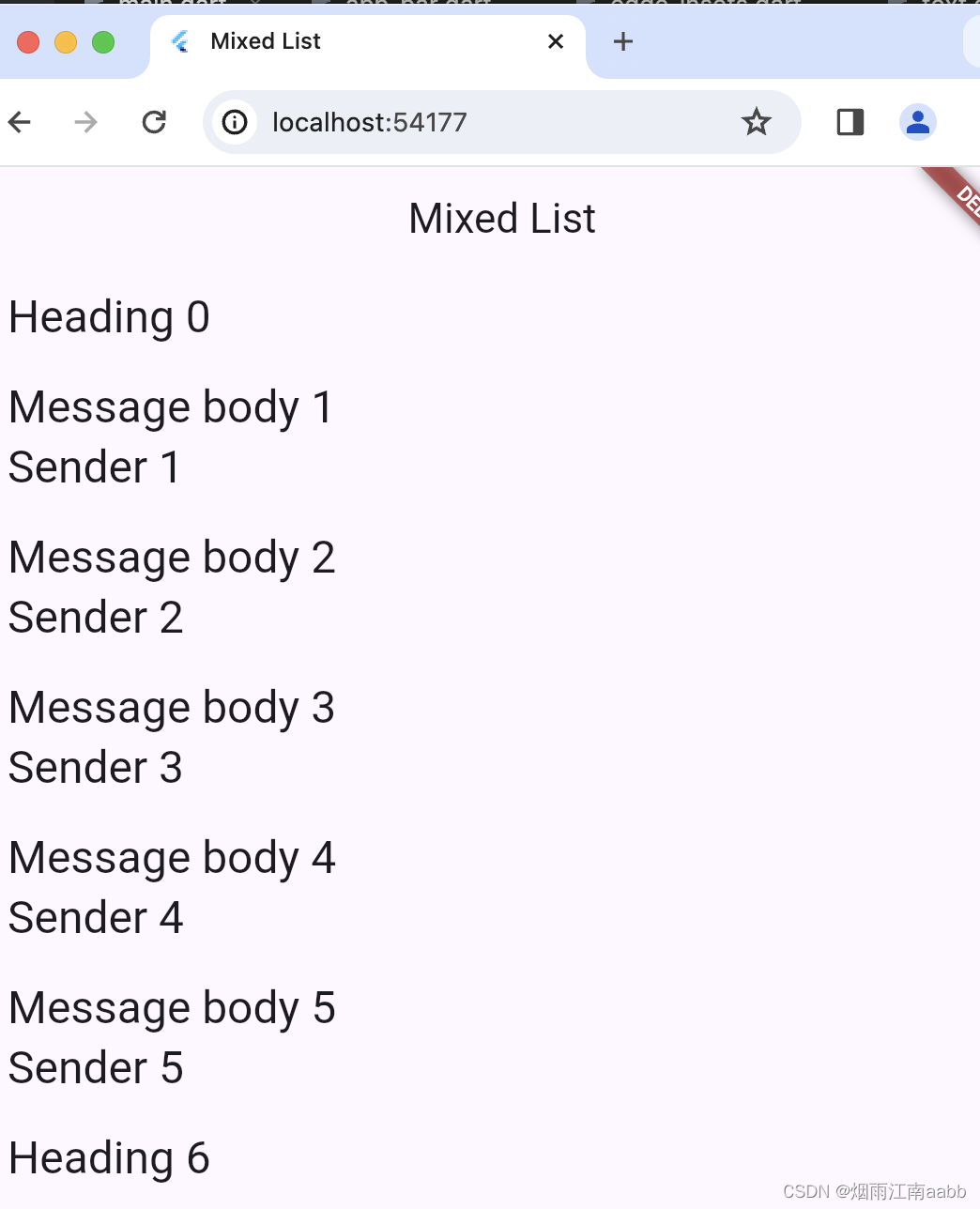
目标:1)项目中,数据源可能涉及不同的模版,显示不同类型的子项,类似RecycleView的itemType, 有多种类型,列表怎么显示?
2)不同的数据源构建列表
一、创建不同的数据源
采用类似RecyclerView的思想,不同的数据源,对应不同的子项Widget进行展现;
因为需要列表项统一展现,因此最好抽取一个子项的公共基类,进行统一处理。
1.1 创建数据源基类
抽取统一基类,列表项显示主标题和副标题。
- 一种子项只显示主标题;
- 另一类子项显示主标题和副标题
/// The base class for the different types of items the list can contain.
abstract class ListItem {/// The title line to show in a list item.Widget buildTitle(BuildContext context);/// The subtitle line, if any, to show in a list item.Widget buildSubtitle(BuildContext context);
}
1.2 创建不同数据源
只有主标题的数据源
/*** 为什么使用implements,而不是extends?* 因为是ListItem的实现类,已经实现ListItem的抽象方法了。* 如果是extends, 意味着HeadingItem不需要实现抽象方法,自身仍然作为抽象类使用*/
class HeadingItem implements ListItem {final String title;/*** 为什么需要const修饰符?*/const HeadingItem(this.title);@overrideWidget buildSubtitle(BuildContext context) {// 创建主标题return Text(title,style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineSmall,);}@overrideWidget buildTitle(BuildContext context) {return const SizedBox.shrink();}
}包含主标题和副标题的数据源
/*** 含有主标题和副标题的列表项*/
class MessageItem implements ListItem {final String title;final String message;const MessageItem(this.title, this.message);@overrideWidget buildSubtitle(BuildContext context) {// 创建主标题return Text(title,style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineSmall,);}@overrideWidget buildTitle(BuildContext context) {// 创建副标题return Text(message,style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineSmall,);}
}二、创建不同数据源的列表
我们知道ListView的子项是ListTile,因此我们需要将数据源填充到ListTile中。
void main() {runApp(MyApp(),);
}class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {const MyApp({super.key});// This widget is the root of your application.@overrideWidget build(BuildContext context) {return MaterialApp(title: 'Flutter Demo',theme: ThemeData(// This is the theme of your application.//// TRY THIS: Try running your application with "flutter run". You'll see// the application has a purple toolbar. Then, without quitting the app,// try changing the seedColor in the colorScheme below to Colors.green// and then invoke "hot reload" (save your changes or press the "hot// reload" button in a Flutter-supported IDE, or press "r" if you used// the command line to start the app).//// Notice that the counter didn't reset back to zero; the application// state is not lost during the reload. To reset the state, use hot// restart instead.//// This works for code too, not just values: Most code changes can be// tested with just a hot reload.colorScheme: ColorScheme.fromSeed(seedColor: Colors.deepPurple),useMaterial3: true,),home: MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'),);}
}@immutable
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {List<ListItem> items = List<ListItem>.generate(1000,(i) => i % 6 == 0? HeadingItem('Heading $i'): MessageItem('Sender $i', 'Message body $i'),);MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect// how it looks.// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are// always marked "final".final String title;@overrideState<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {int _counter = 0;void _incrementCounter() {setState(() {// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen._counter++;});}@overrideWidget build(BuildContext context) {// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done// by the _incrementCounter method above.//// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather// than having to individually change instances of widgets.return Scaffold(appBar: AppBar(// TRY THIS: Try changing the color here to a specific color (to// Colors.amber, perhaps?) and trigger a hot reload to see the AppBar// change color while the other colors stay the same.backgroundColor: Theme.of(context).colorScheme.inversePrimary,// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.title: Text(widget.title),),// 根据数据源创建不同项的列表body: ListView.builder(// 列表项个数itemCount: widget.items.length,// 列表项构建器itemBuilder: (context, index) {// 返回列表项的ListTilereturn ListTile(// 主标题(通过ListItem创建主标题)title: widget.items[index].buildTitle(context),subtitle: widget.items[index].buildSubtitle(context),);},).build(context),floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(onPressed: _incrementCounter,tooltip: 'Increment',child: const Icon(Icons.add),), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.);创建List Tile的时候,采用数据源ListItem进行填充,因为数据源有共同的基类,因此构建ListTile的时候就很方便。
// 根据数据源创建不同项的列表body: ListView.builder(// 列表项个数itemCount: widget.items.length,// 列表项构建器itemBuilder: (context, index) {// 返回列表项的ListTilereturn ListTile(// 主标题(通过ListItem创建主标题)title: widget.items[index].buildTitle(context),subtitle: widget.items[index].buildSubtitle(context),);},).build(context),以下是展现效果。