二叉树的定义:
struct TreeNode
{int val;TreeNode* left;TreeNode* right;TreeNode():val(0),left(nullptr),right(nullptr){}TreeNode(int val):val(val),left(nullptr),right(nullptr){}TreeNode(int val,TreeNode* left,TreeNode* right):val(val),left(left),right(right){}
}
其实二叉树就是一种类似链表结构(故打好链表基础十分重要!)。
各种遍历方法

前序遍历
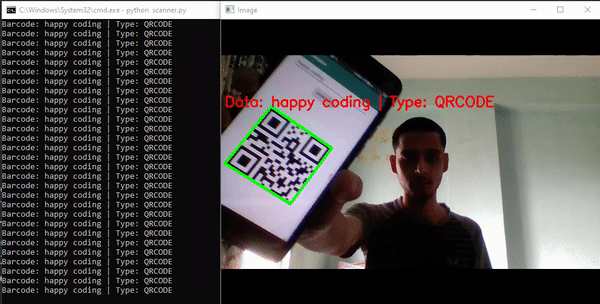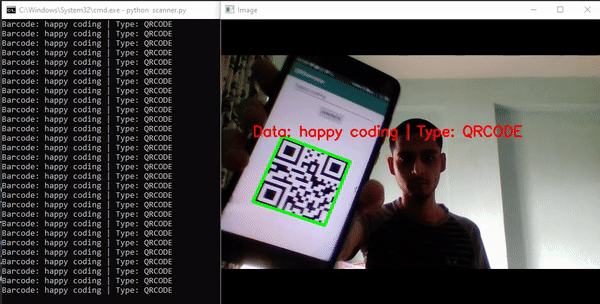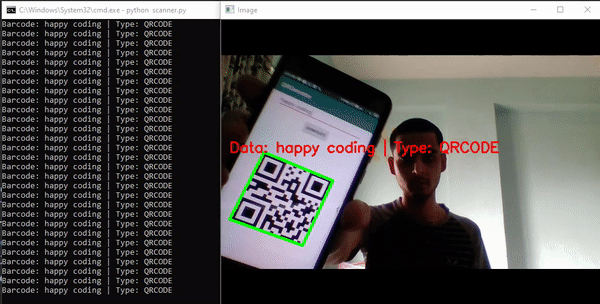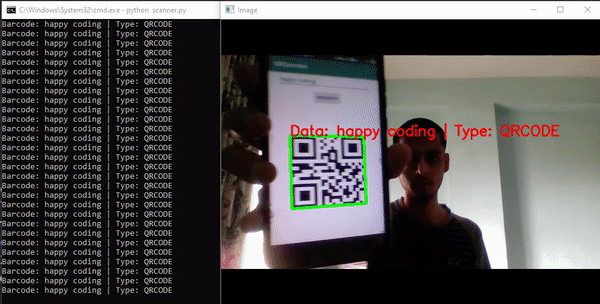
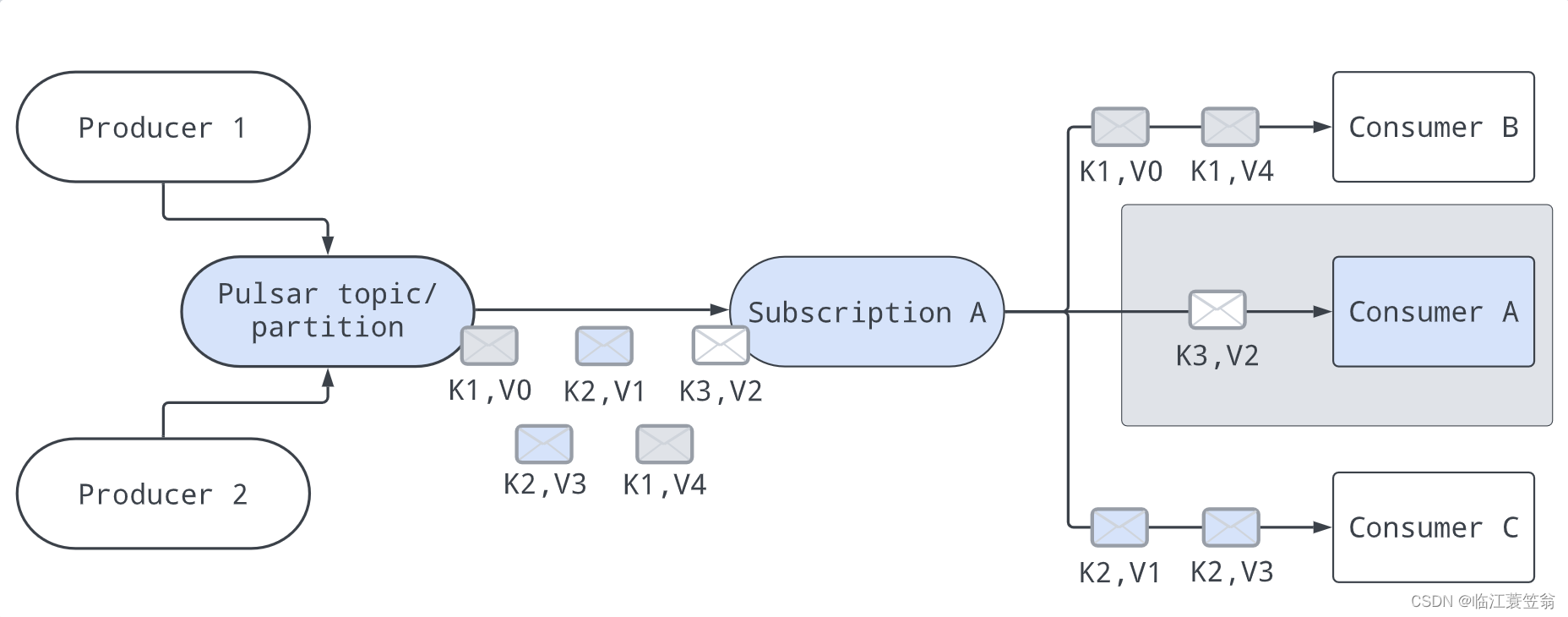
前序遍历的顺序是中左右,用一个图来感受这个过程,前序遍历:5412678
递归法
class Solution {
public:vector<int> result;void preorder(TreeNode* node){if(node==nullptr)return;result.push_back(node->val);preorder(node->left);preorder(node->right);}vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {result.clear();preorder(root);return result;}
};
迭代法
上面我们采用递归能做出来,递归的本质就是栈,故迭代法可用栈这种数据结构!
class Solution {
public:vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> result;stack<TreeNode*> stk;//先判断是否需要push进去,首先需要push一个root进去,不然下面的while循环都进不去if(root==nullptr) return result;stk.push(root);while(!stk.empty()){TreeNode* node=stk.top();stk.pop();result.push_back(node->val);//一个注意点,应该先push右子树,因为栈的特点是先入后出if(node->right)stk.push(node->right);if(node->left)stk.push(node->left);}return result;}
};
中序遍历
递归法
中序遍历的顺序为左中右,参考上面的图,应该是1425768
class Solution {
public:vector<int> result;void inorder(TreeNode* node){if(node==nullptr)return;preorder(node->left);result.push_back(node->val);preorder(node->right);}vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {result.clear();inorder(root);return result;}
};
迭代法
class Solution {
public:vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> result;stack<TreeNode*>stk;if(root==nullptr)return result;TreeNode* cur=root;while(!stk.empty()||cur!=nullptr){if(cur){stk.push(cur);cur=cur->left;}else{cur=stk.top();stk.pop();result.push_back(cur->val);cur=cur->right;}}return result;}
};
后序遍历
后序遍历:左右中,参考上面的图:1247865
递归法
class Solution {
public:vector<int> result;void postorder(TreeNode* node){if(node==nullptr)return;preorder(node->left);preorder(node->right);result.push_back(node->val);}vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {result.clear();postorder(root);return result;}
};
迭代法
对比前序遍历顺序:中左右,后序遍历顺序为:左右中,如果我们将顺序变为:中右左,然后对于结果反转一下,是不是就是正确的呢?
class Solution {
public:vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> result;stack<TreeNode*> stk;if(root==nullptr)return result;stk.push(root);while(!stk.empty()){TreeNode* node=stk.top();stk.pop();result.push_back(node->val);if(node->left)stk.push(node->left);if(node->right)stk.push(node->right);}reverse(result.begin(),result.end());return result;}
};
层序遍历
其实上文的前中后序遍历,在图论中就是DFS(深度优先搜索),而对应还有一种方法,那就是宽度优先搜索(BFS),其实对于BFS而言,用处还是蛮大的,很多需要遍历整个树的问题,用BFS做起来蛮方便的!当然要想实现BFS,也要借用一种数据结构,其用于存储每一层的元素!这种数据结构就是queue
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>>result;queue<TreeNode*> que;if(root==nullptr)return result;que.push(root);while(!que.empty()){int size=que.size();vector<int>vec;//在遍历上一层的同时,也将下一层的节点加入queue,这个过程while(size--){TreeNode* node=que.front();que.pop();vec.push_back(node->val);if(node->left)que.push(node->left);if(node->right)que.push(node->right);}result.push_back(vec);}return result;}
};
二叉树遍历(带有回溯的)
236.二叉树的最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if(root==nullptr||root==p||root==q)return root;TreeNode* left=lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);TreeNode* right=lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);if(left&&right)return root;else if(left==nullptr&&right)return right;else if(left&&right==nullptr)return left;else return nullptr;}
};
做完这道题,明白了公共祖先的问题,都是自顶向上的遍历(采用后序遍历)以及搜索整个树采用:
TreeNode* left=lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);TreeNode* right=lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
同样的一道题:255.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先,但是这道题还有一个特点,每次要遍历左子树还是右子树的时候可以先进行判断,相当于进行剪枝操作了!
分解问题
将一个二叉树分解为左子树和右子树的问题!
构造二叉树
关键点:在于不断确定中间节点,左子树以及右子树!
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& preorder,vector<int>& inorder){if(preorder.size()==0)return nullptr;int rootvalue=preorder[0];TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(rootvalue);int index=0;for(;index<inorder.size();index++){if(inorder[index]==rootvalue)break;}vector<int> leftinorder(inorder.begin(),inorder.begin()+index);vector<int> rightinorder(inorder.begin()+index+1,inorder.end());vector<int> leftpreorder(preorder.begin()+1,preorder.begin()+1+leftinorder.size());vector<int> rightpreorder(preorder.begin()+1+leftinorder.size(),preorder.end());root->left=traversal(leftpreorder,leftinorder);root->right=traversal(rightpreorder,rightinorder);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {if(preorder.size()==0||inorder.size()==0) return nullptr;return traversal(preorder,inorder);}
};
做过这道题,可以试试看
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
二叉搜索树
1.有序的问题!(联系中序遍历),求二叉搜索树中第k个最小值!一般做法:采用中序遍历,将二叉树变为有序数组,一定要采用中序遍历!
230.二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
class Solution {
public:vector<int> result;void inorder(TreeNode* root){if(root==nullptr)return;inorder(root->left);result.push_back(root->val);inorder(root->right);}int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {inorder(root);return result[k-1];}
};
98.验证二叉搜索树
这两道题都是将二叉搜索树的问题转换成数组问题来解决的!故对于二叉搜索树的很多问题一定要学会联系中序遍历!