1.POSIX线程库
pthread线程库是应用层的原生线程库:
- 应用层指的是这个线程库并不是系统接口直接提供的,而是由第三方帮我们提供的。
- 原生指的是大部分Linux系统都会默认带上该线程库。
- 与线程有关的函数构成了一个完整的系列,绝大多数函数的名字都是以“pthread_”打头的。
- 要使用这些函数库,要通过引入头文件<pthreaad.h>。
- 链接这些线程函数库时,要使用编译器命令的“-lpthread”选项。
错误检查:
- 传统的一些函数是,成功返回0,失败返回-1,并且对全局变量errno赋值以指示错误。
- pthreads函数出错时不会设置全局变量errno(而大部分POSIX函数会这样做),而是将错误代码通过返回值返回。
- pthreads同样也提供了线程内的errno变量,以支持其他使用errno的代码。对于pthreads函数的错误,建议通过返回值来判定,因为读取返回值要比读取线程内的errno变量的开销更小。
2.线程创建
创建线程的函数叫做pthread_create
pthread_create函数的函数原型如下:
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);参数说明:
- thread:获取创建成功的线程ID,该参数是一个输出型参数。
- attr:用于设置创建线程的属性,传入NULL表示使用默认属性。
- start_routine:该参数是一个函数地址,表示线程例程,即线程启动后要执行的函数。
- arg:传给线程例程的参数。
返回值说明:
- 线程创建成功返回0,失败返回错误码。
2.1.让主线程创建一个新线程
当一个程序启动时,就有一个进程被操作系统创建,与此同时一个线程也立刻运行,这个线程就叫做主线程。
- 主线程是产生其他子线程的线程。
- 通常主线程必须最后完成某些执行操作,比如各种关闭动作。
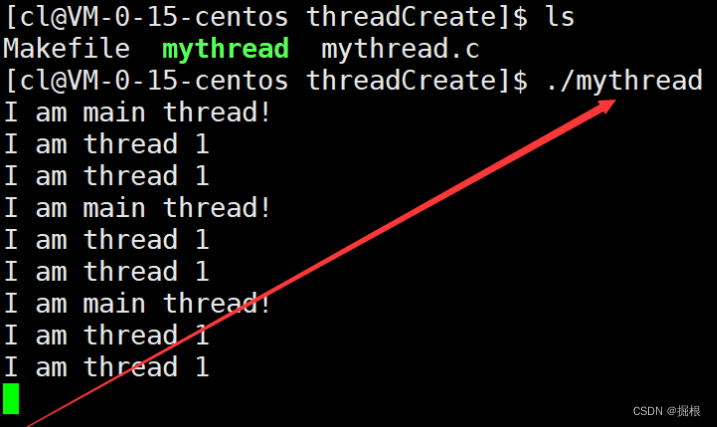
下面我们让主线程调用pthread_create函数创建一个新线程,此后新线程就会跑去执行自己的新例程,而主线程则继续执行后续代码。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;while (1){printf("I am %s\n", msg);sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, NULL, Routine, (void*)"thread 1");while (1){printf("I am main thread!\n");sleep(2);}return 0;
}
运行代码后可以看到,新线程每隔一秒执行一次打印操作,而主线程每隔两秒执行一次打印操作。
当我们用ps axj命令查看当前进程的信息时,虽然此时该进程中有两个线程,但是我们看到的进程只有一个,因为这两个线程都是属于同一个进程的。

使用ps -aL命令,可以显示当前的轻量级进程。
- 默认情况下,不带
-L,看到的就是一个个的进程。 - 带
-L就可以查看到每个进程内的多个轻量级进程。

其中,LWP(Light Weight Process)就是轻量级进程的ID,可以看到显示的两个轻量级进程的PID是相同的,因为它们属于同一个进程。
注意: 在Linux中,应用层的线程与内核的LWP是一一对应的,实际上操作系统调度的时候采用的是LWP,而并非PID,只不过我们之前接触到的都是单线程进程,其PID和LWP是相等的,所以对于单线程进程来说,调度时采用PID和LWP是一样的。
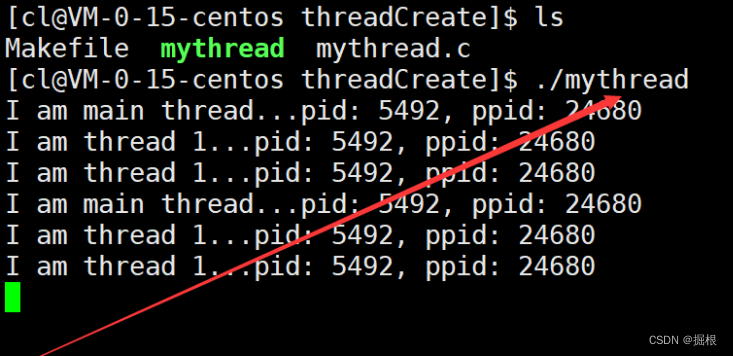
为了进一步证明这两个线程是属于同一个进程的,我们可以让主线程和新线程在执行打印操作时,将自己的PID和PPID也进行打印。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;while (1){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d\n", msg, getpid(), getppid());sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, NULL, Routine, (void*)"thread 1");while (1){printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d\n", getpid(), getppid());sleep(2);}return 0;
}
可以看到主线程和新线程的PID和PPID是一样的,也就是说主线程和新线程虽然是两个执行流,但它们仍然属于同一个进程。
2.2.让主线程创建一批新线程
上面是让主线程创建一个新线程,下面我们让主线程一次性创建五个新线程,并让创建的每一个新线程都去执行Routine函数,也就是说Routine函数会被重复进入,即该函数是会被重入的。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;while (1){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d\n", msg, getpid(), getppid());sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);}while (1){printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d\n", getpid(), getppid());sleep(2);}return 0;
}
运行代码,可以看到这五个新线程是创建成功的。
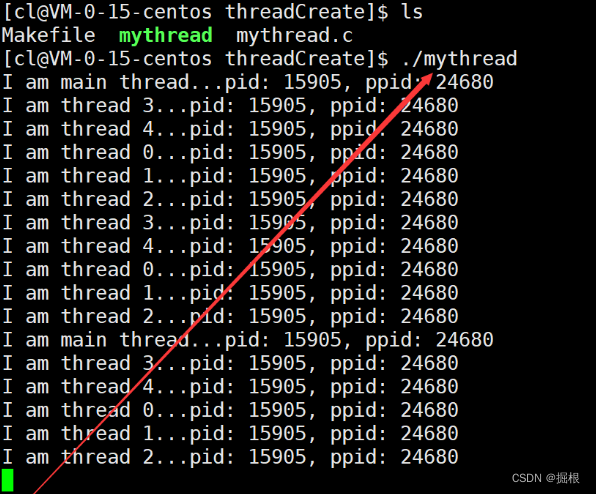
因为主线程和五个新线程都属于同一个进程,所以它们的PID和PPID也都是一样的。
此时我们再用ps -aL命令查看,就会看到六个轻量级进程。

2.3.获取线程ID
常见获取线程ID的方式有两种:
- 创建线程时通过输出型参数获得。
- 通过调用pthread_self函数获得。
pthread_self函数的函数原型如下:
pthread_t pthread_self(void);调用pthread_self函数即可获得当前线程的ID,类似于调用getpid函数获取当前进程的ID。例如,下面代码中在每一个新线程被创建后,主线程都将通过输出型参数获取到的线程ID进行打印,此后主线程和新线程又通过调用pthread_self函数获取到自身的线程ID进行打印。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;while (1){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}while (1){printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(2);}return 0;
}
运行代码,可以看到这两种方式获取到的线程的ID是一样的。

注意: 用pthread_self函数获得的线程ID与内核的LWP的值是不相等的,pthread_self函数获得的是用户级原生线程库的线程ID,而LWP是内核的轻量级进程ID,它们之间是一对一的关系。
3.线程等待
- 首先需要明确的是,一个线程被创建出来,这个线程就如同进程一般,也是需要被等待的。
- 如果主线程不对新线程进行等待,那么这个新线程的资源也是不会被回收的。
- 所以线程需要被等待,如果不等待会产生类似于“僵尸进程”的问题,也就是内存泄漏。
等待线程的函数叫做pthread_join
pthread_join函数的函数原型如下:
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);参数说明:
- thread:被等待线程的ID。
- retval:线程退出时的退出码信息。
返回值说明:
- 线程等待成功返回0,失败返回错误码。
调用该函数的线程将挂起等待,直到ID为thread的线程终止,thread线程以不同的方法终止,通过pthread_join得到的终止状态是不同的。
总结如下:
- 如果thread线程通过return返回,retval所指向的单元里存放的是thread线程函数的返回值。
- 如果thread线程被别的线程调用pthread_cancel异常终止掉,retval所指向的单元里存放的是常数PTHREAD_CANCELED。
- 如果thread线程是自己调用pthread_exit终止的,retval所指向的单元存放的是传给pthread_exit的参数。
- 如果对thread线程的终止状态不感兴趣,可以传NULL给retval参数。
用grep命令进行查找,可以发现PTHREAD_CANCELED实际上就是头文件<pthread.h>里面的一个宏定义,它的值本质就是-1。
grep -ER "PTHREAD_CANCELED" /usr/include/
例如,在下面的代码中我们先不关心线程的退出信息,直接将pthread_join函数的第二次参数设置为NULL,等待线程后打印该线程的编号以及线程ID。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;int count = 0;while (count < 5){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);count++;}return NULL;
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);printf("thread %d[%lu]...quit\n", i, tid[i]);}return 0;
}
运行代码后,可以看到主线程创建的五个新线程在进行五次打印操作后就退出了,而主线程也是成功对这五个线程进行了等待。

下面我们再来看看如何获取线程退出时的退出码,为了便于查看,我们这里将线程退出时的退出码设置为某个特殊的值,并在成功等待线程后将该线程的退出码进行输出。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;int count = 0;while (count < 5){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);count++;}return (void*)2022;
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){void* ret = NULL;pthread_join(tid[i], &ret);printf("thread %d[%lu]...quit, exitcode: %d\n", i, tid[i], (int)ret);}return 0;
}
运行代码,此时我们就拿到了每个线程退出时的退出码信息。

注意: pthread_join函数默认是以阻塞的方式进行线程等待的。
3.1.为什么线程退出时只能拿到线程的退出码?
如果我们等待的是一个进程,那么当这个进程退出时,我们可以通过wait函数或是waitpid函数的输出型参数status,获取到退出进程的退出码、退出信号以及core dump标志。
那为什么等待线程时我们只能拿到退出线程的退出码?难道线程不会出现异常吗?
线程在运行过程中当然也会出现异常,线程和进程一样,线程退出的情况也有三种:
- 代码运行完毕,结果正确。
- 代码运行完毕,结果不正确。
- 代码异常终止。
因此我们也需要考虑线程异常终止的情况,但是pthread_join函数无法获取到线程异常退出时的信息。因为线程是进程内的一个执行分支,如果进程中的某个线程崩溃了,那么整个进程也会因此而崩溃,此时我们根本没办法执行pthread_join函数,因为整个进程已经退出了。
例如,我们在线程的执行例程当中制造一个除零错误,当某一个线程执行到此处时就会崩溃,进而导致整个进程崩溃。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;int count = 0;while (count < 5){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);count++;int a = 1 / 0; //error}return (void*)2022;
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){void* ret = NULL;pthread_join(tid[i], &ret);printf("thread %d[%lu]...quit, exitcode: %d\n", i, tid[i], (int)ret);}return 0;
}
运行代码,可以看到一旦某个线程崩溃了,整个进程也就跟着挂掉了,此时主线程连等待新线程的机会都没有,这也说明了多线程的健壮性不太强,一个进程中只要有一个线程挂掉了,那么整个进程就挂掉了。并且此时我们也不知道是由于哪一个线程崩溃导致的,我们只知道是这个进程崩溃了。
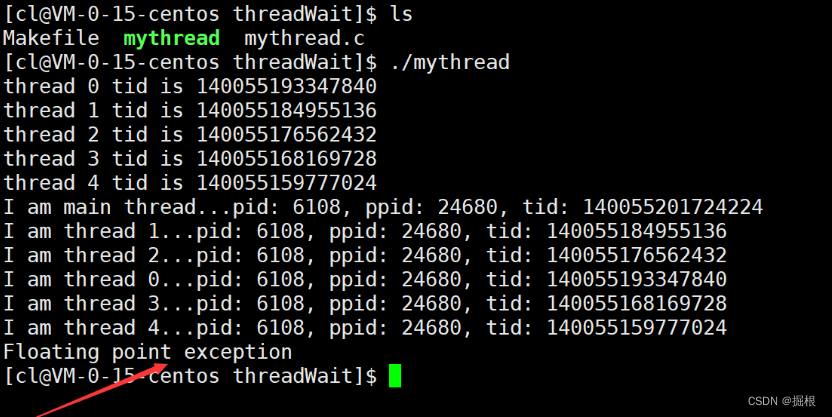
所以pthread_join函数只能获取到线程正常退出时的退出码,用于判断线程的运行结果是否正确。
4.线程终止
如果需要只终止某个线程而不是终止整个进程,可以有三种方法:
- 从线程函数return。
- 线程可以自己调用pthread_exit函数终止自己。
- 一个线程可以调用pthread_cancel函数终止同一进程中的另一个线程。
4.1.return退出
在线程中使用return代表当前线程退出,但是在main函数中使用return代表整个进程退出,也就是说只要主线程退出了那么整个进程就退出了,此时该进程曾经申请的资源就会被释放,而其他线程会因为没有了资源,自然而然的也退出了。
例如,在下面代码中,主线程创建五个新线程后立刻进行return,那么整个进程也就退出了。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;while (1){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);}return (void*)0;
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());return 0;
}
运行代码,并不能看到新线程执行的打印操作,因为主线程的退出导致整个进程退出了。

4.2.pthread_exit函数
pthread_exit函数的功能就是终止线程,pthread_exit函数的函数原型如下:
void pthread_exit(void *retval);参数说明:
- retval:线程退出时的退出码信息。
说明一下:
- 该函数无返回值,跟进程一样,线程结束的时候无法返回它的调用者(自身)。
- pthread_exit或者return返回的指针所指向的内存单元必须是全局的或者是用malloc分配的,不能在线程函数的栈上分配,因为当其他线程得到这个返回指针时,线程函数已经退出了。
例如,在下面代码中,我们使用pthread_exit函数终止线程,并将线程的退出码设置为6666。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;int count = 0;while (count < 5){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);count++;}pthread_exit((void*)6666);
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){void* ret = NULL;pthread_join(tid[i], &ret);printf("thread %d[%lu]...quit, exitcode: %d\n", i, tid[i], (int)ret);}return 0;
}
运行代码可以看到,当线程退出时其退出码就是我们设置的6666。

注意: exit函数的作用是终止进程,任何一个线程调用exit函数也代表的是整个进程终止。
4.3.pthread_cancel函数
线程是可以被取消的,我们可以使用pthread_cancel函数取消某一个线程,pthread_cancel函数的函数原型如下:
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);参数说明:
- thread:被取消线程的ID。
返回值说明:
- 线程取消成功返回0,失败返回错误码。
线程是可以取消自己的,取消成功的线程的退出码一般是-1。例如在下面的代码中,我们让线程执行一次打印操作后将自己取消。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;int count = 0;while (count < 5){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);count++;pthread_cancel(pthread_self());}pthread_exit((void*)6666);
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){void* ret = NULL;pthread_join(tid[i], &ret);printf("thread %d[%lu]...quit, exitcode: %d\n", i, tid[i], (int)ret);}return 0;
}
运行代码,可以看到每个线程执行一次打印操作后就退出了,其退出码不是我们设置的6666而是-1,因为我们是在线程执行pthread_exit函数前将线程取消的。

虽然线程可以自己取消自己,但一般不这样做,我们往往是用于一个线程取消另一个线程,比如主线程取消新线程。
例如,在下面代码中,我们在创建五个线程后立刻又将0、1、2、3号线程取消。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;int count = 0;while (count < 5){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);count++;}pthread_exit((void*)6666);
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}pthread_cancel(tid[0]);pthread_cancel(tid[1]);pthread_cancel(tid[2]);pthread_cancel(tid[3]);printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){void* ret = NULL;pthread_join(tid[i], &ret);printf("thread %d[%lu]...quit, exitcode: %d\n", i, tid[i], (int)ret);}return 0;
}
此时可以发现,0、1、2、3号线程退出时的退出码不是我们设置的6666,而只有未被取消的4号线程的退出码是6666,因为只有4号进程未被取消。

此外,新线程也是可以取消主线程的,例如下面我们让每一个线程都尝试对主线程进行取消。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>pthread_t main_thread;void* Routine(void* arg)
{char* msg = (char*)arg;int count = 0;while (count < 5){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);count++;pthread_cancel(main_thread);}pthread_exit((void*)6666);
}
int main()
{main_thread = pthread_self();pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){void* ret = NULL;pthread_join(tid[i], &ret);printf("thread %d[%lu]...quit, exitcode: %d\n", i, tid[i], (int)ret);}return 0;
}
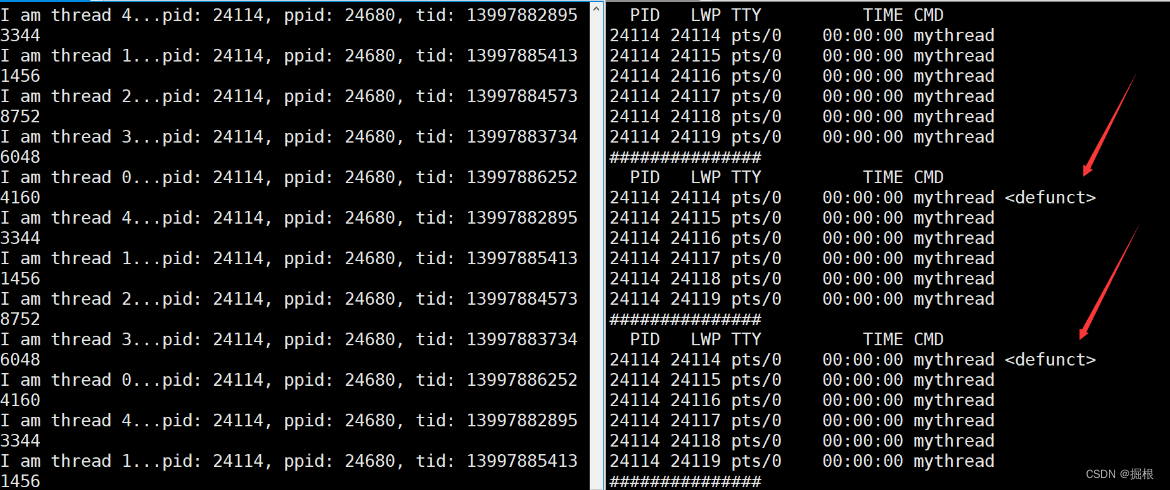
运行代码,同时用以下监控脚本进行实时监控。
while :; do ps -aL | head -1&&ps -aL | grep mythread | grep -v grep;echo "###############";sleep 1;done
可以看到一段时间后,六个线程中PID和LWP相同的线程,也就是主线程右侧显示<defunct>,也就意味着主线程已经被取消了,我们也就看不到后续主线程等待新线程时打印的退出码了。
注意:
- 当采用这种取消方式时,主线程和各个新线程之间的地位是对等的,取消一个线程,其他线程也是能够跑完的,只不过主线程不再执行后续代码了。
- 我们一般都是用主线程去控制新线程,这才符合我们对线程控制的基本逻辑,虽然实验表明新线程可以取消主线程,但是并不推荐该做法。
5.分离线程
- 默认情况下,新创建的线程是joinable的,线程退出后,需要对其进行pthread_join操作,否则无法释放资源,从而造成内存泄漏。
- 但如果我们不关心线程的返回值,join也是一种负担,此时我们可以将该线程进行分离,后续当线程退出时就会自动释放线程资源。
- 一个线程如果被分离了,这个线程依旧要使用该进程的资源,依旧在该进程内运行,甚至这个线程崩溃了一定会影响其他线程,只不过这个线程退出时不再需要主线程去join了,当这个线程退出时系统会自动回收该线程所对应的资源。
- 可以是线程组内其他线程对目标线程进行分离,也可以是线程自己分离。
- joinable和分离是冲突的,一个线程不能既是joinable又是分离的。
分离线程的函数叫做pthread_detach
pthread_detach函数的函数原型如下:
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);参数说明:
- thread:被分离线程的ID。
返回值说明:
- 线程分离成功返回0,失败返回错误码。
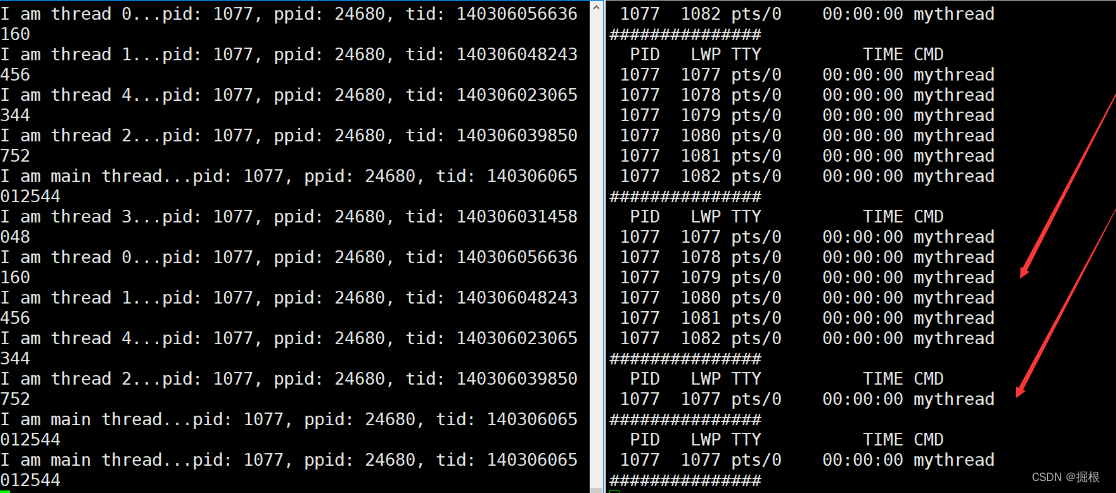
例如,下面我们创建五个新线程后让这五个新线程将自己进行分离,那么此后主线程就不需要在对这五个新线程进行join了。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{pthread_detach(pthread_self());char* msg = (char*)arg;int count = 0;while (count < 5){printf("I am %s...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", msg, getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);count++;}pthread_exit((void*)6666);
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){char* buffer = (char*)malloc(64);sprintf(buffer, "thread %d", i);pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, Routine, buffer);printf("%s tid is %lu\n", buffer, tid[i]);}while (1){printf("I am main thread...pid: %d, ppid: %d, tid: %lu\n", getpid(), getppid(), pthread_self());sleep(1);}return 0;
}
这五个新线程在退出时,系统会自动回收对应线程的资源,不需要主线程进行join。
6.线程ID及进程地址空间布局
- pthread_create函数会产生一个线程ID,存放在第一个参数指向的地址中,该线程ID和内核中的LWP不是一回事。
- 内核中的LWP属于进程调度的范畴,因为线程是轻量级进程,是操作系统调度器的最小单位,所以需要一个数值来唯一表示该线程。
- pthread_create函数第一个参数指向一个虚拟内存单元,该内存单元的地址即为新创建线程的线程ID,这个ID属于NPTL线程库的范畴,线程库的后续操作就是根据该线程ID来操作线程的。
- 线程库NPTL提供的pthread_self函数,获取的线程ID和pthread_create函数第一个参数获取的线程ID是一样的。
pthread_t到底是什么类型呢?
首先,Linux不提供真正的线程,只提供LWP,也就意味着操作系统只需要对内核执行流LWP进行管理,而供用户使用的线程接口等其他数据,应该由线程库自己来管理,因此管理线程时的“先描述,再组织”就应该在线程库里进行。
通过ldd命令可以看到,我们采用的线程库实际上是一个动态库。
进程运行时动态库被加载到内存,然后通过页表映射到进程地址空间中的共享区,此时该进程内的所有线程都是能看到这个动态库的。
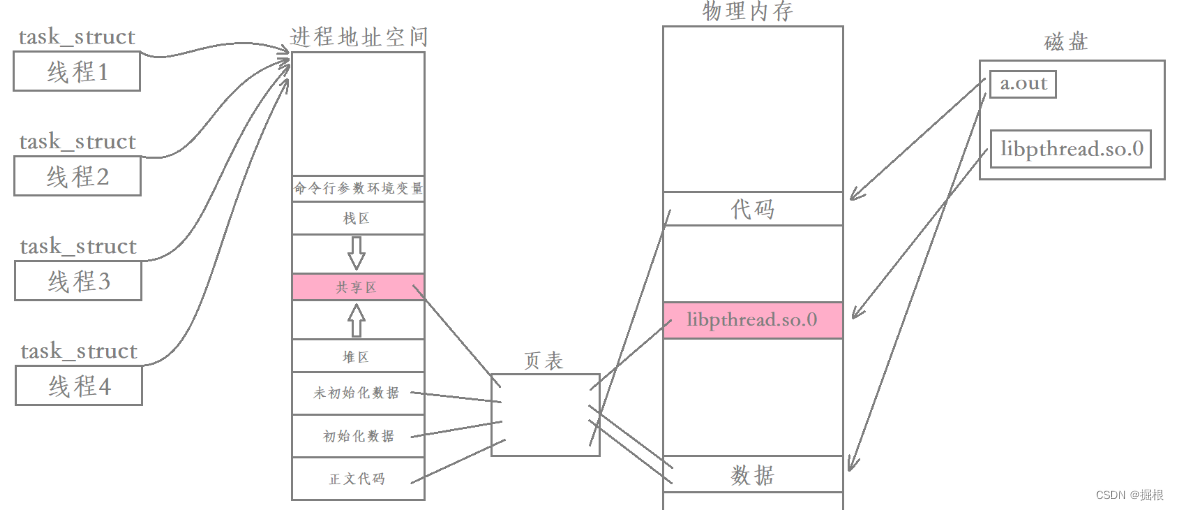
我们说每个线程都有自己私有的栈,其中主线程采用的栈是进程地址空间中原生的栈,而其余线程采用的栈就是在共享区中开辟的。除此之外,每个线程都有自己的struct pthread,当中包含了对应线程的各种属性;每个线程还有自己的线程局部存储,当中包含了对应线程被切换时的上下文数据。
每一个新线程在共享区都有这样一块区域对其进行描述,因此我们要找到一个用户级线程只需要找到该线程内存块的起始地址,然后就可以获取到该线程的各种信息。
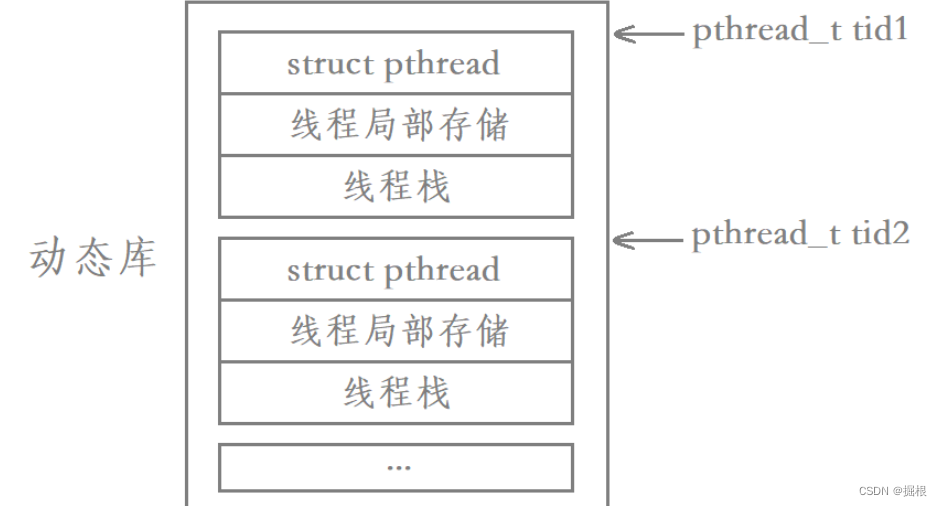
上面我们所用的各种线程函数,本质都是在库内部对线程属性进行的各种操作,最后将要执行的代码交给对应的内核级LWP去执行就行了,也就是说线程数据的管理本质是在共享区的。
pthread_t到底是什么类型取决于实现,但是对于Linux目前实现的NPTL线程库来说,线程ID本质就是进程地址空间共享区上的一个虚拟地址,同一个进程中所有的虚拟地址都是不同的,因此可以用它来唯一区分每一个线程。
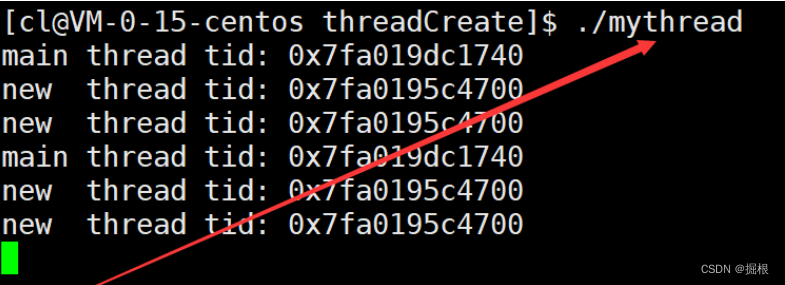
例如,我们也可以尝试按地址的形式对获取到的线程ID进行打印。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>void* Routine(void* arg)
{while (1){printf("new thread tid: %p\n", pthread_self());sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, NULL, Routine, NULL);while (1){printf("main thread tid: %p\n", pthread_self());sleep(2);}return 0;
}
在此之前我们可以说这个打印结果很像一个地址,但是现在我们可以说,这本质就是一个地址。