【Python解决】查询报%d format: a number is required, not str问题
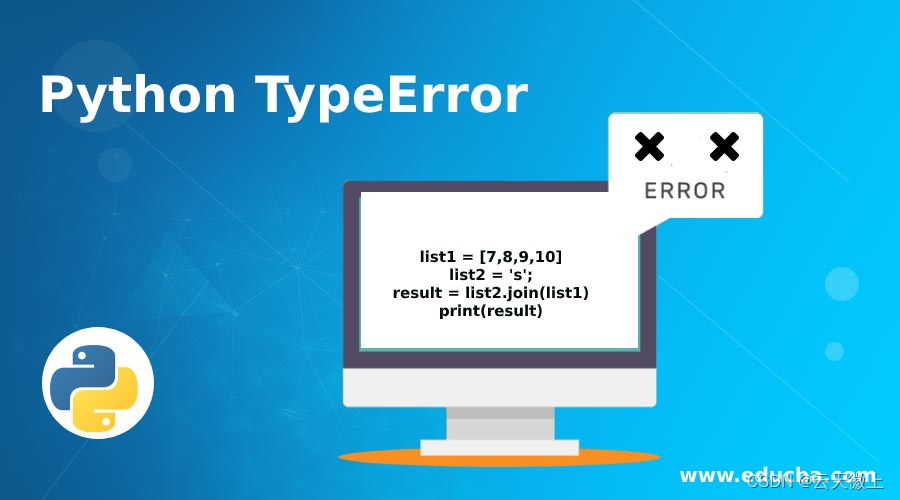
在Python中,字符串格式化是一种常见的操作,用于创建包含变量的字符串。如果你在使用%操作符进行格式化时遇到了%d format: a number is required, not str的错误,这意味着你尝试将一个字符串格式化为整数,但提供了一个字符串类型的参数。本文将深入探讨这一错误的原因,并提供具体的代码示例和解决办法。
错误原因
%d format: a number is required, not str错误通常由以下原因引起:
- 错误的格式化类型:使用
%d格式化字符串,期望的是一个整数,但提供了一个字符串。 - 类型不匹配:在格式化表达式中指定的类型与提供的变量类型不匹配。
错误示例
# 这会引发错误,因为'42'是一个字符串,而不是整数
formatted_string = "The answer is %d" % '42'
解决办法
方法一:确保变量是正确的类型
在进行格式化之前,确保变量是正确的类型。如果需要,可以使用int()函数将字符串转换为整数。
解决办法示例:
number_str = '42'
formatted_string = "The answer is %d" % int(number_str) # 正确使用int()转换
print(formatted_string)
方法二:使用format()方法
format()方法提供了一种更灵活和强大的格式化字符串的方式。
解决办法示例:
number_str = '42'
formatted_string = "The answer is {}".format(int(number_str)) # 使用format()方法
print(formatted_string)
方法三:使用f-string(Python 3.6+)
f-string是Python 3.6及以后版本中引入的一种新的字符串格式化方法。
解决办法示例:
number_str = '42'
formatted_string = f"The answer is {int(number_str)}" # 使用f-string
print(formatted_string)
方法四:使用异常处理
使用try-except块来捕获类型转换中可能出现的异常,并给出错误信息。
解决办法示例:
number_str = '42'try:formatted_string = "The answer is %d" % int(number_str)
except ValueError as e:print(f"Error converting to int: {e}")
方法五:检查变量值
在进行类型转换之前,检查变量值是否适合转换。
解决办法示例:
number_str = '42a'if number_str.isdigit():formatted_string = "The answer is %d" % int(number_str)
else:print(f"Cannot convert '{number_str}' to an integer.")
方法六:使用.isdigit()或isnumeric()方法
在将字符串转换为整数之前,使用.isdigit()或.isnumeric()方法检查字符串是否只包含数字。
解决办法示例:
number_str = '42'if number_str.isdigit():formatted_string = "The answer is %d" % int(number_str)
else:print(f"The string '{number_str}' is not numeric.")
方法七:使用map()函数
如果你需要格式化多个值,可以使用map()函数。
解决办法示例:
numbers_str = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5']
formatted_numbers = map(str, map(int, numbers_str)) # 先转换为整数,再转换为字符串
print(", ".join(formatted_numbers))
方法八:使用正则表达式
如果你需要从字符串中提取数字并格式化,可以使用正则表达式。
解决办法示例:
import retext = "The numbers are 42, 100, and 3.14"
numbers_str = re.findall(r'\d+', text)
numbers = [int(num) for num in numbers_str]
formatted_string = ", ".join(f"{num}" for num in numbers)
print(formatted_string)
方法九:编写单元测试
编写单元测试来验证你的代码能够正确处理不同类型的输入。
解决办法示例:
import unittestclass TestStringFormatting(unittest.TestCase):def test_integer_formatting(self):self.assertEqual("The answer is 42", "The answer is %d" % int('42'))if __name__ == '__main__':unittest.main()
结论
%d format: a number is required, not str错误提示我们在进行字符串格式化时需要确保变量的类型与格式化指定的类型一致。通过确保变量是正确的类型、使用format()方法和f-string、异常处理、检查变量值、使用.isdigit()或.isnumeric()方法、使用map()函数、使用正则表达式,以及编写单元测试,我们可以有效地避免和解决这种类型的错误。希望这些方法能帮助你写出更加健壮和可靠的Python代码。
希望这篇博客能够帮助你和你的读者更好地理解并解决Python中的字符串格式化问题。如果你需要更多的帮助或有其他编程问题,随时欢迎提问。

![[Vue-常见错误]浏览器显示Uncaught runtime errors](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8afee6e64cc548f29f14b90db8148361.png)