本文首发于公众号:机器感知
Voice Conversion、DreamScene、X-SLAM、Panoptic-SLAM、DiffMap、TinySeg

Converting Anyone's Voice: End-to-End Expressive Voice Conversion with a Conditional Diffusion Model
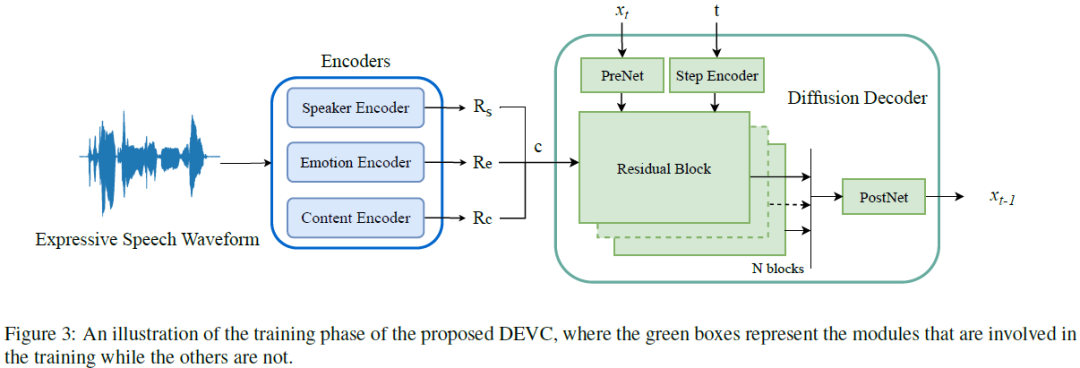
Expressive voice conversion (VC) conducts speaker identity conversion for emotional speakers by jointly converting speaker identity and emotional style. Emotional style modeling for arbitrary speakers in expressive VC has not been extensively explored. Previous approaches have relied on vocoders for speech reconstruction, which makes speech quality heavily dependent on the performance of vocoders. A major challenge of expressive VC lies in emotion prosody modeling. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a fully end-to-end expressive VC framework based on a conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM). We utilize speech units derived from self-supervised speech models as content conditioning, along with deep features extracted from speech emotion recognition and speaker verification systems to model emotional style and speaker identity. Objective and subjective evaluations show the effectiveness of our framework. Codes and samples are publicly available......
DreamScene4D: Dynamic Multi-Object Scene Generation from Monocular Videos
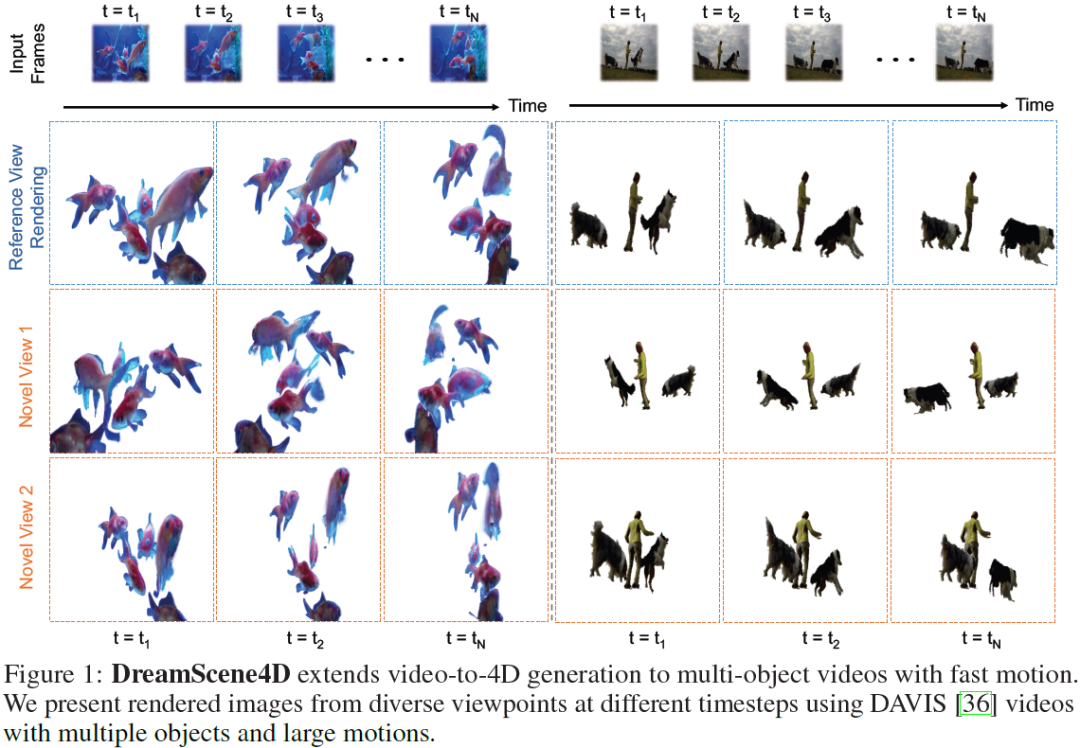

Existing VLMs can track in-the-wild 2D video objects while current generative models provide powerful visual priors for synthesizing novel views for the highly under-constrained 2D-to-3D object lifting. Building upon this exciting progress, we present DreamScene4D, the first approach that can generate three-dimensional dynamic scenes of multiple objects from monocular in-the-wild videos with large object motion across occlusions and novel viewpoints. Our key insight is to design a "decompose-then-recompose" scheme to factorize both the whole video scene and each object's 3D motion. We first decompose the video scene by using open-vocabulary mask trackers and an adapted image diffusion model to segment, track, and amodally complete the objects and background in the video. Each object track is mapped to a set of 3D Gaussians that deform and move in space and time. We also factorize the observed motion into multiple components to handle fast motion. The camera motion can be infe......
X-SLAM: Scalable Dense SLAM for Task-aware Optimization using CSFD
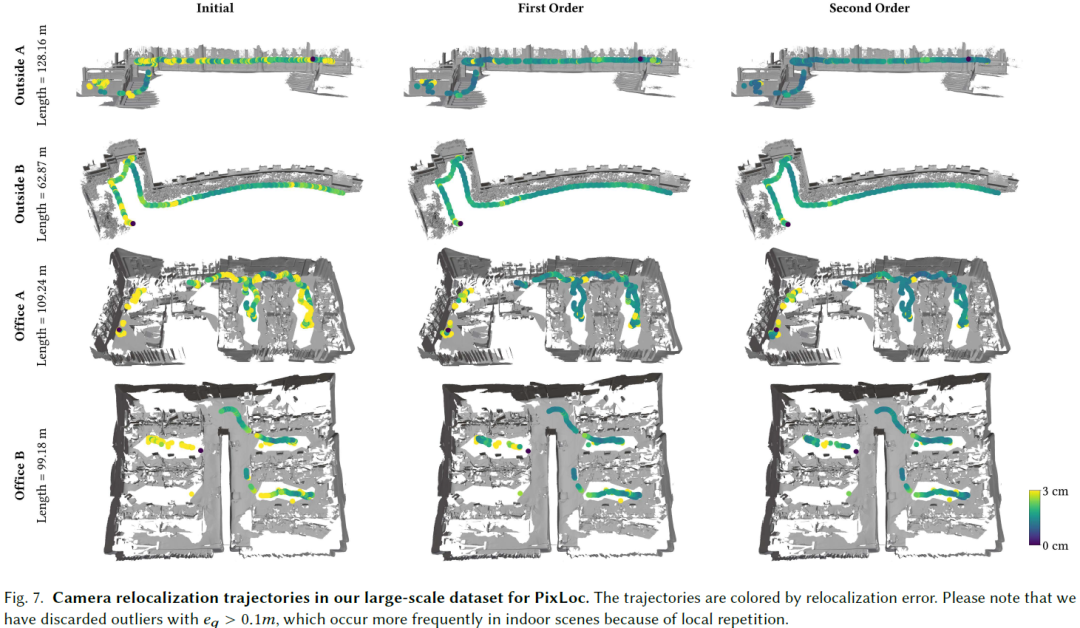
We present X-SLAM, a real-time dense differentiable SLAM system that leverages the complex-step finite difference (CSFD) method for efficient calculation of numerical derivatives, bypassing the need for a large-scale computational graph. The key to our approach is treating the SLAM process as a differentiable function, enabling the calculation of the derivatives of important SLAM parameters through Taylor series expansion within the complex domain. Our system allows for the real-time calculation of not just the gradient, but also higher-order differentiation. This facilitates the use of high-order optimizers to achieve better accuracy and faster convergence. Building on X-SLAM, we implemented end-to-end optimization frameworks for two important tasks: camera relocalization in wide outdoor scenes and active robotic scanning in complex indoor environments. Comprehensive evaluations on public benchmarks and intricate real scenes underscore the improvements in the accuracy of cam......
Panoptic-SLAM: Visual SLAM in Dynamic Environments using Panoptic Segmentation
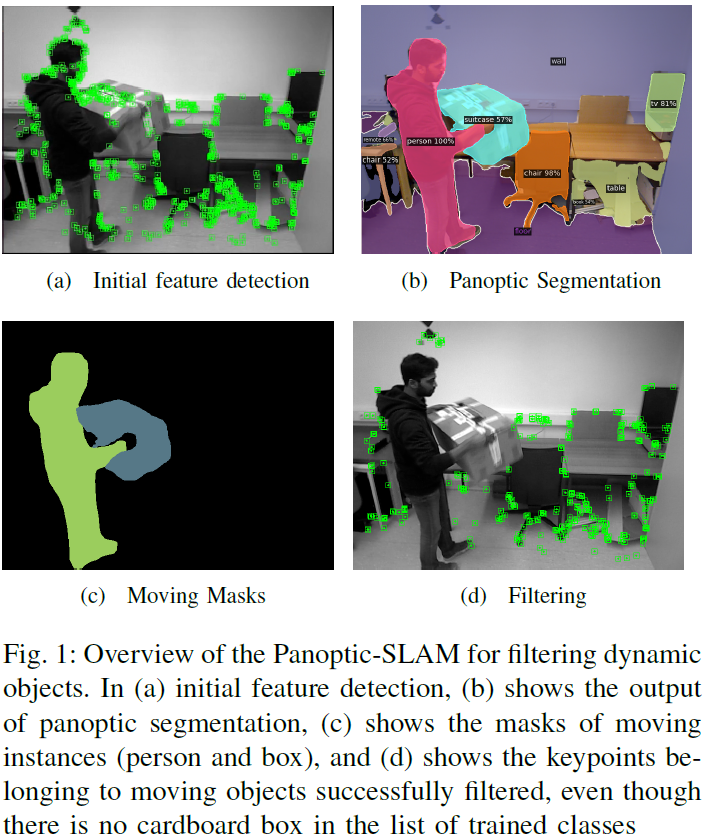
The majority of visual SLAM systems are not robust in dynamic scenarios. The ones that deal with dynamic objects in the scenes usually rely on deep-learning-based methods to detect and filter these objects. However, these methods cannot deal with unknown moving objects. This work presents Panoptic-SLAM, an open-source visual SLAM system robust to dynamic environments, even in the presence of unknown objects. It uses panoptic segmentation to filter dynamic objects from the scene during the state estimation process. Panoptic-SLAM is based on ORB-SLAM3, a state-of-the-art SLAM system for static environments. The implementation was tested using real-world datasets and compared with several state-of-the-art systems from the literature, including DynaSLAM, DS-SLAM, SaD-SLAM, PVO and FusingPanoptic. For example, Panoptic-SLAM is on average four times more accurate than PVO, the most recent panoptic-based approach for visual SLAM. Also, experiments were performed using a quadruped ro......
Characterized Diffusion and Spatial-Temporal Interaction Network for Trajectory Prediction in Autonomous Driving
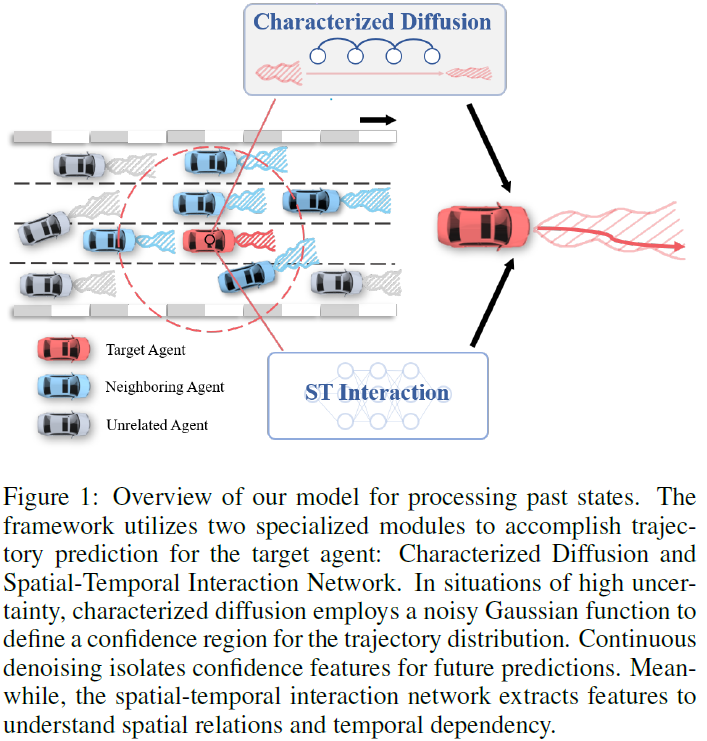
Trajectory prediction is a cornerstone in autonomous driving (AD), playing a critical role in enabling vehicles to navigate safely and efficiently in dynamic environments. To address this task, this paper presents a novel trajectory prediction model tailored for accuracy in the face of heterogeneous and uncertain traffic scenarios. At the heart of this model lies the Characterized Diffusion Module, an innovative module designed to simulate traffic scenarios with inherent uncertainty. This module enriches the predictive process by infusing it with detailed semantic information, thereby enhancing trajectory prediction accuracy. Complementing this, our Spatio-Temporal (ST) Interaction Module captures the nuanced effects of traffic scenarios on vehicle dynamics across both spatial and temporal dimensions with remarkable effectiveness. Demonstrated through exhaustive evaluations, our model sets a new standard in trajectory prediction, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on t......
Probablistic Restoration with Adaptive Noise Sampling for 3D Human Pose Estimation
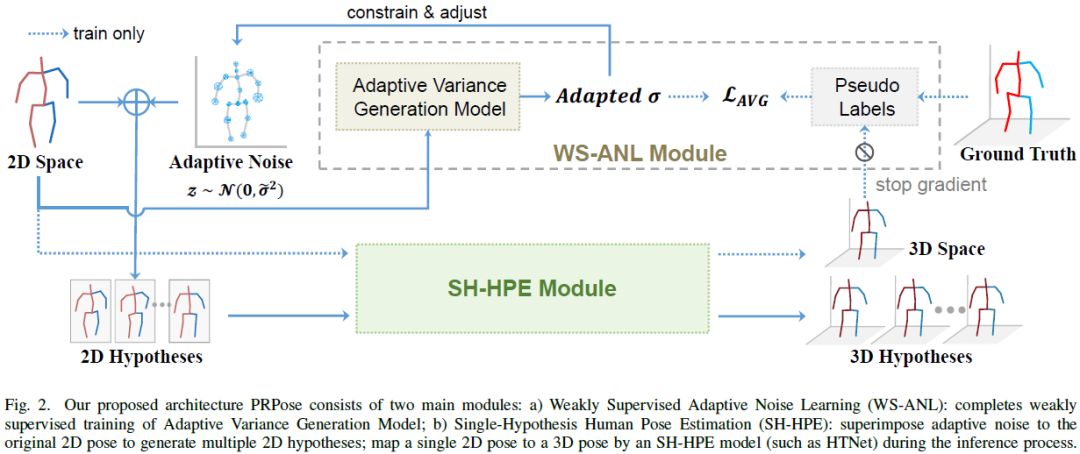
The accuracy and robustness of 3D human pose estimation (HPE) are limited by 2D pose detection errors and 2D to 3D ill-posed challenges, which have drawn great attention to Multi-Hypothesis HPE research. Most existing MH-HPE methods are based on generative models, which are computationally expensive and difficult to train. In this study, we propose a Probabilistic Restoration 3D Human Pose Estimation framework (PRPose) that can be integrated with any lightweight single-hypothesis model. Specifically, PRPose employs a weakly supervised approach to fit the hidden probability distribution of the 2D-to-3D lifting process in the Single-Hypothesis HPE model and then reverse-map the distribution to the 2D pose input through an adaptive noise sampling strategy to generate reasonable multi-hypothesis samples effectively. Extensive experiments on 3D HPE benchmarks (Human3.6M and MPI-INF-3DHP) highlight the effectiveness and efficiency of PRPose. Code is available at: https://github.com......
DiffMap: Enhancing Map Segmentation with Map Prior Using Diffusion Model
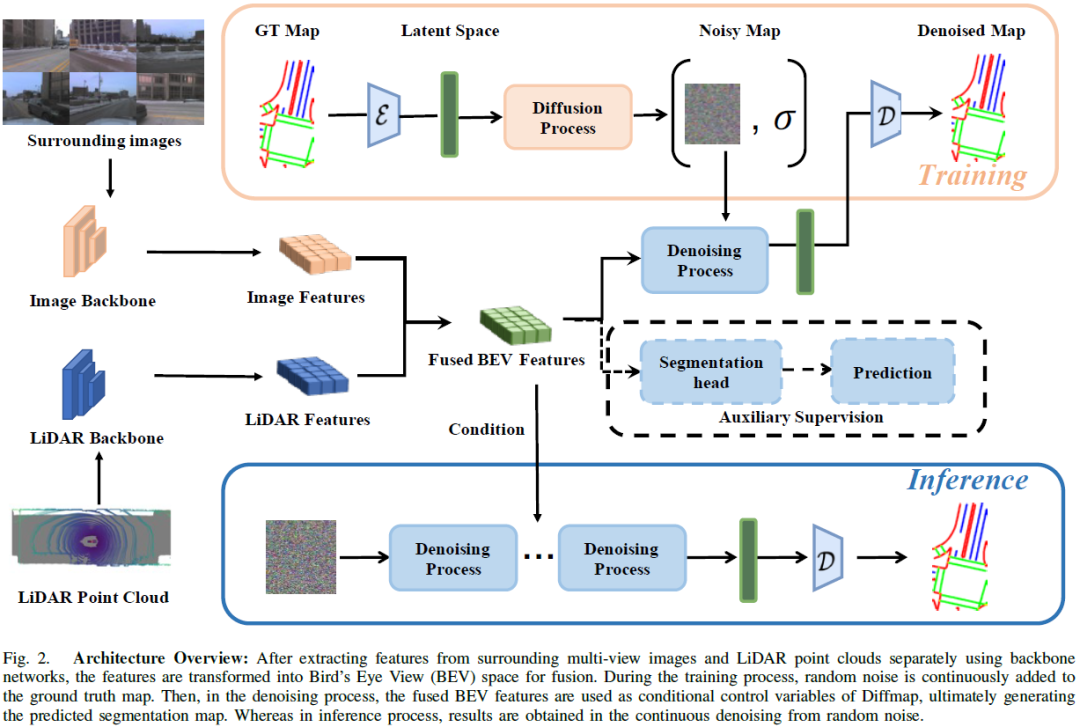
Constructing high-definition (HD) maps is a crucial requirement for enabling autonomous driving. In recent years, several map segmentation algorithms have been developed to address this need, leveraging advancements in Bird's-Eye View (BEV) perception. However, existing models still encounter challenges in producing realistic and consistent semantic map layouts. One prominent issue is the limited utilization of structured priors inherent in map segmentation masks. In light of this, we propose DiffMap, a novel approach specifically designed to model the structured priors of map segmentation masks using latent diffusion model. By incorporating this technique, the performance of existing semantic segmentation methods can be significantly enhanced and certain structural errors present in the segmentation outputs can be effectively rectified. Notably, the proposed module can be seamlessly integrated into any map segmentation model, thereby augmenting its capability to accurately d......
TinySeg: Model Optimizing Framework for Image Segmentation on Tiny Embedded Systems
Image segmentation is one of the major computer vision tasks, which is applicable in a variety of domains, such as autonomous navigation of an unmanned aerial vehicle. However, image segmentation cannot easily materialize on tiny embedded systems because image segmentation models generally have high peak memory usage due to their architectural characteristics. This work finds that image segmentation models unnecessarily require large memory space with an existing tiny machine learning framework. That is, the existing framework cannot effectively manage the memory space for the image segmentation models. This work proposes TinySeg, a new model optimizing framework that enables memory-efficient image segmentation for tiny embedded systems. TinySeg analyzes the lifetimes of tensors in the target model and identifies long-living tensors. Then, TinySeg optimizes the memory usage of the target model mainly with two methods: (i) tensor spilling into local or remote storage and (ii) ......
Efficient and Economic Large Language Model Inference with Attention Offloading
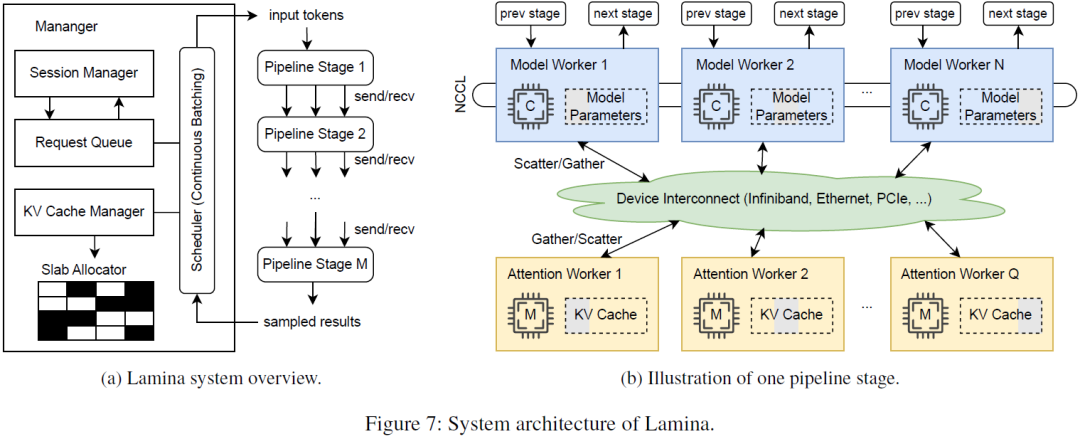
Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) exhibit impressive performance in generative tasks but introduce significant challenges in real-world serving due to inefficient use of the expensive, computation-optimized accelerators. This mismatch arises from the autoregressive nature of LLMs, where the generation phase comprises operators with varying resource demands. Specifically, the attention operator is memory-intensive, exhibiting a memory access pattern that clashes with the strengths of modern accelerators, especially as context length increases. To enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of LLM serving, we introduce the concept of attention offloading. This approach leverages a collection of cheap, memory-optimized devices for the attention operator while still utilizing high-end accelerators for other parts of the model. This heterogeneous setup ensures that each component is tailored to its specific workload, maximizing overall performance and cost efficienc......