1 回文链表
1.1 判断方法
- 第一种(笔试):
- 链表从中间分开,把后半部分的节点放到栈中
- 从链表的头结点开始,依次和弹出的节点比较
- 第二种(面试):
- 反转链表的后半部分,中间节点的下一节点指向空
- 两个指针分别从链表的头和尾出发比较
- 直到左边节点到空或两个节点都到空停止
- 判断结果出来后,要把链表后半部分反转回去。
1.2 代码实现
ublic class IsPalindromList {public static class Node {public int val;public Node next;public Node(int data) {val = data;next = null;}}public static boolean isPalindrom1(Node head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return true;}Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();Node mid = head;Node fast = head;while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {mid = mid.next;fast = fast.next.next;}while (mid.next != null) {mid = mid.next;stack.add(mid);}Node i = head;boolean ans = true;while (stack.size() != 0) {if (i.val != stack.pop().val) {ans = false;break;}i = i.next;}return ans;}public static boolean isPalindrom2(Node head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return true;}// 找到中间节点Node mid = head;Node fast = head;while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {mid = mid.next;fast = fast.next.next;}Node cur = mid;// 后边段链表反转Node pre = null;Node next = null;while (cur != null) {next = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = next;}Node left = head;Node right = pre;boolean ans = true;while (left != null && right != null) {if (left.val != right.val) {ans = false;break;}left = left.next;right = right.next;}cur = pre;pre = null;next = null;while (cur != null) {next = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = next;}return ans;}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = new Node(0);head.next = new Node(1);head.next.next = new Node(2);head.next.next.next = new Node(2);head.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(0);System.out.println(isPalindrom2(head));System.out.println(isPalindrom1(head));}}
2 荷兰国旗
链表的荷兰国旗问题,给定一个链表头节点,一个划分值
- 把链表中小于划分值的放在左边
- 等于划分值的放在中间
- 大于划分值的放在右边。
2.1 解决方法
(其实我第一次写的时候第二种方法比第一种方法写的快,因为思路简单,不绕。)
- 第一种(笔试):
- 把链表的所有节点放在一个节点数组中
- 对这个数组做
partition过程 - 之后把数组每个节点连起来
- 第二种(面试):
- 定义有六个节点,分别代表:大于、等于和小于区域的头和尾
- 链表开始遍历,比划分值小的连在小于区域下方,同时断开节点和之前链表的关系,指向空
- 等于和大于同理
- 遍历完链表之后,开始把小于区域的尾巴和等于区域的头连接,等于区域的尾巴和大于区域的头连接
2.2 代码实现
public class SmallEqualBig {public static class Node {public int val;public Node next;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;next = null;}}public static Node listPartition1(Node head, int pivot) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}int index = 1;Node cur = head;while (cur.next != null) {index++;cur = cur.next;}Node[] arr = new Node[index];cur = head;for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {arr[i] = cur;cur = cur.next;}partition(arr,pivot);for (index = 1; index != arr.length; index++) {arr[index - 1].next = arr[index];}arr[index - 1].next = null;return arr[0];}public static Node listPartition2(Node head, int pivot) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}Node smallHead = null;Node smallTail = null;Node equalHead = null;Node equalTail = null;Node bigHead = null;Node bigTail = null;Node next = null;while (head != null) {next = head.next;head.next = null;if (head.val < pivot) {if (smallHead == null) {smallHead = head;smallTail = head;}else {smallTail.next = head;smallTail = smallTail.next;}} else if (head.val == pivot) {if (equalHead == null) {equalHead = head;equalTail = head;}else {equalTail.next = head;equalTail = equalTail.next;}}else {if (bigHead == null) {bigHead = head;bigTail = head;}else {bigTail.next = head;bigTail = bigTail.next;}}head = next;}if (smallTail != null) {smallTail.next = equalHead;equalTail = equalTail == null ? smallTail : equalTail;}if (equalTail != null) {equalTail.next = bigHead;}return smallHead == null ? (equalHead == null ? bigHead : equalHead) : smallHead;}private static void partition(Node[] arr, int pivot) {int small = -1;int big = arr.length;int index = 0;while (index < big) {if(arr[index].val < pivot) {swap(arr, index++, ++small);} else if (arr[index].val > pivot) {swap(arr, index++, --big);}else {index++;}}}private static void swap(Node[] arr, int i, int j) {Node temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = temp;}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = new Node(9);head.next = new Node(1);head.next.next = new Node(2);head.next.next.next = new Node(6);head.next.next.next.next = new Node(4);head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);Node node = listPartition1(head, 2);while (node != null) {System.out.print(node.val + " ");node = node.next;}System.out.println();Node head2 = new Node(9);head2.next = new Node(1);head2.next.next = new Node(2);head2.next.next.next = new Node(6);head2.next.next.next.next = new Node(4);head2.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);head2.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);Node node1 = listPartition2(head2, 2);while (node1 != null) {System.out.print(node1.val + " ");node1 = node1.next;}}
}
3 复制链表
复制特殊链表,单链表中加了个rand指针,可能指向任意一个节点,也可能指向null
给定这个链表的头节点,完成链表的复制
返回复制的新链表的头节点。时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)
3.1 解决方法
-
方法一(笔试):
- 用HashMap来解决,key是原数组节点,value是复制的数组节点
-
方式二(面试):
-
将复制的新节点插入到原数组的节点中,如1–>2–>3,变成1–>(copy)1–>2–>(copy)2–>3–>(copy)3
-
复制节点的
rand指针指向就是原数组的节点的rand指针的下一节点(下图所示) -
把复制数组拿出来的时候注意复制数组连起来还要把原数组连起来
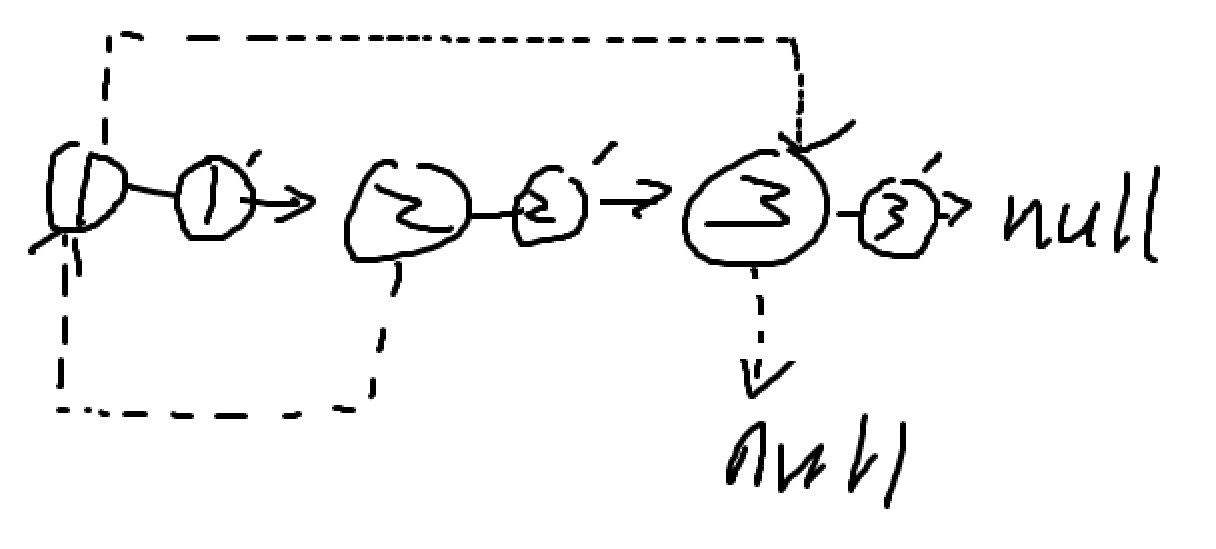
-
3.2 代码实现
public class CopyListWithRandom {public static class Node {public int val;public Node next;public Node rand;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;}}// map方法public static Node copyListWithRandom(Node head) {if (head == null) {return null;}HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();Node cur = head;while (cur != null) {map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));cur = cur.next;}Node ans = map.get(head);cur = head;while (cur != null) {map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);cur = cur.next;}return ans;}// 不借助容器public static Node copyListWithRandom2(Node head) {if (head == null) {return null;}Node cur = head;Node next = null;while (cur != null) {next = cur.next;cur.next = new Node(cur.val);cur.next.next = next;cur = next;}Node copyNode = null;cur = head;while (cur != null) {copyNode = cur.next;copyNode.rand = cur.rand == null ? null : cur.rand.next;cur = copyNode.next;}Node ans = head.next;cur = head;while (cur != null) {next = cur.next.next;copyNode = cur.next;copyNode.next = next == null ? null : next.next;cur.next = next;cur = next;}return ans;}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = new Node(1);Node node2 = new Node(2);Node node3 = new Node(3);head.next = node2;node2.next = node3;head.rand = node3;node2.rand = head;Node node = copyListWithRandom(head);while (node != null) {System.out.println(node.val + " ");System.out.println(node == head);node = node.next;head = head.next;}}
}
4 链表相交
给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,给定头节点1和头节点2.
请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的第一个节点,如果不相交,返回null
时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)
4.1 解决方法
- 先判断两个链表是否有环
- 两个都无环
- 如果两个链表的末尾节点相等,那么就是相交的,用指针先把长的链表走完两个链表的差值后,两个链表开始同时走,直到两个节点相等,就是相交的点
- 如果末尾节点不相等,那么两个链表不相交
- 一个有环一个无环:两个链表不会有相交点
- 两个都有环
- 判断两个链表进环的第一个节点是否是相同的
- 相同:相交,且相交点就在无环的部分中,参考2
- 不相同:从一个链表的入环节点开始找,如果找到了第二个链表的入环节点,那么就相交,返回两个入环节点任意一个,如果转一圈到第一个链表的入环节点还没有找到第二个入环节点,此时不相交。
4.2代码实现
public class FindFirstIntersectNode {public static class Node {public int val;public Node next;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;}}public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) {if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {return null;}Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1);Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2);if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) {return noLoop(head1, head2);}if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) {return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);}return null;}private static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) {Node cur1 = head1;Node cur2 = head2;if (loop1 == loop2) {int n = 0;while (cur1.next != null) {n++;cur1 = cur1.next;}while (cur2.next != null) {n--;cur2 = cur2.next;}cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;n = Math.abs(n);while (n != 0) {n--;cur1 = cur1.next;}while (cur1 != cur2) {cur1 = cur1.next;cur2 = cur2.next;}return cur1;}else {cur1 = loop1.next;while (cur1 != loop1) {if (cur1 == loop2) {return loop2;}cur1 = cur1.next;}return null;}}private static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {Node cur1 = head1;Node cur2 = head2;int n = 0;while (cur1.next != null) {n++;cur1 = cur2.next;}while (cur2.next != null) {n--;cur2 = cur2.next;}if (cur1 != cur2) {return null;}cur1 = n < 0 ? head2 : head1;cur2 = cur1 == head2 ? head1 : head2;n = Math.abs(n);while (n != 0) {n--;cur1 = cur1.next;}while (cur1 != cur2) {cur1 = cur1.next;cur2 = cur2.next;}return cur1;}private static Node getLoopNode(Node head) {if (head.next == null || head.next.next ==null) {return null;}Node slow = head.next;Node fast = head.next.next;while (fast != slow) {if (fast == null) {return null;}slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}fast = head;while (fast != slow) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return fast;}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = new Node(0);head.next = new Node(1);head.next.next = new Node(2);head.next.next.next = new Node(3);head.next.next.next.next = new Node(4);head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;Node head1 = new Node(0);head1.next = new Node(1);head1.next.next = new Node(2);head1.next.next.next = new Node(3);head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(4);head1.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next.next;Node intersectNode = getIntersectNode(head, head1);System.out.println(intersectNode.val);}
}







![[NOIP2006]明明的随机数](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fa38b577b9554a5098aa726526e29207.png)