LeetCode 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
1、题目
题目链接:106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:
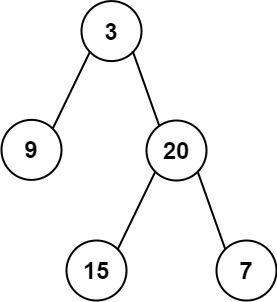
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1]
输出:[-1]
提示:
- 1 <= inorder.length <= 3000
- postorder.length == inorder.length
- -3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000
- inorder 和 postorder 都由 不同 的值组成
- postorder 中每一个值都在 inorder 中
- inorder 保证是树的中序遍历
- postorder 保证是树的后序遍历
2、递归
思路
首先解决这道题我们需要明确给定一棵二叉树,我们是如何对其进行中序遍历与后序遍历的:
中序遍历的顺序是每次遍历左孩子,再遍历根节点,最后遍历右孩子。
后序遍历的顺序是每次遍历左孩子,再遍历右孩子,最后遍历根节点。
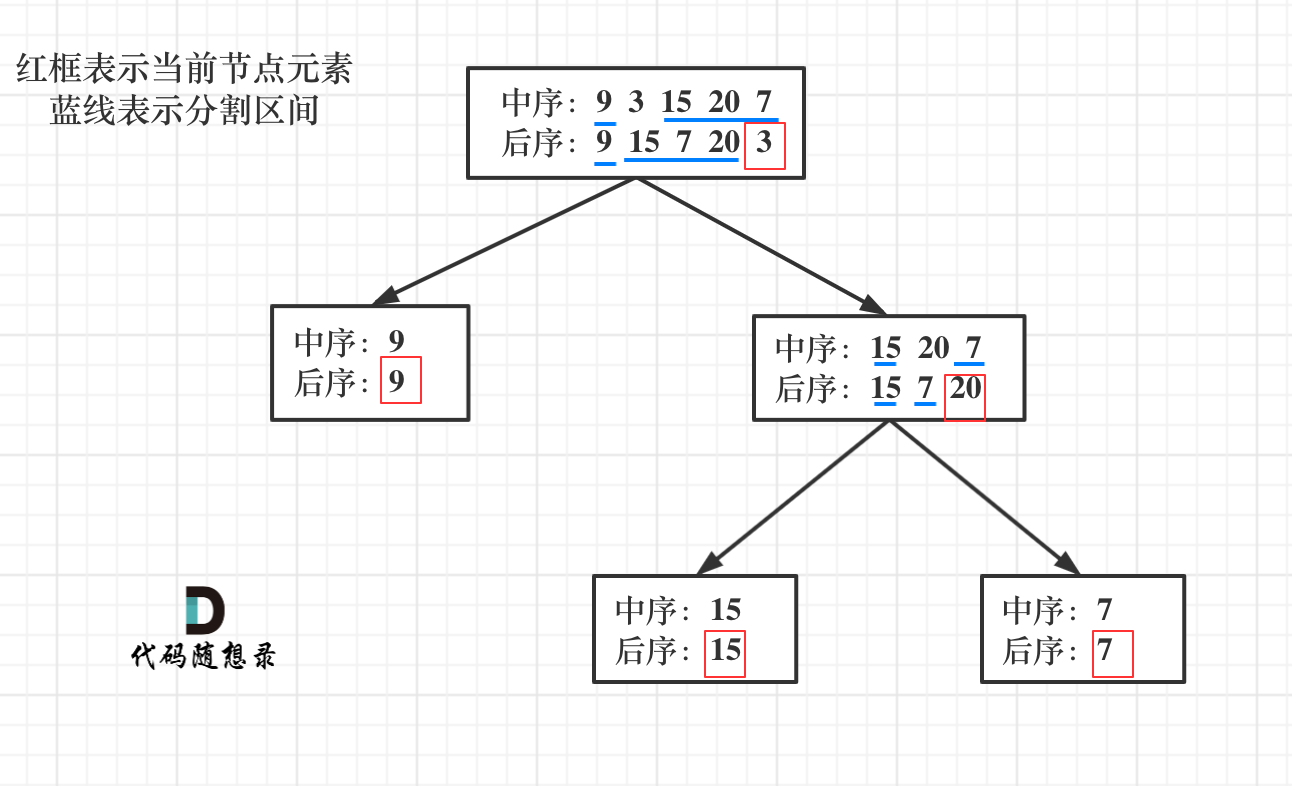
那么如何根据两个顺序构造一个唯一的二叉树,就是以后序数组的最后一个元素为切割点,先切中序数组,根据中序数组,反过来再切后序数组。一层一层切下去,每次后序数组最后一个元素就是节点元素。
流程如图:
那么代码应该怎么写呢?
说到一层一层切割,就应该想到了递归。
来看一下一共分几步:
- 第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
- 第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
- 第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
- 第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
- 第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
- 第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
不难写出如下代码:(先把框架写出来)
TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {// 第一步if (postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;// 第二步:后序遍历数组最后一个元素,就是当前的中间节点int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);// 叶子节点if (postorder.size() == 1) return root;// 第三步:找切割点int delimiterIndex;for (delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < inorder.size(); delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;}// 第四步:切割中序数组,得到 中序左数组和中序右数组// 第五步:切割后序数组,得到 后序左数组和后序右数组// 第六步root->left = traversal(中序左数组, 后序左数组);root->right = traversal(中序右数组, 后序右数组);return root;
}
难点大家应该发现了,就是如何切割,以及边界值找不好很容易乱套。
此时应该注意确定切割的标准,是左闭右开,还有左开右闭,还是左闭右闭,这个就是不变量,要在递归中保持这个不变量。
首先要切割中序数组,为什么先切割中序数组呢?
切割点在后序数组的最后一个元素,就是用这个元素来切割中序数组的,所以必要先切割中序数组。
中序数组相对比较好切,找到切割点(后序数组的最后一个元素)在中序数组的位置,然后切割,如下代码中我坚持左闭右开的原则:
// 找到中序遍历的切割点
int delimiterIndex;
for (delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < inorder.size(); delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;
}// 左闭右开区间:[0, delimiterIndex)
vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex);
// [delimiterIndex + 1, end)
vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex + 1, inorder.end() );
接下来就要切割后序数组了。
首先后序数组的最后一个元素指定不能要了,这是切割点 也是 当前二叉树中间节点的元素,已经用了。
后序数组的切割点怎么找?
后序数组没有明确的切割元素来进行左右切割,不像中序数组有明确的切割点,切割点左右分开就可以了。
此时有一个很重的点,就是中序数组大小一定是和后序数组的大小相同的(这是必然)。
中序数组我们都切成了左中序数组和右中序数组了,那么后序数组就可以按照左中序数组的大小来切割,切成左后序数组和右后序数组。
代码如下:
// postorder 舍弃末尾元素,因为这个元素就是中间节点,已经用过了
postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);// 左闭右开,注意这里使用了左中序数组大小作为切割点:[0, leftInorder.size)
vector<int> leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size());
// [leftInorder.size(), end)
vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end());
此时,中序数组切成了左中序数组和右中序数组,后序数组切割成左后序数组和右后序数组。
接下来可以递归了,代码如下:
root->left = traversal(leftInorder, leftPostorder);
root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);
代码
完整代码如下:
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (postorder.size() == 0) {return nullptr;}// 后序遍历的最后一个元素为根节点的值int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1];// 创建根节点TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);if (postorder.size() == 1) {// 如果后序遍历数组只有一个元素,则直接返回根节点return root;}int delimiterIndex;// 在中序遍历数组中找到根节点的位置for (delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < postorder.size(); delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) {break;}}// 切割中序遍历数组,得到左子树和右子树的中序遍历数组// 左闭右开区间:[0, delimiterIndex)vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex);// 左闭右开区间:[delimiterIndex + 1, end)vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex + 1, inorder.end());// postorder 舍弃末尾元素postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);// 切割后序遍历数组,得到左子树和右子树的后序遍历数组// 依然左闭右开,注意这里使用了左中序数组大小作为切割点// 左闭右开区间:[0, leftInorder.size())vector<int> leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size());// 左闭右开区间:[leftInorder.size(), end)vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end());// 递归构建左子树和右子树,并连接到根节点上root->left = traversal(leftInorder, leftPostorder);root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) {// 如果中序遍历或后序遍历的数组为空,则返回空指针return nullptr;}// 调用traversal函数构建树return traversal(inorder, postorder);}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
3、递归(带日志)
思路
相信大家自己就算是思路清晰, 代码写出来一定是各种问题,所以一定要加日志来调试,看看是不是按照自己思路来切割的,不要大脑模拟,那样越想越糊涂。
加了日志的代码如下:(加了日志的代码不要在leetcode上提交,容易超时)
代码
class Solution {
private:TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);if (postorder.size() == 1) return root;int delimiterIndex;for (delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < inorder.size(); delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;}vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex);vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex + 1, inorder.end() );postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);vector<int> leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size());vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end());// 以下为日志cout << "----------" << endl;cout << "leftInorder :";for (int i : leftInorder) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "rightInorder :";for (int i : rightInorder) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "leftPostorder :";for (int i : leftPostorder) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "rightPostorder :";for (int i : rightPostorder) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;root->left = traversal(leftInorder, leftPostorder);root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);return root;}
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;return traversal(inorder, postorder);}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
4、递归(索引)
思路
此时应该发现了,如上的代码性能并不好,因为每层递归定义了新的vector(就是数组),既耗时又耗空间,但上面的代码是最好理解的,为了方便读者理解,所以用如上的代码来讲解。
下面给出用下标索引写出的代码版本:(思路是一样的,只不过不用重复定义vector了,每次用下标索引来分割)
代码
class Solution {
private:// 中序区间:[inorderBegin, inorderEnd),后序区间[postorderBegin, postorderEnd)TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, int inorderBegin, int inorderEnd, vector<int>& postorder, int postorderBegin, int postorderEnd) {if (postorderBegin == postorderEnd) return NULL;int rootValue = postorder[postorderEnd - 1];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);if (postorderEnd - postorderBegin == 1) return root;int delimiterIndex;for (delimiterIndex = inorderBegin; delimiterIndex < inorderEnd; delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;}// 切割中序数组// 左中序区间,左闭右开[leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd)int leftInorderBegin = inorderBegin;int leftInorderEnd = delimiterIndex;// 右中序区间,左闭右开[rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd)int rightInorderBegin = delimiterIndex + 1;int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd;// 切割后序数组// 左后序区间,左闭右开[leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd)int leftPostorderBegin = postorderBegin;int leftPostorderEnd = postorderBegin + delimiterIndex - inorderBegin; // 终止位置是 需要加上 中序区间的大小size// 右后序区间,左闭右开[rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd)int rightPostorderBegin = postorderBegin + (delimiterIndex - inorderBegin);int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd - 1; // 排除最后一个元素,已经作为节点了root->left = traversal(inorder, leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd);root->right = traversal(inorder, rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd);return root;}
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;// 左闭右开的原则return traversal(inorder, 0, inorder.size(), postorder, 0, postorder.size());}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
5、递归(索引带日志)
思路
那么这个版本写出来依然要打日志进行调试,打日志的版本如下:(该版本不要在leetcode上提交,容易超时)
代码
class Solution {
private:TreeNode* traversal (vector<int>& inorder, int inorderBegin, int inorderEnd, vector<int>& postorder, int postorderBegin, int postorderEnd) {if (postorderBegin == postorderEnd) return NULL;int rootValue = postorder[postorderEnd - 1];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);if (postorderEnd - postorderBegin == 1) return root;int delimiterIndex;for (delimiterIndex = inorderBegin; delimiterIndex < inorderEnd; delimiterIndex++) {if (inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;}// 切割中序数组// 左中序区间,左闭右开[leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd)int leftInorderBegin = inorderBegin;int leftInorderEnd = delimiterIndex;// 右中序区间,左闭右开[rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd)int rightInorderBegin = delimiterIndex + 1;int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd;// 切割后序数组// 左后序区间,左闭右开[leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd)int leftPostorderBegin = postorderBegin;int leftPostorderEnd = postorderBegin + delimiterIndex - inorderBegin; // 终止位置是 需要加上 中序区间的大小size// 右后序区间,左闭右开[rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd)int rightPostorderBegin = postorderBegin + (delimiterIndex - inorderBegin);int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd - 1; // 排除最后一个元素,已经作为节点了cout << "----------" << endl;cout << "leftInorder :";for (int i = leftInorderBegin; i < leftInorderEnd; i++) {cout << inorder[i] << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "rightInorder :";for (int i = rightInorderBegin; i < rightInorderEnd; i++) {cout << inorder[i] << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "leftpostorder :";for (int i = leftPostorderBegin; i < leftPostorderEnd; i++) {cout << postorder[i] << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "rightpostorder :";for (int i = rightPostorderBegin; i < rightPostorderEnd; i++) {cout << postorder[i] << " ";}cout << endl;root->left = traversal(inorder, leftInorderBegin, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderBegin, leftPostorderEnd);root->right = traversal(inorder, rightInorderBegin, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderBegin, rightPostorderEnd);return root;}
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;return traversal(inorder, 0, inorder.size(), postorder, 0, postorder.size());}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
6、递归(使用unordered_map)
思路
为了高效查找根节点元素在中序遍历数组中的下标,我们选择创建哈希表来存储中序序列,即建立一个(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表。
代码
class Solution {int post_idx;unordered_map<int, int> idx_map;
public:TreeNode* helper(int in_left, int in_right, vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder){// 如果这里没有节点构造二叉树了,就结束if (in_left > in_right) {return nullptr;}// 选择 post_idx 位置的元素作为当前子树根节点int root_val = postorder[post_idx];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root_val);// 根据 root 所在位置分成左右两棵子树int index = idx_map[root_val];// 下标减一post_idx--;// 构造右子树root->right = helper(index + 1, in_right, inorder, postorder);// 构造左子树root->left = helper(in_left, index - 1, inorder, postorder);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {// 从后序遍历的最后一个元素开始post_idx = (int)postorder.size() - 1;// 建立(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表int idx = 0;for (auto& val : inorder) {idx_map[val] = idx++;}return helper(0, (int)inorder.size() - 1, inorder, postorder);}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
7、迭代
思路
为了高效查找根节点元素在中序遍历数组中的下标,我们选择创建哈希表来存储中序序列,即建立一个(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表。
代码
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {// 如果后序遍历数组为空,则返回空指针if (postorder.size() == 0) {return nullptr;}// 创建根节点,其值为后序遍历数组的最后一个元素auto root = new TreeNode(postorder[postorder.size() - 1]);// 创建一个栈,用于存储节点指针auto s = stack<TreeNode*>();// 将根节点入栈s.push(root);// 初始化中序遍历数组的索引int inorderIndex = inorder.size() - 1;// 从后序遍历数组的倒数第二个元素开始遍历for (int i = int(postorder.size()) - 2; i >= 0; i--) {// 当前遍历的后序遍历数组的值int postorderVal = postorder[i];// 获取栈顶节点auto node = s.top();// 如果栈顶节点的值不等于中序遍历数组当前索引的值if (node->val != inorder[inorderIndex]) {// 将当前后序遍历数组的值作为右子节点,并创建新的节点node->right = new TreeNode(postorderVal);// 将右子节点入栈s.push(node->right);} else {// 当栈不为空且栈顶节点的值等于中序遍历数组当前索引的值时while (!s.empty() && s.top()->val == inorder[inorderIndex]) {// 弹出栈顶节点node = s.top();s.pop();// 中序遍历数组索引减一inorderIndex--;}// 将当前后序遍历数组的值作为左子节点,并创建新的节点node->left = new TreeNode(postorderVal);// 将左子节点入栈s.push(node->left);}}// 返回根节点return root;}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)



![[Cmake Qt]找不到文件ui_xx.h的问题?有关Qt工程的问题,看这篇文章就行了。](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/4d470e5051ee4aa4918a1c7adee44b25.png)