添加链接描述
背景
假设数据存放在在unsigned char* m_pData 里面,宽和高分别是:m_nDataWidth m_nDataHeight
给定缩放比例:fXZoom fYZoom,返回缩放后的unsigned char* dataZoom
这里采用最简单的缩放算法即:
根据比例计算原图和缩放后图坐标的对应关系:缩放后图坐标*缩放比例 = 原图坐标
原始代码 未优化
#pragma once
class zoomBlock
{
public:zoomBlock() {};~zoomBlock();void zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom);void zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom);void test(float fXZoom =0.5, float fYZoom=0.5);void init(int DataWidth, int DataHeight);
private:void computeSrcValues(int* srcValues, size_t size, float zoom, int dataSize);private:unsigned char* m_pData = nullptr;float m_fXZoom = 1 ;//x轴缩放比例 m_nXZoom=1时 不缩放float m_fYZoom = 1 ;//y轴缩放比例int m_nDataWidth = 0;int m_nDataHeight = 0;
};#include "zoomBlock.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#define SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(p) { if( (p) != NULL ) delete[] (p); (p) = NULL; }zoomBlock::~zoomBlock()
{SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(m_pData);
}
void zoomBlock::init(int DataWidth, int DataHeight)
{m_nDataWidth = DataWidth;m_nDataHeight = DataHeight;m_pData = new unsigned char[m_nDataWidth* m_nDataHeight];for (int i = 0; i < m_nDataWidth * m_nDataHeight; ++i){m_pData[i] = static_cast<unsigned char>(i); // Replace this with your data initialization logic}
}void zoomBlock::zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;for (size_t row = 0; row < nZoomDataHeight; row++){for (size_t column = 0; column < nZoomDataWidth; column ++){//1int srcx = std::min(int(row / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcy = std::min(int(column / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);//2int srcPos = srcx * m_nDataHeight + srcy;int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}
}void zoomBlock::test(float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
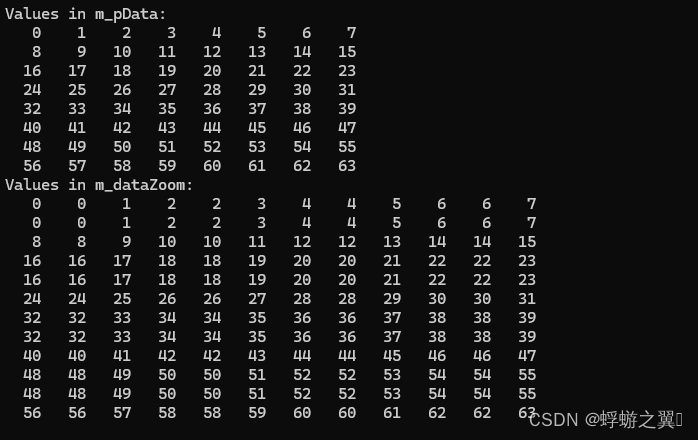
{init(8,8);std::cout << "Values in m_pData:" << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < m_nDataWidth * m_nDataHeight; ++i){std::cout << std::setw(4) << static_cast<int>(m_pData[i]) << " ";if ((i + 1) % m_nDataWidth == 0) { // Adjust the value based on your datastd::cout << std::endl;}}unsigned char* dataZoom = new unsigned char[fXZoom * m_nDataWidth * fYZoom * m_nDataHeight];zoomData(dataZoom, fXZoom, fYZoom);// Print or inspect the values in m_dataZoomint nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;std::cout << "Values in m_dataZoom:" << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < nZoomDataHeight * nZoomDataWidth; ++i){std::cout << std::setw(4)<< static_cast<int>(dataZoom[i]) << " ";if ((i + 1) % nZoomDataWidth == 0) { // Adjust the value based on your datastd::cout << std::endl;}}SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(dataZoom);}
测试代码
int main()
{zoomBlock zoomBlocktest;zoomBlocktest.test(1.5,1.5);return 0;
}
其中函数
·void zoomBlock::zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)·
没有使用任何加速优化,现在来分析它。
sse128
我们知道sse128可以一次性处理4个int类型,所以我们把最后一层for循环改成,4个坐标的算法,不满4个的单独计算
void zoomBlock::zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;for (size_t row = 0; row < nZoomDataHeight; row++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 4;for (size_t column = 0; column < nZoomDataWidth - remian; column += 4){//第一个坐标int srcx = std::min(int(row / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcy = std::min(int(column / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcx * m_nDataHeight + srcy;int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];//第二个坐标int srcx1 = std::min(int((row+1) / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcy1 = std::min(int((column+1) / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos1 = srcx1 * m_nDataHeight + srcy1;int desPos1 = (row+1) * nZoomDataHeight + column+1;dataZoom[desPos1] = m_pData[srcPos1];//第3个坐标// 。。。//第4个坐标// 。。。}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t column = nZoomDataWidth - remian; column < nZoomDataWidth; column++){int srcx = std::min(int(row / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcy = std::min(int(column / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcx * m_nDataHeight + srcy;int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}
}
上面 一次处理四个坐标的代码要改成sse的代码
在最里层的循环里面,每次都要计算 row / fYZoom 和 column / fXZoom,这个实际上可以挪出for循环,计算一次存到数组里
数据坐标desPos和srcPos ,必须放在最内存的循环里
所以我们用calculateSrcIndex函数单独处理 row / fYZoom 和 column / fXZoom,希望达到如下效果:
void calculateSrcIndex(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom,int max)
{for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){srcValues[i] = std::min(int(i/zoom),max);}
}
改成sse:
void calculateSrcIndex(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom,int max)
{__m128i mmIndex, mmSrcValue, mmMax;mmMax = _mm_set1_epi32(max);float zoomReciprocal = 1.0f / zoom;int remian = size % 4;for (size_t i = 0; i < size - remian; i += 4){mmIndex = _mm_set_epi32(i + 3, i + 2, i + 1, i);mmSrcValue = _mm_cvtps_epi32(_mm_mul_ps(_mm_cvtepi32_ps(mmIndex), _mm_set1_ps(zoomReciprocal)));// Ensure srcValues are within the valid range [0, max]mmSrcValue = _mm_min_epi32(mmSrcValue, mmMax);// Store the result to the srcValues array_mm_storeu_si128(reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(&srcValues[i]), mmSrcValue);}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t i = size - remian; i < size; i++){srcValues[i] = std::min(int(i / zoom), max);}
}
解释:
这里主要处理int型数据,为了使用sse加速,要使用__m128i类型来存储4个int
加载int到__m128i:
-
__m128i _mm_set1_epi32(int i);
这个指令是使用1个i,来设置__m128i,将__m128i看做4个32位的部分,则每个部分都被赋为i; -
__m128i _mm_set_epi32(int i3, int i2,int i1, int i0);
说明:使用4个int(32bits)变量来设置__m128i变量;
返回值:如果返回值__m128i,分为r0,r1,r2,r3返回值规则如下:
r0 := i0
r1 := i1
r2 := i2
r3 := i3
- __m128i _mm_cvtps_epi32 (__m128 a)
Converts packed 32-bit integers in a to packed single-precision (32-bit) floating-point elements.
加载float到__m128
- __m128 _mm_set1_ps(float w)
对应于_mm_load1_ps的功能,不需要字节对齐,需要多条指令。(r0 = r1 = r2 = r3 = w) - __m128 _mm_cvtepi32_ps (__m128i a)
Converts packed 32-bit integers in a to packed single-precision (32-bit) floating-point elements.
float乘法
__m128 dst = _mm_mul_ps (__m128 a, __m128 b)
将a, b中的32位浮点数相乘,结果打包给dst
取最小值
__m128i _mm_min_epi32 (__m128i a, __m128i b)
Compare packed signed 32-bit integers in a and b, and store packed minimum values in dst.
Operation
FOR j := 0 to 3
i := j*32
dst[i+31:i] := MIN(a[i+31:i], b[i+31:i])
ENDFOR
所以代码修改为
int* srcX = new int[nZoomDataHeight];int* srcY = new int[nZoomDataWidth];calculateSrcIndex(srcX, nZoomDataHeight, fXZoom , m_nDataHeight - 1);calculateSrcIndex(srcY, nZoomDataWidth, fYZoom, m_nDataWidth - 1);for (size_t row = 0; row < nZoomDataHeight; row++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 4;for (size_t column = 0; column < nZoomDataWidth - remian; column += 4){//第一个坐标int srcPos = srcX[row] * m_nDataHeight + srcY[column];int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];...}}
然后把坐标的计算转为sse
void zoomBlock::zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;int* srcX = new int[nZoomDataWidth];int* srcY = new int[nZoomDataHeight];calculateSrcIndex(srcX, nZoomDataWidth, fXZoom, m_nDataWidth - 1);calculateSrcIndex(srcY, nZoomDataHeight, fYZoom, m_nDataHeight - 1);for (size_t y = 0; y < nZoomDataHeight; y++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 4;for (size_t x = 0; x < nZoomDataWidth - remian; x += 4){__m128i mmsrcX = _mm_set_epi32(srcX[x + 3], srcX[x + 2], srcX[x+1], srcX[x]);__m128i srcPosIndices = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_set1_epi32(srcY[y] * m_nDataWidth),mmsrcX);__m128i desPosIndices = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_set1_epi32(y * nZoomDataWidth),_mm_set_epi32(x + 3, x + 2, x + 1, x));dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[0]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[0]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[1]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[1]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[2]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[2]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[3]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[3]];/*cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[0] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[0] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[1] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[1] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[2] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[2] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[3] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[3] << endl;*/}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t x = nZoomDataWidth - remian; x < nZoomDataWidth; x++){int srcy = std::min(int(y / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcx = std::min(int(x / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcy * m_nDataHeight + srcx;int desPos = y * nZoomDataHeight + x;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}delete[] srcX;delete[] srcY;
}
完整的代码
#pragma once
class zoomBlock
{
public:zoomBlock() {};~zoomBlock();void zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom);void zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom);void test(float fXZoom =0.5, float fYZoom=0.5);void init(int DataWidth, int DataHeight);
private:inline void calculateSrcIndex(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom, int max);private:unsigned char* m_pData = nullptr;float m_fXZoom = 1 ;//x轴缩放比例 m_nXZoom=1时 不缩放float m_fYZoom = 1 ;//y轴缩放比例int m_nDataWidth = 0;int m_nDataHeight = 0;
};#include "zoomBlock.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<immintrin.h>
using namespace std;
#define SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(p) { if( (p) != NULL ) delete[] (p); (p) = NULL; }zoomBlock::~zoomBlock()
{SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(m_pData);
}
void zoomBlock::init(int DataWidth, int DataHeight)
{m_nDataWidth = DataWidth;m_nDataHeight = DataHeight;m_pData = new unsigned char[m_nDataWidth* m_nDataHeight];for (int i = 0; i < m_nDataWidth * m_nDataHeight; ++i){m_pData[i] = static_cast<unsigned char>(i); // Replace this with your data initialization logic}
}void zoomBlock::zoomData(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;for (size_t y = 0; y < nZoomDataHeight; y++){for (size_t x = 0; x < nZoomDataWidth; x ++){//1int srcy = std::min(int(y / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcx = std::min(int(x / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);//2int srcPos = srcy * m_nDataWidth + srcx;int desPos = y * nZoomDataWidth + x;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}
}inline void zoomBlock::calculateSrcIndex(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom,int max)
{__m128i mmIndex, mmSrcValue, mmMax;mmMax = _mm_set1_epi32(max);float zoomReciprocal = 1.0f / zoom;int remian = size % 4;for (size_t i = 0; i < size - remian; i += 4){mmIndex = _mm_set_epi32(i + 3, i + 2, i + 1, i);mmSrcValue = _mm_cvttps_epi32(_mm_mul_ps(_mm_cvtepi32_ps(mmIndex), _mm_set1_ps(zoomReciprocal)));// Ensure srcValues are within the valid range [0, max]mmSrcValue = _mm_min_epi32(mmSrcValue, mmMax);// Store the result to the srcValues array_mm_storeu_si128(reinterpret_cast<__m128i*>(&srcValues[i]), mmSrcValue);}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t i = size - remian; i < size; i++){srcValues[i] = std::min(int(i / zoom), max);}
}void zoomBlock::zoomDataSSE128(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;int* srcX = new int[nZoomDataWidth];int* srcY = new int[nZoomDataHeight];calculateSrcIndex(srcX, nZoomDataWidth, fXZoom, m_nDataWidth - 1);calculateSrcIndex(srcY, nZoomDataHeight, fYZoom, m_nDataHeight - 1);for (size_t y = 0; y < nZoomDataHeight; y++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 4;for (size_t x = 0; x < nZoomDataWidth - remian; x += 4){/*int srcPos = srcx * m_nDataHeight + srcy;int desPos = row * nZoomDataHeight + column;*///dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];//__m128i mmsrcY = _mm_loadu_si128((__m128i*)(srcY));__m128i mmsrcX = _mm_set_epi32(srcX[x + 3], srcX[x + 2], srcX[x+1], srcX[x]);__m128i srcPosIndices = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_set1_epi32(srcY[y] * m_nDataWidth),mmsrcX);__m128i desPosIndices = _mm_add_epi32(_mm_set1_epi32(y * nZoomDataWidth),_mm_set_epi32(x + 3, x + 2, x + 1, x));dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[0]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[0]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[1]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[1]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[2]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[2]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m128i_i32[3]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[3]];/*cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[0] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[0] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[1] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[1] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[2] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[2] << endl;cout << "srcPosIndices: " << srcPosIndices.m128i_i32[3] << " , desPosIndices : " << desPosIndices.m128i_i32[3] << endl;*/}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSEfor (size_t x = nZoomDataWidth - remian; x < nZoomDataWidth; x++){int srcy = std::min(int(y / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcx = std::min(int(x / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcy * m_nDataHeight + srcx;int desPos = y * nZoomDataHeight + x;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}delete[] srcX;delete[] srcY;
}void zoomBlock::test(float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{init(8,4);std::cout << "Values in m_pData:" << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < m_nDataWidth * m_nDataHeight; ++i){std::cout << std::setw(4) << static_cast<int>(m_pData[i]) << " ";if ((i + 1) % m_nDataWidth == 0) { // Adjust the value based on your datastd::cout << std::endl;}}int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;unsigned char* dataZoom = new unsigned char[nZoomDataWidth * nZoomDataHeight];zoomDataSSE128(dataZoom, fXZoom, fYZoom);//zoomData(dataZoom, fXZoom, fYZoom);// Print or inspect the values in m_dataZoomstd::cout << "Values in m_dataZoom:" << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < nZoomDataHeight * nZoomDataWidth; ++i){std::cout << std::setw(4)<< static_cast<int>(dataZoom[i]) << " ";if ((i + 1) % nZoomDataWidth == 0) { // Adjust the value based on your datastd::cout << std::endl;}}SAFE_DELETE_ARRAY(dataZoom);}int main()
{zoomBlock zoomBlocktest;zoomBlocktest.test(2,1);return 0;
}

AVX 256
inline void zoomBlock::calculateSrcIndex256(int* srcValues, int size, float zoom, int max)
{__m256i ymmIndex, ymmSrcValue, ymmMax;ymmMax = _mm256_set1_epi32(max);float zoomReciprocal = 1.0f / zoom;int remian = size % 8;for (size_t i = 0; i < size - remian; i += 8){ymmIndex = _mm256_set_epi32(i + 7, i + 6, i + 5, i + 4, i + 3, i + 2, i + 1, i);ymmSrcValue = _mm256_cvtps_epi32(_mm256_mul_ps(_mm256_cvtepi32_ps(ymmIndex), _mm256_set1_ps(zoomReciprocal)));// Ensure srcValues are within the valid range [0, max]ymmSrcValue = _mm256_min_epi32(ymmSrcValue, ymmMax);// Store the result to the srcValues array_mm256_storeu_si256(reinterpret_cast<__m256i*>(&srcValues[i]), ymmSrcValue);}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without AVX2for (size_t i = size - remian; i < size; i++){srcValues[i] = std::min(int(i / zoom), max);}
}
void zoomBlock::zoomDataAVX2(unsigned char* dataZoom, float fXZoom, float fYZoom)
{int nZoomDataWidth = fXZoom * m_nDataWidth;int nZoomDataHeight = fYZoom * m_nDataHeight;int* srcX = new int[nZoomDataWidth];int* srcY = new int[nZoomDataHeight];calculateSrcIndex(srcX, nZoomDataWidth, fXZoom, m_nDataWidth - 1);calculateSrcIndex(srcY, nZoomDataHeight, fYZoom, m_nDataHeight - 1);for (size_t y = 0; y < nZoomDataHeight; y++){int remian = nZoomDataWidth % 8;for (size_t x = 0; x < nZoomDataWidth - remian; x += 8){__m256i ymmSrcX = _mm256_set_epi32(srcX[x + 7], srcX[x + 6], srcX[x + 5], srcX[x + 4],srcX[x + 3], srcX[x + 2], srcX[x + 1], srcX[x]);__m256i srcPosIndices = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_set1_epi32(srcY[y] * m_nDataWidth),ymmSrcX);__m256i desPosIndices = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_set1_epi32(y * nZoomDataWidth),_mm256_set_epi32(x + 7, x + 6, x + 5, x + 4, x + 3, x + 2, x + 1, x));dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[0]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[0]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[1]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[1]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[2]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[2]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[3]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[3]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[4]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[4]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[5]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[5]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[6]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[6]];dataZoom[desPosIndices.m256i_i32[7]] = m_pData[srcPosIndices.m256i_i32[7]];}// Process the remaining elements (if any) without AVX2for (size_t x = nZoomDataWidth - remian; x < nZoomDataWidth; x++){int srcy = std::min(int(y / fYZoom), m_nDataHeight - 1);int srcx = std::min(int(x / fXZoom), m_nDataWidth - 1);int srcPos = srcy * m_nDataWidth + srcx;int desPos = y * nZoomDataWidth + x;dataZoom[desPos] = m_pData[srcPos];}}delete[] srcX;delete[] srcY;
}