比较推荐的是用@para注解,我们一步一步讲
1. 查询一个实体类对象
若查询出的数据只有一条,可以通过实体类对象接收查询结果
查询一个实体类对象,根据id查询
SelectMapper.java
package com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper;import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.bean.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;public interface SelectMapper {// 查询一个实体类对象,但查询所有男生的信息public User findUserByIdAndId(@Param("id") int id);
}
SelectMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper.SelectMapper"><select id="findUserByIdAndId" resultType="User2">select * from user where id = #{id}</select>
</mapper>
测试输出
package com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.test;import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.bean.User;
import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper.SelectMapper;
import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.utils.SqlSessionUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
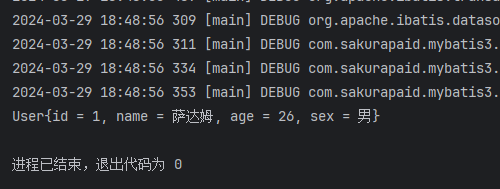
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;public class SelecTest {@Testpublic void test(){// 从SqlSessionUtils工具类中获取SqlSessionSqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);User userByIdAndId = mapper.findUserByIdAndId(1);if (userByIdAndId != null) {System.out.println(userByIdAndId);} else {System.out.println("没有这个用户");}}
}
2. 查询一个list集合
当需要查询一个实体类集合,且预期结果可能包含多个匹配项(如查询所有男性用户)时,直接使用实体类对象接收查询结果会导致编译错误。这是因为查询结果为多条数据,与单个实体类对象的期望类型不符。


为正确处理这种情况,应改用List集合(或其他可容纳多个元素的集合类型)来接收查询得到的多个数据项。
查询所有用户对象
SelectMapper.java
package com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper;import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.bean.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;import java.util.List;public interface SelectMapper {// 查询一个实体类对象,根据id查询public User findUserByIdAndId(@Param("id") int id);// 查询对象,但查询所有用户public List<User> findAllUser();
}
SelectMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper.SelectMapper"><select id="findUserByIdAndId" resultType="User2">select * from user where id = #{id}</select><select id="findAllUser" resultType="User2">select * from user</select>
</mapper>

测试输出
package com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.test;import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.bean.User;
import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper.SelectMapper;
import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.utils.SqlSessionUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.List;public class SelecTest {@Testpublic void test(){// 从SqlSessionUtils工具类中获取SqlSessionSqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);// 查询一个实体类对象,根据id查询/*User userByIdAndId = mapper.findUserByIdAndId(1);if (userByIdAndId != null) {System.out.println(userByIdAndId);} else {System.out.println("没有这个用户");}*/// 查询对象,但查询所有男用户List<User> allUser = mapper.findAllUser();if (allUser != null) {for (User user : allUser) {System.out.println(user);}} else {System.out.println("没有这个用户");}}
}
package com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.test;import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.bean.User;
import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper.SelectMapper;
import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.utils.SqlSessionUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.List;public class SelecTest {@Testpublic void test(){// 从SqlSessionUtils工具类中获取SqlSessionSqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);// 查询一个实体类对象,根据id查询/*User userByIdAndId = mapper.findUserByIdAndId(1);if (userByIdAndId != null) {System.out.println(userByIdAndId);} else {System.out.println("没有这个用户");}*/// 查询对象,但查询所有男用户List<User> allUser = mapper.findAllUser();if (allUser != null) {for (User user : allUser) {System.out.println(user);}} else {System.out.println("没有这个用户");}}
}


3. 查询单个数据
比如查询语句的结果不是要查询一个实体类或者实体类集合
在MyBatis中,对于Java中常用的类型都设置了类型别名
例如:这写都是在Mybatis官方文档上找到的
mybatis – MyBatis 3 | 配置
在MyBatis的XML映射文件中,可以这样使用类型别名:
<!-- 使用resultType映射到单个实体类 -->
<select id="selectUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.example.User">SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = #{id}
</select><!-- 使用resultType映射到基本类型(如整数) -->
<select id="countUsers" parameterType="void" resultType="int">SELECT COUNT(*) FROM users
</select><!-- 使用resultType映射到实体类集合 -->
<select id="selectAllUsers" parameterType="void" resultType="com.example.User">SELECT * FROM users
</select><!-- 使用resultType映射到List<Map<String, Object>>类型 -->
<select id="selectUserDetails" parameterType="int" resultType="map">SELECT id, name, email, age FROM users WHERE id = #{id}
</select>上述例子中:
- resultType="com.example.User"表明查询结果将被映射到User实体类。
- resultType="_int"使用了别名_int,代表查询结果是整数类型(可能是Integer或int,具体取决于MyBatis配置)。
- resultType="list"使用了别名list,表示查询结果将被映射到一个List类型的集合,其中元素类型由SQL查询的列数据决定。
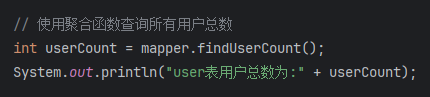
使用聚合函数查询所有用户总数
SelectMapper.java
package com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper;import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.bean.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;import java.util.List;public interface SelectMapper {// 查询一个实体类对象,根据id查询public User findUserByIdAndId(@Param("id") int id);// 查询对象,但查询所有用户public List<User> findAllUser();// 使用聚合函数查询所有用户总数public int findUserCount();
}
SelectMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper.SelectMapper"><select id="findUserByIdAndId" resultType="User2">select * from user where id = #{id}</select><select id="findAllUser" resultType="User2" >select * from user</select><select id="findUserCount" resultType="java.lang.Integer">select count(*) from user</select>
</mapper>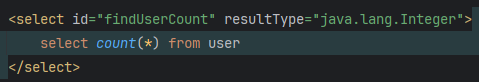
测试输出
package com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.test;import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.bean.User;
import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper.SelectMapper;
import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.utils.SqlSessionUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;public class SelecTest {@Testpublic void test(){// 从SqlSessionUtils工具类中获取SqlSessionSqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);User userByIdAndId = mapper.findUserByIdAndId(1);if (userByIdAndId != null) {System.out.println(userByIdAndId);} else {System.out.println("没有这个用户");}}
}

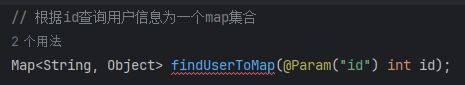
4. 查询一条数据为map集合
当查询结果无法直接映射到某个实体类,或者需要以更灵活的方式组织数据(如跨表查询、聚合查询等)时,查询结果转为Map集合尤为实用。
SelectMapper.java
package com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper;import com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.bean.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;public interface SelectMapper {// 查询一个实体类对象,根据id查询User findUserByIdAndId(@Param("id") int id);// 查询对象,但查询所有用户List<User> findAllUser();// 使用聚合函数查询所有用户总数int findUserCount();// 根据id查询用户信息为一个map集合Map<String, Object> findUserToMap(@Param("id") int id);
}
SelectMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.sakurapaid.mybatis3.select.mapper.SelectMapper"><select id="findUserByIdAndId" resultType="User2">select * from user where id = #{id}</select><select id="findAllUser" resultType="User2" >select * from user</select><select id="findUserCount" resultType="java.lang.Integer">select count(*) from user</select><select id="findUserToMap" resultType="java.util.Map">select * from user where id = #{id}</select>
</mapper>
测试输出
// 根据id查询用户信息为一个map集合
Map<String, Object> userToMap = mapper.findUserToMap(1);
System.out.println(userToMap);
5. 查询多条数据为map集合
5.1. 方式一
List<Map<String, Object>>
查询结果是一个List,其中每个元素是一个Map,表示一条数据。Map的键为字段名,值为字段值。适用于需要保持查询结果顺序,或者需要进行进一步集合操作(如过滤、排序等)的情况。
SelectMapper.java
// 查询所有用户信息为map集合
List<Map<String, Object>> findAllUserToMap();SelectMapper.xml
<select id="findAllUserToMap" resultType="java.util.Map">select * from user
</select>测试输出
// 查询所有用户信息为map集合
List<Map<String, Object>> allUserToMap = mapper.findAllUserToMap();
for (Map<String, Object> map : allUserToMap) {System.out.println(map);
}
5.2. 方式二
Map<String, Map<String, Object>>
查询结果是一个Map,其键由指定的字段(如"id")值决定,值为一个表示单条数据的Map。这种方式将数据以特定字段为索引组织起来,方便根据该字段快速查找或遍历数据。适用于需要根据特定字段(如"id")直接访问某条数据的场景。
如使用使用@MapKey("id")注解指定Map的键为数据记录的"id"字段。
SelectMapper.java
// 查询所有用户信息为map集合
@MapKey("id")
Map<String, Object> findAllUserToMap();SelectMapper.xml
<select id="findAllUserToMap" resultType="java.util.Map">select * from user
</select>测试输出
// 查询所有用户信息为map集合
Map<String, Object> allUserToMap = mapper.findAllUserToMap();
System.out.println(allUserToMap);输出结果
{1={sex=男, name=萨达姆, id=1, age=26}, 2={sex=男, name=小王, id=2, age=19}, 3={sex=女, name=小红, id=3, age=18}, 4={sex=男, name=小明, id=4, age=18}}











![一、图片隐写[Stegsolve、binwalk、010editor、WaterMark、BlindWaterMark、文件头尾]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/99a60fd05c67431d979f5683c3f4c577.png)