Spring提供了一些接口来让我们定制bean 及扩展容器。
1 定制Bean
我们可以通过bean及容器的生命周期回调及一些Aware接口来定制bean。
1.1 生命周期回调
1.1.1 InitializingBean 与 DisposableBean
我们可以通过让Bean 实现InitializingBean 及DisposableBean 接口,当容器初始化完bean后会调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet()方法,当容器销毁bean前会调用DisposableBean接口的destroy()方法。
上面这两个接口方法在JSR-250中,可以使用@PostConstruct 及@PreDestory注释来代替。
也可以在xml的bean标签的init-method 的属性指定bean中的一个实例方法来作为初始化方法(与afterPropertiesSet()作用一致)。
在xml的bean标签的destory-method属性指定bean中的一个实例方法作为销毁方法(与destroy()作用一致)。
在beans 标签中通过default-init-method及default-destroy-method属性用来指定bean默认的初始化及销毁的方法名。
可以将bean中指定初始化方法(销毁方法)、继承InitializingBean或DisposableBean及使用@PostConstruct或@PreDestory注释这三种方案组合一起使用。
初始化方法的执行顺序为:@PostConstruct -> afterPropertiesSet() -> init-method 属性。
销毁方法的执行顺序为:@PreDestory -> destroy() -> destroy-method属性。
public class InitService implements InitializingBean {public InitService() {System.out.println("initService 实例化");}private String name;public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;System.out.println("赋值完成:" + name);}public void customInit() {System.out.println("init-method指定的customInit()");}@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet");}public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/article/article.xml");applicationContext.getBean(InitService.class);}
}<bean class="article.InitService" init-method="customInit"/>1.1.2 启动和关闭的回调
Lifecycle 接口定义了三个跟生命周期相关的方法:start() 启动,stop() 停止,isRuning() 是否运行。某些Io C容器实现了这个接口的方法,LifecycleProcessor接口扩展了Lifecycle接口并新增两个方法:onRefresh() 及 onClose()。
public interface Lifecycle {void start();void stop();boolean isRunning();
}public interface LifecycleProcessor extends Lifecycle {void onRefresh();void onClose();
}当spring context被启动时会调用容器的start方法,当关闭时候会调用容器的stop()方法。同时bean也可以实现这个接口,当容器被调用start方法时,bean的start方法也会被调用。
在bean中,所依赖的bean会被先创建,也可以指定depend-on关系来控制bean的创建顺序。对于那些没有直接依赖关系的,但是我们想指定start()被调用顺序,这时bean可以通过实现Phased接口来控制被调用的顺序。该接口有个getPhase()方法返回一个int类型,值越小越先启动,越小越后关闭。而没有实现Phased接口的Bean,值为0.
注意,Lifecycle 是针对的是常规启动关闭情况,如果想在热启动或其他自动启动模式下触发,那么应该使用SmartLifecycle接口。
public class StartService1 implements Lifecycle, Phased {public StartService1() {System.out.println("StartService1 实例化");}private boolean running = false;@Overridepublic void start() {System.out.println("StartService1 启动");running = true;}@Overridepublic void stop() {System.out.println("StartService1 关闭");running = false;}@Overridepublic boolean isRunning() {return running;}@Overridepublic int getPhase() {return -1; // 比没有实现Phased接口的Bean更先调用start()}public static void main(String[] args) {ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/article/article.xml");applicationContext.start(); // 手动发出启动的信号}
}public class StartService2 implements Lifecycle {public StartService2() {System.out.println("StartService2实例化");}private boolean running = false;@Overridepublic void start() {System.out.println("StartService2 启动");running = true;}@Overridepublic void stop() {System.out.println("StartService2 关闭");running = false;}@Overridepublic boolean isRunning() {return running;}
}<bean class="article.StartService2" lazy-init="false"/>
<bean class="article.StartService1" lazy-init="false"/>在上面的代码中,ConfigurableApplicationContext接口继承Lifecycle接口。而ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的一个祖先类AbstractApplicationContext 实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext的方法。
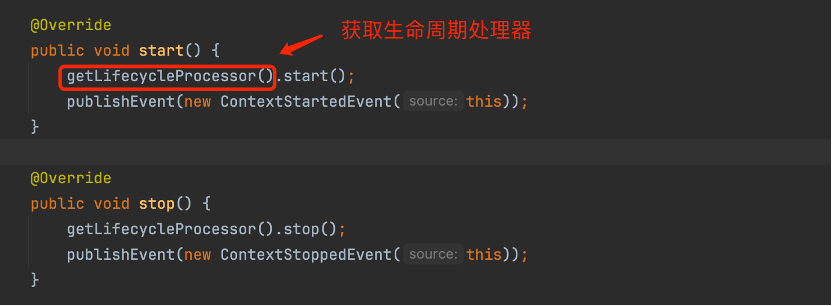
图 AbstractApplicationContext类中的start 方法
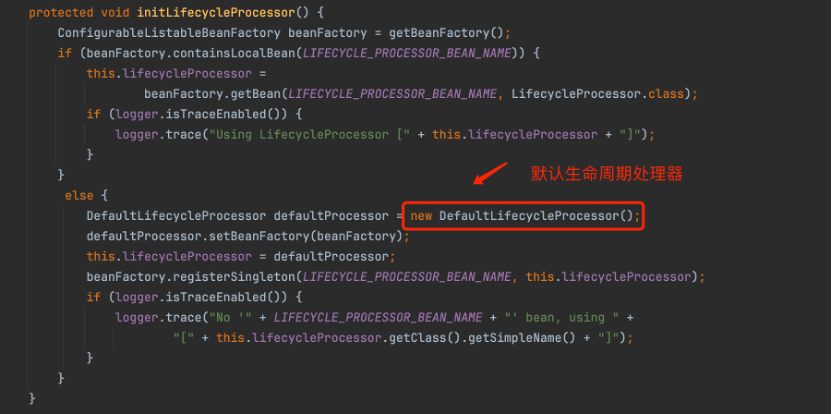
图 AbstractApplicationContext类中初始化生命周期处理器的方法
而在DefaultLifecycleProcessor类中的start方法内部,调用了该类的实例方法startBeans。
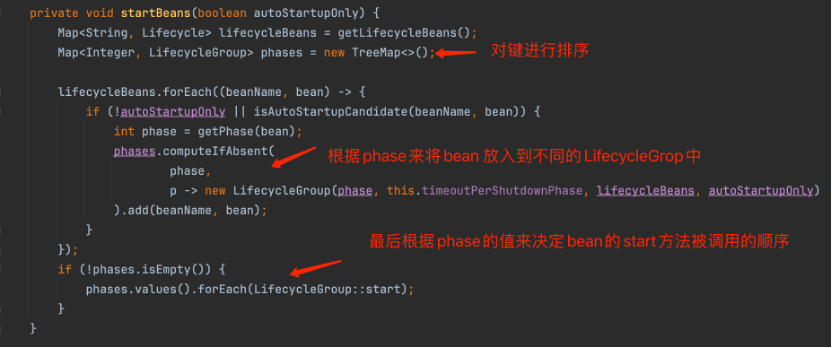
图 DefaultLifecycleProcessor 的startBeans方法
在非Web 环境的容器中,要安全的来关闭容器,需要调用ConfigurableApplicationContext的registerShutdownHook实例方法,来让JVM关闭前能调用容器的stop方法。
而Web环境的容器实现了安全关闭容器的方法。
1.2 Aware 接口
Spring 提供了广泛的Aware回调接口,让bean向容器指示它们需要特定的基础结构依赖关系。
| ApplicationContextAware | 向bean提供ApplicationContext变量。 |
| ApplicationEventPublisherAware | 发布ApplicationContext的事件。 |
| BeanClassLoaderAware | 用于加载bean类。 |
| BeanFactoryAware | 向bean提供BeanFactory变量。 |
| BeanNameAware | 向bean提供bean的命名。 |
| BootstrapContextAware | 当前容器里的资源适配器BootstrapContext |
| LoadTimeWeaverAware | 定义的weaver用于在加载时处理类定义。 |
| MessageSourceAware | 配置解析消息的策略(支持参数化与国际化)。 |
| NotificationPublisherAware | Spring JMX 通知的发布者。 |
| ResourceLoaderAware | 配置用于低级访问资源的加载器。 |
| ServletConfigAware | 当前在容器运行的ServletConfig。 |
| ServletContextAware | 当前在容器运行的ServletContext。 |
表 Spring提供的Aware接口
2 定义Bean的继承关系
子bean 可以从父bean继承配置数据,子bean可以根据需要覆盖某些值或添加其他值。使用这种继承关系可以节省大量的键入工作,这是一种模版形式。
如果bean 标签的abstract属性标志为true,那么这个bean将不会被实例化(class属性的值为空),但是可以被子bean继承。
public class ChildrenService {private String name;private Integer age;private String address;public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public void setAddress(String address) {this.address = address;}public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/article/article.xml");ChildrenService childrenService = applicationContext.getBean(ChildrenService.class);System.out.println(childrenService);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "ChildrenService{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", address='" + address + '\'' +'}';}
}<bean id="fatherBean" abstract="true"><property name="name" value="默认名"/><property name="age" value="28"/></bean><bean class="article.ChildrenService" parent="fatherBean"><property name="name" value="黄先生"/><property name="address" value="深圳"/></bean>3 容器扩展
可以通过向容器中插入实现了特定接口的实例来对容器进行扩展,而不必通过继承ApplicationContext的方式。
3.1 BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor 接口提供了可以覆盖容器实例化逻辑或依赖逻辑的方法。bean 先由容器实例化,然后由BeanPostProcessor进行操作。并且可以向容器中插入多个这里的实例,控制执行顺序,则还需要实现Ordered接口。
public class CustomBeanPostProcessor1 implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered {@Overridepublic int getOrder() {return 1; // 越小越先执行}@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("CustomBeanPostProcessor1 postProcessBeforeInitialization() 实例化之前");return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);}@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("CustomBeanPostProcessor1 postProcessAfterInitialization() 实例化之后");return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);}
}public class CustomBeanPostProcessor2 implements BeanPostProcessor, Ordered {@Overridepublic int getOrder() {return 2;}@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("CustomBeanPostProcessor2 postProcessBeforeInitialization() 实例化之前");return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);}@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("CustomBeanPostProcessor2 postProcessAfterInitialization() 实例化之后");return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);}
}<bean class="article.CustomBeanPostProcessor1"/>
<bean class="article.CustomBeanPostProcessor2"/>3.2 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 定制配置元数据
IoC容器允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor 读取配置元数据,并可能在实例化之前更改元数据。同样允许配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor。当被注入到容器时会自动运行。
Spring 定义了多个实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的类。
3.2.1 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
通过配置Properties的方式来取代bean中定义的占位符。
使用标准的Java Properties 格式将bean定义中的属性值外部化到一个单独的文件中。这样可以使部署时能自定义特定于环境的属性,如数据库host和帐号密码,而无需修改容器的一个或多个xml中bean定义的属性。
public class DataService {private String host;private String username;private String password;public void setHost(String host) {this.host = host;}public void setUsername(String username) {this.username = username;}public void setPassword(String password) {this.password = password;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "DataService{" +"host='" + host + '\'' +", username='" + username + '\'' +", password='" + password + '\'' +'}';}public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/article/article.xml");DataService dataService = applicationContext.getBean(DataService.class);System.out.println(dataService);}
}// data.properties
jdbc.host=localhost
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123<bean class="org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer"><property name="location" value="classpath:article/data.properties"/>
</bean>
<bean class="article.DataService"><property name="host" value="${jdbc.host}"/><property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>3.2.1 PropertyOverrideConfigurer
可以覆盖任何bean 中的任何属性。
public class StudentService {private String name;private Integer age;public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "StudentService{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/article/article.xml");StudentService studentService = applicationContext.getBean(StudentService.class);System.out.println(studentService); // 输出值 StudentService{name='newName', age=1}}
}<bean id="studentService" class="article.StudentService"><property name="name" value="小柚柚"/><property name="age" value="3"/></bean><bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyOverrideConfigurer"><property name="properties"><props><prop key="studentService.name">newName</prop><prop key="studentService.age">1</prop></props></property></bean>