- 不是一个机器学习算法
- 是一种基于搜索的最优化方法
- 作用:最小化一个损失函数
- 梯度上升法:最大化一个效用函数
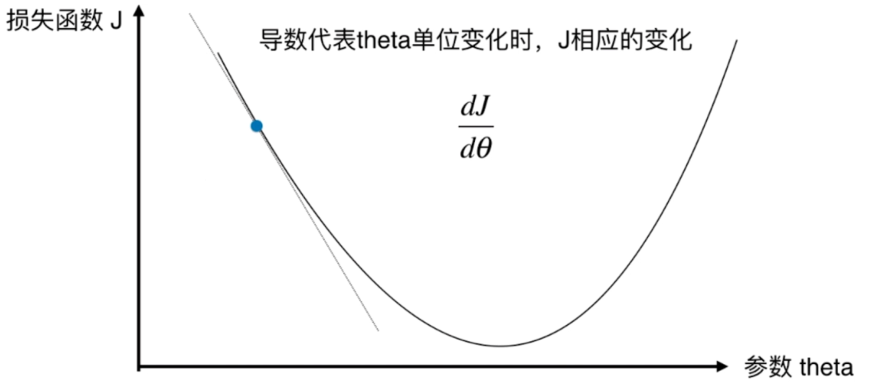


并不是所有函数都有唯一的极值点

解决方法:
- 多次运行,随机化初始点
- 梯度下降法的初始点也是一个超参数
代码演示
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plot_x = np.linspace(-1., 6., 141)
plot_y = (plot_x-2.5)**2 - 1.
plt.plot(plot_x, plot_y)
plt.show()

梯度下降法
epsilon = 1e-8
eta = 0.1
def J(theta):return (theta-2.5)**2 - 1.def dJ(theta):return 2*(theta-2.5)theta = 0.0
while True:gradient = dJ(theta)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradientif(abs(J(theta) - J(last_theta)) < epsilon):breakprint(theta)
print(J(theta))

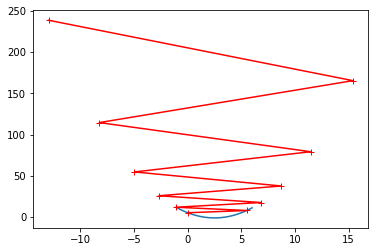
可视化
theta = 0.0
theta_history = [theta]
while True:gradient = dJ(theta)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradienttheta_history.append(theta)if(abs(J(theta) - J(last_theta)) < epsilon):breakplt.plot(plot_x, J(plot_x))
plt.plot(np.array(theta_history), J(np.array(theta_history)), color="r", marker='+')
plt.show()

封装
def gradient_descent(initial_theta, eta, epsilon=1e-8):theta = initial_thetatheta_history.append(initial_theta)while True:gradient = dJ(theta)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradienttheta_history.append(theta)if(abs(J(theta) - J(last_theta)) < epsilon):breakdef plot_theta_history():plt.plot(plot_x, J(plot_x))plt.plot(np.array(theta_history), J(np.array(theta_history)), color="r", marker='+')plt.show()
eta = 0.01时
eta = 0.01
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0, eta)
plot_theta_history()

eta = 0.001时
eta = 0.001
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0, eta)
plot_theta_history()

eta = 0.8时
eta = 0.8
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0, eta)
plot_theta_history()

优化 避免死循环
def J(theta):try:return (theta-2.5)**2 - 1.except:return float('inf')
def gradient_descent(initial_theta, eta, n_iters = 1e4, epsilon=1e-8):theta = initial_thetai_iter = 0theta_history.append(initial_theta)while i_iter < n_iters:gradient = dJ(theta)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradienttheta_history.append(theta)if(abs(J(theta) - J(last_theta)) < epsilon):breaki_iter += 1return
eta = 1.1时
eta = 1.1
theta_history = []
gradient_descent(0, eta, n_iters=10)
plot_theta_history()
多元线性回归中的梯度下降法




代码
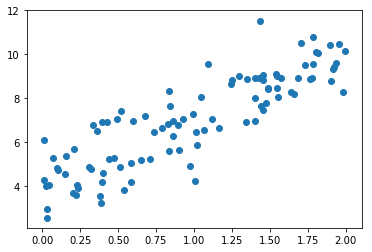
生成数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(666)
x = 2 * np.random.random(size=100)
y = x * 3. + 4. + np.random.normal(size=100)
X = x.reshape(-1, 1)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
使用梯度下降法训练
def J(theta, X_b, y):try:return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta))**2) / len(X_b)except:return float('inf')def dJ(theta, X_b, y):res = np.empty(len(theta))res[0] = np.sum(X_b.dot(theta) - y)for i in range(1, len(theta)):res[i] = (X_b.dot(theta) - y).dot(X_b[:,i])return res * 2 / len(X_b)def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters = 1e4, epsilon=1e-8):theta = initial_thetacur_iter = 0while cur_iter < n_iters:gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradientif(abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):breakcur_iter += 1return theta
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x), 1)), x.reshape(-1,1)])
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
eta = 0.01theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta)

封装
def fit_gd(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4):"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Linear Regression模型"""assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"def J(theta, X_b, y):try:return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta)) ** 2) / len(y)except:return float('inf')def dJ(theta, X_b, y):res = np.empty(len(theta))res[0] = np.sum(X_b.dot(theta) - y)for i in range(1, len(theta)):res[i] = (X_b.dot(theta) - y).dot(X_b[:, i])return res * 2 / len(X_b)def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):theta = initial_thetacur_iter = 0while cur_iter < n_iters:gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradientif (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):breakcur_iter += 1return thetaX_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta, n_iters)self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]return self
全:
import numpy as np
from .metrics import r2_scoreclass LinearRegression:def __init__(self):"""初始化Linear Regression模型"""self.coef_ = Noneself.intercept_ = Noneself._theta = Nonedef fit_normal(self, X_train, y_train):"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train训练Linear Regression模型"""assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])self._theta = np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y_train)self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]return selfdef fit_gd(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4):"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Linear Regression模型"""assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"def J(theta, X_b, y):try:return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta)) ** 2) / len(y)except:return float('inf')def dJ(theta, X_b, y):res = np.empty(len(theta))res[0] = np.sum(X_b.dot(theta) - y)for i in range(1, len(theta)):res[i] = (X_b.dot(theta) - y).dot(X_b[:, i])return res * 2 / len(X_b)def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):theta = initial_thetacur_iter = 0while cur_iter < n_iters:gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradientif (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):breakcur_iter += 1return thetaX_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta, n_iters)self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]return selfdef predict(self, X_predict):"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \"must fit before predict!"assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict])return X_b.dot(self._theta)def score(self, X_test, y_test):"""根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""y_predict = self.predict(X_test)return r2_score(y_test, y_predict)def __repr__(self):return "LinearRegression()"
线性回归中使用梯度下降法


优化代码
def dJ(theta, X_b, y):return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y) * 2. / len(y)
import numpy as np
from .metrics import r2_scoreclass LinearRegression:def __init__(self):"""初始化Linear Regression模型"""self.coef_ = Noneself.intercept_ = Noneself._theta = Nonedef fit_normal(self, X_train, y_train):"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train训练Linear Regression模型"""assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])self._theta = np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y_train)self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]return selfdef fit_gd(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4):"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Linear Regression模型"""assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"def J(theta, X_b, y):try:return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta)) ** 2) / len(y)except:return float('inf')def dJ(theta, X_b, y):return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y) * 2. / len(y)def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):theta = initial_thetacur_iter = 0while cur_iter < n_iters:gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradientif (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):breakcur_iter += 1return thetaX_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta, n_iters)self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]return selfdef predict(self, X_predict):"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \"must fit before predict!"assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict])return X_b.dot(self._theta)def score(self, X_test, y_test):"""根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""y_predict = self.predict(X_test)return r2_score(y_test, y_predict)def __repr__(self):return "LinearRegression()"代码测试
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
boston = datasets.load_boston()
X = boston.data
y = boston.targetX = X[y < 50.0]
y = y[y < 50.0]
from playML.model_selection import train_test_splitX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, seed=666)
from playML.LinearRegression import LinearRegressionlin_reg1 = LinearRegression()
%time lin_reg1.fit_normal(X_train, y_train)
lin_reg1.score(X_test, y_test)
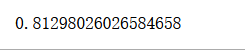
使用梯度下降法
lin_reg2 = LinearRegression()
lin_reg2.fit_gd(X_train, y_train)

更改eta值
lin_reg2.fit_gd(X_train, y_train, eta=0.000001)
lin_reg2.score(X_test, y_test)

再优化
%time lin_reg2.fit_gd(X_train, y_train, eta=0.000001, n_iters=1e6)
lin_reg2.score(X_test, y_test)


归一化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerstandardScaler = StandardScaler()
standardScaler.fit(X_train)
X_train_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_train)lin_reg3 = LinearRegression()
%time lin_reg3.fit_gd(X_train_standard, y_train)
X_test_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_test)
lin_reg3.score(X_test_standard, y_test)

随机梯度下降法 Stochastic Gradient Descent

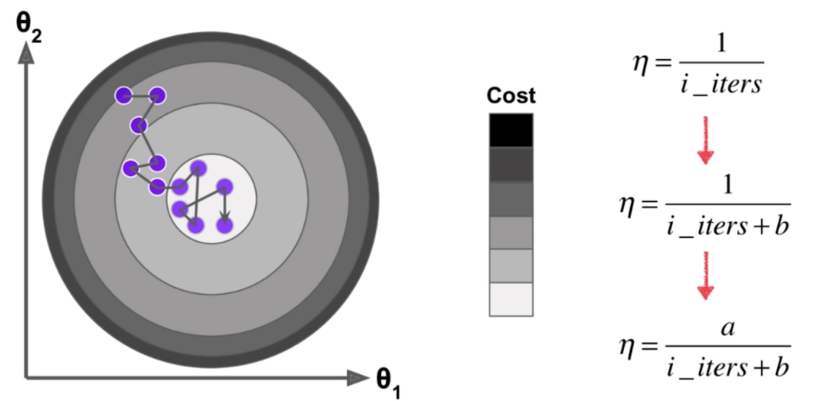
模拟退化的思想

代码
批量梯度下降法
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
m = 100000x = np.random.normal(size=m)
X = x.reshape(-1,1)
y = 4.*x + 3. + np.random.normal(0, 3, size=m)
def J(theta, X_b, y):try:return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta)) ** 2) / len(y)except:return float('inf')def dJ(theta, X_b, y):return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y) * 2. / len(y)def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):theta = initial_thetacur_iter = 0while cur_iter < n_iters:gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradientif (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):breakcur_iter += 1return theta
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X), 1)), X])
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
eta = 0.01
theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta)

随机梯度下降法
def dJ_sgd(theta, X_b_i, y_i):return 2 * X_b_i.T.dot(X_b_i.dot(theta) - y_i)def sgd(X_b, y, initial_theta, n_iters):t0, t1 = 5, 50def learning_rate(t):return t0 / (t + t1)theta = initial_thetafor cur_iter in range(n_iters):rand_i = np.random.randint(len(X_b))gradient = dJ_sgd(theta, X_b[rand_i], y[rand_i])theta = theta - learning_rate(cur_iter) * gradientreturn theta
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X), 1)), X])
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
theta = sgd(X_b, y, initial_theta, n_iters=m//3)

封装
def fit_sgd(self, X_train, y_train, n_iters=50, t0=5, t1=50):"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Linear Regression模型"""assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"assert n_iters >= 1def dJ_sgd(theta, X_b_i, y_i):return X_b_i * (X_b_i.dot(theta) - y_i) * 2.def sgd(X_b, y, initial_theta, n_iters=5, t0=5, t1=50):def learning_rate(t):return t0 / (t + t1)theta = initial_thetam = len(X_b)for i_iter in range(n_iters):indexes = np.random.permutation(m)X_b_new = X_b[indexes,:]y_new = y[indexes]for i in range(m):gradient = dJ_sgd(theta, X_b_new[i], y_new[i])theta = theta - learning_rate(i_iter * m + i) * gradientreturn theta
import numpy as np
from .metrics import r2_scoreclass LinearRegression:def __init__(self):"""初始化Linear Regression模型"""self.coef_ = Noneself.intercept_ = Noneself._theta = Nonedef fit_normal(self, X_train, y_train):"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train训练Linear Regression模型"""assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])self._theta = np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y_train)self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]return selfdef fit_bgd(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4):"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Linear Regression模型"""assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"def J(theta, X_b, y):try:return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta)) ** 2) / len(y)except:return float('inf')def dJ(theta, X_b, y):return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y) * 2. / len(y)def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):theta = initial_thetacur_iter = 0while cur_iter < n_iters:gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradientif (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):breakcur_iter += 1return thetaX_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta, n_iters)self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]return selfdef fit_sgd(self, X_train, y_train, n_iters=50, t0=5, t1=50):"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Linear Regression模型"""assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"assert n_iters >= 1def dJ_sgd(theta, X_b_i, y_i):return X_b_i * (X_b_i.dot(theta) - y_i) * 2.def sgd(X_b, y, initial_theta, n_iters=5, t0=5, t1=50):def learning_rate(t):return t0 / (t + t1)theta = initial_thetam = len(X_b)for i_iter in range(n_iters):indexes = np.random.permutation(m)X_b_new = X_b[indexes,:]y_new = y[indexes]for i in range(m):gradient = dJ_sgd(theta, X_b_new[i], y_new[i])theta = theta - learning_rate(i_iter * m + i) * gradientreturn thetaX_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])initial_theta = np.random.randn(X_b.shape[1])self._theta = sgd(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, n_iters, t0, t1)self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]return selfdef predict(self, X_predict):"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \"must fit before predict!"assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict])return X_b.dot(self._theta)def score(self, X_test, y_test):"""根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""y_predict = self.predict(X_test)return r2_score(y_test, y_predict)def __repr__(self):return "LinearRegression()"真实使用我们自己的SGD
from sklearn import datasetsboston = datasets.load_boston()
X = boston.data
y = boston.targetX = X[y < 50.0]
y = y[y < 50.0]
from playML.model_selection import train_test_splitX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, seed=666)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerstandardScaler = StandardScaler()
standardScaler.fit(X_train)
X_train_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_train)
X_test_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_test)
from playML.LinearRegression import LinearRegressionlin_reg = LinearRegression()
lin_reg.fit_sgd(X_train_standard, y_train, n_iters=100)
lin_reg.score(X_test_standard, y_test)
scikit-learn中的SGD
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressorsgd_reg = SGDRegressor()
sgd_reg.fit(X_train_standard, y_train)
sgd_reg.score(X_test_standard, y_test)

sgd_reg = SGDRegressor(n_iter=50)
sgd_reg.fit(X_train_standard, y_train)
sgd_reg.score(X_test_standard, y_test)

关于梯度的调试


生成数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(666)
X = np.random.random(size=(1000, 10))true_theta = np.arange(1, 12, dtype=float)
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X), 1)), X])
y = X_b.dot(true_theta) + np.random.normal(size=1000)
def J(theta, X_b, y):try:return np.sum((y - X_b.dot(theta))**2) / len(X_b)except:return float('inf')
def dJ_math(theta, X_b, y):return X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta) - y) * 2. / len(y)
def dJ_debug(theta, X_b, y, epsilon=0.01):res = np.empty(len(theta))for i in range(len(theta)):theta_1 = theta.copy()theta_1[i] += epsilontheta_2 = theta.copy()theta_2[i] -= epsilonres[i] = (J(theta_1, X_b, y) - J(theta_2, X_b, y)) / (2 * epsilon)return res
def gradient_descent(dJ, X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters = 1e4, epsilon=1e-8):theta = initial_thetacur_iter = 0while cur_iter < n_iters:gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)last_theta = thetatheta = theta - eta * gradientif(abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):breakcur_iter += 1return theta
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X), 1)), X])
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
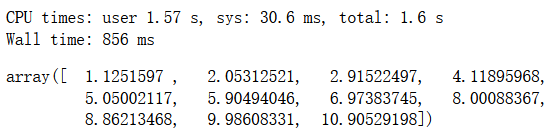
eta = 0.01%time theta = gradient_descent(dJ_debug, X_b, y, initial_theta, eta)
theta

%time theta = gradient_descent(dJ_math, X_b, y, initial_theta, eta)
theta