使用IDEA进入某个类之后,按ctrl+F12,或者alt+数字7,可查看该实现类的大纲。


package exercise;import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.function.Consumer;public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Set<String> s = new HashSet<>();//添加元素//如果当前元素是第一次添加,那么可以添加成功,返回true//如果当前元素是第二次添加,那么添加失败,返回falseboolean s1 = s.add("sundhine");boolean s2 = s.add("sundhine");System.out.println(s1 + " " + s2);s.add("jiuselu");s.add("lulushui");//存、取顺序不一致System.out.println(s);System.out.println("----------------------------");//迭代器遍历Iterator<String> it = s.iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {String next = it.next();System.out.println(next);}System.out.println("----------------------------");//增强for遍历for (String string : s) {System.out.println(string);}System.out.println("----------------------------");//Lambdas.forEach(string -> System.out.println(string));}
}


package exercise;import java.util.Objects;public class Demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.创建对象Student s1 = new Student("sunshien", 23);Student s2 = new Student("sunshien", 23);//2.如果没有重写hashCode方法,不同对象计算出的哈希值是不同的//如果已经重写hashCode方法,不同的对象只要属性值相同,计算出的哈希值就是一样的System.out.println(s1.hashCode());System.out.println(s2.hashCode());//在小部分情况下,不同的属性或者不同的地址值计算出来的哈希值也有可能一样}
}class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}/*** 获取** @return name*/public String getName() {return name;}/*** 设置** @param name*/public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}/*** 获取** @return age*/public int getAge() {return age;}/*** 设置** @param age*/public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, age);}public String toString() {return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";}
}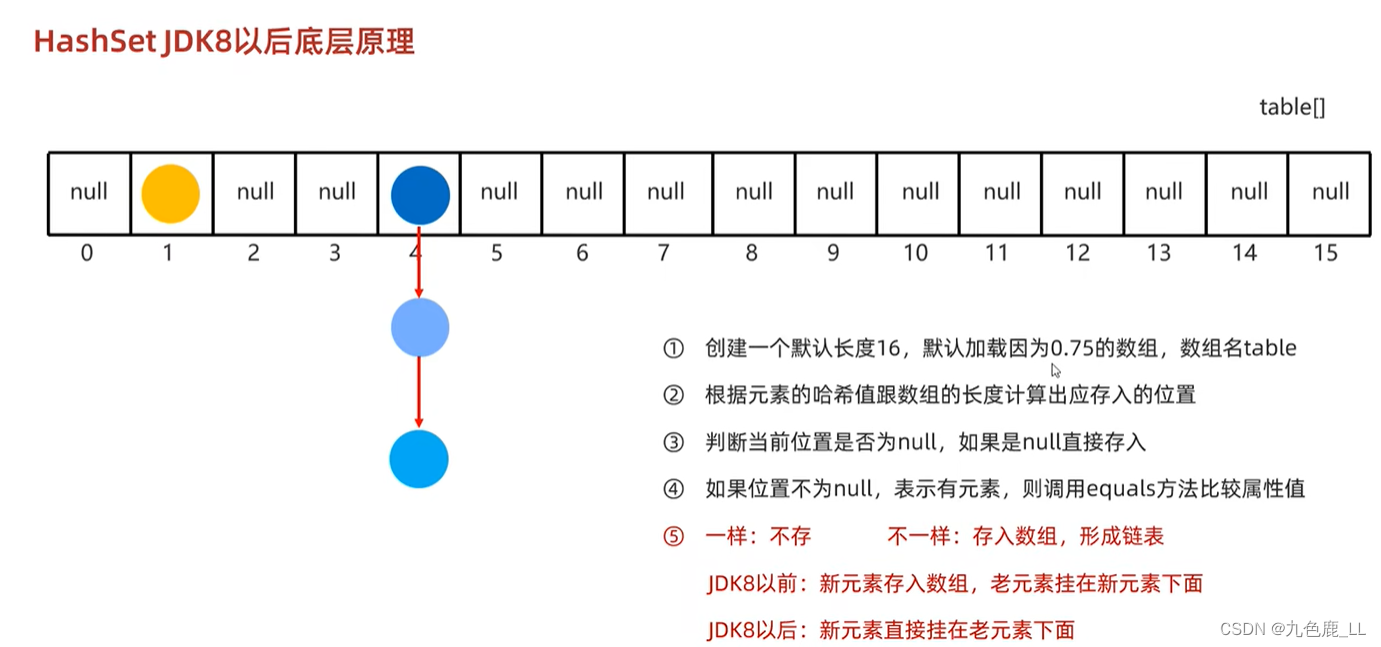
1.加载因子是hashSet的扩容时机,当数组中存了 16*0.75 = 12后(本题为例),原数组就会扩充为原先的两倍。

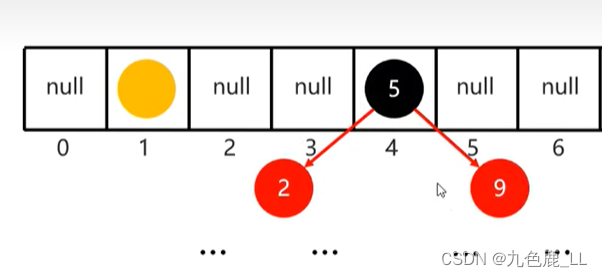

package exercise;import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;public class Demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) {Student s1 = new Student("sunshine", 23);Student s2 = new Student("sunshine", 23);Student s3 = new Student("jiuselu", 24);Student s4 = new Student("lulushui", 23);HashSet<Student> h = new HashSet<>();h.add(s1);h.add(s2);h.add(s3);h.add(s4);for (Student student : h) {System.out.println(student);}}
}class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}/*** 获取** @return name*/public String getName() {return name;}/*** 设置** @param name*/public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}/*** 获取** @return age*/public int getAge() {return age;}/*** 设置** @param age*/public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, age);}public String toString() {return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";}
}
ctrl+shift+上\下箭头可实现某行代码上下移动。
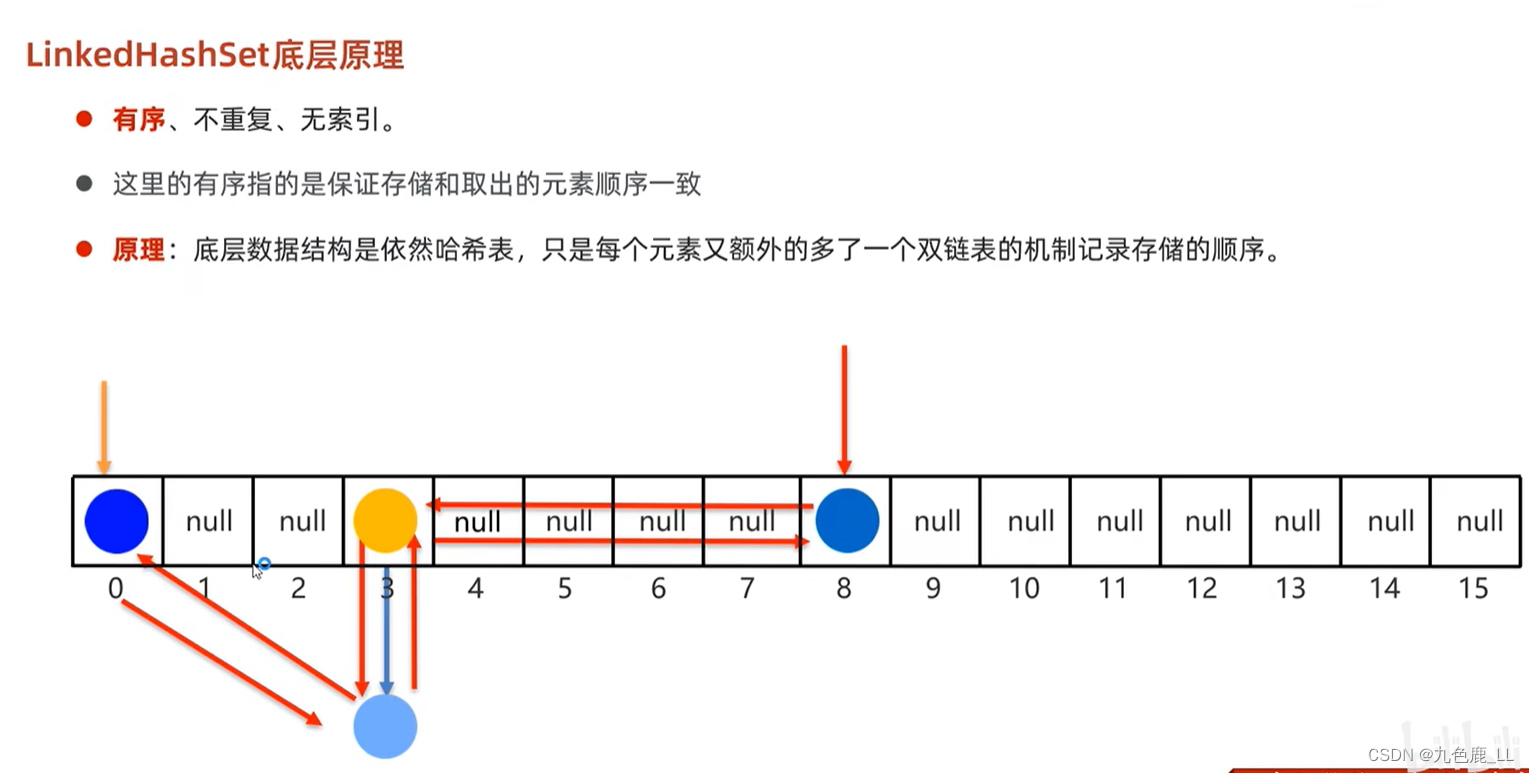
package exercise;import java.util.LinkedHashSet;public class Demo6 {public static void main(String[] args) {Student s1 = new Student("sunshine", 23);Student s2 = new Student("sunshine", 23);Student s3 = new Student("jiuselu", 24);Student s4 = new Student("lulushui", 23);LinkedHashSet<Student> l = new LinkedHashSet<>();l.add(s1);l.add(s2);l.add(s3);l.add(s4);for (Student student : l) {System.out.println(student);}}
}


package exercise;import java.util.TreeSet;public class Demo7 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet<Integer> t = new TreeSet<>();t.add(1);t.add(8);t.add(7);t.add(4);//默认从小到大排序System.out.println(t);}
}

package exercise;import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.TreeSet;public class Demo7 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet<Student> t = new TreeSet<>();Student s1 = new Student("sunshine", 23);Student s3 = new Student("jiuselu", 24);Student s4 = new Student("lulushui", 25);t.add(s1);t.add(s3);t.add(s4);for (Student student : t) {System.out.println(student);}//hashcode和equals方法:哈希表有关的,所以student不用重写。//Treeset:底层是黑树}
}
//泛型要写明类型
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {private String name;private int age;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}/*** 获取** @return name*/public String getName() {return name;}/*** 设置** @param name*/public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}/*** 获取** @return age*/public int getAge() {return age;}/*** 设置** @param age*/public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String toString() {return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {//指定排序的规则//只看年龄,按照年龄升序排列return this.getAge() - o.getAge();/*this:表示当前要添加的元素o:表示已经在红黑树存在的元素返回值:负数:认为要添加的元素是小的,存左边正数:认为要添加的元素是大的,存右边认为要添加的元素已经存在,舍弃*/}
}上述练习实现了第一种排序方式


package exercise;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;public class Demo8 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<String>() {@Override//o1:表示当前要添加的元素//o2:表示已经在红黑树存在的元素//返回值规则跟之前是一样的public int compare(String o1, String o2) {//按长度排序int i = o1.length() - o2.length();i = i == 0 ? o1.compareTo(o2) : i;return i;}});ts.add("c");ts.add("ab");ts.add("df");ts.add("qwer");System.out.println(ts);}
}
package exercise;import java.util.TreeSet;public class Demo9 {public static void main(String[] args) {Student s1 = new Student("sunshine", 23, 23, 34, 45);Student s2 = new Student("jiuselu", 24, 23, 34, 45);Student s3 = new Student("lulushui", 25, 23, 34, 45);Student s4 = new Student("sunshine1", 23, 23, 34, 45);Student s5 = new Student("sunshine2", 23, 23, 34, 45);TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<>();ts.add(s1);ts.add(s2);ts.add(s3);ts.add(s4);ts.add(s5);for (Student t : ts) {System.out.println(t);}}
}class Student implements Comparable<Student> {private String name;private int age;private int chinese;private int math;private int english;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age, int chinese, int math, int english) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.chinese = chinese;this.math = math;this.english = english;}/*** 获取** @return name*/public String getName() {return name;}/*** 设置** @param name*/public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}/*** 获取** @return age*/public int getAge() {return age;}/*** 设置** @param age*/public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}/*** 获取** @return chinese*/public int getChinese() {return chinese;}/*** 设置** @param chinese*/public void setChinese(int chinese) {this.chinese = chinese;}/*** 获取** @return math*/public int getMath() {return math;}/*** 设置** @param math*/public void setMath(int math) {this.math = math;}/*** 获取** @return english*/public int getEnglish() {return english;}/*** 设置** @param english*/public void setEnglish(int english) {this.english = english;}public String toString() {return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + ", chinese = " + chinese + ", math = " + math + ", english = " + english + "sum =" + this.getChinese() + this.getEnglish() + this.getMath()+"}";}//方式一:@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {int sum1 = this.getChinese() + this.getEnglish() + this.getMath();System.out.println(sum1);int sum2 = o.getChinese() + o.getEnglish() + o.getMath();int i = sum1 - sum2;i = i == 0 ? this.chinese - o.chinese : i;i = i == 0 ? this.math - o.math : i;i = i == 0 ? this.english - o.english : i;i = i == 0 ? this.getAge() - o.getAge() : i;i = i == 0 ? this.getName().compareTo(o.getName()) : i;return i;}
}

Java中toString()方法的作用:它通常只是为了方便输出,比如System.out.println(xx),括号里面的“xx”如果不是String类型的话,就自动调用xx的toString()方法。