接上篇 Bootstrap源码-客户端
1 Handler的添加过程
Netty有一个强大和灵活之处就是基于Pipeline的自定义Handler机制。基于此,可以像添加插件一样自由组合各种各样的Handler来完成业务逻辑。例如,需要处理HTTP数据,那么就可以在Pipeline前添加一个针对HTTP编解码的Handler,然后添加自己的业务逻辑的Handler,这样网络上的数据流就像通过一个管道一样,从不同的Handler中流过并进行编解码,最终到达自定义的Handler中。
先看一下Handler是如何及何时添加到ChannelPipeline中的。看一段用户代码片段:
bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true).handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder());pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder());pipeline.addLast(new ChatClientHandler());System.out.println("初始化channel:" + socketChannel);}});这段代码就实现了Handler的添加功能,Bootstrap的handler方法接收一个ChannelHandler,而我们传入的参数是一个派生于抽象类ChannelInitializer的匿名类,它也实现了ChannelHandler接口,来看一下ChannelInitializer类,代码如下:
public abstract class ChannelInitializer<C extends Channel> extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {private static final InternalLogger logger = InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(ChannelInitializer.class);private final ConcurrentMap<ChannelHandlerContext, Boolean> initMap = PlatformDependent.newConcurrentHashMap();public ChannelInitializer() {}protected abstract void initChannel(C var1) throws Exception;public final void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {if (this.initChannel(ctx)) {ctx.pipeline().fireChannelRegistered();} else {ctx.fireChannelRegistered();}}public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {logger.warn("Failed to initialize a channel. Closing: " + ctx.channel(), cause);ctx.close();}public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {if (ctx.channel().isRegistered()) {this.initChannel(ctx);}}private boolean initChannel(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {if (this.initMap.putIfAbsent(ctx, Boolean.TRUE) == null) {try {this.initChannel(ctx.channel());} catch (Throwable var6) {this.exceptionCaught(ctx, var6);} finally {this.remove(ctx);}return true;} else {return false;}}private void remove(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {try {ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.pipeline();if (pipeline.context(this) != null) {pipeline.remove(this);}} finally {this.initMap.remove(ctx);}}
}ChannelInitializer是一个抽象类,它有一个抽象方法initChannel(),我们的匿名类正是实现了这个方法,并在这个方法中添加了自定义的Handler。这个initChannel方法是在ChannelInitializer的channelRegistered()方法中被调用的。
接下来关注一下channelRegistered方法。从上面的代码中可以看到,在channelRegistered方法中,会调用initChannel方法,将自定义的Handler添加到ChannelPipeline中,然后调用ctx.pipeline().remove(this)方法将自己从ChannelPipeline中删除。
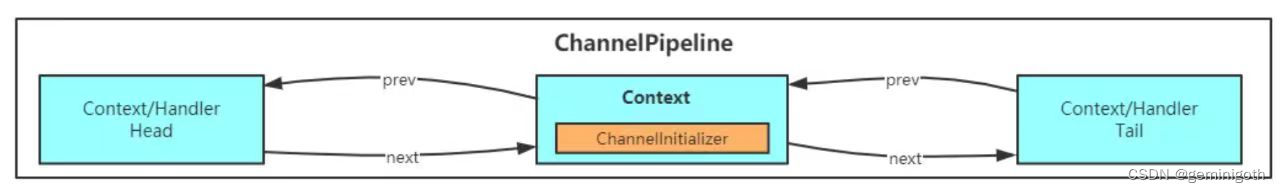
一开始,ChannelPipeline中只有三个Handler,分别是Head、Tail和我们添加的ChannelInitializer,如下图所示:
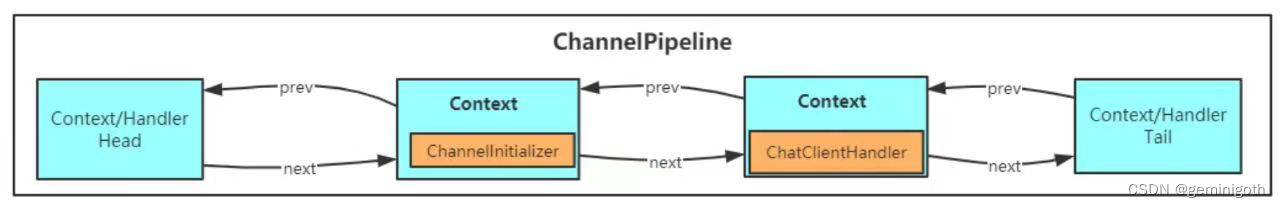
接着调用 initChannel方法,添加自定义的Handler,如下图:
最后将 ChannelInitializer删除,如下图:
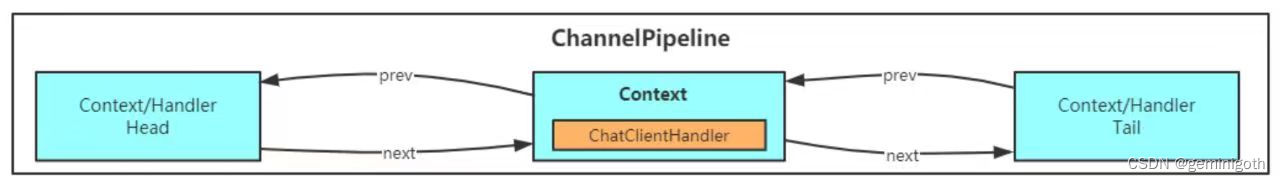
分析到这里,我们已经简单了解了自定义的Handler是如何添加到ChannelPipeline中的,后面在进行深入探讨。
2 客户端发起连接请求
经过前面的分析,我们已经大致了解了Netty客户端初始化时所做的工作,接下来分析一下客户端是如何发起TCP连接的。
客户端通过调用Bootstrap的connect方法进行连接。在connect方法中进行一些参数检查,并调用doConnect方法,代码如下:
private static void doConnect(final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise connectPromise) {final Channel channel = connectPromise.channel();channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {public void run() {if (localAddress == null) {channel.connect(remoteAddress, connectPromise);} else {channel.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, connectPromise);}connectPromise.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);}});}在doConnect方法中,eventLoop线程会调用Channel的connect方法,而这个Channel的具体类型实际就是NioSocketChannel,前面已经分析过。继续跟踪channel.connect()方法,发现它调用的是DefaultChannelPipeline的connect方法,Pipeline的connect方法代码如下:
public final ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {return this.tail.connect(remoteAddress, promise);}前面分析过,Tail是一个TailContext的实例,而TailContext又是AbstractChannelHandlerContext的子类,并且没有实现connect方法,因此这里调用的其实是AbstractChannelHandlerContext的connect方法,看一下这个方法的代码:
public ChannelFuture connect(final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {if (remoteAddress == null) {throw new NullPointerException("remoteAddress");} else if (!this.validatePromise(promise, false)) {return promise;} else {final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = this.findContextOutbound();EventExecutor executor = next.executor();if (executor.inEventLoop()) {next.invokeConnect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);} else {safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {public void run() {next.invokeConnect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);}}, promise, (Object)null);}return promise;}}上面有一行非常关键的代码,
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = this.findContextOutbound();这里调用findContextOutbound方法,从DefaultChannelPipeline内的双向链表的Tail开始,不断向前找到第一个Outbound为true的AbstractChannelHandlerContext,然后调用它的invokeConnect方法,代码如下:
private void invokeConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {if (this.invokeHandler()) {try {((ChannelOutboundHandler)this.handler()).connect(this, remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);} catch (Throwable var5) {notifyOutboundHandlerException(var5, promise);}} else {this.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);}}前面提到,在DefaultChannelPipeline的构造器中,实例化两个对象:Head和Tail,并形成了双向链表的头和尾。Head是HeadContext的实例,它实现了ChannelOunboundHandler接口,并挨它的Ounbound设置为true。因此在findContextOutbound方法中,找到的AbstractChannelHandlerContext对象其实就是Head,进而在invokeConnect方法中,向上转换为ChannelOuntboundHandler就问题了。而又因为HeadContext重写了connect方法,所以实际上调用的是HeadContext的connect方法。接着跟踪HeadContext的connect方法。
public void connect(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {this.unsafe.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);}这个方法connect很简单,只是调用了Unsafe的connect方法。回顾一下HeadContext的构造器,就会发现这个Unsafe方法其实就是pipeline.channel().unsafe返回的Channel的Unsafe属性。到这里为止,已经知道,其实是AbstractNioByteChannel.NioByteUnsafe内部类转了一大圈。最后,找到创建Socket连接的关键代码继续跟踪,其实调用的就是AbstractNioUnsafe的connect方法。
public final void connect(final SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {if (promise.setUncancellable() && this.ensureOpen(promise)) {try {if (AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise != null) {throw new ConnectionPendingException();}boolean wasActive = AbstractNioChannel.this.isActive();if (AbstractNioChannel.this.doConnect(remoteAddress, localAddress)) {this.fulfillConnectPromise(promise, wasActive);} else {AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise = promise;AbstractNioChannel.this.requestedRemoteAddress = remoteAddress;int connectTimeoutMillis = AbstractNioChannel.this.config().getConnectTimeoutMillis();if (connectTimeoutMillis > 0) {AbstractNioChannel.this.connectTimeoutFuture = AbstractNioChannel.this.eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {public void run() {ChannelPromise connectPromise = AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise;ConnectTimeoutException cause = new ConnectTimeoutException("connection timed out: " + remoteAddress);if (connectPromise != null && connectPromise.tryFailure(cause)) {AbstractNioUnsafe.this.close(AbstractNioUnsafe.this.voidPromise());}}}, (long)connectTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}promise.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {if (future.isCancelled()) {if (AbstractNioChannel.this.connectTimeoutFuture != null) {AbstractNioChannel.this.connectTimeoutFuture.cancel(false);}AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise = null;AbstractNioUnsafe.this.close(AbstractNioUnsafe.this.voidPromise());}}});}} catch (Throwable var6) {promise.tryFailure(this.annotateConnectException(var6, remoteAddress));this.closeIfClosed();}}}在这个connect方法中,又调用了doConnect方法,注意,这个方法并不是AbstractNioUnsafe的方法,而是AbstractNioChannel的抽象方法。doConnect方法是在NioSocketChannel中实现的,因此,进入NioSocketChannel的doConnect方法,代码如下:
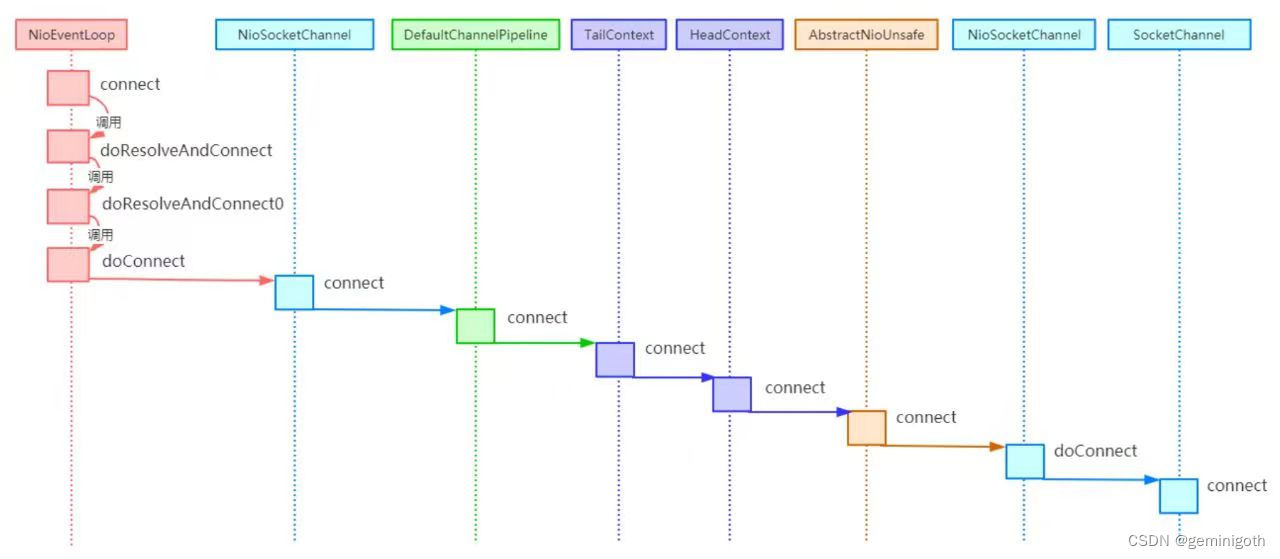
protected boolean doConnect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {if (localAddress != null) {this.doBind0(localAddress);}boolean success = false;boolean var5;try {boolean connected = this.javaChannel().connect(remoteAddress);if (!connected) {this.selectionKey().interestOps(8);}success = true;var5 = connected;} finally {if (!success) {this.doClose();}}return var5;}上面代码的功能是,首先获取Java NIO的SocketChannel,然后获取NioSocketChannel 的newSocket方法返回的SocketChannel对象;在调用SocketChannel的connect方法完成Java NIO底层的Socket连接。总结一下,客户端Bootstrap发起连接请求的流程可以用如下时序图直观展示:




![[C语言]指针详解一、数组指针、二维数组传参、函数指针](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9e750ae0636e49f8882e4e52c3416845.png)