Title
题目
SAM-Med3D
01
文献速递介绍
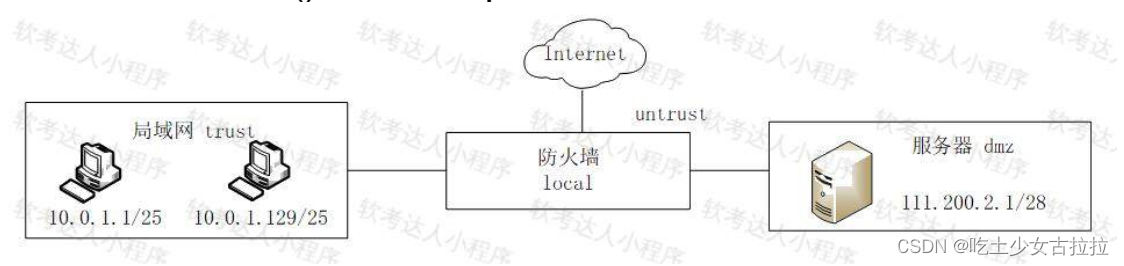
医学图像分析已成为现代医疗保健不可或缺的基石,辅助诊断、治疗计划和进一步的医学研究]。在这一领域中最重要的挑战之一是精确分割体积医学图像。尽管众多方法在一系列目标上展现了值得称赞的有效性,但现有的分割技术倾向于专门针对特定器官或病变。这种倾向是由体积医学图像的固有特性所决定的,比如3D解剖结构的复杂性和体积医学注释的有限性。因此,这种专业化阻碍了方法的泛化能力,给更广泛的临床应用带来了实际挑战。
最近,“分割任何模型”(SAM),一个用超过10亿掩码训练的视觉基础模型(VFM),在众多领域展现了令人印象深刻的零样本分割性能。SAM的兴起为加速数据注释和提高体积医学图像分析的方法论泛化能力引入了新的可能性。然而,研究指出,由于对医学图像知识的显著缺乏,SAM对医学领域的原生适用性是有限的。一个直接的解决方案是通过医学图像进行微调以将医学知识注入SAM。MedSAM通过使用110万掩码对解码器进行微调实现了这一点,使SAM能够在医学成像中得到应用。SAM-Med2D通过使用适配器和约2000万掩码进行全面适配,展示了在一般医学图像分割中的显著能力。然而,这些方法必须采用逐片处理体积图像的方法:将3D数据分解成2D切片,独立处理每个切片,然后将2D结果聚合成3D预测。如之前的评估所示,由于忽略了切片间的3D空间信息,逐片处理方式在3D医学图像上的性能并不理想。
Abstract-Background
摘要
Although the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated impressive per formance in 2D natural image segmentation, its application to 3D volumetric medical images reveals significant shortcomings, namely suboptimal performance and unstable prediction, necessitating an excessive number of prompt points to attain the desired outcomes. These issues can hardly be addressed by fine-tuning
SAM on medical data because the original 2D structure of SAM neglects 3D spatial information. In this paper, we introduce SAM-Med3D, the most comprehensive study to modify SAM for 3D medical images. Our approach is characterized by its comprehensiveness in two primary aspects: firstly, by comprehensively reformulat ing SAM to a thorough 3D architecture trained on a comprehensively processed large-scale volumetric medical dataset; and secondly, by providing a comprehen sive evaluation of its performance. Specifically, we train SAM-Med3D with over 131K 3D masks and 247 categories. Our SAM-Med3D excels at capturing 3D spatial information, exhibiting competitive performance with significantly fewer prompt points than the top-performing fine-tuned SAM in the medical domain. We then evaluate its capabilities across 15 datasets and analyze it from multiple per spectives, including anatomical structures, modalities, targets, and generalization abilities. Our approach, compared with SAM, showcases pronouncedly enhanced efficiency and broad segmentation capabilities for 3D volumetric medical images. Our code is released at https://github.com/uni-medical/SAM-Med3D.
尽管“分割任何模型”(SAM)在2D自然图像分割方面展示了令人印象深刻的性能,但其应用于3D体积医学图像时却显示出明显的不足,主要表现为次优的性能和不稳定的预测,需要过多的提示点才能达到期望的结果。仅仅通过在医学数据上微调SAM难以解决这些问题,因为SAM的原始2D结构忽略了3D空间信息。在本文中,我们介绍了SAM-Med3D,这是修改SAM以适应3D医学图像的最全面的研究。我们的方法在两个主要方面表现出全面性:首先,全面重新构思SAM到一个彻底的3D架构,并在一个全面处理的大规模体积医学数据集上进行训练;其次,提供了其性能的全面评估。具体来说,我们用超过131K的3D掩码和247个类别训练SAM-Med3D。我们的SAM-Med3D擅长捕捉3D空间信息,在医学领域的顶尖微调SAM中,以显著更少的提示点展示了具有竞争力的性能。然后,我们在15个数据集上评估其能力,并从多个角度进行分析,包括解剖结构、模态、目标和泛化能力。与SAM相比,我们的方法明显提高了效率,并为3D体积医学图像展示了广泛的分割能力。我们的代码已在https://github.com/uni-medical/SAM-Med3D发布。
Conclusions
结论
In this study, we present SAM-Med3D, a holistic 3D SAM model for volumetric medical image segmentation, trained from scratch on a large-scale 3D medical image dataset. Our SAM-Med3D employs 3D positional encodings in different components to directly integrate 3D spatial information, and exhibit excellent performance on volumetric medical image segmentation. SAM-Med3D achieves a 32.90% improvement than SAM when provided with 1 point per volume, indicating its excellent usability to generate better outcomes in volumetric medical segmentation tasks with significantly fewer prompt points. Furthermore, we conduct an extensive evaluation from diverse perspectives to explore the capacities of SAM-Med3D. For various anatomical structures like bone, heart and muscle, our SAM-Med3D outperforms other methods with a clear margin when limited prompt is provided. Our SAM-Med3D consistently excels in different modalities and various organs and lesions. Additionally, we test the transferability of SAM-Med3D. Validated on two frequently used benchmarks, SAM-Med3D has the potential to work as a powerful pre-trained model for 3D medical image transformer. Setting aside the numerical result gap between 2D SAM methods and our SAM-Med3D, a well trained 3D SAM model should inherently exhibit superior inter-slice consistency and usability, as observed in the visual results. While 3D models enhance usability, prompts within volumetric images 13Axial Coronal Axial SagittalCT: Gluteus Maximus MRI: Kidney Axial Coronal MRI (FLAIR): Edematend to be sparser compared to the densely annotated 2D slices used in slice-by-slice inference. This sparsity places significant demands on the 3D model’s ability to capture spatial information and effectively utilize sparse prompts, thereby increasing the training complexity. In our approach, we address this issue by employing a fully learnable 3D structure to better model the spatial information in 3D space. Despite this, there remains a plethora of avenues for future exploration, such as the development of novel 3D prompt forms and training strategies that are more suited to 3D contexts.
在本研究中,我们提出了SAM-Med3D,一个全面的3D SAM模型,用于体积医学图像分割,从头开始在一个大规模的3D医学图像数据集上进行训练。我们的SAM-Med3D在不同组件中采用了3D位置编码,直接整合了3D空间信息,并在体积医学图像分割上展现出了卓越的性能。与每个体积提供1个点的情况下的SAM相比,SAM-Med3D实现了32.90%的改进,表明其在需要显著更少的提示点的体积医学分割任务中具有出色的可用性。
此外,我们从多个角度进行了广泛的评估,以探索SAM-Med3D的能力。对于像骨骼、心脏和肌肉这样的各种解剖结构,当提供有限的提示时,我们的SAM-Med3D以明显的优势超越了其他方法。我们的SAM-Med3D在不同的模态、各种器官和病变中始终表现出色。此外,我们测试了SAM-Med3D的可转移性。在两个常用的基准测试上验证,SAM-Med3D有潜力作为3D医学图像变换器的强大预训练模型。
撇开2D SAM方法和我们的SAM-Med3D之间的数值结果差异不谈,一个训练有素的3D SAM模型应该天生就表现出更优的切片间一致性和可用性,正如在视觉结果中观察到的那样。虽然3D模型提高了可用性,但在体积图像中的提示与逐片推理中使用的密集标注的2D切片相比,倾向于更稀疏。这种稀疏性对3D模型捕捉空间信息的能力和有效利用稀疏提示提出了重大要求,从而增加了训练的复杂性。在我们的方法中,我们通过采用完全可学习的3D结构来更好地建模3D空间中的空间信息来解决这个问题。尽管如此,仍然存在大量的未来探索途径,如开发更适合3D情境的新型3D提示形式和训练策略。
Method
方法
4.1 Revisit SAM
The Segment Anything Model (SAM) presents a robust architectural design for promptable image segmentation tasks, primarily tailored for 2D natural images. SAM’s architecture can be divided into
three core components: Image encoder SAM leverages an MAE pre-trained Vision Transformer (ViT) to extract representations. This component utilizes 2D patch embeddings combined with learnable position encodings to turn the input image into image embeddings. Prompt encoder This module can handle both sparse (points, boxes) and dense (masks) prompts. Sparse prompts are represented using frozen 2D absolute positional encodings and then combined with learned embeddings specific to each prompt type. Dense prompts are encoded with a 2D convolution neck to generate dense prompt embeddings. Mask decoder A lightweight structure is adopted to efficiently map the image embedding with aset of prompt embeddings to an output mask. Four steps are contained in each transformer layer:
(1) self-attention on tokens; (2) cross-attention between tokens and the image embedding; (3) token updates using a point-wise MLP; (4) cross-attention that updates the image embedding with prompt details. After processing through the transformer layers, the feature map undergoes up-sampling and is subsequently converted into segmentation masks using an MLP. Notably, all the transformer layers
capture only 2D geometric information during the forward pass.
“分割任何模型”(SAM)提供了一个强大的架构设计,用于可提示的图像分割任务,主要针对2D自然图像。SAM的架构可以分为三个核心组件:
图像编码器 SAM利用预训练的视觉变换器(ViT)中的MAE来提取表示。该组件利用2D补丁嵌入结合可学习的位置编码,将输入图像转换为图像嵌入。
提示编码器 该模块可以处理稀疏(点、框)和密集(掩码)提示。稀疏提示使用冻结的2D绝对位置编码表示,然后与每种提示类型特定的学习嵌入结合。密集提示通过2D卷积颈部编码,以生成密集提示嵌入。
掩码解码器 采用轻量级结构有效地将图像嵌入与一组提示嵌入映射到输出掩码。每个变换器层包含四个步骤:(1)对令牌进行自注意;(2)令牌与图像嵌入之间的交叉注意;(3)使用点式MLP更新令牌;(4)更新图像嵌入与提示细节的交叉注意。通过变换器层处理后,特征图进行上采样,随后使用MLP转换为分割掩码。值得注意的是,所有的变换器层在前向传播过程中仅捕获2D几何信息。
Figure
图

Figure 1: Illustration of SAM [**21], fine-tuned SAM (SAM-Med2D [6]), and our SAM-Med3D on 3D Volumetric Medical Images. Both SAM and SAM-Med2D take N prompt points (one for each slice) whereas SAM-Med3D uses a single prompt point for the entire 3D volume. Here, N corresponds to the number of slices containing the target object. The top-left corner provides a schematic of the Axial, Coronal, and Sagittal views. For a given 3D input, we visualize the 3D, coronal, and multiple axial views. The numbers in brackets indicate the index of each axial slice.
图1:对3D体积医学图像的SAM、经过微调的SAM(SAM-Med2D )以及我们的SAM-Med3D的示意图。SAM和SAM-Med2D采用N个提示点(每个切片一个),而SAM-Med3D对整个3D体积使用单个提示点。这里的N*对应于包含目标对象的切片数量。左上角提供了轴向、冠状和矢状视图的示意图。对于给定的3D输入,我们可视化了3D、冠状和多个轴向视图。括号中的数字表示每个轴向切片的索引。
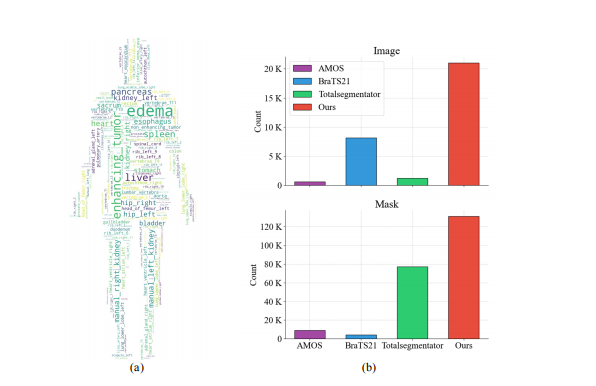
Figure 2: (a) The word cloud maps for all training data category statistics. There are 247 categories in our training data. (b) Comparison of counts of images and masks in the 3D medical image datasets we collected for training. Our dataset consists of 21K 3D images with corresponding 131K 3D masks, while AMOS , TotalSegmentator have less than 2K images, and BraTS21 has less than 10K masks.
图2:(a) 所有训练数据类别统计的词云图。我们的训练数据中有247个类别。(b) 我们收集用于训练的3D医学图像数据集中图像和掩码数量的比较。我们的数据集包含21K 3D图像及其对应的131K 3D掩码,而AMOS、TotalSegmentator的图像不到2K,BraTS21的掩码不到10K。
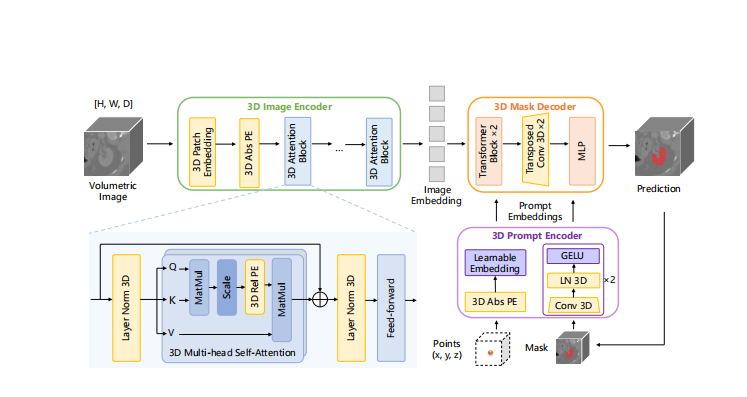
Figure 3: The modified 3D architecture of our SAM-Med3D. The original 2D components are transformed into their 3D counterparts, encompassing a 3D image encoder, 3D prompt encoder, and 3D mask decoder. 3D convolution, 3D positional encoding (PE) and 3D layer norm are employed to construct the 3D model.
图3:我们的SAM-Med3D修改后的3D架构。原始的2D组件被转换为它们的3D对应部分,包括3D图像编码器、3D提示编码器和3D掩码解码器。使用3D卷积、3D位置编码(PE)和3D层归一化来构建3D模型。

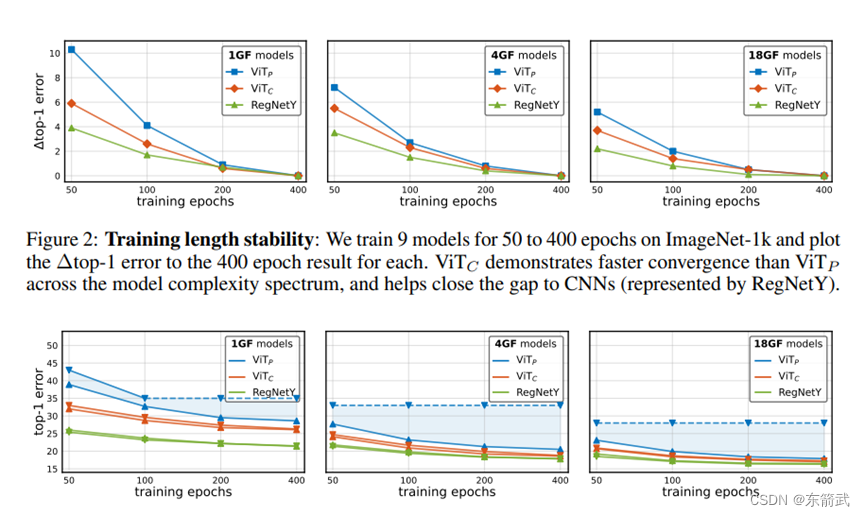
Figure 4: (a-c) Performance comparison across different modalities with varying numbers of points. Notably, while SAM-Med2D was trained on the US (Ultrasound) modality and SAM-Med3D was not, SAM-Med3D still exhibits competitive performance. (d) Comparison of the Dice coefficient between SAM-Med3D and the top-performing 2D fine-tuned SAM model, SAM-Med2D across 34 major organs and 5 kinds of lesions. and represent seen and unseen lesions.
图4:(a-c) 在不同模态下使用不同数量的点进行性能比较。值得注意的是,虽然SAM-Med2D是在US(超声)模态上训练的,而SAM-Med3D没有,但SAM-Med3D仍展示了有竞争力的性能。(d) 在34个主要器官和5种类型的病变中,SAM-Med3D与表现最佳的2D微调SAM模型,SAM-Med2D 之间的Dice系数比较。和分别代表已见和未见的病变。
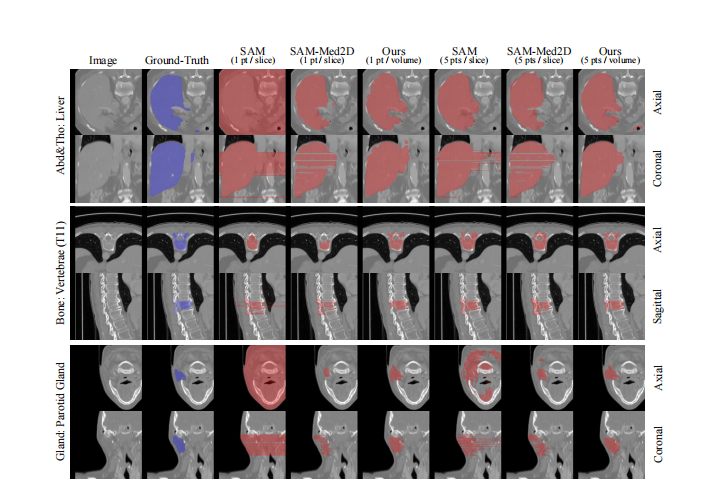
Figure 5: Visualization of SAM, SAM-Med2D, and our proposed SAM-Med3D across diverse anatomical structures for varying numbers of point. We present both axial slices and coronal/sagittal views to comprehensively illustrate the 3D results. Abd&Tho denotes Abdominal and Thorax.
图5:在不同的解剖结构中,对于不同数量的点,可视化SAM、SAM-Med2D和我们提出的SAM-Med3D。我们展示了轴向切片和冠状/矢状视图,以全面说明3D结果。Abd&Tho表示腹部和胸部。
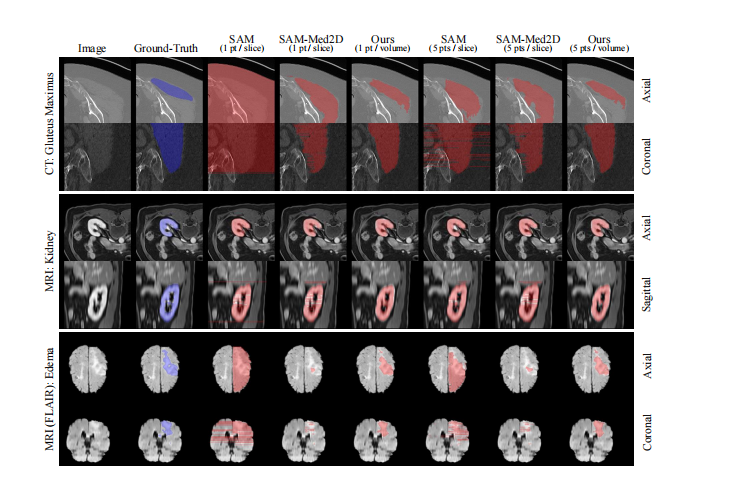
Figure 6: Visualization of SAM, SAM-Med2D, and our proposed SAM-Med3D across various modalities for varying numbers of point. We present both axial slices and coronal/sagittal views to comprehensively illustrate the 3D results.
图6:在不同模态中,对于不同数量的点,可视化SAM、SAM-Med2D和我们提出的SAM-Med3D。我们展示了轴向切片和冠状/矢状视图,以全面说明3D结果。
Table
表
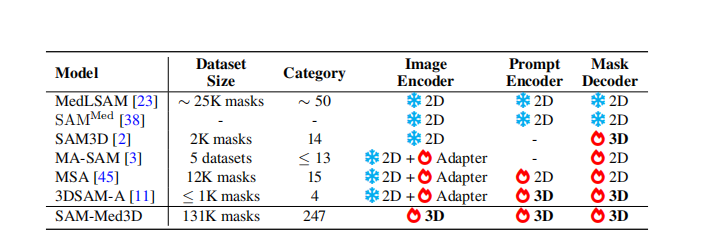
Table 1: Comparison of SAM models for 3D volumetric medical images. Our SAM-Med3D employs a fully learnable 3D architecture with large-scale training data, instead of frozen 2D layers with adapters. and ] denotes frozen and learnable.
表1:对3D体积医学图像的SAM模型比较。我们的SAM-Med3D采用完全可学习的3D架构和大规模训练数据,而不是使用适配器的冻结2D层。和]表示冻结和可学习。
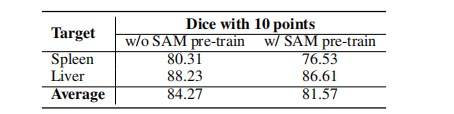
Table 2: Preliminary experiment investigating the reusability of 2D SAM pre-trained Weights in SAM-Med3D. Experimental details are consistent with Section 5.1.
表2:初步实验探索2D SAM预训练权重在SAM-Med3D中的可重用性。实验细节与第5.1节一致。
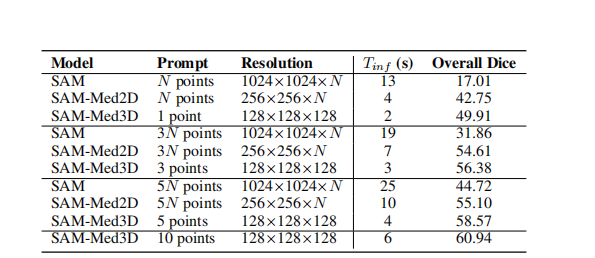
Table 3: Quantitative comparison of different methods on our evaluation dataset, detailed in Section 3.Here, N denotes the count of slices containing the target object (10 ≤ N ≤ 200). T**inf (Inference time) is calculated with N=100, excluding the time for image processing and simulated prompt generation.
表3:在第3节详述的我们的评估数据集上,不同方法的定量比较。这里,N表示包含目标对象的切片数量(10 ≤ N ≤ 200)。T**inf(推理时间)是在N=100的条件下计算的,不包括图像处理和模拟提示生成的时间。
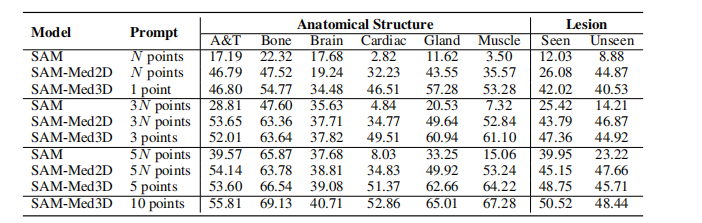
Table 4: Comparison from the perspective of anatomical structure and lesion. A&T represents Abdominal and Thorax targets. N denotes the count of slices containing the target object (10 ≤ N ≤200).
表4:从解剖结构和病变的角度进行比较。A&T代表腹部和胸部目标。N表示包含目标对象的切片数量(10 ≤ N ≤ 200)。
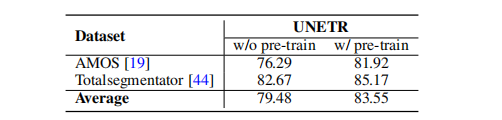
Table 5: Transferability evaluation for the fully-supervised 3D medical image segmentation. We trained the state-of-the-art ViT-based segmentation model (i.e. UNETR ), both with and without our SAM-Med3D pre-trained ViT encoder, to assess the benefits of pre-training.
表5:对全监督3D医学图像分割的可转移性评估。我们训练了最先进的基于ViT的分割模型(即UNETR [),分别使用和不使用我们的SAM-Med3D预训练ViT编码器,以评估预训练的好处。