Keras 3 在 TPU 上的肺炎分类
作者:Amy MiHyun Jang
创建日期:2020/07/28
最后修改时间:2024/02/12
描述:TPU 上的医学图像分类。
在 Colab 中查看
GitHub 源
简介 + 设置
本教程将介绍如何构建 X 射线图像分类模型 预测 X 线扫描是否显示肺炎的存在。
import re
import os
import random
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plttry:tpu = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver.connect()print("Device:", tpu.master())strategy = tf.distribute.TPUStrategy(tpu)
except:strategy = tf.distribute.get_strategy()
print("Number of replicas:", strategy.num_replicas_in_sync)
Device: grpc://10.0.27.122:8470 INFO:tensorflow:Initializing the TPU system: grpc://10.0.27.122:8470 INFO:tensorflow:Initializing the TPU system: grpc://10.0.27.122:8470 INFO:tensorflow:Clearing out eager caches INFO:tensorflow:Clearing out eager caches INFO:tensorflow:Finished initializing TPU system. INFO:tensorflow:Finished initializing TPU system. WARNING:absl:[`tf.distribute.TPUStrategy`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/distribute/TPUStrategy) is deprecated, please use the non experimental symbol [`tf.distribute.TPUStrategy`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/distribute/TPUStrategy) instead. INFO:tensorflow:Found TPU system: INFO:tensorflow:Found TPU system: INFO:tensorflow:*** Num TPU Cores: 8 INFO:tensorflow:*** Num TPU Cores: 8 INFO:tensorflow:*** Num TPU Workers: 1 INFO:tensorflow:*** Num TPU Workers: 1 INFO:tensorflow:*** Num TPU Cores Per Worker: 8 INFO:tensorflow:*** Num TPU Cores Per Worker: 8 INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0, CPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0, CPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:XLA_CPU:0, XLA_CPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:XLA_CPU:0, XLA_CPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0, CPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0, CPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:0, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:0, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:1, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:1, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:2, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:2, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:3, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:3, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:4, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:4, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:5, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:5, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:6, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:6, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:7, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU:7, TPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU_SYSTEM:0, TPU_SYSTEM, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:TPU_SYSTEM:0, TPU_SYSTEM, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:XLA_CPU:0, XLA_CPU, 0, 0) INFO:tensorflow:*** Available Device: _DeviceAttributes(/job:worker/replica:0/task:0/device:XLA_CPU:0, XLA_CPU, 0, 0) Number of replicas: 8 我们需要一个指向我们数据的 Google Cloud 链接,以便使用 TPU 加载数据。 下面,我们定义了我们将在此示例中使用的关键配置参数。 要在 TPU 上运行,此示例必须在 Colab 上,并选择 TPU 运行时。
AUTOTUNE = tf.data.AUTOTUNE
BATCH_SIZE = 25 * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
IMAGE_SIZE = [180, 180]
CLASS_NAMES = ["NORMAL", "PNEUMONIA"]
加载数据
我们使用的 Cell 的胸部 X 光数据将数据分为 training 和 test 文件。让我们首先加载训练 TFRecords。
train_images = tf.data.TFRecordDataset("gs://download.tensorflow.org/data/ChestXRay2017/train/images.tfrec"
)
train_paths = tf.data.TFRecordDataset("gs://download.tensorflow.org/data/ChestXRay2017/train/paths.tfrec"
)ds = tf.data.Dataset.zip((train_images, train_paths))
让我们数一数我们有多少次健康/正常的胸部 X 光片,以及有多少 肺炎胸部 X 光片我们有:
COUNT_NORMAL = len([filenamefor filename in train_pathsif "NORMAL" in filename.numpy().decode("utf-8")]
)
print("Normal images count in training set: " + str(COUNT_NORMAL))COUNT_PNEUMONIA = len([filenamefor filename in train_pathsif "PNEUMONIA" in filename.numpy().decode("utf-8")]
)
print("Pneumonia images count in training set: " + str(COUNT_PNEUMONIA))
Normal images count in training set: 1349 Pneumonia images count in training set: 3883 请注意,被归类为肺炎的图像比正常情况多得多。这 显示我们的数据不平衡。我们稍后会纠正这种不平衡 在我们的笔记本中。
我们想将每个文件名映射到相应的 (image, label) 对。以下内容 方法将帮助我们做到这一点。
由于我们只有两个标签,因此我们将对标签进行编码,以便 或 肺炎和/或表示正常。1True0False
def get_label(file_path):# convert the path to a list of path componentsparts = tf.strings.split(file_path, "/")# The second to last is the class-directoryif parts[-2] == "PNEUMONIA":return 1else:return 0def decode_img(img):# convert the compressed string to a 3D uint8 tensorimg = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img, channels=3)# resize the image to the desired size.return tf.image.resize(img, IMAGE_SIZE)def process_path(image, path):label = get_label(path)# load the raw data from the file as a stringimg = decode_img(image)return img, labelds = ds.map(process_path, num_parallel_calls=AUTOTUNE)
让我们将数据拆分为训练和验证数据集。
ds = ds.shuffle(10000)
train_ds = ds.take(4200)
val_ds = ds.skip(4200)
让我们可视化 (image, label) 对的形状。
for image, label in train_ds.take(1):print("Image shape: ", image.numpy().shape)print("Label: ", label.numpy())
Image shape: (180, 180, 3) Label: False 同时加载测试数据并设置其格式。
test_images = tf.data.TFRecordDataset("gs://download.tensorflow.org/data/ChestXRay2017/test/images.tfrec"
)
test_paths = tf.data.TFRecordDataset("gs://download.tensorflow.org/data/ChestXRay2017/test/paths.tfrec"
)
test_ds = tf.data.Dataset.zip((test_images, test_paths))test_ds = test_ds.map(process_path, num_parallel_calls=AUTOTUNE)
test_ds = test_ds.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
可视化数据集
首先,让我们使用缓冲预取,这样我们就可以在没有 I/O 的情况下从磁盘生成数据 变为阻塞。
请注意,大型图像数据集不应缓存在内存中。我们在这里做 因为数据集不是很大,我们想在 TPU 上训练。
def prepare_for_training(ds, cache=True):# This is a small dataset, only load it once, and keep it in memory.# use `.cache(filename)` to cache preprocessing work for datasets that don't# fit in memory.if cache:if isinstance(cache, str):ds = ds.cache(cache)else:ds = ds.cache()ds = ds.batch(BATCH_SIZE)# `prefetch` lets the dataset fetch batches in the background while the model# is training.ds = ds.prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)return ds
调用训练数据的下一个批次迭代。
train_ds = prepare_for_training(train_ds)
val_ds = prepare_for_training(val_ds)image_batch, label_batch = next(iter(train_ds))
定义在批处理中显示图像的方法。
def show_batch(image_batch, label_batch):plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))for n in range(25):ax = plt.subplot(5, 5, n + 1)plt.imshow(image_batch[n] / 255)if label_batch[n]:plt.title("PNEUMONIA")else:plt.title("NORMAL")plt.axis("off")
由于该方法将 NumPy 数组作为其参数,因此请在 batches 以 NumPy 数组形式返回张量。
show_batch(image_batch.numpy(), label_batch.numpy())

构建 CNN
为了使我们的模型更加模块化和更容易理解,让我们定义一些块。如 我们正在构建一个卷积神经网络,我们将创建一个卷积块和一个密集的 layer 块。
此 CNN 的体系结构受到本文的启发。
import os
os.environ['KERAS_BACKEND'] = 'tensorflow'import keras
from keras import layersdef conv_block(filters, inputs):x = layers.SeparableConv2D(filters, 3, activation="relu", padding="same")(inputs)x = layers.SeparableConv2D(filters, 3, activation="relu", padding="same")(x)x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)outputs = layers.MaxPool2D()(x)return outputsdef dense_block(units, dropout_rate, inputs):x = layers.Dense(units, activation="relu")(inputs)x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)outputs = layers.Dropout(dropout_rate)(x)return outputs
以下方法将定义函数来为我们构建模型。
图像最初的值范围为 [0, 255]。CNN 与较小的 CNN 配合得更好 numbers 来调整它,以便根据我们的输入进行缩小。
Dropout 图层很重要,因为它们 降低模型过拟合的可能性。我们希望用一个具有一个节点的层来结束模型,因为这将是确定 X 射线是否显示的二进制输出 存在肺炎。Dense
def build_model():inputs = keras.Input(shape=(IMAGE_SIZE[0], IMAGE_SIZE[1], 3))x = layers.Rescaling(1.0 / 255)(inputs)x = layers.Conv2D(16, 3, activation="relu", padding="same")(x)x = layers.Conv2D(16, 3, activation="relu", padding="same")(x)x = layers.MaxPool2D()(x)x = conv_block(32, x)x = conv_block(64, x)x = conv_block(128, x)x = layers.Dropout(0.2)(x)x = conv_block(256, x)x = layers.Dropout(0.2)(x)x = layers.Flatten()(x)x = dense_block(512, 0.7, x)x = dense_block(128, 0.5, x)x = dense_block(64, 0.3, x)outputs = layers.Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(x)model = keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)return model
更正数据不平衡
在这个例子的前面部分,我们看到数据不平衡,分类的图像更多 作为肺炎比正常。我们将通过使用类加权来纠正这个问题:
initial_bias = np.log([COUNT_PNEUMONIA / COUNT_NORMAL])
print("Initial bias: {:.5f}".format(initial_bias[0]))TRAIN_IMG_COUNT = COUNT_NORMAL + COUNT_PNEUMONIA
weight_for_0 = (1 / COUNT_NORMAL) * (TRAIN_IMG_COUNT) / 2.0
weight_for_1 = (1 / COUNT_PNEUMONIA) * (TRAIN_IMG_COUNT) / 2.0class_weight = {0: weight_for_0, 1: weight_for_1}print("Weight for class 0: {:.2f}".format(weight_for_0))
print("Weight for class 1: {:.2f}".format(weight_for_1))
Initial bias: 1.05724 Weight for class 0: 1.94 Weight for class 1: 0.67 类别 (Normal) 的权重比类别 (Pneumonia) 的权重高得多。由于法线图像较少,因此将对每个法线图像进行加权 more 来平衡数据,因为 CNN 在训练数据平衡时效果最佳。01
训练模型
定义回调
checkpoint 回调保存了模型的最佳权重,因此下次我们想使用 模型,我们不必花时间训练它。提前停止回调停止 当模型开始停滞时,甚至更糟糕的是,当 模型开始过拟合。
checkpoint_cb = keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint("xray_model.keras", save_best_only=True)early_stopping_cb = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(patience=10, restore_best_weights=True
)
我们还希望调整我们的学习率。学习率过高会导致模型 发散。学习速率太小会导致模型太慢。我们 实现下面的指数学习率调度方法。
initial_learning_rate = 0.015
lr_schedule = keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay(initial_learning_rate, decay_steps=100000, decay_rate=0.96, staircase=True
)
拟合模型
对于我们的指标,我们希望包括 precision 和 recall,因为它们将为 更了解我们的模型有多好。准确率告诉我们 labels 是正确的。由于我们的数据不平衡,准确性可能会给人一种歪曲的感觉 一个好的模型(即始终预测 PNEUMONIA 的模型将准确率为 74%,但并非如此 一个很好的模型)。
精度是 TP 和假阳性之和的真阳性 (TP) 数 (FP) 的 Shell。它显示标记的阳性实际正确的比例。
召回率是 TP 和假负数 (FN) 之和的 TP 数。它显示了什么 实际阳性的比例是正确的。
由于图像只有两个可能的标签,因此我们将使用 二进制交叉熵损失。当我们拟合模型时,请记住指定类权重 我们之前定义过。因为我们使用的是 TPU,所以训练会很快 - 小于 2 分钟。
with strategy.scope():model = build_model()METRICS = [keras.metrics.BinaryAccuracy(),keras.metrics.Precision(name="precision"),keras.metrics.Recall(name="recall"),]model.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=lr_schedule),loss="binary_crossentropy",metrics=METRICS,)history = model.fit(train_ds,epochs=100,validation_data=val_ds,class_weight=class_weight,callbacks=[checkpoint_cb, early_stopping_cb],
)
Epoch 1/100 WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/data/ops/multi_device_iterator_ops.py:601: get_next_as_optional (from tensorflow.python.data.ops.iterator_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Use `tf.data.Iterator.get_next_as_optional()` instead. WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/data/ops/multi_device_iterator_ops.py:601: get_next_as_optional (from tensorflow.python.data.ops.iterator_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Use `tf.data.Iterator.get_next_as_optional()` instead. 21/21 [==============================] - 12s 568ms/step - loss: 0.5857 - binary_accuracy: 0.6960 - precision: 0.8887 - recall: 0.6733 - val_loss: 34.0149 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7180 - val_precision: 0.7180 - val_recall: 1.0000 Epoch 2/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 128ms/step - loss: 0.2916 - binary_accuracy: 0.8755 - precision: 0.9540 - recall: 0.8738 - val_loss: 97.5194 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7180 - val_precision: 0.7180 - val_recall: 1.0000 Epoch 3/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 167ms/step - loss: 0.2384 - binary_accuracy: 0.9002 - precision: 0.9663 - recall: 0.8964 - val_loss: 27.7902 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7180 - val_precision: 0.7180 - val_recall: 1.0000 Epoch 4/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 173ms/step - loss: 0.2046 - binary_accuracy: 0.9145 - precision: 0.9725 - recall: 0.9102 - val_loss: 10.8302 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7180 - val_precision: 0.7180 - val_recall: 1.0000 Epoch 5/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 174ms/step - loss: 0.1841 - binary_accuracy: 0.9279 - precision: 0.9733 - recall: 0.9279 - val_loss: 3.5860 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7103 - val_precision: 0.7162 - val_recall: 0.9879 Epoch 6/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 185ms/step - loss: 0.1600 - binary_accuracy: 0.9362 - precision: 0.9791 - recall: 0.9337 - val_loss: 0.3014 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8895 - val_precision: 0.8973 - val_recall: 0.9555 Epoch 7/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 130ms/step - loss: 0.1567 - binary_accuracy: 0.9393 - precision: 0.9798 - recall: 0.9372 - val_loss: 0.6763 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7810 - val_precision: 0.7760 - val_recall: 0.9771 Epoch 8/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 131ms/step - loss: 0.1532 - binary_accuracy: 0.9421 - precision: 0.9825 - recall: 0.9385 - val_loss: 0.3169 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8895 - val_precision: 0.8684 - val_recall: 0.9973 Epoch 9/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 184ms/step - loss: 0.1457 - binary_accuracy: 0.9431 - precision: 0.9822 - recall: 0.9401 - val_loss: 0.2064 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9273 - val_precision: 0.9840 - val_recall: 0.9136 Epoch 10/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 132ms/step - loss: 0.1201 - binary_accuracy: 0.9521 - precision: 0.9869 - recall: 0.9479 - val_loss: 0.4364 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8605 - val_precision: 0.8443 - val_recall: 0.9879 Epoch 11/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 127ms/step - loss: 0.1200 - binary_accuracy: 0.9510 - precision: 0.9863 - recall: 0.9469 - val_loss: 0.5197 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8508 - val_precision: 1.0000 - val_recall: 0.7922 Epoch 12/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 186ms/step - loss: 0.1077 - binary_accuracy: 0.9581 - precision: 0.9870 - recall: 0.9559 - val_loss: 0.1349 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9486 - val_precision: 0.9587 - val_recall: 0.9703 Epoch 13/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 173ms/step - loss: 0.0918 - binary_accuracy: 0.9650 - precision: 0.9914 - recall: 0.9611 - val_loss: 0.0926 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9700 - val_precision: 0.9837 - val_recall: 0.9744 Epoch 14/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 130ms/step - loss: 0.0996 - binary_accuracy: 0.9612 - precision: 0.9913 - recall: 0.9559 - val_loss: 0.1811 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9419 - val_precision: 0.9956 - val_recall: 0.9231 Epoch 15/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 129ms/step - loss: 0.0898 - binary_accuracy: 0.9643 - precision: 0.9901 - recall: 0.9614 - val_loss: 0.1525 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9486 - val_precision: 0.9986 - val_recall: 0.9298 Epoch 16/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 128ms/step - loss: 0.0941 - binary_accuracy: 0.9621 - precision: 0.9904 - recall: 0.9582 - val_loss: 0.5101 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8527 - val_precision: 1.0000 - val_recall: 0.7949 Epoch 17/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 125ms/step - loss: 0.0798 - binary_accuracy: 0.9636 - precision: 0.9897 - recall: 0.9607 - val_loss: 0.1239 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9622 - val_precision: 0.9875 - val_recall: 0.9595 Epoch 18/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 126ms/step - loss: 0.0821 - binary_accuracy: 0.9657 - precision: 0.9911 - recall: 0.9623 - val_loss: 0.1597 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9322 - val_precision: 0.9956 - val_recall: 0.9096 Epoch 19/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 143ms/step - loss: 0.0800 - binary_accuracy: 0.9657 - precision: 0.9917 - recall: 0.9617 - val_loss: 0.2538 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9109 - val_precision: 1.0000 - val_recall: 0.8758 Epoch 20/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 127ms/step - loss: 0.0605 - binary_accuracy: 0.9738 - precision: 0.9950 - recall: 0.9694 - val_loss: 0.6594 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8566 - val_precision: 1.0000 - val_recall: 0.8003 Epoch 21/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 167ms/step - loss: 0.0726 - binary_accuracy: 0.9733 - precision: 0.9937 - recall: 0.9701 - val_loss: 0.0593 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9816 - val_precision: 0.9945 - val_recall: 0.9798 Epoch 22/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 126ms/step - loss: 0.0577 - binary_accuracy: 0.9783 - precision: 0.9951 - recall: 0.9755 - val_loss: 0.1087 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9729 - val_precision: 0.9931 - val_recall: 0.9690 Epoch 23/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 125ms/step - loss: 0.0652 - binary_accuracy: 0.9729 - precision: 0.9924 - recall: 0.9707 - val_loss: 1.8465 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7180 - val_precision: 0.7180 - val_recall: 1.0000 Epoch 24/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 124ms/step - loss: 0.0538 - binary_accuracy: 0.9783 - precision: 0.9951 - recall: 0.9755 - val_loss: 1.5769 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7180 - val_precision: 0.7180 - val_recall: 1.0000 Epoch 25/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 167ms/step - loss: 0.0549 - binary_accuracy: 0.9776 - precision: 0.9954 - recall: 0.9743 - val_loss: 0.0590 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9777 - val_precision: 0.9904 - val_recall: 0.9784 Epoch 26/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 131ms/step - loss: 0.0677 - binary_accuracy: 0.9719 - precision: 0.9924 - recall: 0.9694 - val_loss: 2.6008 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.6928 - val_precision: 0.9977 - val_recall: 0.5735 Epoch 27/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 127ms/step - loss: 0.0469 - binary_accuracy: 0.9833 - precision: 0.9971 - recall: 0.9804 - val_loss: 1.0184 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8605 - val_precision: 0.9983 - val_recall: 0.8070 Epoch 28/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 126ms/step - loss: 0.0501 - binary_accuracy: 0.9790 - precision: 0.9961 - recall: 0.9755 - val_loss: 0.3737 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9089 - val_precision: 0.9954 - val_recall: 0.8772 Epoch 29/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 128ms/step - loss: 0.0548 - binary_accuracy: 0.9798 - precision: 0.9941 - recall: 0.9784 - val_loss: 1.2928 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7907 - val_precision: 1.0000 - val_recall: 0.7085 Epoch 30/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 129ms/step - loss: 0.0370 - binary_accuracy: 0.9860 - precision: 0.9980 - recall: 0.9829 - val_loss: 0.1370 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9612 - val_precision: 0.9972 - val_recall: 0.9487 Epoch 31/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 125ms/step - loss: 0.0585 - binary_accuracy: 0.9819 - precision: 0.9951 - recall: 0.9804 - val_loss: 1.1955 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.6870 - val_precision: 0.9976 - val_recall: 0.5655 Epoch 32/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 140ms/step - loss: 0.0813 - binary_accuracy: 0.9695 - precision: 0.9934 - recall: 0.9652 - val_loss: 1.0394 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8576 - val_precision: 0.9853 - val_recall: 0.8138 Epoch 33/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 128ms/step - loss: 0.1111 - binary_accuracy: 0.9555 - precision: 0.9870 - recall: 0.9524 - val_loss: 4.9438 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.5911 - val_precision: 1.0000 - val_recall: 0.4305 Epoch 34/100 21/21 [==============================] - 3s 130ms/step - loss: 0.0680 - binary_accuracy: 0.9726 - precision: 0.9921 - recall: 0.9707 - val_loss: 2.8822 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7267 - val_precision: 0.9978 - val_recall: 0.6208 Epoch 35/100 21/21 [==============================] - 4s 187ms/step - loss: 0.0784 - binary_accuracy: 0.9712 - precision: 0.9892 - recall: 0.9717 - val_loss: 0.3940 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.9390 - val_precision: 0.9942 - val_recall: 0.9204 可视化模型性能
让我们绘制训练集和验证集的模型准确率和损失。请注意, 没有为此笔记本指定随机种子。对于您的笔记本,可能会有轻微的 方差。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 4, figsize=(20, 3))
ax = ax.ravel()for i, met in enumerate(["precision", "recall", "binary_accuracy", "loss"]):ax[i].plot(history.history[met])ax[i].plot(history.history["val_" + met])ax[i].set_title("Model {}".format(met))ax[i].set_xlabel("epochs")ax[i].set_ylabel(met)ax[i].legend(["train", "val"])
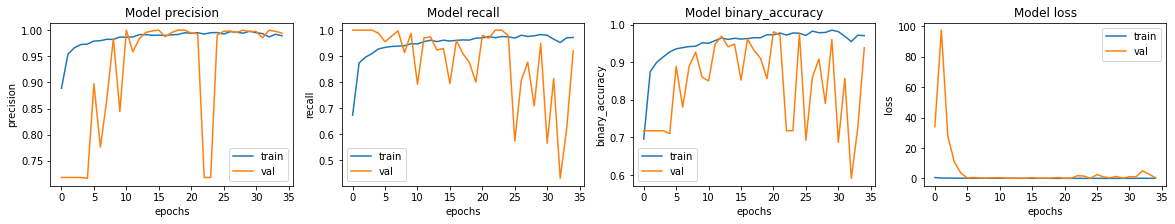
我们看到模型的准确率约为 95%。
预测和评估结果
让我们根据测试数据评估模型!
model.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True)
4/4 [==============================] - 3s 708ms/step - loss: 0.9718 - binary_accuracy: 0.7901 - precision: 0.7524 - recall: 0.9897 {'binary_accuracy': 0.7900640964508057, 'loss': 0.9717951416969299, 'precision': 0.752436637878418, 'recall': 0.9897436499595642} 我们看到,测试数据的准确性低于验证的准确性 设置。这可能表示过拟合。
我们的召回率大于我们的精确率,这表明几乎所有的肺炎图像都是 识别正确,但一些正常图像被错误识别。我们应该致力于 提高我们的精度。
for image, label in test_ds.take(1):plt.imshow(image[0] / 255.0)plt.title(CLASS_NAMES[label[0].numpy()])prediction = model.predict(test_ds.take(1))[0]
scores = [1 - prediction, prediction]for score, name in zip(scores, CLASS_NAMES):print("This image is %.2f percent %s" % ((100 * score), name))
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:3: DeprecationWarning: In future, it will be an error for 'np.bool_' scalars to be interpreted as an index This is separate from the ipykernel package so we can avoid doing imports until This image is 47.19 percent NORMAL This image is 52.81 percent PNEUMONIA