x)
{assert(pos);SListNode* cur = pos->next;SListNode* new = BuySListNode(x);if (new == NULL){perror("malloc faild");exit(-1);}pos->next = new;new->next = cur;}
🍍 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pos->next); //检查是否是尾节点SListNode* cur = pos->next;pos->next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;
}
在这里注意一下pos是否为尾节点
🍌单链表整体代码的实现
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int SLDatatype;
typedef struct SListNode
{SLDatatype val;struct SListNode* next;}SListNode;// 动态申请一个节点
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLDatatype x)
{SListNode* cur = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));if (cur == NULL){perror("malloc faild");exit(-1);}cur->val = x;cur->next = NULL;return cur;
}// 单链表打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* ps)
{SListNode* cur = ps;while (cur){printf("%d->", cur->val);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SListNode** ps, SLDatatype x)
{SListNode* new = BuySListNode(x);if (*ps == NULL){*ps = new;}else{SListNode* cur = *ps;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = new;}
}// 单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SListNode** ps, SLDatatype x)
{第一种方法://SListNode* new = BuySListNode(x);//if (*ps == NULL)//{// *ps = new;//}//else//{// SListNode* cur = *ps;// *ps = new;// new->next = cur;//}//第二种方法:SListNode* new = BuySListNode(x);new->next = *ps;*ps = new;}// 单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode** ps)
{assert(*ps);//防止链表为空if ((*ps)->next == NULL)//只有一个节点{free(*ps);*ps = NULL;}else //两个节点及以上{SListNode* cur = *ps;while (cur->next->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}free(cur->next); cur->next = NULL;}
}// 单链表头删
void SListPopFront(SListNode** ps)
{assert(ps);assert(*ps);//防止链表为空//链表不为空SListNode* cur = *ps;*ps = cur->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;
}// 单链表查找
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* ps, SLDatatype x)
{assert(ps);SListNode* cur = ps;while (cur){if (cur->val == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLDatatype x)
{assert(pos);SListNode* cur = pos->next;SListNode* new = BuySListNode(x);if (new == NULL){perror("malloc faild");exit(-1);}pos->next = new;new->next = cur;}// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pos->next); //检查是否是尾节点SListNode* cur = pos->next;pos->next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;
}void test1()
{int n = 0;SListNode* plist = NULL;SListPushBack(&plist, 100);//尾插SListPushBack(&plist, 200);//尾插SListPushBack(&plist, 300);//尾插SListPushBack(&plist, 400);//尾插SListPrint(plist);//打印SListPushFront(&plist, 900);//头插SListPushFront(&plist, 800);//头插SListPushFront(&plist, 700);//头插SListPushFront(&plist, 600);//头插SListPrint(plist);//打印SListPopBack(&plist);//尾删SListPrint(plist);//打印SListPopFront(&plist);//头删SListPrint(plist);//打印SListNode* pos = SListFind(plist, 200);//查找if (pos != NULL){printf("找到了\n");}else{printf("找不到\n");}SListInsertAfter(pos, 999);//在pos位置之后插入xSListPrint(plist);SListEraseAfter(pos);//删除pos位置之后的值SListPrint(plist);
}int main()
{test1();return 0;
}
传地址的时候注意:有一些函数只需要传一级指针就可以了,而有些函数需要传二级指针。在这里一级指针直接传结构体就可以了,这是因为我们定义的是指针的结构体,而二级指针就需要传结构体的地址了。