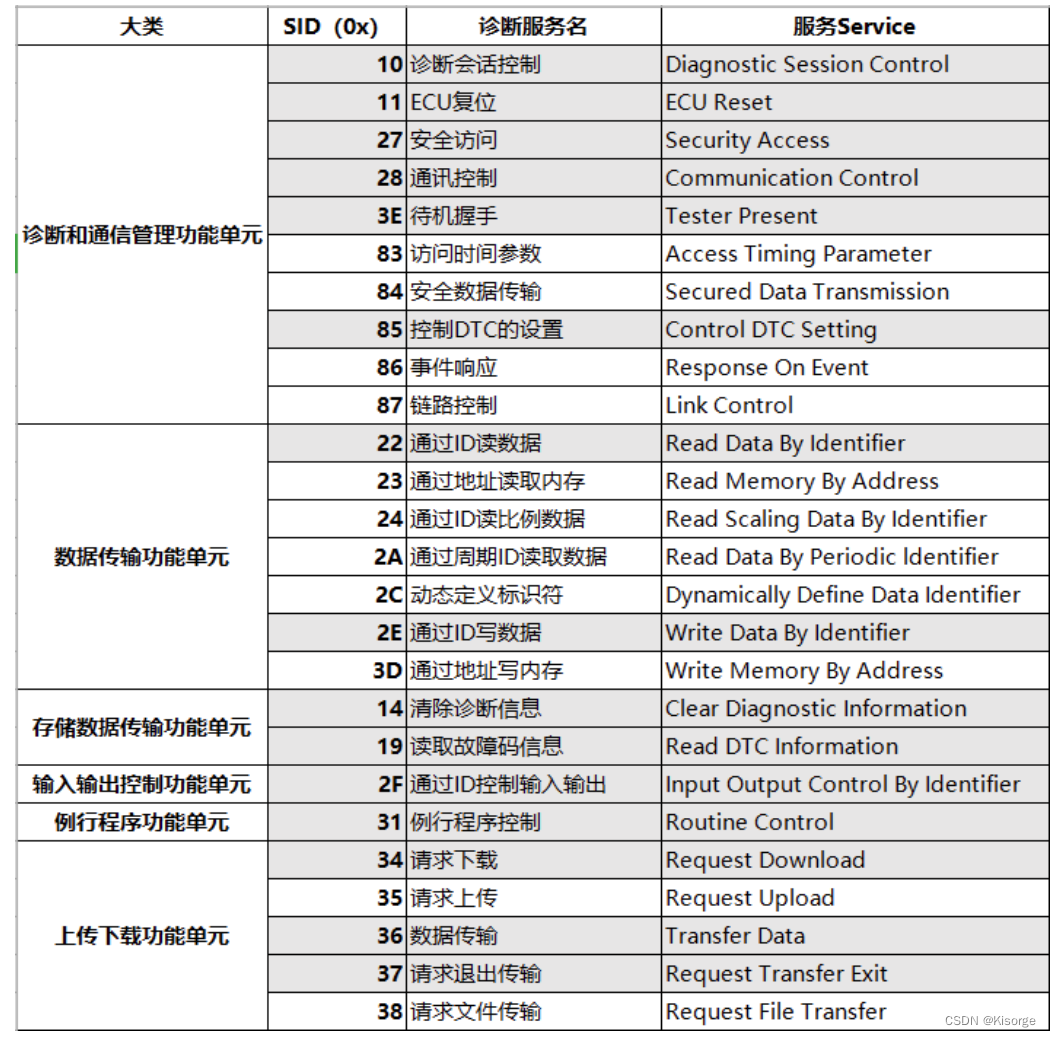
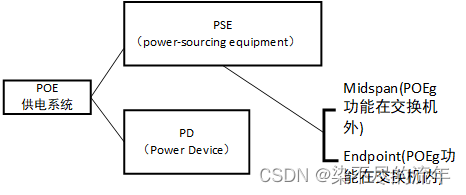
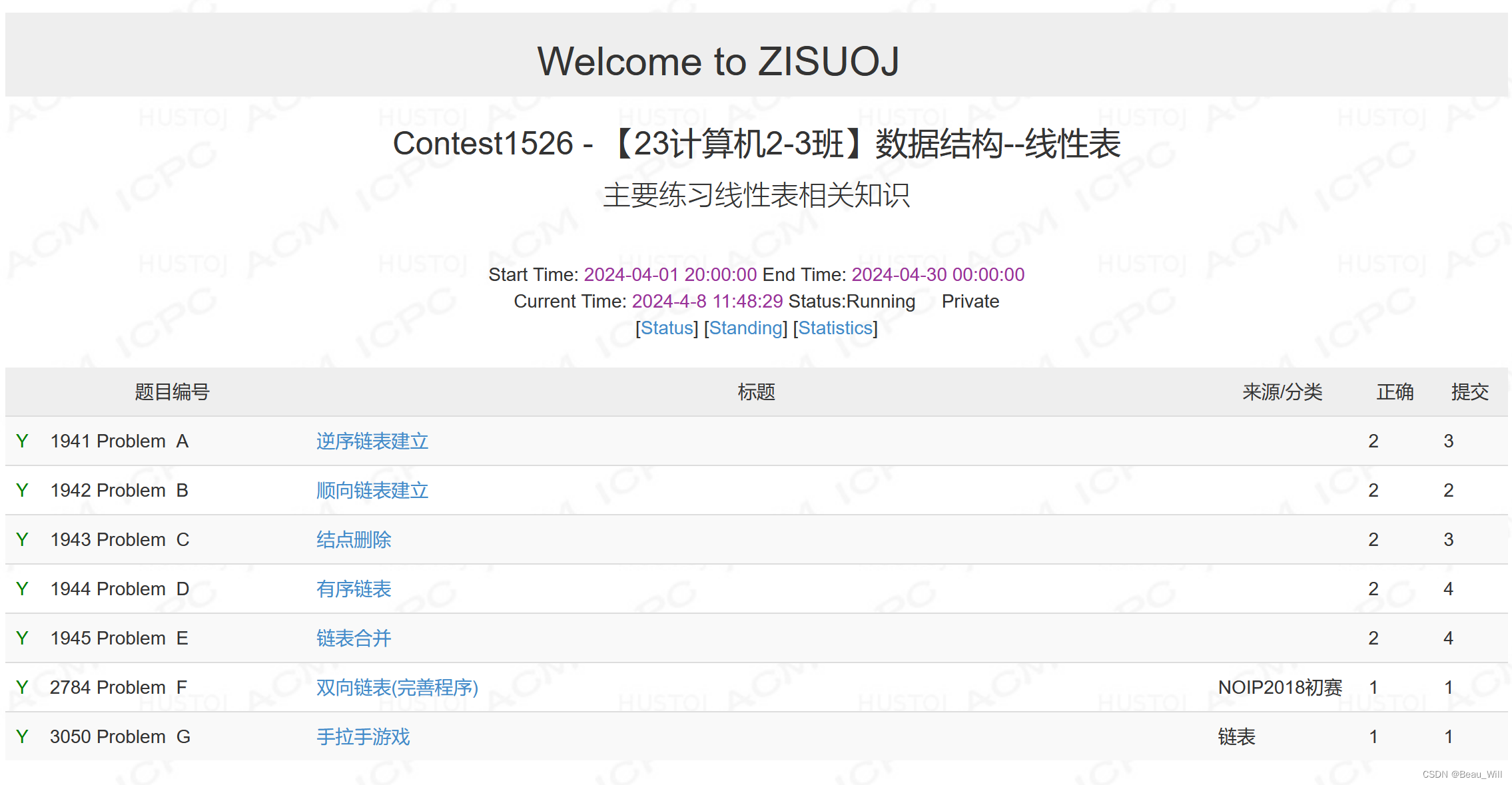
题目列表:
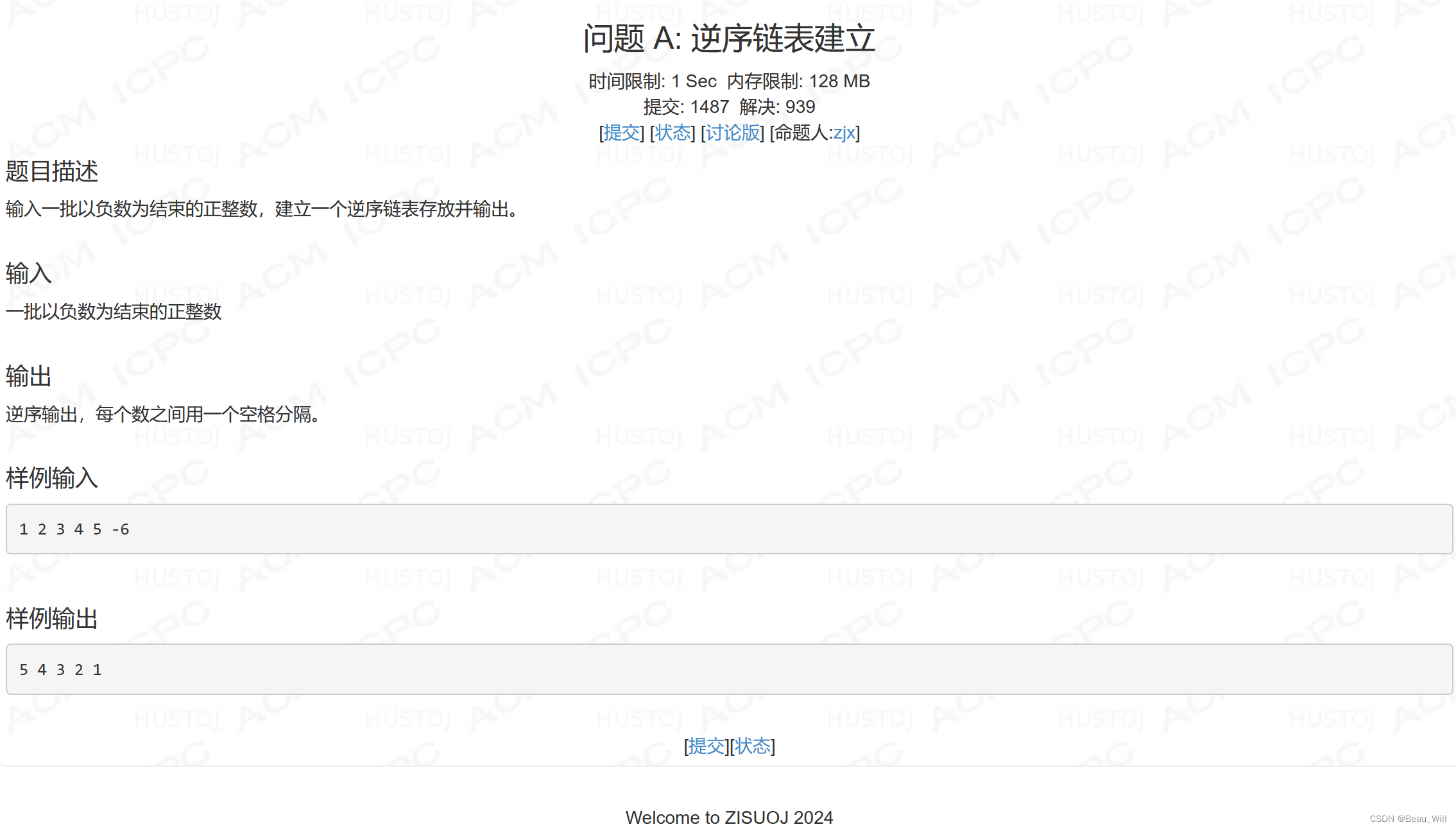
问题 A: 逆序链表建立
思路:
可以使用头插法插入所有元素后正序遍历输出或者使用尾插法逆序遍历,推荐使用双链表。这是链表系列的第一个题,那这个题下面的参考题解的各种解法我会尽可能写全一些。
参考题解1(数组模拟单链表使用头插法及正序遍历):
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
constexpr int N = 1e5+5;
int head,e[N],ne[N],idx;//数组模拟链表
void init(){//初始化链表 head=-1;idx=0;
}
void add(int x){//头插法,插入x e[idx]=x,ne[idx]=head,head=idx++;
}
void solve(){init();int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0){add(t);}for(int i = head;i!=-1;i=ne[i]){int j = e[i];cout << j << ' ';}cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);int T = 1;//cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}参考题解2(数组模拟双链表使用头插法顺序遍历):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
constexpr int N = 1e5+5;
int e[N],l[N],r[N],idx;
void init(){r[0]=1,l[1]=0,idx=2;
}
void add_to_head(int x){e[idx]=x,r[idx]=r[0],l[idx]=0,r[0]=idx++;
}
void solve(){init();int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) add_to_head(t);for(int i = 0;i!=1;i=r[i]){if(i==0) continue;int j = e[i];cout << j << ' ';}cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);int T = 1;
// cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}参考题解3(数组模拟双链表使用尾插法逆序遍历):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
constexpr int N = 1e5+5;
int e[N],l[N],r[N],idx;
void init(){r[0]=1,l[1]=0,idx=2;
}
void add_to_tail(int x){e[idx]=x,r[idx]=1,l[idx]=l[1],l[1]=idx++;
}
void solve(){init();int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) add_to_tail(t);for(int i = 1;i!=0;i=l[i]){if(i==1) continue;int j = e[i];cout << j << ' ';}cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);int T = 1;
// cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}参考题解4(使用stl的双链表list头插法顺序遍历):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
list<int> a;
void solve(){int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) a.push_front(t);for(auto i = a.begin();i!=a.end();i++){cout << *i << ' ';}cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);int T = 1;
// cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}参考题解5(使用stl的双链表list尾插法逆序遍历):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
list<int> a;
void solve(){int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) a.push_back(t);for(auto i = a.rbegin();i!=a.rend();i++){cout << *i << ' ';}cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);int T = 1;
// cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}参考题解6(手搓单链表):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ElemType int
struct LNode{ElemType data;LNode *next;
};
LNode *init(){LNode *head;head=(LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));head->next=NULL;return head;
}
void add_to_head(LNode *head,ElemType x){LNode *p;p = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));p->data=x;p->next=head->next;head->next=p;
}
void add_to_tail(LNode *head,ElemType x){LNode *p;p = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));p->data=x;p->next=NULL;if(head->next==NULL){head->next=p;}else{LNode *q;q=head->next;while(q->next!=NULL) q=q->next;q->next=p;}
}
LNode *find_x(LNode *head,ElemType x){LNode *p;p = head->next;while(p->data!=x&&p->next!=NULL){p=p->next;}if(p->next==NULL) return head;else return p;
}
void delete_k(LNode *head,LNode *p){if(head->next==NULL){cout << "delete is failed.\n";}LNode *q;q = head;while(q->next!=p){q=q->next;}q->next=p->next;free(p);
}
LNode *find_max_element(LNode *head,ElemType &max_element){if(head->next==NULL) return head;LNode *p,*q;p = head->next;while(p->next!=NULL){if(p->data>max_element){max_element=p->data;q = p;}p=p->next;}if(p->data>max_element){max_element=p->data;q = p;}return q;
}
LNode *sort_LNode(LNode *head){if(head->next==NULL){cout << "the LNode which you wanna sort is empty!\n";return head;}LNode *p,*q,*pos;p = head;q = init();ElemType max_element = -1;pos=find_max_element(p,max_element);while(pos!=p){add_to_head(q,pos->data);delete_k(p,pos);max_element = -1;pos=find_max_element(p,max_element);}return q;
}
LNode *merge_LNode(LNode *head1,LNode *head2){if(head1->next==NULL&&head2->next==NULL){cout << "two of LNodes is empty!\n";return head1;}LNode *p;p = head1;while(p->next!=NULL){p=p->next;}p->next=head2->next;free(head2);return head1;
}
void print(LNode *head){if(head->next==NULL){cout << "This LNode is empty!\n";return;}LNode *p;p=head->next;while(p->next!=NULL){cout << p->data << ' ';p=p->next;}cout << p->data << '\n';
}
void solve(){LNode *L = init();ElemType t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) add_to_head(L,t);print(L);
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);int T = 1;
// cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}问题 B: 顺向链表建立
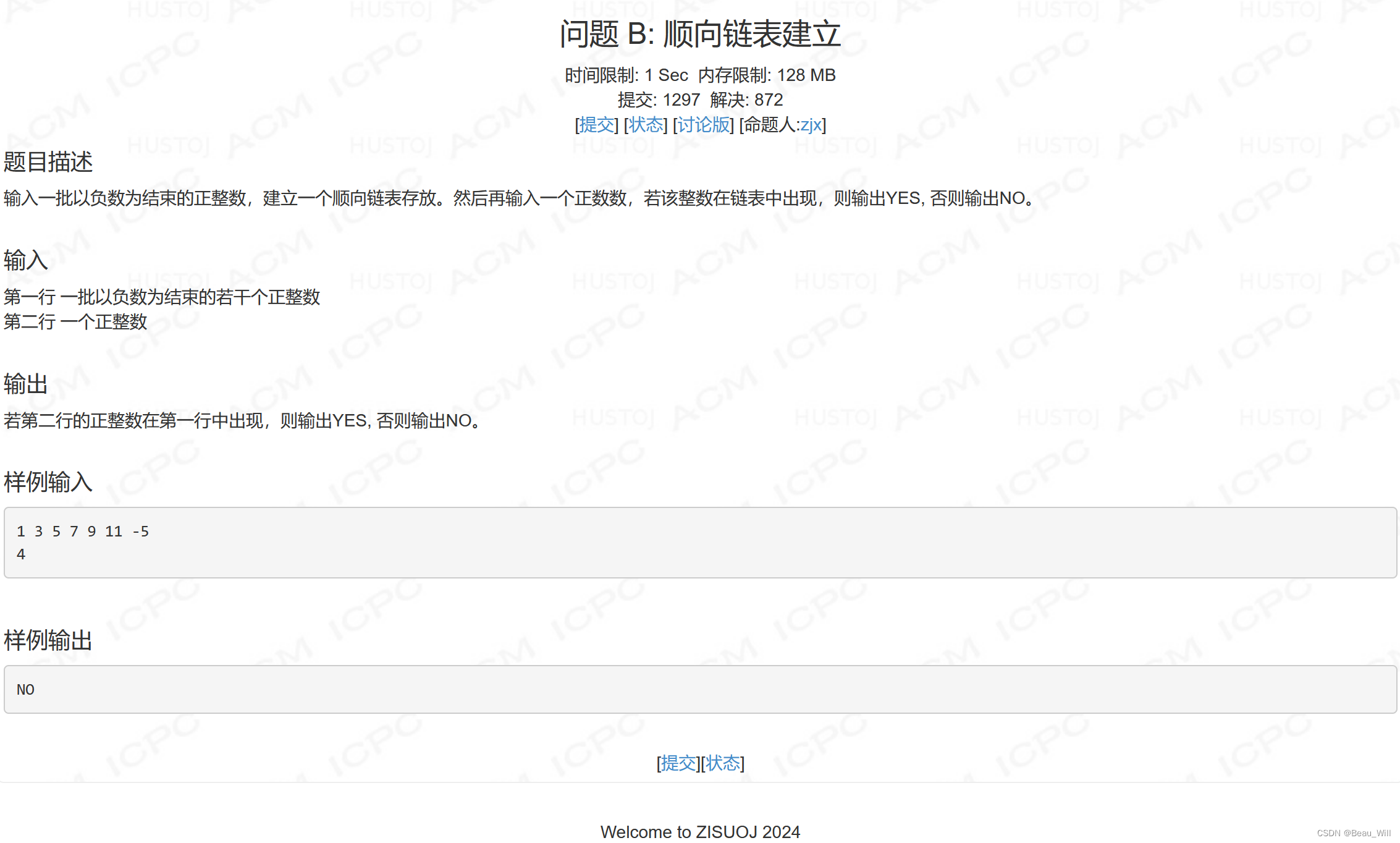
思路:
这个题头插还是尾插法不影响查找,只要遍历一遍链表判断即可。
参考题解1(数组模拟单链表):
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
constexpr int N = 1e5+5;
int head,e[N],ne[N],idx;//数组模拟链表
void init(){//链表初始化 head=-1;idx=0;
}
void add(int x){//头插法 e[idx]=x,ne[idx]=head,head=idx++;
}
void solve(){init();int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) add(t);int x;cin >> x;for(int i = head;i!=-1;i=ne[i]){int j = e[i];if(x==j){cout << "YES\n";return;}}cout << "NO\n";
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);int T = 1;//cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}参考题解2(使用stl的list):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
list<int> a;
void solve(){int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) a.push_back(t);int x;cin >> x;for(auto i = a.begin();i!=a.end();i++){if(*i==x){cout << "YES\n";return;}}cout << "NO\n";
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);int T = 1;
// cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}问题 C: 结点删除
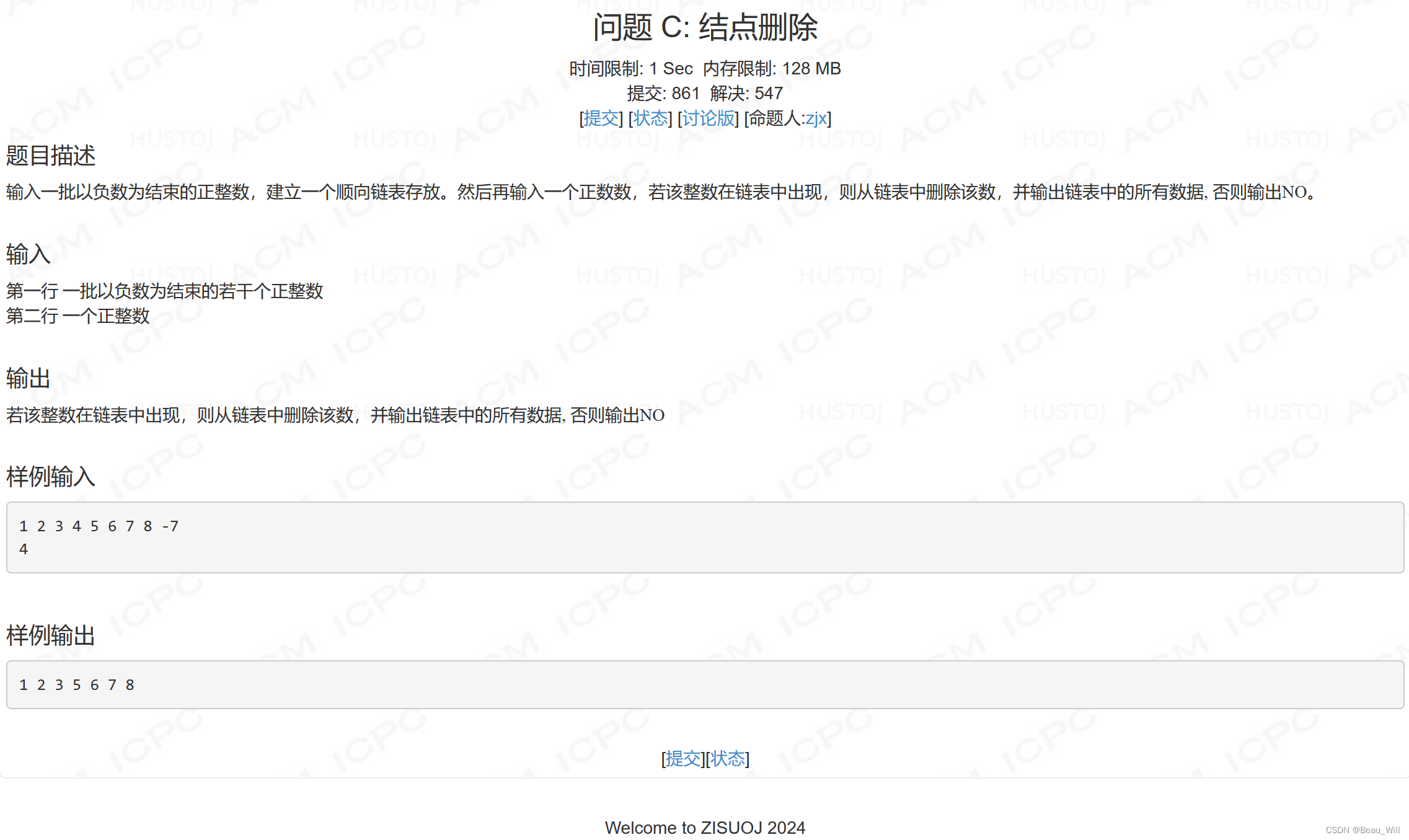
思路:
其实题目的意思,如果重复出现要找的数都要删除它,这里既以使用数组模拟双链表删除,但使用stl的list进行删除指定元素更加便捷。
参考题解:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
list<int> a;
void solve(){int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) a.push_back(t);int x;cin >> x;//要查找的数 if(find(a.begin(),a.end(),x)==a.end()) cout << "NO\n";else{a.remove(x);for(auto i=a.begin();i!=a.end();i++) cout << *i << ' ';cout << '\n';}
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);int T = 1;
// cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}问题 D: 有序链表
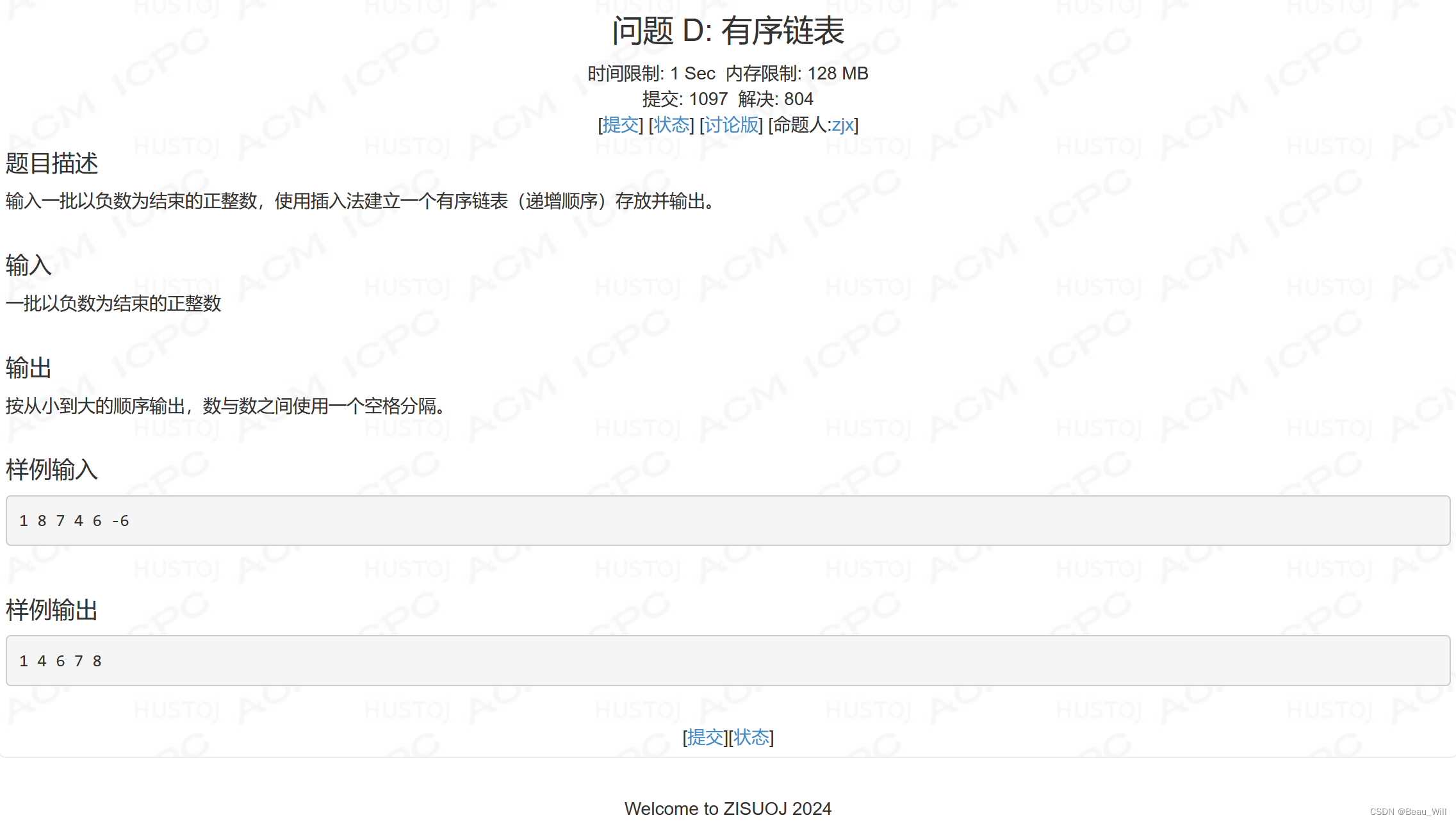
思路:
可以使用数组模拟两个单链表,每次循环找第一个链表里的最大值,然后将这个最大值头插到第二个链表并删除第一个链表中的该节点,最后遍历输出第二个链表即可。当然,用stl的list写起来更快。
参考题解1(数组模拟两个单链表求解):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
constexpr int N = 1e4+5;
int e1[N],l1[N],r1[N],idx1;
int e2[N],l2[N],r2[N],idx2;
void init(int (&l)[N],int (&r)[N],int &idx){r[0]=1,l[1]=0,idx=2;
}
void add(int (&e)[N],int (&l)[N],int (&r)[N],int &idx,int k,int x){e[idx]=x;r[idx]=r[k],l[idx]=k;l[r[k]]=idx,r[l[k]]=idx++;
}
void remove(int (&l)[N],int (&r)[N],int k){l[r[k]]=l[k],r[l[k]]=r[k];
}
void solve(){init(l1,r1,idx1);//初始化链表 int t,cnt=0;//cnt用于记录链表的大小(元素个数)while(cin >> t,t>=0) add(e1,l1,r1,idx1,0,t),cnt++;int maxn=-1,maxidx;init(l2,r2,idx2);//初始化结果链表 for(int k = 1;k<=cnt;k++){maxn=-1;for(int i = 0;i!=1;i=r1[i]){if(i==0) continue;int j = e1[i];if(j>maxn){maxn=j;maxidx=i;}}add(e2,l2,r2,idx2,0,maxn);remove(l1,r1,maxidx);}for(int i = 0;i!=1;i=r2[i]){if(i==0) continue;int j = e2[i];cout << j << ' ';}cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);int T = 1;//cin >> T;while(T--) solve(); return 0;
}参考题解2(使用stl的list求解):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
list<int> a;
void solve(){int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) a.push_back(t);a.sort();for(auto i = a.begin();i!=a.end();i++) cout << *i << ' ';cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);int T = 1;
// cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}问题 E: 链表合并

思路:
同理,可以用数组模拟三个双链表,然后循环找前两个链表中的最大值,然后头插到第三个链表中并且删除指定链表中的指定节点,最后遍历输出第三个链表即可。stl的list也能轻松解决。
参考题解1(使用数组模拟三个双链表解决):
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
constexpr int N = 1e4+5;
int e1[N],l1[N],r1[N],idx1;
int e2[N],l2[N],r2[N],idx2;
int e3[N],l3[N],r3[N],idx3;
void init(int (&l)[N],int (&r)[N],int &idx){r[0]=1,l[1]=0,idx=2;
}
void add_to_k(int (&e)[N],int (&l)[N],int (&r)[N],int &idx,int k,int x){e[idx]=x;r[idx]=r[k],l[idx]=k;l[r[k]]=idx,r[l[k]]=idx++;
}
void remove(int (&l)[N],int (&r)[N],int k){l[r[k]]=l[k],r[l[k]]=r[k];
}
void solve(){init(l1,r1,idx1);init(l2,r2,idx2);int t,cnt1=0,cnt2=0;//cnt记录链表的大小 while(cin >> t,t>=0) add_to_k(e1,l1,r1,idx1,0,t),cnt1++;while(cin >> t,t>=0) add_to_k(e2,l2,r2,idx2,0,t),cnt2++;init(l3,r3,idx3);int maxn = -1,maxidx,flag=0;for(int x = 0;x<cnt1+cnt2;x++){maxn=-1;for(int i = 0;i!=1;i=r1[i]){if(i==0) continue;int j = e1[i];if(j>maxn){flag=1;maxn = j;maxidx = i;}}for(int i = 0;i!=1;i=r2[i]){if(i==0) continue;int j = e2[i];if(j>maxn){flag=2;maxn=j;maxidx=i;}}add_to_k(e3,l3,r3,idx3,0,maxn);if(flag==1){remove(l1,r1,maxidx);}else{//flag==2remove(l2,r2,maxidx);}}for(int i = 0;i!=1;i=r3[i]){if(i==0) continue;int j = e3[i];cout << j << ' ';}cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);int T = 1;//cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}参考题解2(stl yyds):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
list<int> a,b;
void solve(){int t;while(cin >> t,t>=0) a.push_back(t);while(cin >> t,t>=0) b.push_back(t);a.splice(a.end(),b);a.sort();for(auto i = a.begin();i!=a.end();i++) cout << *i << ' ';cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);int T = 1;
// cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}问题 F: 双向链表(完善程序)
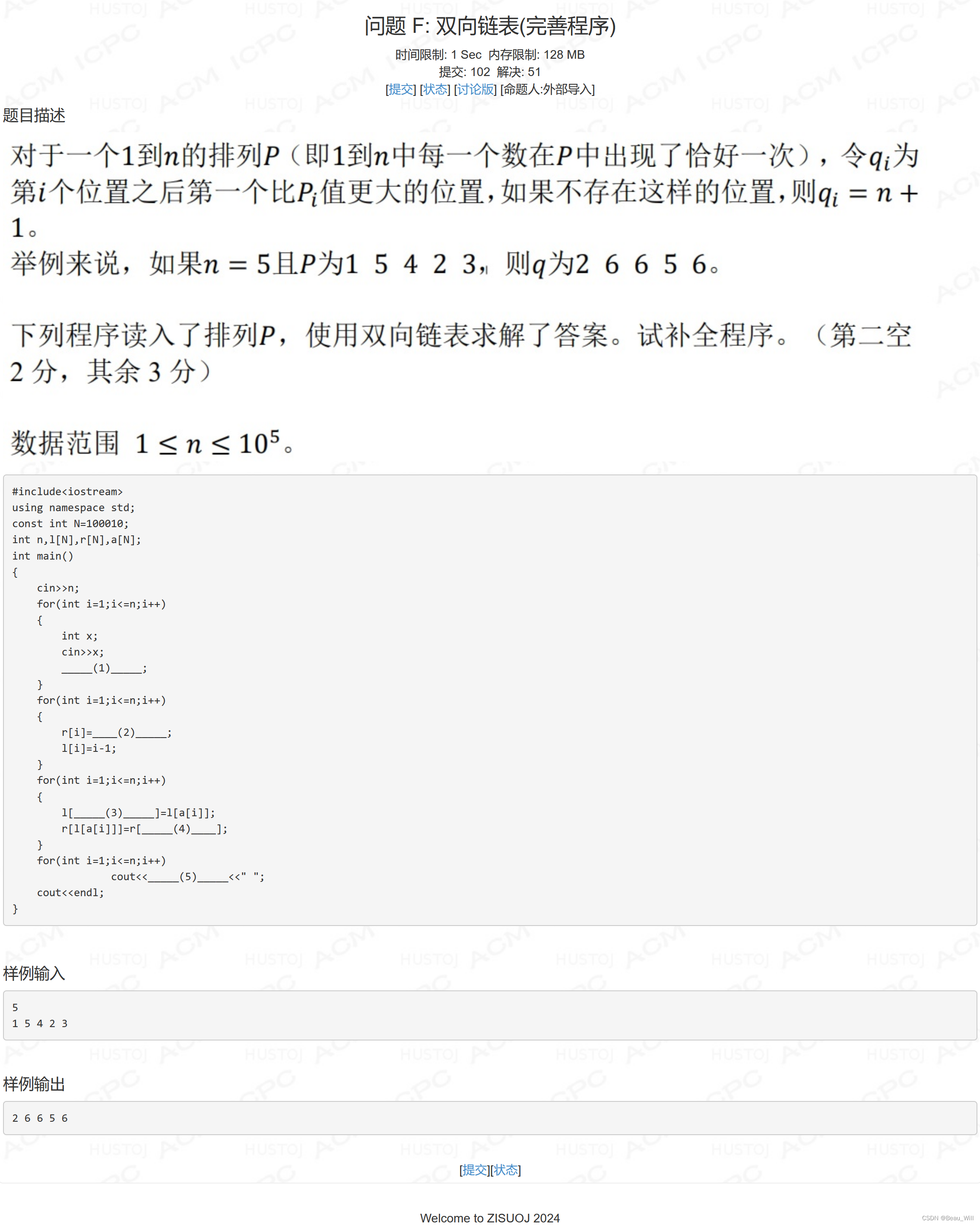
思路:
数组模拟双链表的填空题,想明白最后题目要我们输出的右侧第一个大于它的数,我们可以让每个结点的后继指向第一个大于它的数(若没有,则指向n+1)。
参考题解:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
int n,l[N],r[N],a[N];
int main()
{cin>>n;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){int x;cin>>x;
// _____(1)_____;a[x]=i;}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
// r[i]=____(2)_____;r[i]=i+1;l[i]=i-1;}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
// l[_____(3)_____]=l[a[i]];
// r[l[a[i]]]=r[_____(4)____];l[r[a[i]]]=l[a[i]];r[l[a[i]]]=r[a[i]];}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
// cout<<_____(5)_____<<" ";cout<<r[i]<<" ";cout<<endl;return 0;
}问题 G: 手拉手游戏

思路:
这是上一题F题的具体应用,把F题的代码修改一下搬过来即可。
参考题解:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e2+5;
int n;
int e[N],l[N],r[N],idx;
void solve(){cin >> n;string s;cin >> s;s=' '+s;for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++){int x = s[i]-'0';e[x]=i; }for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++){l[i]=i-1,r[i]=i+1;}for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++){l[r[e[i]]]=l[e[i]];r[l[e[i]]]=r[e[i]];}for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++){cout << r[i];}cout << '\n';
}
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);int T = 1;//cin >> T;while(T--) solve();return 0;
}