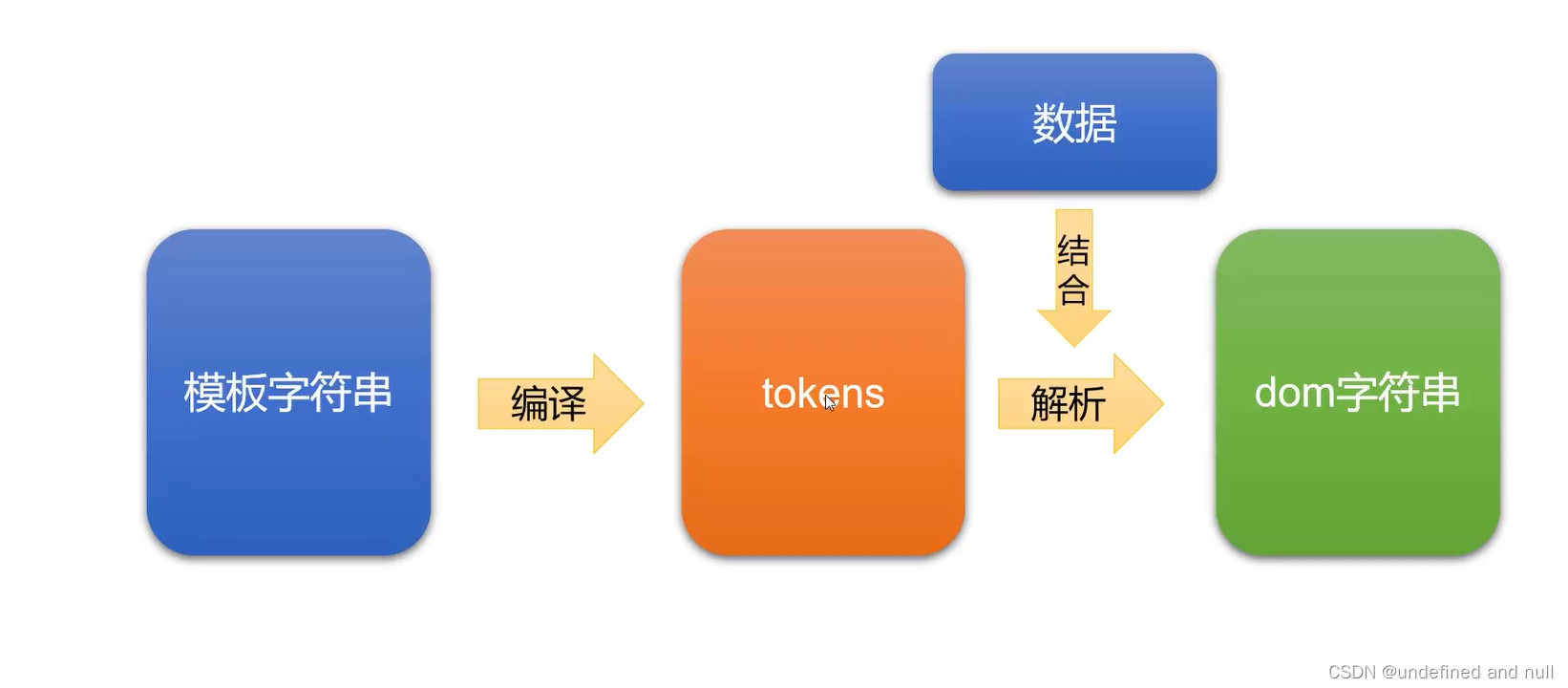
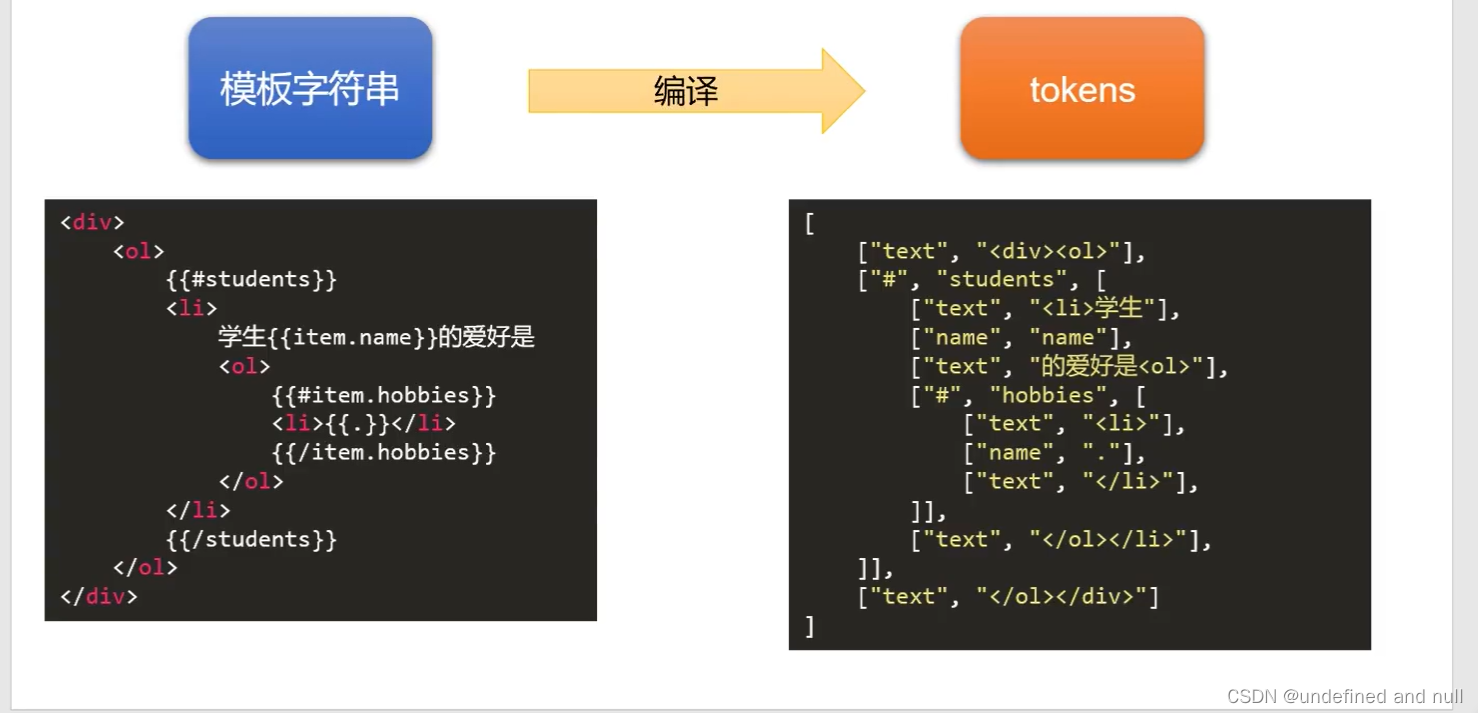
vue之mustache库的机理其实是将模板字符串转化为tokens 然后再将 tokens 转化为 dom字符串,如下图
对于一般的将模板字符串转化为dom字符串,这样不能实现复杂的功能
let data = {name:'小王',age:18
}
let templateStr = `<h1>我叫{{name}},我今年{{age}}岁<h1>
`
templateStr = templateStr.trim()let htmlStr = templateStr.replace(/\{{(\w+)}}/g,function(match,$1,index){//第一个参数为他寻找的部分,第二个为捕获的东西,第三个所在的位置,第四个为该字符串return data[$1] })
console.log(htmlStr) //我叫小王,我今年18岁将模板字符串转化为tokens
前面已经知道了musache的工作原理为 将模板字符串转化为tokens,然后再将tokens转化为BOM字符串所以此小节的任务为:
class Scanner {constructor (templateStr ){//将模板字符串写到实例身上this.templateStr = templateStr//指针this.pos = 0//尾巴,刚开始为字符串本身this.tail = templateStr}//让指针跳过目标,进而扫描后面的内容scan(target){this.pos += target.lengththis.tail = this.templateStr.substring(this.pos)}//扫描字符串,直到扫描到目标,返回目标之前的字符串scanUtil(target) {let recordPosValue = this.pos//如果该字符串的地一个元素即该目标的索引不为0时,说明指针还需要往右走while(this.tail.indexOf(target)!=0&&this.pos<this.templateStr.length){this.pos++;//尾巴变为pos后面的部分this.tail = this.templateStr.substring(this.pos)}return this.templateStr.substring(recordPosValue,this.pos)}
}
export default function becomeEasyToken (templateStr){let token = []//实例化一个扫描器,针对模板字符串工作let scanner = new Scanner(templateStr)while(scanner.pos<templateStr.length){let word;word = scanner.scanUtil('{{');if(word !=''){token.push(["text",word])}scanner.scan('{{')word = scanner.scanUtil("}}")if(word !=''){if(word[0] == "#"){token.push(["#",word.substring(1)])}else if(word[0]=="/"){token.push(['/',word.substring(1)])}else{token.push(["name",word])}}scanner.scan("}}")}return token
}以上代码没有处理 "#" 的循环功能 ,所以还必须添加一个函数,并对该返回值稍加修改
import foldToken from "./foldToken";
export default function becomeEasyToken (templateStr){let token = []//实例化一个扫描器,针对模板字符串工作let scanner = new Scanner(templateStr)while(scanner.pos<templateStr.length){let word;word = scanner.scanUtil('{{');if(word !=''){token.push(["text",word])}scanner.scan('{{')word = scanner.scanUtil("}}")if(word !=''){if(word[0] == "#"){token.push(["#",word.substring(1)])}else if(word[0]=="/"){token.push(['/',word.substring(1)])}else{token.push(["name",word])}}scanner.scan("}}")}return foldToken(token)
}
export default function foldToken(tokens) {//结果数组let nestedTokens = []//栈结构,存放小tokenslet section = [];//与nestedTokens指向的是同一数组,该数组为一级数组let collentor = nestedTokensfor (const item of tokens) {switch (item[0]) {case "#"://进栈section.push(item)collentor.push(item)//创建新一级的数组collentor = item[2] = [] break;case "/"://出栈section.pop(item)//如果都出完了,则回到一级数组,还没出完则回到其上一级collentor = section.length>0?section[section.length-1][2]:nestedTokensbreak;default://仅负责给各级数组添加 "text" 元素collentor.push(item)}}return nestedTokens;
}效果展示: