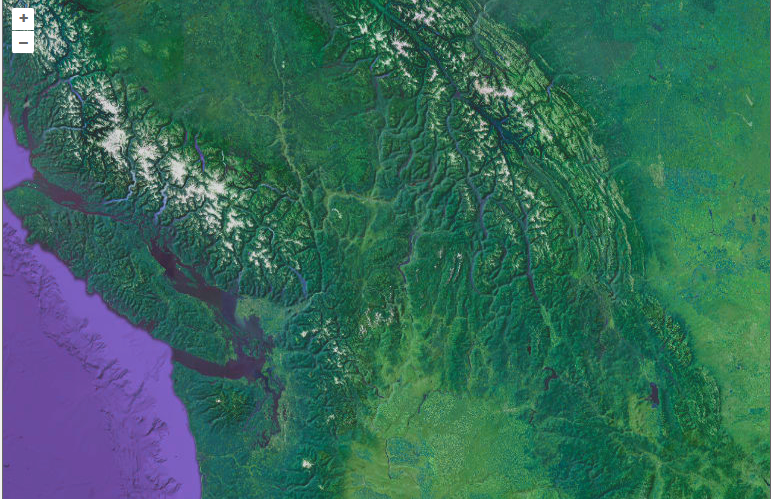
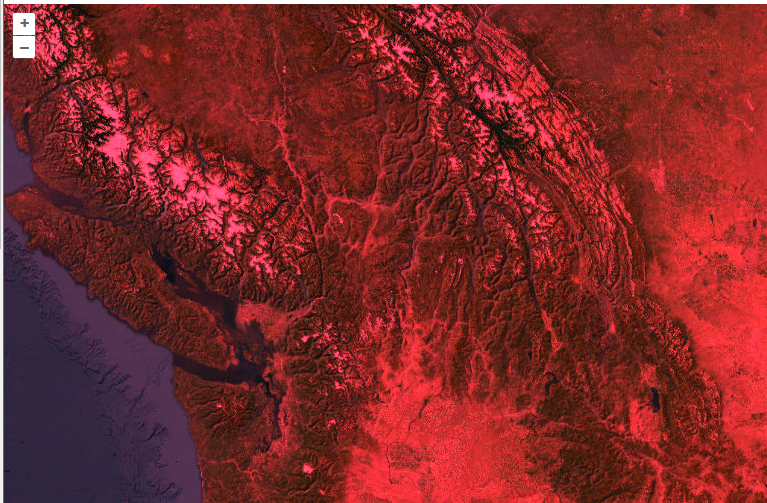
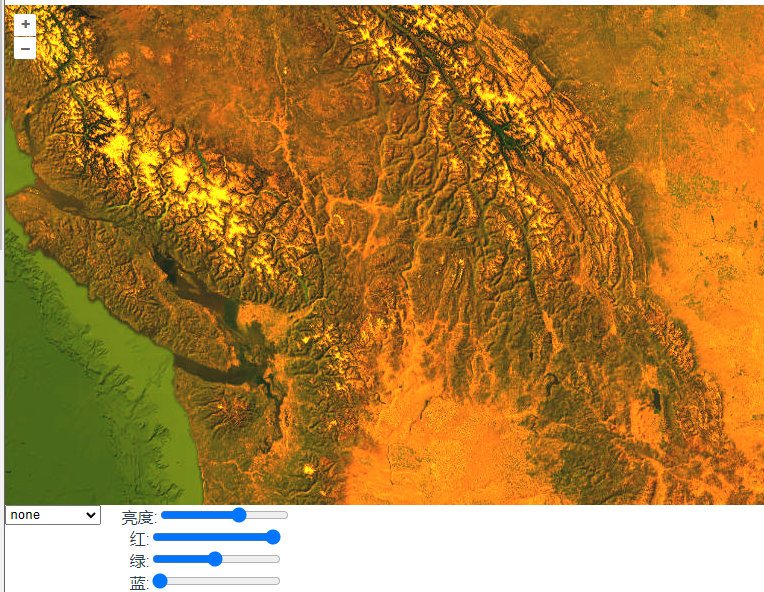
这篇是对滤镜的总结,方便工作中直接使用。
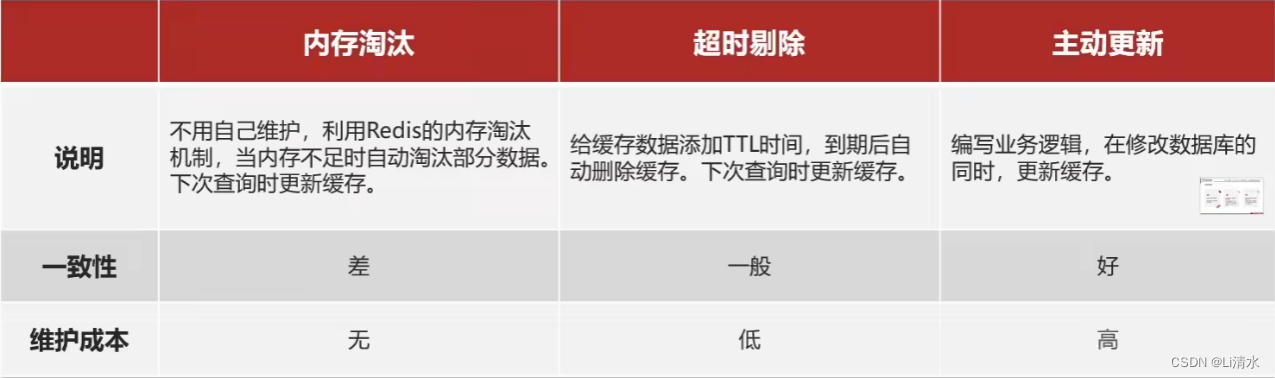
想要调整图层的颜色,有两种方法。
方法一:
加载图层时使用tileLoadFunction函数拿到context添加canvas滤镜效果。
this.imagery = new TileLayer({source: new XYZ({url: "https://server.arcgisonline.com/arcgis/rest/services/World_Imagery/MapServer/tile/{z}/{y}/{x}",crossOrigin: "anonymous",tileLoadFunction: function (imageTile, src) {let img = new Image();// 设置图片不从缓存取,从缓存取可能会出现跨域,导致加载失败img.setAttribute("crossOrigin", "anonymous");img.onload = function () {let canvas = document.createElement("canvas");let w = img.width;let h = img.height;canvas.width = w;canvas.height = h;let context = canvas.getContext("2d");context.filter ="grayscale(0%) invert(15%) sepia(0%) hue-rotate(75deg) saturate(200%) brightness(100%) contrast(100%)";// grayscale 灰度 invert反相 sepia将图像转化成深褐色 saturate饱和度 brightness暗度 contrast对比度context.drawImage(img, 0, 0, w, h, 0, 0, w, h);imageTile.getImage().src = canvas.toDataURL("image/png");};img.src = src;},}),});方法二:
利用postrender事件手动获取像素数据修改每一个像素点的值。
this.imagery.on("postrender", (event) => {this.convolve(event.context, this.selectedKernel);});convolve(context, kernel) {const canvas = context.canvas;const width = canvas.width;const height = canvas.height;// 假设 kernel 是一个归一化的卷积核矩阵,其大小为 size x sizeconst size = Math.sqrt(kernel.length);const half = Math.floor(size / 2);// 获取输入图像数据const inputData = context.getImageData(0, 0, width, height).data;// 创建一个新的 ImageData 对象用于输出图像数据const output = context.createImageData(width, height);const outputData = output.data;// 遍历每个像素for (let pixelY = 0; pixelY < height; ++pixelY) {const pixelsAbove = pixelY * width;for (let pixelX = 0; pixelX < width; ++pixelX) {let r = 0,g = 0,b = 0,a = 0;// 遍历卷积核for (let kernelY = 0; kernelY < size; ++kernelY) {for (let kernelX = 0; kernelX < size; ++kernelX) {let weight = kernel[kernelY * size + kernelX];const neighborY = Math.min(height - 1,Math.max(0, pixelY + kernelY - half));const neighborX = Math.min(width - 1,Math.max(0, pixelX + kernelX - half));const inputIndex = (neighborY * width + neighborX) * 4;// 累加加权后的像素值r += inputData[inputIndex] * weight;g += inputData[inputIndex + 1] * weight;b += inputData[inputIndex + 2] * weight;a += inputData[inputIndex + 3] * weight;}}const outputIndex = (pixelsAbove + pixelX) * 4;outputData[outputIndex] = r;outputData[outputIndex + 1] = g;outputData[outputIndex + 2] = b;outputData[outputIndex + 3] = kernel.normalized ? a : 255; // 如果卷积核是归一化的,则使用计算后的 alpha,否则设为 255//添加红绿蓝通道的值outputData[outputIndex] *= this.palette.red;outputData[outputIndex + 1] *= this.palette.green;outputData[outputIndex + 2] *= this.palette.blue;//添加亮度outputData[outputIndex] += this.palette.brightness;outputData[outputIndex + 1] += this.palette.brightness;outputData[outputIndex + 2] += this.palette.brightness;}}context.putImageData(output, 0, 0);},如果要添加模糊、锐化、浮雕等效果需要进行卷积核相关的操作,如果只是修改颜色则不需要。
两种方法总结:
第一种比较简单,代码较少。
第二种代码较多,但是修改的自由度比较高,可以添加更多的效果。
第二种方法的原理可以看这篇:
四十七、openlayers官网示例Image Filters——给地图添加锐化、浮雕、边缘等滤镜效果-CSDN博客
完整代码:
<template><div class="box"><h1>滤镜效果</h1><div id="map" class="map"></div><div class="tools"><selectid="kernel"name="kernel"style="height: 20px; margin-right: 20px"@change="paletteChange"v-model="kernelValue"><option v-for="(value, key, index) in kernels" :key="index">{{ key }}</option></select><div><label for="brightness">亮度:</label><inputtype="range"v-model.number="palette.brightness"id="brightness"min="-100"max="100"value="0"@change="paletteChange"/><br /><label for="redInput">红:</label><inputtype="range"v-model="palette.red"id="redInput"min="0"max="2"step="0.01"@change="paletteChange"/><br /><label for="redInput">绿:</label><inputtype="range"v-model="palette.green"id="greenInput"min="0"max="2"step="0.01"@change="paletteChange"/><br /><label for="redInput">蓝:</label><inputtype="range"v-model="palette.blue"id="blueInput"min="0"max="2"step="0.01"@change="paletteChange"/></div></div></div>
</template><script>
import Map from "ol/Map.js";
import View from "ol/View.js";
import XYZ from "ol/source/XYZ.js";
import { fromLonLat } from "ol/proj.js";
import { Tile as TileLayer, Vector as VectorLayer } from "ol/layer.js";
import { OGCMapTile, Vector as VectorSource } from "ol/source.js";
export default {name: "",components: {},data() {return {map: null,extentData: "",palette: {brightness: 0,red: 1,green: 1,blue: 1,},imagery: null,//卷积核kernels: {none: [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0], //无sharpen: [0, -1, 0, -1, 5, -1, 0, -1, 0], //锐化滤波器sharpenless: [0, -1, 0, -1, 10, -1, 0, -1, 0], //增强图像的边缘和细节,但比 sharpen 更强烈。blur: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], //平滑滤波器,通过对邻域像素值求平均来模糊图像shadow: [1, 2, 1, 0, 1, 0, -1, -2, -1], //阴影滤波器emboss: [-2, 1, 0, -1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2], //浮雕滤波器edge: [0, 1, 0, 1, -4, 1, 0, 1, 0], //边缘检测滤波器},kernelValue: "none",selectedKernel: "",};},computed: {},created() {},mounted() {this.initMap();this.selectedKernel = this.normalize(this.kernels[this.kernelValue]);this.imagery.on("postrender", (event) => {this.convolve(event.context, this.selectedKernel);});},methods: {convolve(context, kernel) {const canvas = context.canvas;const width = canvas.width;const height = canvas.height;// 假设 kernel 是一个归一化的卷积核矩阵,其大小为 size x sizeconst size = Math.sqrt(kernel.length);const half = Math.floor(size / 2);// 获取输入图像数据const inputData = context.getImageData(0, 0, width, height).data;// 创建一个新的 ImageData 对象用于输出图像数据const output = context.createImageData(width, height);const outputData = output.data;// 遍历每个像素for (let pixelY = 0; pixelY < height; ++pixelY) {const pixelsAbove = pixelY * width;for (let pixelX = 0; pixelX < width; ++pixelX) {let r = 0,g = 0,b = 0,a = 0;// 遍历卷积核for (let kernelY = 0; kernelY < size; ++kernelY) {for (let kernelX = 0; kernelX < size; ++kernelX) {let weight = kernel[kernelY * size + kernelX];const neighborY = Math.min(height - 1,Math.max(0, pixelY + kernelY - half));const neighborX = Math.min(width - 1,Math.max(0, pixelX + kernelX - half));const inputIndex = (neighborY * width + neighborX) * 4;// 累加加权后的像素值r += inputData[inputIndex] * weight;g += inputData[inputIndex + 1] * weight;b += inputData[inputIndex + 2] * weight;a += inputData[inputIndex + 3] * weight;}}const outputIndex = (pixelsAbove + pixelX) * 4;outputData[outputIndex] = r;outputData[outputIndex + 1] = g;outputData[outputIndex + 2] = b;outputData[outputIndex + 3] = kernel.normalized ? a : 255; // 如果卷积核是归一化的,则使用计算后的 alpha,否则设为 255//添加红绿蓝通道的值outputData[outputIndex] *= this.palette.red;outputData[outputIndex + 1] *= this.palette.green;outputData[outputIndex + 2] *= this.palette.blue;//添加亮度outputData[outputIndex] += this.palette.brightness;outputData[outputIndex + 1] += this.palette.brightness;outputData[outputIndex + 2] += this.palette.brightness;}}context.putImageData(output, 0, 0);},normalize(kernel) {// 获取卷积核的长度const len = kernel.length;// 创建一个与卷积核相同长度的新数组const normal = new Array(len);let i,sum = 0;// 计算卷积核中所有元素的总和for (i = 0; i < len; ++i) {sum += kernel[i];}// 如果总和小于等于0,设置sum为1并标记为未归一化if (sum <= 0) {normal.normalized = false;sum = 1;} else {// 如果总和大于0,标记为已归一化normal.normalized = true;}// 将卷积核中的每个元素除以总和,得到归一化后的值for (i = 0; i < len; ++i) {normal[i] = kernel[i] / sum;}// 返回归一化后的卷积核return normal;},initMap() {this.imagery = new TileLayer({source: new XYZ({url: "https://server.arcgisonline.com/arcgis/rest/services/World_Imagery/MapServer/tile/{z}/{y}/{x}",crossOrigin: "anonymous",// tileLoadFunction: function (imageTile, src) {// let img = new Image();// // 设置图片不从缓存取,从缓存取可能会出现跨域,导致加载失败// img.setAttribute("crossOrigin", "anonymous");// img.onload = function () {// let canvas = document.createElement("canvas");// let w = img.width;// let h = img.height;// canvas.width = w;// canvas.height = h;// let context = canvas.getContext("2d");// context.filter =// "grayscale(0%) invert(15%) sepia(0%) hue-rotate(75deg) saturate(200%) brightness(100%) contrast(100%)";// // grayscale 灰度 invert反相 sepia将图像转化成深褐色 saturate饱和度 brightness暗度 contrast对比度// context.drawImage(img, 0, 0, w, h, 0, 0, w, h);// imageTile.getImage().src = canvas.toDataURL("image/png");// };// img.src = src;// },}),});this.map = new Map({layers: [this.imagery],target: "map",view: new View({center: fromLonLat([-120, 50]),zoom: 6,}),});},paletteChange() {console.log("this.palette", this.palette);this.selectedKernel = this.normalize(this.kernels[this.kernelValue]);this.map.render();},},
};
</script><style lang="scss" scoped>
#map {width: 100%;height: 500px;
}
.box {height: 100%;
}
.tools {display: flex;
}
</style>