LSTM中文新闻分类
- 一、导包
- 二、读取数据
- 三、数据预处理
- 1.分词、去掉停用词和数字、字母转换成小写等
- 2.新闻文本标签数值化
- 三、创建词汇表/词典
- 1.data.Field()
- 2.空格切分等
- 3.构建词汇表/词典
- 使用训练集构建单词表,vectors=None:没有使用预训练好的词向量,而是使用的是随机初始化的词向量,默认是100维
- 这里面的20002,多的那两个应该是
- 四、构造数据集迭代器,方便批处理
- batch.cutword[0]和batch.cutword[1]
- batch.cutword[0]:表示的是一批数据也就是64条新闻,每条新闻都会被分词,分成一个一个的词语,每个词语在词典中的索引,最后面的1表示的是不足400,填充的<pad>对应在词典中的索引为1。
- batch.cutword[1]:表示的是一批数据也就是64条新闻,每条新闻对应所有新闻中的索引号。
- 五、搭建LSTM网络
- r_out, (h_n, h_c)分别是:
- r_out是最终输出结果y(根据今天,昨天和日记)
- h_n是隐藏层的输出结果s(根据昨天)
- h_c是长期信息的输出结果c(根据日记)
- 六、LSTM网络的训练
- 七、LSTM网络的测试
一、导包
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
fonts = FontProperties(fname = "/Library/Fonts/华文细黑.ttf")
import re
import string
import copy
import time
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,confusion_matrix
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.utils.data as Data
import jieba
jieba.setLogLevel(jieba.logging.INFO)
from torchtext.legacy import data
from torchtext.vocab import Vectors
#从 PyTorch 的拓展库 torchtext 中导入了 Vectors 类,该类用于处理词向量(word embeddings)
二、读取数据
train_df = pd.read_csv("data/lstm/cnews/cnews.train.txt",sep="\t",header=None,names = ["label","text"])
val_df = pd.read_csv("data/lstm/cnews/cnews.val.txt",sep="\t",header=None,names = ["label","text"])
test_df = pd.read_csv("data/lstm/cnews/cnews.test.txt",sep="\t",header=None,names = ["label","text"])
train_df.head(5)

三、数据预处理
stop_words = pd.read_csv("data/lstm/cnews/中文停用词库.txt",header=None,names = ["text"])
1.分词、去掉停用词和数字、字母转换成小写等
## 对中文文本数据进行预处理,去除一些不需要的字符,分词,去停用词,等操作
def chinese_pre(text_data):## 字母转化为小写,去除数字,text_data = text_data.lower()text_data = re.sub("\d+", "", text_data)## 分词,使用精确模式text_data = list(jieba.cut(text_data,cut_all=False)) ## 去停用词和多余空格text_data = [word.strip() for word in text_data if word not in stop_words.text.values]## 处理后的词语使用空格连接为字符串text_data = " ".join(text_data)return text_data
train_df["cutword"] = train_df.text.apply(chinese_pre)
val_df["cutword"] = val_df.text.apply(chinese_pre)
test_df["cutword"] = test_df.text.apply(chinese_pre)
## 预处理后的结果保存为新的文件
train_df[["label","cutword"]].to_csv("data/lstm/cnews_train.csv",index=False)
val_df[["label","cutword"]].to_csv("data/lstm/cnews_val.csv",index=False)
test_df[["label","cutword"]].to_csv("data/lstm/cnews_test.csv",index=False)
train_df.cutword.head()

train_df = pd.read_csv("data/lstm/cnews_train.csv")
val_df = pd.read_csv("data/lstm/cnews_val.csv")
test_df = pd.read_csv("data/lstm/cnews_test.csv")
2.新闻文本标签数值化
labelMap = {"体育": 0,"娱乐": 1,"家居": 2,"房产": 3,"教育": 4,"时尚": 5,"时政": 6,"游戏": 7,"科技": 8,"财经": 9}
train_df["labelcode"] =train_df["label"].map(labelMap)
val_df["labelcode"] =val_df["label"].map(labelMap)
test_df["labelcode"] =test_df["label"].map(labelMap)
train_df.head()

train_df[["labelcode","cutword"]].to_csv("data/lstm/cnews_train2.csv",index=False)
val_df[["labelcode","cutword"]].to_csv("data/lstm/cnews_val2.csv",index=False)
test_df[["labelcode","cutword"]].to_csv("data/lstm/cnews_test2.csv",index=False)
三、创建词汇表/词典
1.data.Field()
data.Field参数与方法详解
2.空格切分等
按照空格进行分词,cutword是序列数据,labelcode不是序列数据
## 使用torchtext库进行数据准备
# 定义文件中对文本和标签所要做的操作
"""
sequential=True:表明输入的是序列数据
tokenize="spacy":使用spacy切分词语
use_vocab=True: 创建词汇表
batch_first=True: batch优先的数据方式
fix_length=400 :每个句子固定长度为400,不足会默认使用 <pad> 符号填充
"""
## 定义文本切分方法,因为前面已经做过处理,所以直接使用空格切分即可
mytokenize = lambda x: x.split()
TEXT = data.Field(sequential=True, tokenize=mytokenize, include_lengths=True, use_vocab=True,batch_first=True, fix_length=400)
LABEL = data.Field(sequential=False, use_vocab=False, pad_token=None, unk_token=None)
## 对所要读取的数据集的列进行处理
text_data_fields = [("labelcode", LABEL), # 对标签的操作("cutword", TEXT) # 对文本的操作
]
## 读取数据
traindata,valdata,testdata = data.TabularDataset.splits(path="data/lstm", format="csv", train="cnews_train2.csv", fields=text_data_fields, validation="cnews_val2.csv",test = "cnews_test2.csv", skip_header=True
)
len(traindata),len(valdata),len(testdata)
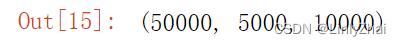
## 检查一个样本的标签和文本
em = traindata.examples[0]
print(em.labelcode)
print(em.cutword)

3.构建词汇表/词典
使用训练集构建单词表,vectors=None:没有使用预训练好的词向量,而是使用的是随机初始化的词向量,默认是100维
TEXT.build_vocab(traindata,max_size=20000,vectors = None)
LABEL.build_vocab(traindata)
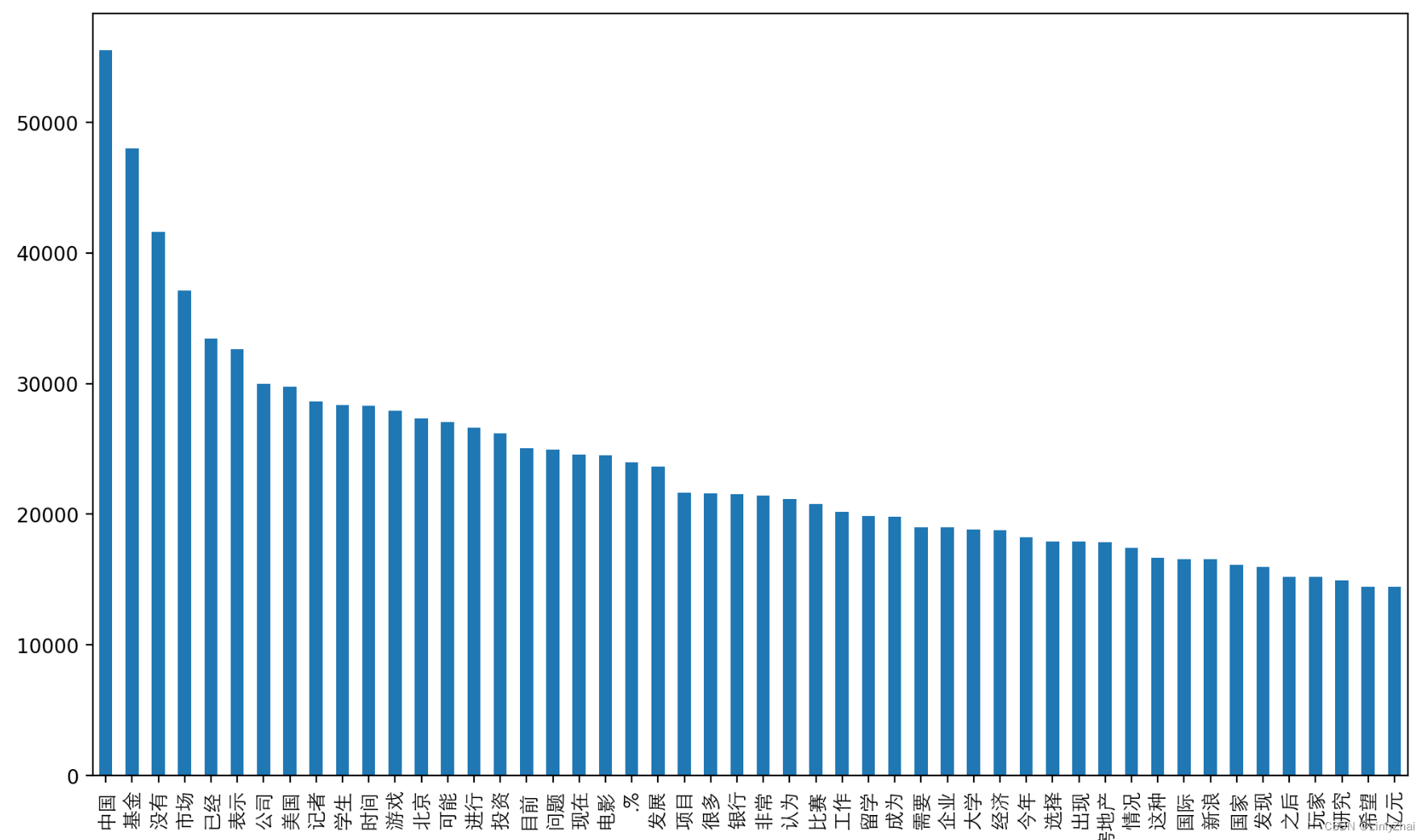
## 可视化训练集中的前50个高频词
word_fre = TEXT.vocab.freqs.most_common(n=50)
word_fre = pd.DataFrame(data=word_fre,columns=["word","fre"])
word_fre.plot(x="word", y="fre", kind="bar",legend=False,figsize=(12,7))
plt.xticks(rotation = 90,fontproperties = fonts,size = 10)
plt.show()print("词典的词数:",len(TEXT.vocab.itos))
print("前10个单词:\n",TEXT.vocab.itos[0:10])
## 类别标签的数量和类别
print("类别标签情况:",LABEL.vocab.freqs)
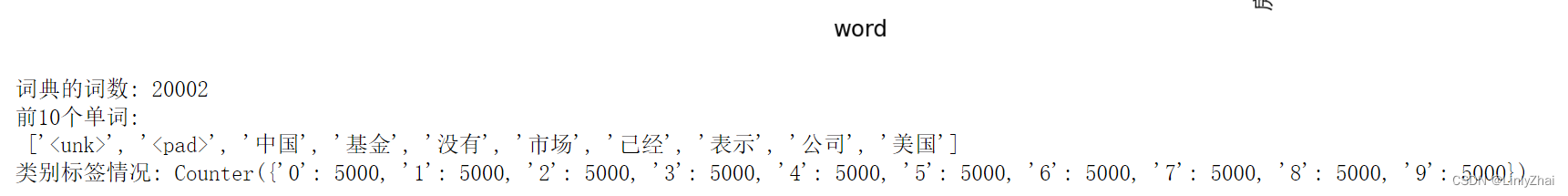
这里面的20002,多的那两个应该是

四、构造数据集迭代器,方便批处理
## 定义一个迭代器,将类似长度的示例一起批处理。
BATCH_SIZE = 64
train_iter = data.BucketIterator(traindata,batch_size = BATCH_SIZE)
val_iter = data.BucketIterator(valdata,batch_size = BATCH_SIZE)
test_iter = data.BucketIterator(testdata,batch_size = BATCH_SIZE)
## 获得一个batch的数据,对数据进行内容进行介绍
for step, batch in enumerate(train_iter): if step > 0:break
## 针对一个batch 的数据,可以使用batch.labelcode获得数据的类别标签
print("数据的类别标签:\n",batch.labelcode)
## batch.cutword[0]是文本对应的标签向量
print("数据的尺寸:",batch.cutword[0].shape)
## batch.cutword[1] 对应每个batch使用的原始数据中的索引
print("数据样本数:",len(batch.cutword[1]))

batch.cutword[0]和batch.cutword[1]
batch.cutword[0]:表示的是一批数据也就是64条新闻,每条新闻都会被分词,分成一个一个的词语,每个词语在词典中的索引,最后面的1表示的是不足400,填充的对应在词典中的索引为1。
batch.cutword[1]:表示的是一批数据也就是64条新闻,每条新闻对应所有新闻中的索引号。

## 获得一个batch的数据,对数据进行内容进行介绍
for step, batch in enumerate(train_iter): textdata,target = batch.cutword[0],batch.labelcode.view(-1)if step > 0:break
# ## 针对一个batch 的数据,可以使用batch.labelcode获得数据的类别标签
# print("数据的类别标签:\n",batch.labelcode)
# ## batch.cutword[0]是文本对应的标签向量
# print("数据的尺寸:",batch.cutword[0].shape)
# ## batch.cutword[1] 对应每个batch使用的原始数据中的索引
# print("数据样本数:",len(batch.cutword[1]))
五、搭建LSTM网络
class LSTMNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, vocab_size,embedding_dim, hidden_dim, layer_dim, output_dim):"""vocab_size:词典长度embedding_dim:词向量的维度hidden_dim: RNN神经元个数layer_dim: RNN的层数output_dim:隐藏层输出的维度(分类的数量)"""super(LSTMNet, self).__init__()self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim ## RNN神经元个数self.layer_dim = layer_dim ## RNN的层数## 对文本进行词向量处理self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)# LSTM + 全连接层self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, layer_dim,batch_first=True)self.fc1 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)def forward(self, x):embeds = self.embedding(x)# r_out shape (batch, time_step, output_size)# h_n shape (n_layers, batch, hidden_size) LSTM 有两个 hidden states, h_n 是分线, h_c 是主线# h_c shape (n_layers, batch, hidden_size)r_out, (h_n, h_c) = self.lstm(embeds, None) # None 表示 hidden state 会用全0的 state# 选取最后一个时间点的out输出out = self.fc1(r_out[:, -1, :]) return outr_out, (h_n, h_c)分别是:
r_out是最终输出结果y(根据今天,昨天和日记)
h_n是隐藏层的输出结果s(根据昨天)
h_c是长期信息的输出结果c(根据日记)
vocab_size = len(TEXT.vocab)
embedding_dim = 100
hidden_dim = 128
layer_dim = 1
output_dim = 10
lstmmodel = LSTMNet(vocab_size, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, layer_dim, output_dim)
lstmmodel

六、LSTM网络的训练
## 定义网络的训练过程函数
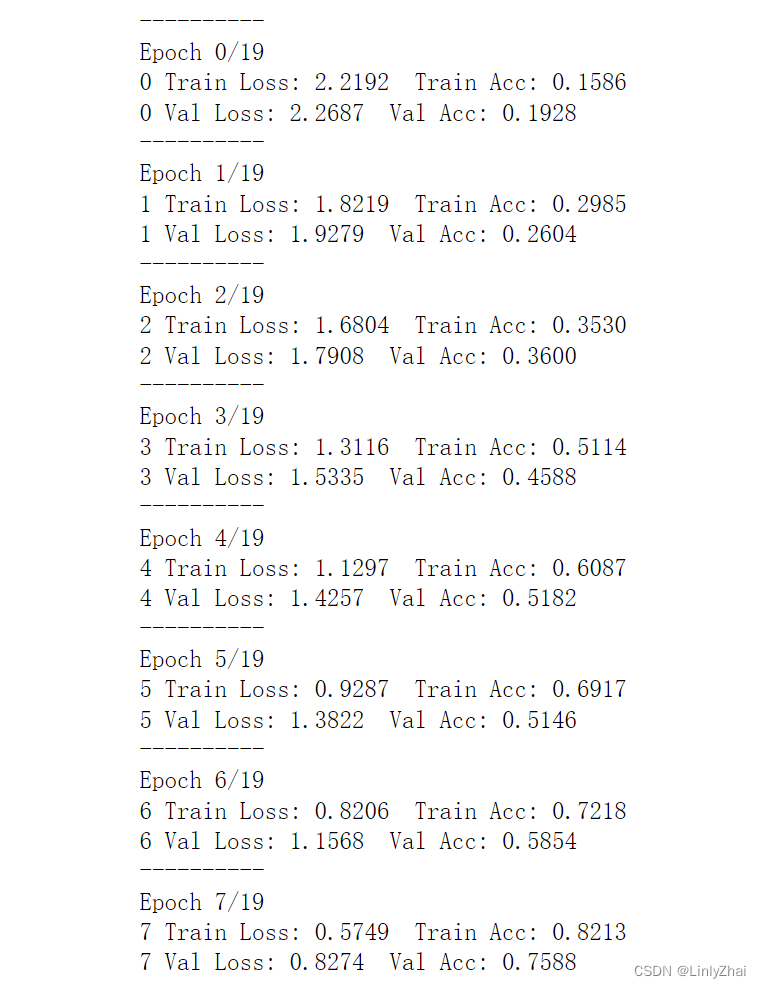
def train_model2(model,traindataloader, valdataloader,criterion, optimizer,num_epochs=25,):"""model:网络模型;traindataloader:训练数据集;valdataloader:验证数据集,;criterion:损失函数;optimizer:优化方法;num_epochs:训练的轮数"""train_loss_all = []train_acc_all = []val_loss_all = []val_acc_all = []since = time.time()for epoch in range(num_epochs):print('-' * 10)print('Epoch {}/{}'.format(epoch, num_epochs - 1))# 每个epoch有两个阶段,训练阶段和验证阶段train_loss = 0.0train_corrects = 0train_num = 0val_loss = 0.0val_corrects = 0val_num = 0model.train() ## 设置模型为训练模式for step,batch in enumerate(traindataloader):textdata,target = batch.cutword[0],batch.labelcode.view(-1)out = model(textdata)pre_lab = torch.argmax(out,1) # 预测的标签loss = criterion(out, target) # 计算损失函数值optimizer.zero_grad() #梯度清零 loss.backward() #损失函数反向传播optimizer.step() #更新梯度train_loss += loss.item() * len(target)train_corrects += torch.sum(pre_lab == target.data)train_num += len(target)## 计算一个epoch在训练集上的损失和精度train_loss_all.append(train_loss / train_num)train_acc_all.append(train_corrects.double().item()/train_num)print('{} Train Loss: {:.4f} Train Acc: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, train_loss_all[-1], train_acc_all[-1]))## 计算一个epoch的训练后在验证集上的损失和精度model.eval() ## 设置模型为训练模式评估模式 for step,batch in enumerate(valdataloader):textdata,target = batch.cutword[0],batch.labelcode.view(-1)out = model(textdata)pre_lab = torch.argmax(out,1)loss = criterion(out, target) val_loss += loss.item() * len(target)val_corrects += torch.sum(pre_lab == target.data)val_num += len(target)## 计算一个epoch在训练集上的损失和精度val_loss_all.append(val_loss / val_num)val_acc_all.append(val_corrects.double().item()/val_num)print('{} Val Loss: {:.4f} Val Acc: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, val_loss_all[-1], val_acc_all[-1]))train_process = pd.DataFrame(data={"epoch":range(num_epochs),"train_loss_all":train_loss_all,"train_acc_all":train_acc_all,"val_loss_all":val_loss_all,"val_acc_all":val_acc_all}) return model,train_process
# 定义优化器
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(lstmmodel.parameters(), lr=0.0003)
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 损失函数
## 对模型进行迭代训练,对所有的数据训练EPOCH轮
lstmmodel,train_process = train_model2(lstmmodel,train_iter,val_iter,loss_func,optimizer,num_epochs=20)
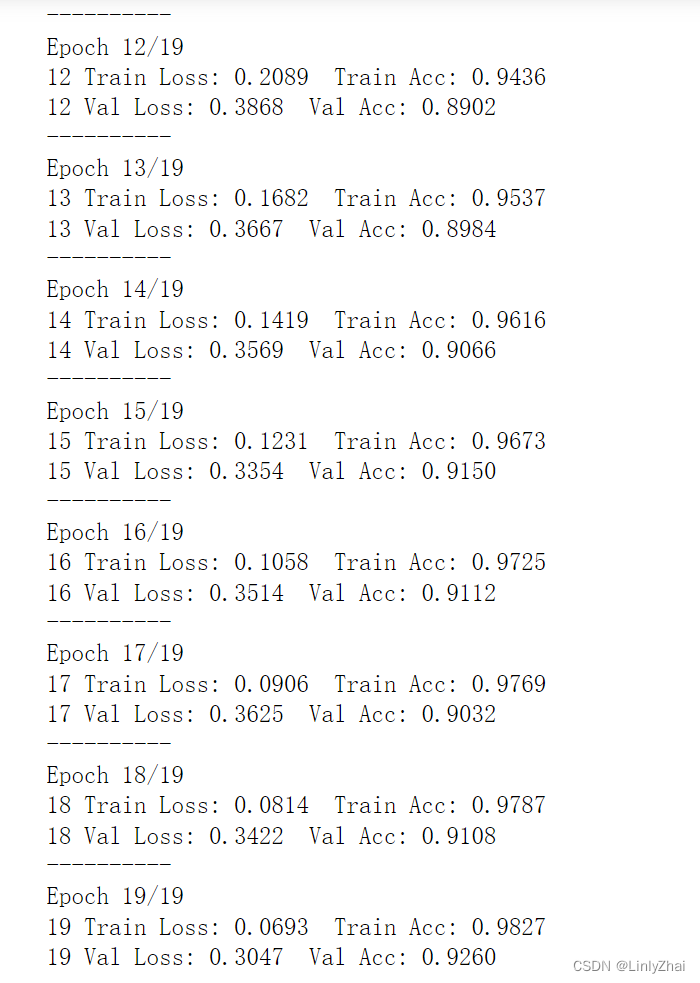
## 输出结果保存和数据保存
torch.save(lstmmodel,"data/lstm/lstmmodel.pkl")
## 导入保存的模型
lstmmodel = torch.load("data/lstm/lstmmodel.pkl")
lstmmodel
## 保存训练过程
train_process.to_csv("data/lstm/lstmmodel_process.csv",index=False)
train_process
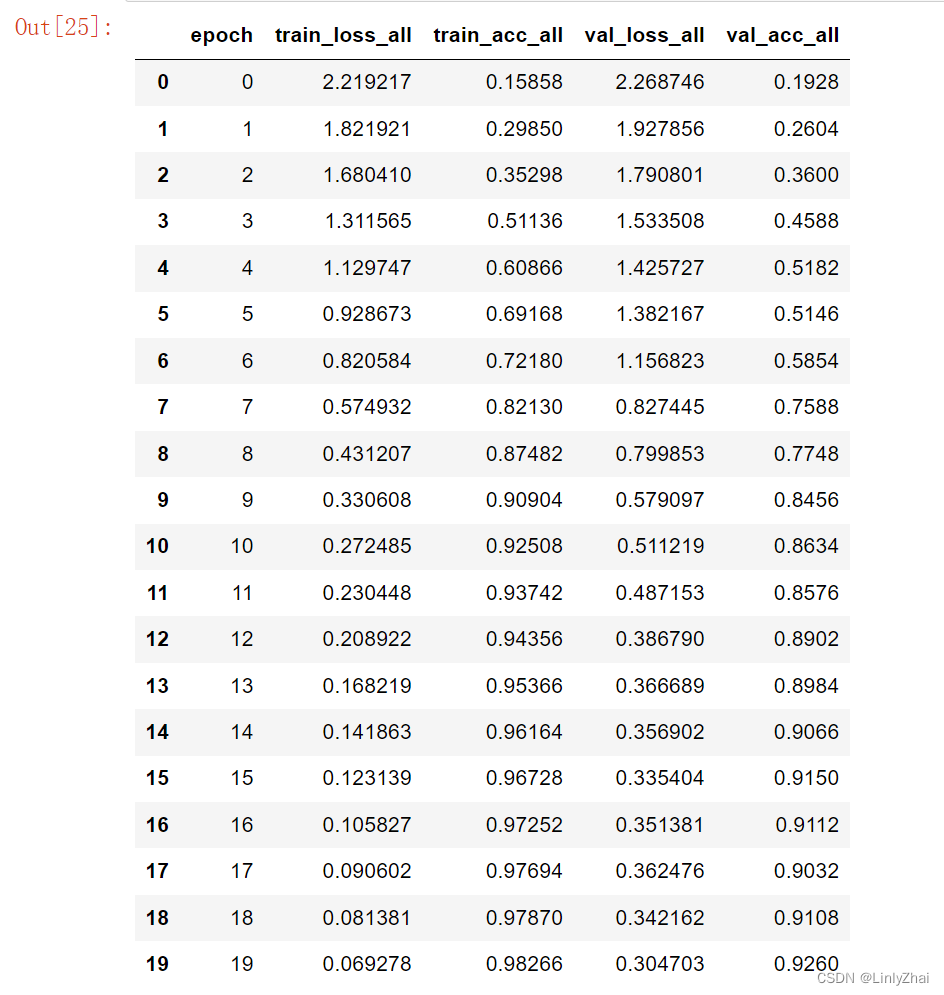
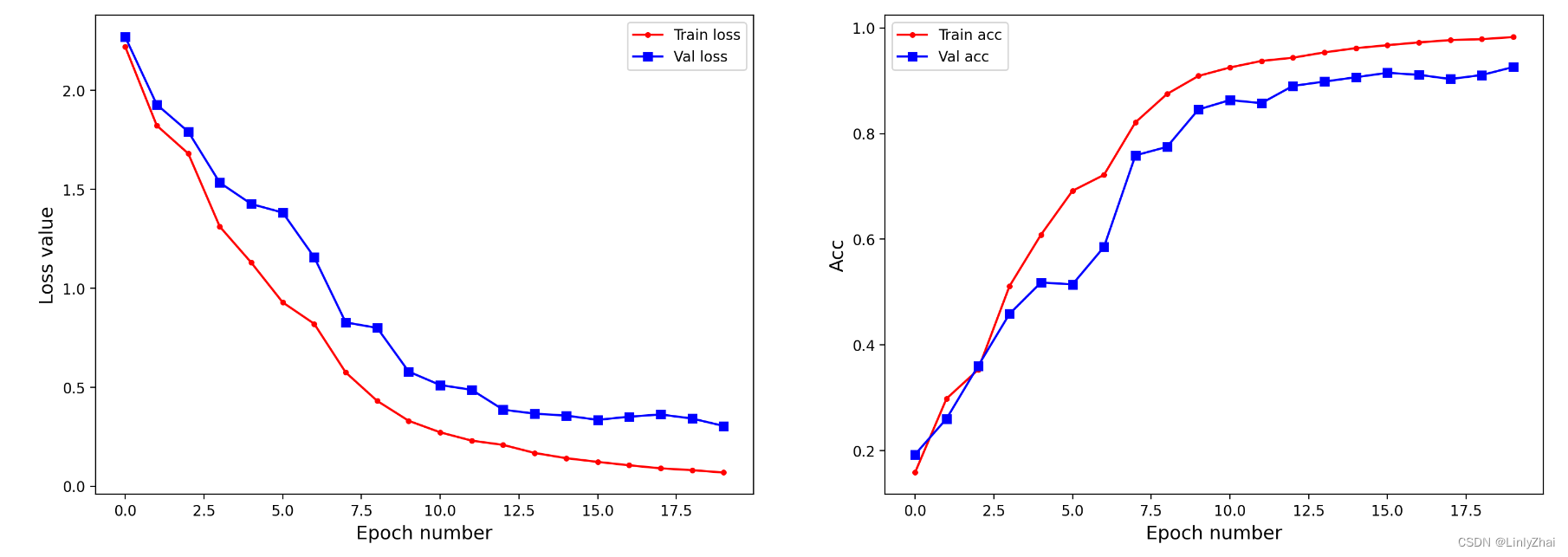
## 可视化模型训练过程中
plt.figure(figsize=(18,6))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(train_process.epoch,train_process.train_loss_all,"r.-",label = "Train loss")
plt.plot(train_process.epoch,train_process.val_loss_all,"bs-",label = "Val loss")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Epoch number",size = 13)
plt.ylabel("Loss value",size = 13)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.plot(train_process.epoch,train_process.train_acc_all,"r.-",label = "Train acc")
plt.plot(train_process.epoch,train_process.val_acc_all,"bs-",label = "Val acc")
plt.xlabel("Epoch number",size = 13)
plt.ylabel("Acc",size = 13)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
七、LSTM网络的测试
## 对测试集进行预测并计算精度
lstmmodel.eval() ## 设置模型为训练模式评估模式
test_y_all = torch.LongTensor()
pre_lab_all = torch.LongTensor()
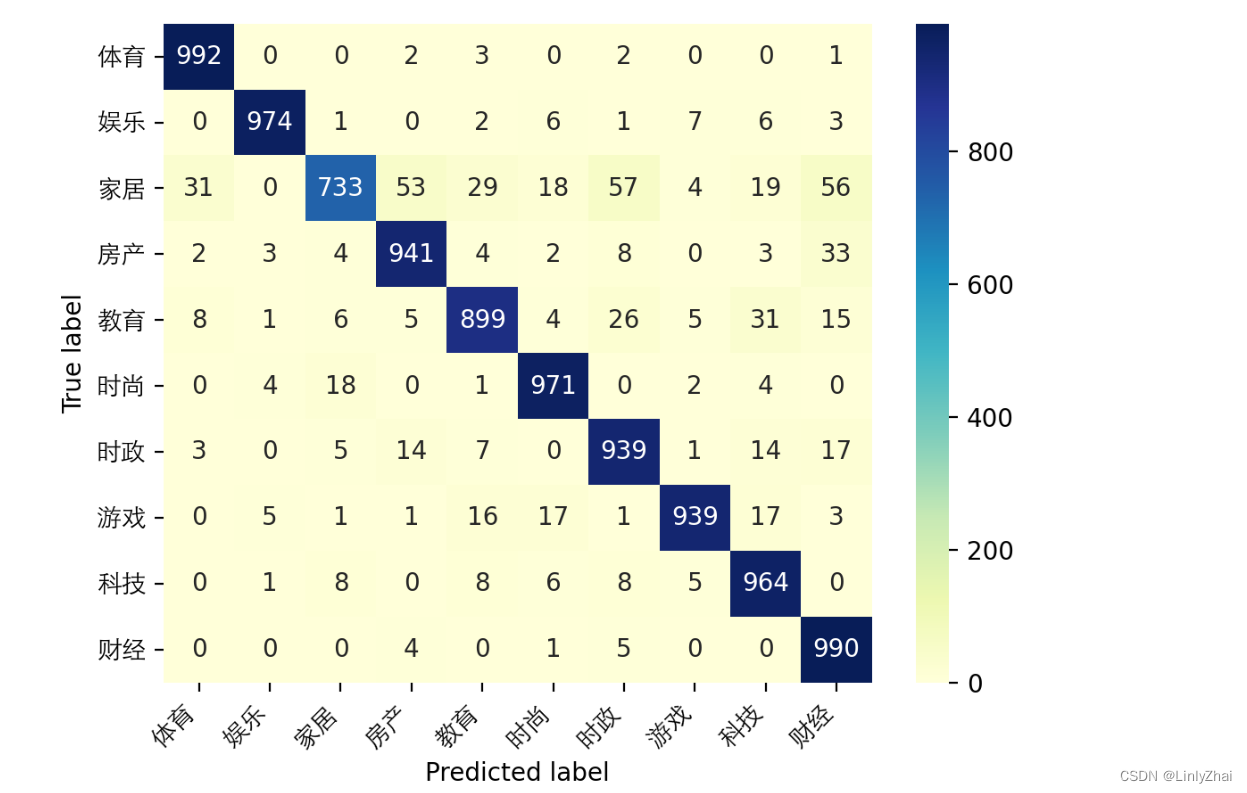
for step,batch in enumerate(test_iter):textdata,target = batch.cutword[0],batch.labelcode.view(-1)out = lstmmodel(textdata)pre_lab = torch.argmax(out,1)test_y_all = torch.cat((test_y_all,target)) ##测试集的标签pre_lab_all = torch.cat((pre_lab_all,pre_lab))##测试集的预测标签acc = accuracy_score(test_y_all,pre_lab_all)
print("在测试集上的预测精度为:",acc)
## 计算混淆矩阵并可视化
class_label = ["体育","娱乐","家居","房产","教育","时尚","时政","游戏","科技","财经"]
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(test_y_all,pre_lab_all)
df_cm = pd.DataFrame(conf_mat, index=class_label, columns=class_label)
heatmap = sns.heatmap(df_cm, annot=True, fmt="d",cmap="YlGnBu")
heatmap.yaxis.set_ticklabels(heatmap.yaxis.get_ticklabels(), rotation=0,ha='right',fontproperties = fonts)
heatmap.xaxis.set_ticklabels(heatmap.xaxis.get_ticklabels(), rotation=45,ha='right',fontproperties = fonts)
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
plt.show()
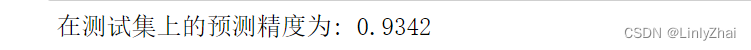


![[mysql 基于C++实现数据库连接池 连接池的使用] 持续更新中](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/4a9a02ef547d45dcb9e5094eb407ae6e.png)