文章目录
- 层序遍历
- 102. 二叉树的层序遍历
- 思路一:递归
- 思路二:层序遍历-迭代-借助队列
- 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
- 思路:层序遍历后翻转数组result即可
- 199.二叉树的右视图
- 思路:通过list数组储存每一层末尾值
- 637.二叉树的层平均值
- 思路:通过list数组储存均值
- 429.N 叉树的层序遍历
- 思路:依次判断并储存孩子节点
- 515.在每个树行中找最大值
- 思路:每一层储存最大值Integer.MIN_VALUE
- 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 思路
- 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
- 思路:【和前一题相同】
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 思路:每层deep+1
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
- 思路:
- 226.翻转二叉树
- 1.递归法DFS
- 代码
- 2.层序遍历BFS
- 代码:
- 101. 对称二叉树
- 思路:-使用后序遍历 左右中
- 递归法
- 递归代码
层序遍历
层序遍历一个二叉树。就是从左到右一层一层的去遍历二叉树。这种遍历的方式和我们之前讲过的都不太一样。
需要借用一个辅助数据结构即队列来实现,队列先进先出,符合一层一层遍历的逻辑,而用栈先进后出适合模拟深度优先遍历也就是递归的逻辑。
而这种层序遍历方式就是图论中的广度优先遍历,只不过我们应用在二叉树上。
使用队列实现二叉树广度优先遍历,动画如
102. 二叉树的层序遍历

思路一:递归
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {DFS(root,0);return resList;}//递归public void DFS(TreeNode root,Integer deep){if(root==null)return; //终止条件deep++;if(resList.size()<deep){//当层级增加时,list的Item也增加,利用list的索引值进行层级界定// 每一层一个item储存对应层的节点元素List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>();resList.add(item);}resList.get(deep-1).add(root.val);//根据对应的层数储存节点DFS(root.left,deep);DFS(root.right,deep);}
}
思路二:层序遍历-迭代-借助队列
先建立【储存每一层的result数组】
【建立队列】保存每一层的树节点,方便取值。
将root放入队列中,队列不为空时进行循环。
建立每一层的item数组,储存数值
题解

代码:
注意: queue的size一定要提前固定,因为queue的大小是动态变化的
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode>queue = new LinkedList<>();List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();if(root!=null){queue.add(root);//放入根节点}while(!queue.isEmpty()){// 新建一个临时列表 tmp ,用于存储当前层打印结果List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList<>();// 队列放入每一层节点的个数// 循环次数为当前层节点数// // 这里一定要使用固定大小size,不要使用que.size(),因为que.size是不断变化的int len=queue.size();for(int i=len;i>0;i--){TreeNode node=queue.poll();tmp.add(node.val);if(node.left!=null){queue.add(node.left);}if(node.right!=null){queue.add(node.right);}}res.add(tmp);}return res;}
}
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
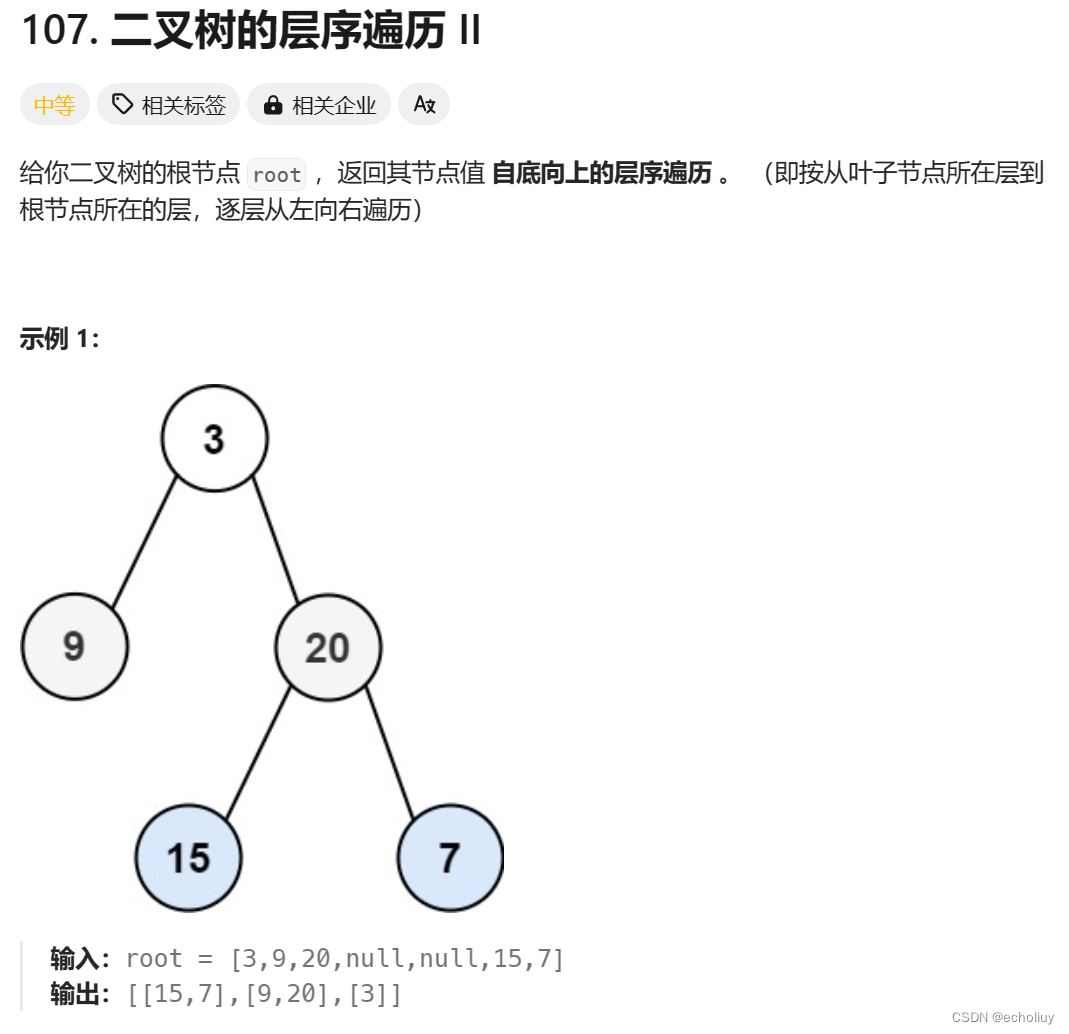
思路:层序遍历后翻转数组result即可
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();if(root!=null){queue.add(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()){List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();int len = queue.size();for(int i=len;i>0;i--){TreeNode node = queue.poll();tmp.add(node.val);if(node.left!=null){queue.add(node.left);}if(node.right!=null){queue.add(node.right);}}res.add(tmp);}// return res;List<List<Integer>> res1 = new ArrayList<>();for(int i=res.size()-1;i>=0;i--){res1.add(res.get(i));}return res1;}
}
199.二叉树的右视图
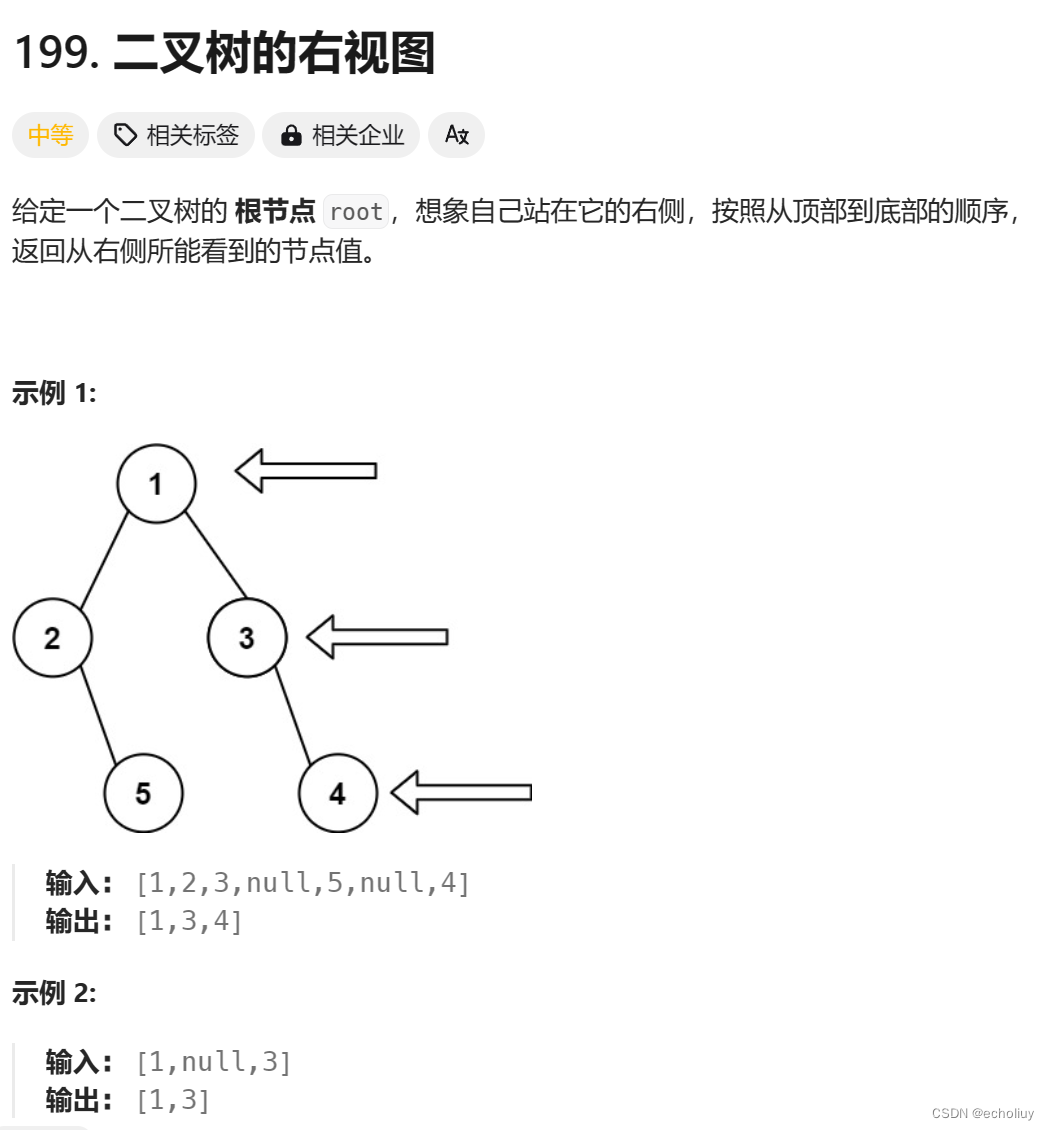
思路:通过list数组储存每一层末尾值
层序遍历的时候,判断是否遍历到单层的最后面的元素,如果是,就放进result数组中,随后返回result就可以了。
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {// List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();if(root!=null){queue.add(root);}List<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();//储存最终结果while(!queue.isEmpty()){int len=queue.size();// List<Integer>temp=new ArrayList<>();for(int i=len;i>0;i--){TreeNode node=queue.poll();if(i==1){//浏览到数组的最后一个,储存list.add(node.val);}if(node.left!=null){queue.add(node.left);}if(node.right!=null){queue.add(node.right);}}}return list;}
}
637.二叉树的层平均值
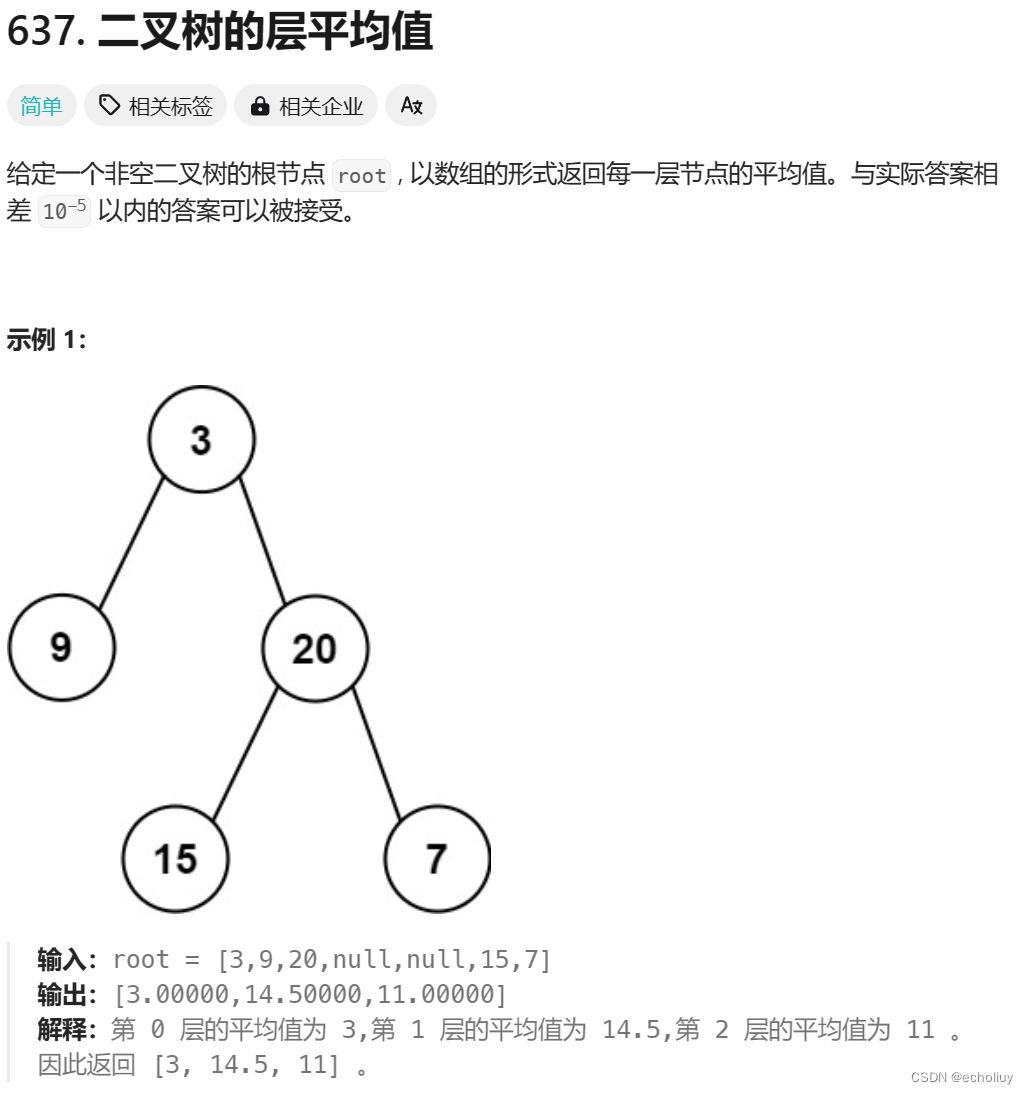
思路:通过list数组储存均值
本题就是层序遍历的时候把一层求个总和在取一个均值。
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();if(root!=null){queue.add(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()){// List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();int len = queue.size();double temp=0;for(int i=len;i>0;i--){TreeNode node = queue.poll();// list.add(node.val);temp+=node.val;if(node.left!=null){queue.add(node.left);}if(node.right!=null){queue.add(node.right);}}list.add(temp/len);}return list;}
}
429.N 叉树的层序遍历
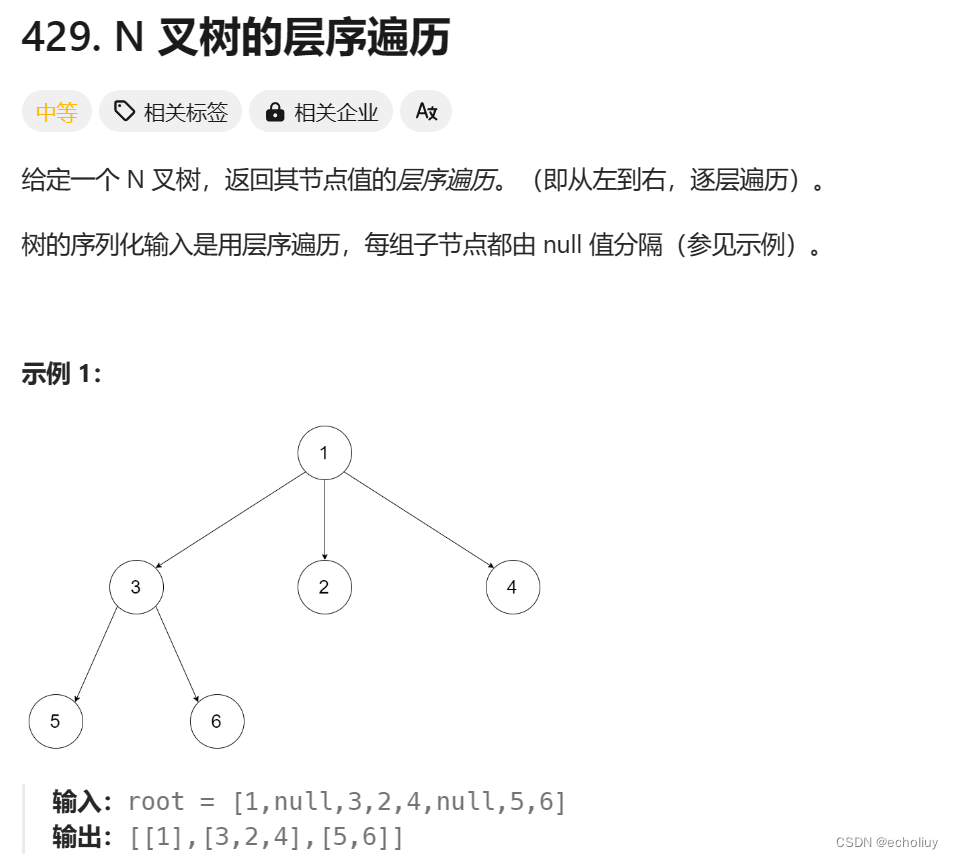
思路:依次判断并储存孩子节点
注意:
// List<Node> children = node.children;// if(children==null||children.size()==0){// continue;// }// for(Node child:children){或者 两种方法for(Node child:node.children){if(child!=null){queue.add(child);}}
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {public int val;public List<Node> children;public Node() {}public Node(int _val) {val = _val;}public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {val = _val;children = _children;}
};
*/class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();Queue<Node> queue =new LinkedList<>();if(root!=null){queue.add(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()){List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>();int len=queue.size();for(int i=0;i<len;i++){Node node=queue.poll();item.add(node.val);// List<Node> children = node.children;// if(children==null||children.size()==0){// continue;// }for(Node child:node.children){if(child!=null){queue.add(child);}}}res.add(item);}return res;}
}
515.在每个树行中找最大值
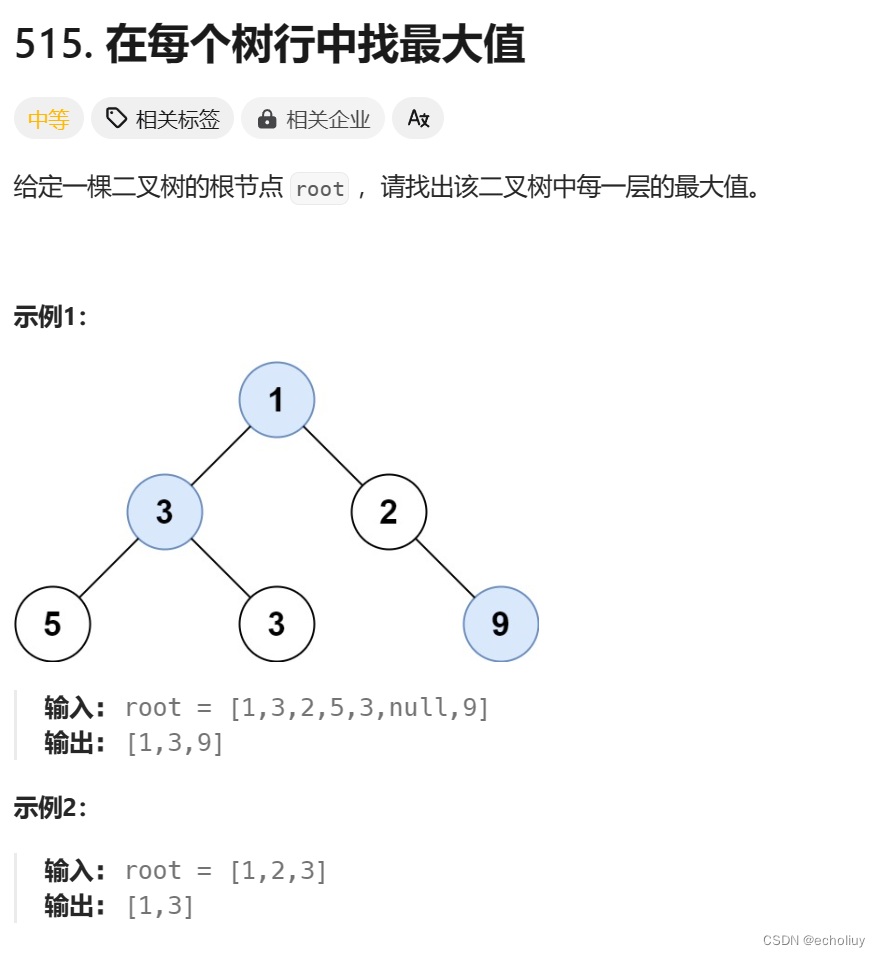
思路:每一层储存最大值Integer.MIN_VALUE
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();if(root!=null){queue.add(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()){int len=queue.size();int num=Integer.MIN_VALUE;for(int i=0;i<len;i++){TreeNode node = queue.poll();num=Math.max(num,node.val);if(node.left!=null){queue.add(node.left);}if(node.right!=null){queue.add(node.right);}}res.add(num);}return res;}
}
116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针

思路
本题依然是层序遍历,只不过在单层遍历的时候记录一下本层的头部节点,然后在遍历的时候让前一个节点指向本节点就可以了
class Solution {public Node connect(Node root) {Queue<Node>queue = new LinkedList<>();if(root!=null){queue.add(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()){int len=queue.size();Node pre=null;Node node =null;for(int i=0;i<len;i++){if(i==0){//记录头部节点pre=queue.poll();node=pre;}else{//让头部节点指向本节点node=queue.poll();pre.next=node;pre=pre.next;}if(node.left!=null){queue.add(node.left);}if(node.right!=null){queue.add(node.right);}}pre.next=null;}return root;}
}
117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II

思路:【和前一题相同】
104.二叉树的最大深度
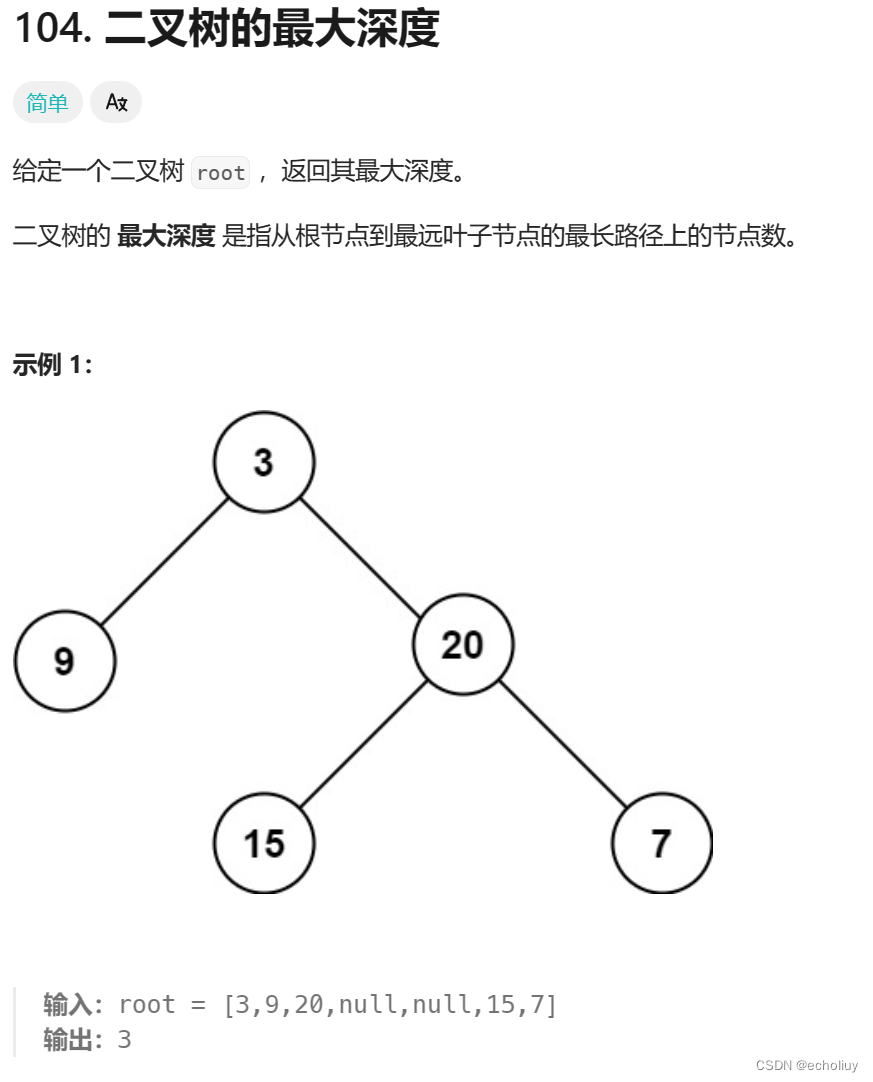
思路:每层deep+1
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode>queue = new LinkedList<>();int deep=0;if(root!=null){queue.add(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()){deep++;int len=queue.size();for(int i=0;i<len;i++){TreeNode node = queue.poll();if(node.left!=null)queue.add(node.left);if(node.right!=null)queue.add(node.right);}}return deep;}
}
111.二叉树的最小深度
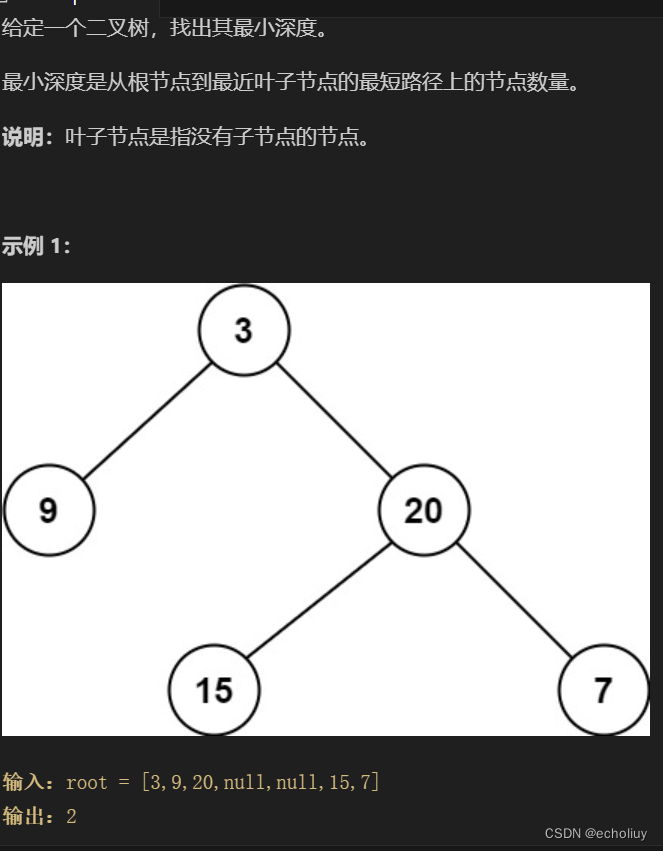
思路:
相对于 104.二叉树的最大深度 ,本题还也可以使用层序遍历的方式来解决,思路是一样的。
需要注意的是,只有当左右孩子都为空的时候,才说明遍历的最低点了。如果其中一个孩子为空则不是最低点
class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();int deep=0;if(root!=null){queue.add(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()){int len=queue.size();deep++;for(int i=0;i<len;i++){TreeNode node =queue.poll();if(node.left!=null)queue.add(node.left);if(node.right!=null)queue.add(node.right);if(node.left==null&&node.right==null){return deep;}}}return deep;}
}
226.翻转二叉树

注意只要把每一个节点的左右孩子翻转一下,就可以达到整体翻转的效果
这道题目使用前序遍历和后序遍历都可以,唯独中序遍历不方便,因为中序遍历会把某些节点的左右孩子翻转了两次!建议拿纸画一画,就理解了
那么层序遍历可以不可以呢?依然可以的!只要把每一个节点的左右孩子翻转一下的遍历方式都是可以的!
1.递归法DFS
把每一个节点的左右孩子都进行翻转

代码
- 后序遍历
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if(root==null){return root;}invertTree(root.left);//左invertTree(root.right);//右// 交换 //中TreeNode temp=null;temp=root.left;root.left=root.right;root.right=temp;return root;}
}
- 前序遍历
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if(root==null){return root;}// 交换 //中TreeNode temp=null;temp=root.left;root.left=root.right;root.right=temp;return root;invertTree(root.left); //左invertTree(root.right); //右}
}
2.层序遍历BFS
在添加左右节点前,进行左右节点的交换。
代码:
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {// if(root==null){// return root;// }Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();if(root!=null){queue.add(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()){int len = queue.size();for(int i=0;i<len;i++){TreeNode node=queue.poll();TreeNode tmp=null;// 交换tmp=node.right;node.right=node.left;node.left = tmp;// 放入左右节点if(node.left!=null){queue.add(node.left);}if(node.right!=null){queue.add(node.right);}}}return root;}
}
101. 对称二叉树

思路:-使用后序遍历 左右中
首先想清楚,判断对称二叉树要比较的是哪两个节点,要比较的可不是左右节点!
对于二叉树是否对称,要比较的是根节点的左子树与右子树是不是相互翻转的,理解这一点就知道了其实我们要比较的是两个树(这两个树是根节点的左右子树),所以在递归遍历的过程中,也是要同时遍历两棵树。
递归法
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
因为我们要比较的是根节点的两个子树是否是相互翻转的,进而判断这个树是不是对称树,所以要比较的是两个树,参数自然也是左子树节点和右子树节点。
返回值自然是bool类型。
代码如下:
bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right)
- 确定终止条件
要比较两个节点数值相不相同,首先要把两个节点为空的情况弄清楚!否则后面比较数值的时候就会操作空指针了。
节点为空的情况有:(注意我们比较的其实不是左孩子和右孩子,所以如下我称之为左节点右节点)
- 左节点为空,右节点不为空,不对称,return false
- 左不为空,右为空,不对称 return false
- 左右都为空,对称,返回true
此时已经排除掉了节点为空的情况,那么剩下的就是左右节点不为空:
- 左右都不为空,比较节点数值,不相同就return false
if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false;
else if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false;
else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;
else if (left->val != right->val) return false; // 注意这里我没有使用else
注意上面最后一种情况,我没有使用else,而是else if, 因为我们把以上情况都排除之后,剩下的就是 左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况。
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
此时才进入单层递归的逻辑,单层递归的逻辑就是处理 左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况。
- 比较二叉树外侧是否对称:传入的是左节点的左孩子,右节点的右孩子。
- 比较内侧是否对称,传入左节点的右孩子,右节点的左孩子。
- 如果左右都对称就返回true ,有一侧不对称就返回false 。
bool outside = compare(left->left, right->right); // 左子树:左、 右子树:右
bool inside = compare(left->right, right->left); // 左子树:右、 右子树:左
bool isSame = outside && inside; // 左子树:中、 右子树:中(逻辑处理)
return isSame;
递归代码
class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {return Compare(root.left,root.right);}public boolean Compare(TreeNode left,TreeNode right){if(left==null&&right==null){return true;}// if(left==null&&right!=null){// return false;// } // if(left!=null&&right==null){// return false;// }// if(left.val!=right.val){// return false;// }if (left==null||right==null||left.val != right.val) {return false;}// 比较外侧boolean outside = Compare(left.left,right.right);// 比较内侧boolean inside = Compare(left.right,right.left);return outside&&inside;}
}