【Seata源码学习 】篇五 分支事务注册
1.远程服务调用绑定XID
回到事务模版方法类TransactionalTemplate中
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);Object rs;try {// Do Your Business// 执行执行拦截器链路rs = business.execute();} catch (Throwable ex) {// 3. The needed business exception to rollback.// 如果抛出异常,判断异常是否在指定的范围中(默认为Throwable类及其子类)// 执行异常回滚的前后钩子方法// 如果当前事务的角色是 launcher 也就是 TM ,通过TmNettyRemotingClient 向TC发送一个 GlobalRollbackRequest 同步消息// 并记录TC返回的当前事务状态StatuscompleteTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);throw ex;}
beginTransaction 开启全局事务我们已经在上一篇看过了,最终会将TC返回到XID绑定到RootContext中,并且TC会将全局事务会话持久化,通常我们使用DB,那么将会往seata数据库的global_table中插入一条数据。
接下来就要执行拦截器链路,最后一个拦截器执行完毕后如果无异常就要执行目标方法。调用目标方法通常会使用到第三方的RPC框架,例如 Fegin,RestTemplate等等
在引入的spring-cloud-seata包下,基于SpringbootStater机制,将会自动装配四个配置类,我们就看最常用的SeataFeignClientAutoConfiguration

public class SeataFeignClientAutoConfiguration {public SeataFeignClientAutoConfiguration() {}@Bean@Scope("prototype")@ConditionalOnClass(name = {"com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommand"})@ConditionalOnProperty(name = {"feign.hystrix.enabled"},havingValue = "true")Feign.Builder feignHystrixBuilder(BeanFactory beanFactory) {return SeataHystrixFeignBuilder.builder(beanFactory);}@Bean@Scope("prototype")@ConditionalOnClass(name = {"com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.SphU"})@ConditionalOnProperty(name = {"feign.sentinel.enabled"},havingValue = "true")Feign.Builder feignSentinelBuilder(BeanFactory beanFactory) {return SeataSentinelFeignBuilder.builder(beanFactory);}@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBean@Scope("prototype")Feign.Builder feignBuilder(BeanFactory beanFactory) {return SeataFeignBuilder.builder(beanFactory);}
}
实际上无论是否集成hystrix或者sentinel , 最终构建的都是 SeataFeignClient 对象
static Feign.Builder builder(BeanFactory beanFactory) {return SentinelFeign.builder().retryer(Retryer.NEVER_RETRY).client(new SeataFeignClient(beanFactory));}而SeataFeignClient在发送请求时,会将Request进行修改
com.alibaba.cloud.seata.feign.SeataFeignClient#execute
public Response execute(Request request, Request.Options options) throws IOException {//修改请求信息Request modifiedRequest = this.getModifyRequest(request);return this.delegate.execute(modifiedRequest, options);}
private Request getModifyRequest(Request request) {//获取开启全局事务时绑定到RootContext中到XIDString xid = RootContext.getXID();if (StringUtils.isEmpty(xid)) {return request;} else {// 放到请求头中Map<String, Collection<String>> headers = new HashMap(16);headers.putAll(request.headers());List<String> seataXid = new ArrayList();seataXid.add(xid);headers.put("TX_XID", seataXid);// 返回添加了 TX_XID 请求头的新Requestreturn Request.create(request.method(), request.url(), headers, request.body(), request.charset());}}
这里需要注意一点,在发起RPC调用时,需要保证跟开启全局事务的方法在同一个线程中,因为RootContext是将XID存储在ThreadLocal中,每个Thread都绑定了自己的ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap,而ThreadLocal.get就是从当前线程中获取ThreadLocalMap,再去获取存储在线程中的变量。
2.数据源代理
public class SeataDataSourceAutoConfiguration {/*** The bean seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.*/@Bean(BEAN_NAME_SEATA_AUTO_DATA_SOURCE_PROXY_CREATOR)@ConditionalOnMissingBean(SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator.class)public SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator seataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(SeataProperties seataProperties) {// spring上下文中添加SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreatorreturn new SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator(seataProperties.isUseJdkProxy(),seataProperties.getExcludesForAutoProxying(), seataProperties.getDataSourceProxyMode());}
}
SeataAutoDataSourceProxyCreator 继承了 AbstractAutoProxyCreator
private Object[] buildAdvisors(String dataSourceProxyMode) {// 使用 SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice 对目标方法进行拦截Advice advice = new SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice(dataSourceProxyMode);return new Object[]{new DefaultIntroductionAdvisor(advice)};}@Overrideprotected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource customTargetSource) {return advisors;}@Overrideprotected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {//排除指定列表的beanif (excludes.contains(beanClass.getName())) {return true;}//对数据源对象进行拦截return SeataProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass);}protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {// we only care DataSource beanif (!(bean instanceof DataSource)) {return bean;}// when this bean is just a simple DataSource, not SeataDataSourceProxyif (!(bean instanceof SeataDataSourceProxy)) {Object enhancer = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);// this mean this bean is either excluded by user or had been proxy beforeif (bean == enhancer) {return bean;}// else, build proxy, put <origin, proxy> to holder and return enhancerDataSource origin = (DataSource) bean;// 创建代理类 AT模式为 DataSourceProxy XA模式为 DataSourceProxyXASeataDataSourceProxy proxy = buildProxy(origin, dataSourceProxyMode);// 将 DataSource 与 SeataDataSourceProxy 映射缓存DataSourceProxyHolder.put(origin, proxy);return enhancer;}
io.seata.spring.annotation.datasource.SeataAutoDataSourceProxyAdvice#invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {// check whether current context is expectedif (!inExpectedContext()) {return invocation.proceed();}Method method = invocation.getMethod();String name = method.getName();Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();Method declared;try {declared = DataSource.class.getDeclaredMethod(name, parameterTypes);} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {// mean this method is not declared by DataSourcereturn invocation.proceed();}// switch invoke instance to its proxyDataSource origin = (DataSource) invocation.getThis();SeataDataSourceProxy proxy = DataSourceProxyHolder.get(origin);Object[] args = invocation.getArguments();// 方法由 SeataDataSourceProxy 代理类执行return declared.invoke(proxy, args);}
获取Connection对象
假设当前为seata的全局事务模式为AT,当原始数据源调用getConnection方法获取连接时,实际上调用的是DataSourceProxy.getConnection方法,拿到的是ConnectionProxy对象
@Overridepublic ConnectionProxy getConnection() throws SQLException {Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection();return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);}@Overridepublic ConnectionProxy getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection(username, password);return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);}
获取Statement对象
AbstractConnectionProxy
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {Statement targetStatement = getTargetConnection().createStatement();return new StatementProxy(this, targetStatement);}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {String dbType = getDbType();// support oracle 10.2+PreparedStatement targetPreparedStatement = null;if (BranchType.AT == RootContext.getBranchType()) {List<SQLRecognizer> sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(sql, dbType);if (sqlRecognizers != null && sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);if (sqlRecognizer != null && sqlRecognizer.getSQLType() == SQLType.INSERT) {TableMeta tableMeta = TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(dbType).getTableMeta(getTargetConnection(),sqlRecognizer.getTableName(), getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId());String[] pkNameArray = new String[tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().size()];tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().toArray(pkNameArray);targetPreparedStatement = getTargetConnection().prepareStatement(sql,pkNameArray);}}}if (targetPreparedStatement == null) {targetPreparedStatement = getTargetConnection().prepareStatement(sql);}return new PreparedStatementProxy(this, targetPreparedStatement, sql);}
而获取的Statement 与 PreparedStatement 分别是 StatementProxy 与 PreparedStatementProxy,而两者都是由ExecuteTemplate来执行sql语句,假设RM此时要执行的业务是更新操作
public static <T, S extends Statement> T execute(List<SQLRecognizer> sqlRecognizers,StatementProxy<S> statementProxy,StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback,Object... args) throws SQLException {// 如果当前即不需要全局锁 并且事务类型不为AT模式,那么直接执行原生SQLif (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && BranchType.AT != RootContext.getBranchType()) {// Just work as original statementreturn statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);}// 获取数据源类型String dbType = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().getDbType();if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(statementProxy.getTargetSQL(),dbType);}Executor<T> executor;if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);} else {if (sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);// 区分当前执行的SQL语句类型switch (sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {case INSERT:executor = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(InsertExecutor.class, dbType,new Class[]{StatementProxy.class, StatementCallback.class, SQLRecognizer.class},new Object[]{statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer});break;// 假设当前执行的是UPDATAE语句case UPDATE:executor = new UpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);break;case DELETE:executor = new DeleteExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);break;case SELECT_FOR_UPDATE:executor = new SelectForUpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);break;case INSERT_ON_DUPLICATE_UPDATE:switch (dbType) {case JdbcConstants.MYSQL:case JdbcConstants.MARIADB:executor =new MySQLInsertOrUpdateExecutor(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);break;default:throw new NotSupportYetException(dbType + " not support to INSERT_ON_DUPLICATE_UPDATE");}break;default:executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);break;}} else {executor = new MultiExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizers);}}T rs;try {// 执行器执行SQL语句rs = executor.execute(args);} catch (Throwable ex) {if (!(ex instanceof SQLException)) {// Turn other exception into SQLExceptionex = new SQLException(ex);}throw (SQLException) ex;}return rs;}
UPDATE语句使用的是UpdateExecutor执行器,而UpdateExecutor的类关系图如下
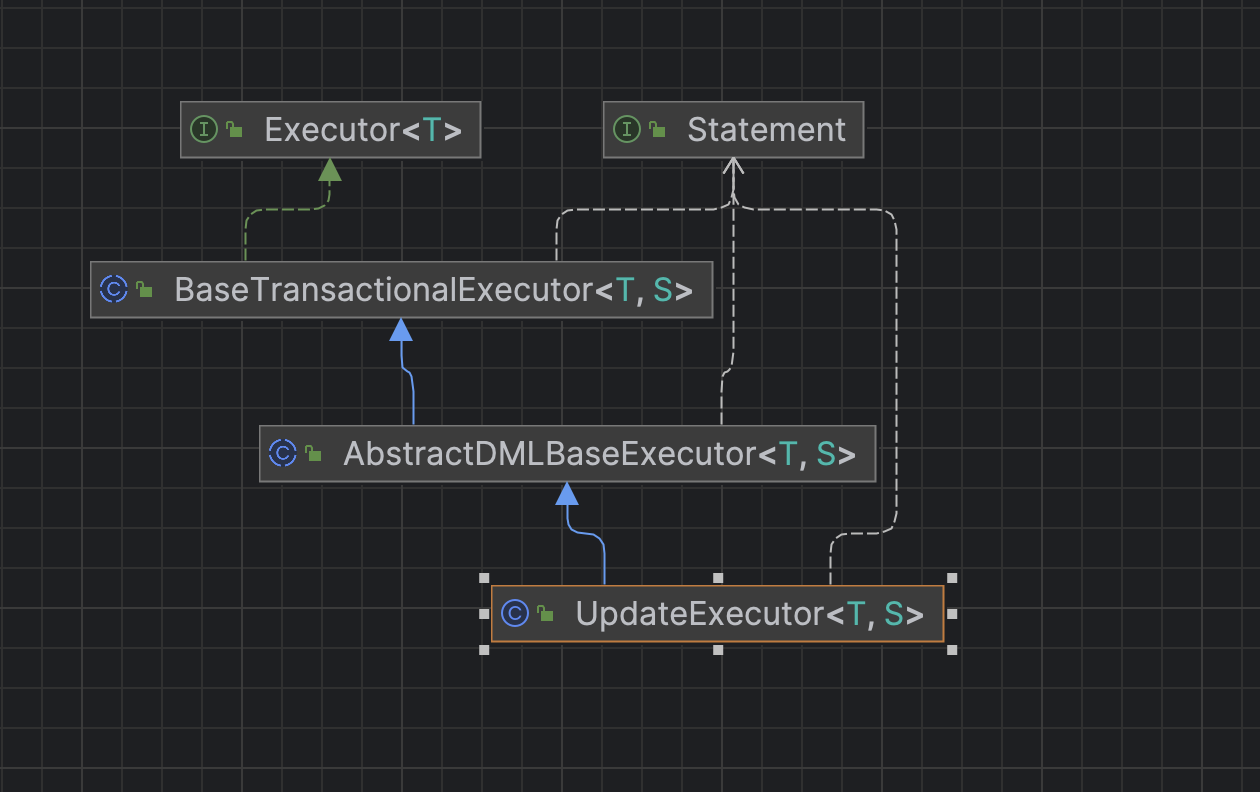
由父类BaseTransactionalExecutor 调用execute方法,将RootContext中的XID绑定到StatementProxy中,并标识是否需要全局锁
public T execute(Object... args) throws Throwable {String xid = RootContext.getXID();if (xid != null) {statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().bind(xid);}statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().setGlobalLockRequire(RootContext.requireGlobalLock());return doExecute(args);}
关闭自动提交事务并执行sql
接着调用子类AbstractDMLBaseExecutor的doExecute方法,主要是关闭自动提交,然后执行 executeAutoCommitFalse 方法
public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();// connectionProxy.getAutoCommit() 会判断原始数据源对象是否是自动提交事务 (JDBC默认提交事务)// 但在seata中 即使原始数据源是自动化提交,在 executeAutoCommitTrue 方法中也会关闭自动提交事务if (connectionProxy.getAutoCommit()) {// 将自动提交设置为false,再调用executeAutoCommitFalsereturn executeAutoCommitTrue(args);} else {return executeAutoCommitFalse(args);}}
io.seata.rm.datasource.exec.AbstractDMLBaseExecutor#executeAutoCommitFalse
protected T executeAutoCommitFalse(Object[] args) throws Exception {// 要求当前数据源是MYSQL, 且不能是多主键if (!JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equalsIgnoreCase(getDbType()) && isMultiPk()) {throw new NotSupportYetException("multi pk only support mysql!");}// 封装前镜像数据 TableRecords 记录了每一个字段对应的值,且获取的是当前最新的数据TableRecords beforeImage = beforeImage();// 执行sql语句T result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);int updateCount = statementProxy.getUpdateCount();//修改成功if (updateCount > 0) {//封装后镜像数据TableRecords afterImage = afterImage(beforeImage);//将前后镜像打包成回滚日志 其中包括全局锁信息prepareUndoLog(beforeImage, afterImage);}return result;}
博主使用的seata版本是1.5.2,此版本不支持多主键.
为了保证前镜像获取的数据是最新的,创建SQL查询语句时会拼接 FOR UPDATE ,使用当前读的方式。成功修改数据后,会将修改后的数据也构建成镜像数据,最后由前后镜像一起组成回滚日志。
提交事务
由于我们获取的数据源连接对象时ConnectionProxy,因此提交事务时也时此对象进行提交
io.seata.rm.datasource.ConnectionProxy#commit
public void commit() throws SQLException {try {//由lockRetryPolicy手动提交事务 支持全局锁获取失败重试机制lockRetryPolicy.execute(() -> {doCommit();return null;});} catch (SQLException e) {if (targetConnection != null && !getAutoCommit() && !getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {// 如果出现SQLException 异常 回滚本地事务,向TC报告,并移除RootContext中的全局事务XIDrollback();}throw e;} catch (Exception e) {throw new SQLException(e);}}
io.seata.rm.datasource.ConnectionProxy#doCommit
private void doCommit() throws SQLException {//全局事务XID不为空if (context.inGlobalTransaction()) {processGlobalTransactionCommit();//要求全局锁} else if (context.isGlobalLockRequire()) {processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks();} else {//都不是直接提交targetConnection.commit();}}
io.seata.rm.datasource.ConnectionProxy#processGlobalTransactionCommit
public void commit() throws SQLException {try {//由lockRetryPolicy手动提交事务 支持全局锁获取失败重试机制// 如果是获取全局锁失败,将会重试lockRetryPolicy.execute(() -> {doCommit();return null;});} catch (SQLException e) {if (targetConnection != null && !getAutoCommit() && !getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {// 如果出现SQLException 异常 回滚本地事务,向TC报告,并移除RootContext中的全局事务XIDrollback();}throw e;} catch (Exception e) {throw new SQLException(e);}}
由lockRetryPolicy手动提交事务,而如果出现全局锁冲突,将会在线程休眠后重试
io.seata.rm.datasource.ConnectionProxy.LockRetryPolicy#execute
protected <T> T doRetryOnLockConflict(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {LockRetryController lockRetryController = new LockRetryController();while (true) {try {return callable.call();} catch (LockConflictException lockConflict) {//先回滚本地事务onException(lockConflict);// AbstractDMLBaseExecutor#executeAutoCommitTrue the local lock is releasedif (connection.getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()&& lockConflict.getCode() == TransactionExceptionCode.LockKeyConflictFailFast) {lockConflict.setCode(TransactionExceptionCode.LockKeyConflict);}//休眠10秒收重试lockRetryController.sleep(lockConflict);} catch (Exception e) {onException(e);throw e;}}}
io.seata.rm.datasource.ConnectionProxy#processGlobalTransactionCommit
private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {try {//在回滚日志已经准备好的情况下 向TC注册分支事务,并将分支事务ID保存到ConnectionContext中register();} catch (TransactionException e) {recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());}try {// 将回滚日志刷新到数据库中 等待和本地事务一起提交UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);//本地事务提交targetConnection.commit();} catch (Throwable ex) {LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);report(false);throw new SQLException(ex);}if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) {report(true);}context.reset();}
Undo回滚日志将和本地事务一起提交,但在提交前,需要先注册分支事务ID
io.seata.rm.AbstractResourceManager#branchRegister
public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid, String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {try {BranchRegisterRequest request = new BranchRegisterRequest();request.setXid(xid);request.setLockKey(lockKeys);request.setResourceId(resourceId);request.setBranchType(branchType);request.setApplicationData(applicationData);BranchRegisterResponse response = (BranchRegisterResponse) RmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {throw new RmTransactionException(response.getTransactionExceptionCode(), String.format("Response[ %s ]", response.getMsg()));}return response.getBranchId();} catch (TimeoutException toe) {throw new RmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC Timeout", toe);} catch (RuntimeException rex) {throw new RmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BranchRegisterFailed, "Runtime", rex);}}
注册分支事务需要将当前全局事务的XID,全局锁,资源信息,分支事务类型以及应用数据,一起构建成BranchRegisterRequest消息发送给TC,具体如下数据所示
{"branchType": "AT","lockKey": "product_table:1","resourceId": "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata-test","typeCode": 11,"xid": "xxx.xx.xx.xxx:8091:1378562425205329921"
}
3.TC处理 BranchRegisterRequest 消息
TC在处理 BranchRegisterRequest消息 依然也是 ServerOnRequestProcessor,最终交由AbstractTCInboundHandle进行处理
io.seata.server.AbstractTCInboundHandler#handle(io.seata.core.protocol.transaction.BranchRegisterRequest, io.seata.core.rpc.RpcContext)
public BranchRegisterResponse handle(BranchRegisterRequest request, final RpcContext rpcContext) {BranchRegisterResponse response = new BranchRegisterResponse();exceptionHandleTemplate(new AbstractCallback<BranchRegisterRequest, BranchRegisterResponse>() {@Overridepublic void execute(BranchRegisterRequest request, BranchRegisterResponse response)throws TransactionException {try {//真正处理分支注册doBranchRegister(request, response, rpcContext);} catch (StoreException e) {throw new TransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedStore, String.format("branch register request failed. xid=%s, msg=%s", request.getXid(), e.getMessage()), e);}}}, request, response);return response;}
io.seata.server.coordinator.DefaultCoordinator#doBranchRegister
@Overrideprotected void doBranchRegister(BranchRegisterRequest request, BranchRegisterResponse response,RpcContext rpcContext) throws TransactionException {MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());// 获取分支IDresponse.setBranchId(core.branchRegister(request.getBranchType(), request.getResourceId(), rpcContext.getClientId(),request.getXid(), request.getApplicationData(), request.getLockKey()));}
io.seata.server.coordinator.DefaultCore#branchRegister
@Overridepublic Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid,String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {// 当前事务类型为AT模式,返回 ATCore 在调用 branchRegister 方法return getCore(branchType).branchRegister(branchType, resourceId, clientId, xid,applicationData, lockKeys);}
io.seata.server.coordinator.AbstractCore#branchRegister
public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid,String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {GlobalSession globalSession = assertGlobalSessionNotNull(xid, false);return SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {// 全局事务当前必须是激活且是beging状态 否则抛出异常globalSessionStatusCheck(globalSession);globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());//注册分支事务回话(将分支事务信息绑定上全局事务XID)BranchSession branchSession = SessionHelper.newBranchByGlobal(globalSession, branchType, resourceId,applicationData, lockKeys, clientId);MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_BRANCH_ID, String.valueOf(branchSession.getBranchId()));//加全局锁branchSessionLock(globalSession, branchSession);try {//将分支事务会话添加到全局事务会话到集合中,并向监听器添加onAddBranch事件,将分支事务会话持久到数据库中globalSession.addBranch(branchSession);} catch (RuntimeException ex) {//如果出现异常,从数据库中删除分支事务信息branchSessionUnlock(branchSession);throw new BranchTransactionException(FailedToAddBranch, String.format("Failed to store branch xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(),branchSession.getBranchId()), ex);}if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {LOGGER.info("Register branch successfully, xid = {}, branchId = {}, resourceId = {} ,lockKeys = {}",globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId(), resourceId, lockKeys);}return branchSession.getBranchId();});}
首先会判断当前全局事务的状态,接着创建一个新的BranchSession对象,生成branchId,并绑定上XID;接着就是尝试加全局锁,加锁失败会抛出异常;然后再将分支事务会话添加到全局事务会话到集合中,并向监听器添加onAddBranch事件,将分支事务会话持久到数据库中,并返回分支事务ID。如果此过程出现异常,则会删除分支事务信息。
判断全局事务状态
// 全局事务当前必须是激活且是beging状态 否则抛出异常globalSessionStatusCheck(globalSession);
io.seata.server.coordinator.AbstractCore#globalSessionStatusCheck
protected void globalSessionStatusCheck(GlobalSession globalSession) throws GlobalTransactionException {//全局事务必须是激活状态if (!globalSession.isActive()) {throw new GlobalTransactionException(GlobalTransactionNotActive, String.format("Could not register branch into global session xid = %s status = %s, cause by globalSession not active",globalSession.getXid(), globalSession.getStatus()));}//全局事务必须是begin状态if (globalSession.getStatus() != GlobalStatus.Begin) {throw new GlobalTransactionException(GlobalTransactionStatusInvalid, String.format("Could not register branch into global session xid = %s status = %s while expecting %s",globalSession.getXid(), globalSession.getStatus(), GlobalStatus.Begin));}}
全局事务当前必须是激活且是beging状态 否则抛出异常
注册分支事务
BranchSession branchSession = SessionHelper.newBranchByGlobal(globalSession, branchType, resourceId,applicationData, lockKeys, clientId);
io.seata.server.session.SessionHelper#newBranchByGlobal(io.seata.server.session.GlobalSession, io.seata.core.model.BranchType, java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.lang.String)
public static BranchSession newBranchByGlobal(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchType branchType, String resourceId,String applicationData, String lockKeys, String clientId) {//创建新的BranchSession对象BranchSession branchSession = new BranchSession();//分别绑定XID,事务ID,新生成的分支事务id 并设置事务类型与资源信息,锁信息,RM客户端信息(服务名和id)branchSession.setXid(globalSession.getXid());branchSession.setTransactionId(globalSession.getTransactionId());branchSession.setBranchId(UUIDGenerator.generateUUID());branchSession.setBranchType(branchType);branchSession.setResourceId(resourceId);branchSession.setLockKey(lockKeys);branchSession.setClientId(clientId);branchSession.setApplicationData(applicationData);return branchSession;}
最终的分支信息如图所示
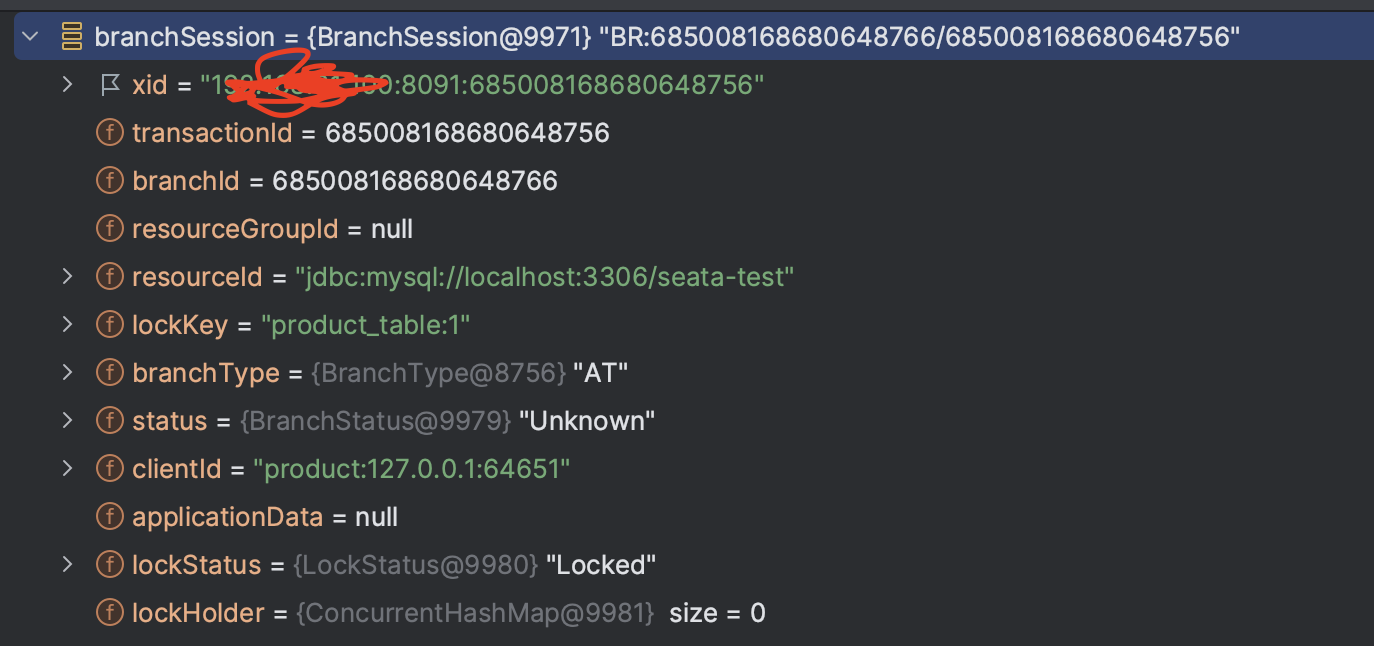
添加全局锁
//加全局锁branchSessionLock(globalSession, branchSession);
io.seata.server.transaction.at.ATCore#branchSessionLock
@Overrideprotected void branchSessionLock(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession)throws TransactionException {String applicationData = branchSession.getApplicationData();boolean autoCommit = true;boolean skipCheckLock = false;//applicationData为空 往下走if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(applicationData)) {if (objectMapper == null) {objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();}try {Map<String, Object> data = objectMapper.readValue(applicationData, HashMap.class);Object clientAutoCommit = data.get(AUTO_COMMIT);if (clientAutoCommit != null && !(boolean)clientAutoCommit) {autoCommit = (boolean)clientAutoCommit;}Object clientSkipCheckLock = data.get(SKIP_CHECK_LOCK);if (clientSkipCheckLock instanceof Boolean) {skipCheckLock = (boolean)clientSkipCheckLock;}} catch (IOException e) {LOGGER.error("failed to get application data: {}", e.getMessage(), e);}}try {//加全局锁if (!branchSession.lock(autoCommit, skipCheckLock)) {throw new BranchTransactionException(LockKeyConflict,String.format("Global lock acquire failed xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(),branchSession.getBranchId()));}} catch (StoreException e) {if (e.getCause() instanceof BranchTransactionException) {throw new BranchTransactionException(((BranchTransactionException)e.getCause()).getCode(),String.format("Global lock acquire failed xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(),branchSession.getBranchId()));}throw e;}}
io.seata.server.session.BranchSession#lock(boolean, boolean)
public boolean lock(boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) throws TransactionException {if (this.getBranchType().equals(BranchType.AT)) {//获取锁资源管理器执行加速操作return LockerManagerFactory.getLockManager().acquireLock(this, autoCommit, skipCheckLock);}return true;}
无论是哪种锁资源管理器,其调用acquireLock都是走的父类AbstractLockManager的方法
io.seata.server.lock.AbstractLockManager#acquireLock(io.seata.server.session.BranchSession, boolean, boolean)
@Overridepublic boolean acquireLock(BranchSession branchSession, boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) throws TransactionException {if (branchSession == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("branchSession can't be null for memory/file locker.");}// lockKey通常是由 表名 + 主键组成String lockKey = branchSession.getLockKey();if (StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(lockKey)) {// no lockreturn true;}// get locks of branch// 使用 ; 分割lockKey 获取RowLock集合,RowLock封装了 XID,分支事务ID,表民,主键等信息List<RowLock> locks = collectRowLocks(branchSession);if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(locks)) {// no lockreturn true;}// 获取枷锁操作对象,调用acquireLock方法return getLocker(branchSession).acquireLock(locks, autoCommit, skipCheckLock);}我们就看 DataBaseLocker 是怎么加锁的
public boolean acquireLock(List<RowLock> locks, boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) {// 首先RowLock集合对象不能为空if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(locks)) {// no lockreturn true;}try {return lockStore.acquireLock(convertToLockDO(locks), autoCommit, skipCheckLock);} catch (StoreException e) {throw e;} catch (Exception t) {LOGGER.error("AcquireLock error, locks:{}", CollectionUtils.toString(locks), t);return false;}}
io.seata.server.storage.db.lock.LockStoreDataBaseDAO#acquireLock(java.util.List<io.seata.core.store.LockDO>, boolean, boolean)
public boolean acquireLock(List<LockDO> lockDOs, boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) {Connection conn = null;PreparedStatement ps = null;ResultSet rs = null;Set<String> dbExistedRowKeys = new HashSet<>();boolean originalAutoCommit = true;if (lockDOs.size() > 1) {lockDOs = lockDOs.stream().filter(LambdaUtils.distinctByKey(LockDO::getRowKey)).collect(Collectors.toList());}try {conn = lockStoreDataSource.getConnection();if (originalAutoCommit = conn.getAutoCommit()) {conn.setAutoCommit(false);}List<LockDO> unrepeatedLockDOs = lockDOs;//check lockif (!skipCheckLock) {boolean canLock = true;//query// select * from lock_table where row_key in ( ? ) order by status desc// RowKey 由数据库资源信息 + 表名 + 主键组成String checkLockSQL = LockStoreSqlFactory.getLogStoreSql(dbType).getCheckLockableSql(lockTable, lockDOs.size());ps = conn.prepareStatement(checkLockSQL);for (int i = 0; i < lockDOs.size(); i++) {ps.setString(i + 1, lockDOs.get(i).getRowKey());}rs = ps.executeQuery();String currentXID = lockDOs.get(0).getXid();boolean failFast = false;// 如果在lock_tabel中根据 RowKey 找到了记录,需要判断当前xid是否与数据库中的xid是否一致// 如果不一致 加速失败while (rs.next()) {String dbXID = rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_XID);if (!StringUtils.equals(dbXID, currentXID)) {if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {String dbPk = rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_PK);String dbTableName = rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_TABLE_NAME);long dbBranchId = rs.getLong(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_BRANCH_ID);LOGGER.info("Global lock on [{}:{}] is holding by xid {} branchId {}", dbTableName, dbPk, dbXID, dbBranchId);}if (!autoCommit) {int status = rs.getInt(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_STATUS);if (status == LockStatus.Rollbacking.getCode()) {failFast = true;}}canLock = false;break;}// 将已经存在的全局锁缓冲起来dbExistedRowKeys.add(rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_ROW_KEY));}if (!canLock) {// 加锁失败 回滚保存分支事务信息的sqlconn.rollback();if (failFast) {throw new StoreException(new BranchTransactionException(LockKeyConflictFailFast));}return false;}// If the lock has been exists in db, remove it from the lockDOsif (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(dbExistedRowKeys)) {unrepeatedLockDOs = lockDOs.stream().filter(lockDO -> !dbExistedRowKeys.contains(lockDO.getRowKey())).collect(Collectors.toList());}if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(unrepeatedLockDOs)) {conn.rollback();return true;}}// lockif (unrepeatedLockDOs.size() == 1) {LockDO lockDO = unrepeatedLockDOs.get(0);// 生成sql语句,将全局锁信息插入到lock_table表中if (!doAcquireLock(conn, lockDO)) {if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {LOGGER.info("Global lock acquire failed, xid {} branchId {} pk {}", lockDO.getXid(), lockDO.getBranchId(), lockDO.getPk());}conn.rollback();return false;}} else {if (!doAcquireLocks(conn, unrepeatedLockDOs)) {if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {LOGGER.info("Global lock batch acquire failed, xid {} branchId {} pks {}", unrepeatedLockDOs.get(0).getXid(),unrepeatedLockDOs.get(0).getBranchId(), unrepeatedLockDOs.stream().map(lockDO -> lockDO.getPk()).collect(Collectors.toList()));}conn.rollback();return false;}}conn.commit();return true;} catch (SQLException e) {throw new StoreException(e);} finally {IOUtil.close(rs, ps);if (conn != null) {try {if (originalAutoCommit) {conn.setAutoCommit(true);}conn.close();} catch (SQLException e) {}}}}
注册全局锁之前会根据RowKey查询全局锁信息是否已经存在,生成的查询语句如下
select * from lock_table where row_key in ( ? ) order by status desc
RowKey如下所示
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata-test^^^product_table^^^1
如果locktable表中已经有数据了,则比较数据中XID与当前当前的xid是否一致,如果不一致说明已经被其他全局事务加了锁,则标记当前加锁失败,并抛出异常;如果一致,则将当前的RowKey缓冲到set集合中。最后调用LockStoreDataBaseDAO.doAcquireLock方法将锁信息保存到数据库lock_table表中。
持久化分支信息
成功添加上全局锁后,就要将分支事务会话添加到全局事务会话到集合中,并向监听器添加onAddBranch事件,将分支事务会话持久到数据库中
globalSession.addBranch(branchSession);
io.seata.server.session.GlobalSession#addBranch
public void addBranch(BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {// 分支事务持久化lifecycleListener.onAddBranch(this, branchSession);}// 将分支事务标记为已注册状态branchSession.setStatus(BranchStatus.Registered);// 将分支事务添加到GlobalSession到List集合中add(branchSession);}
返回分支事务ID
return branchSession.getBranchId();
最后携带刚生成的分支事务ID返回BranchRegisterResponse消息给到RM